Abstract
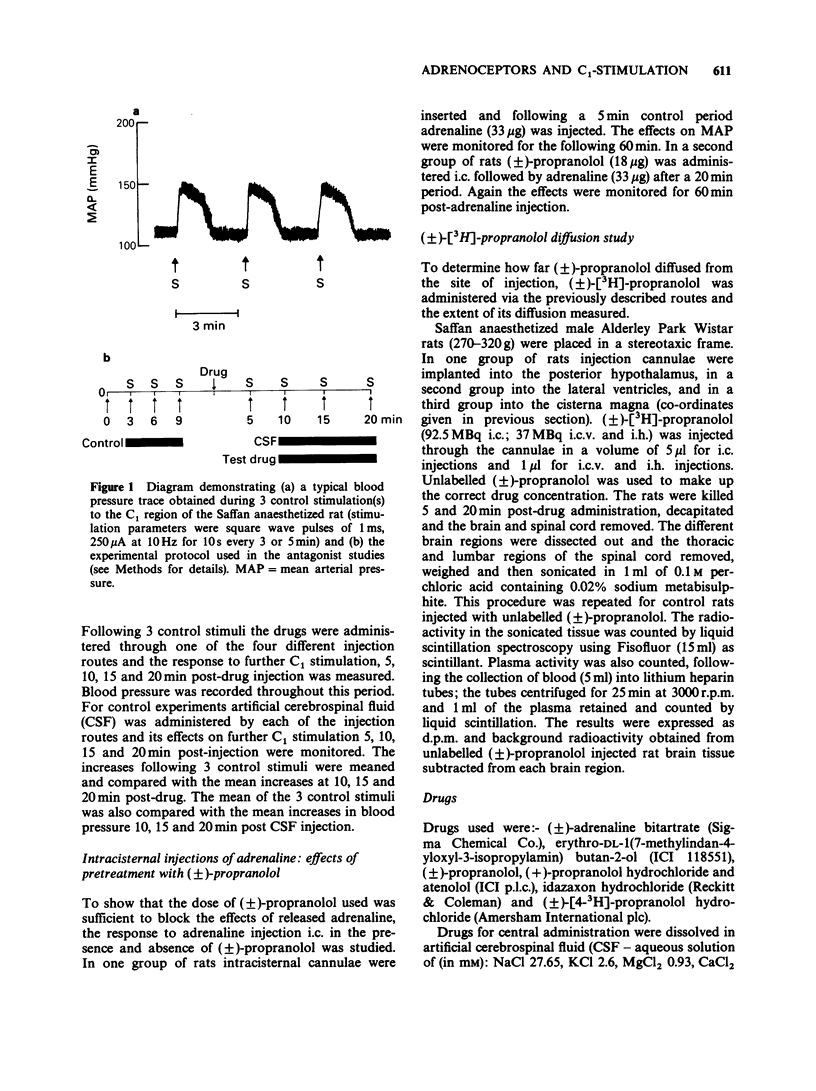
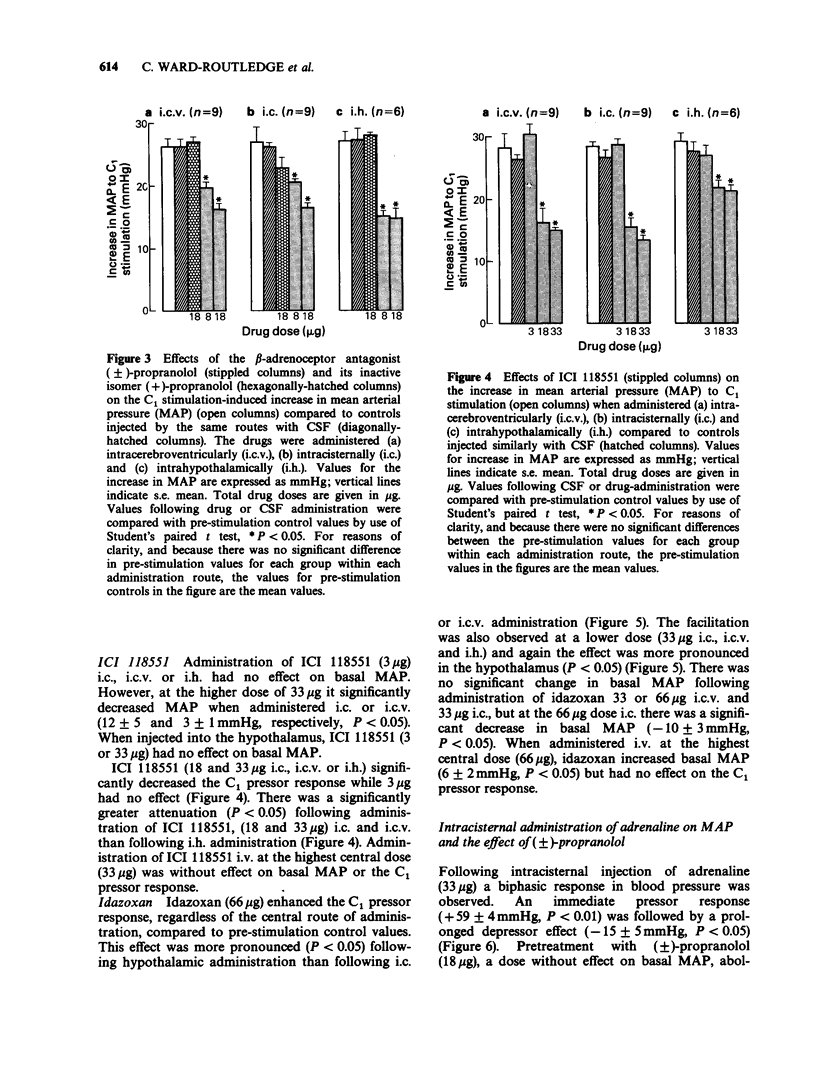
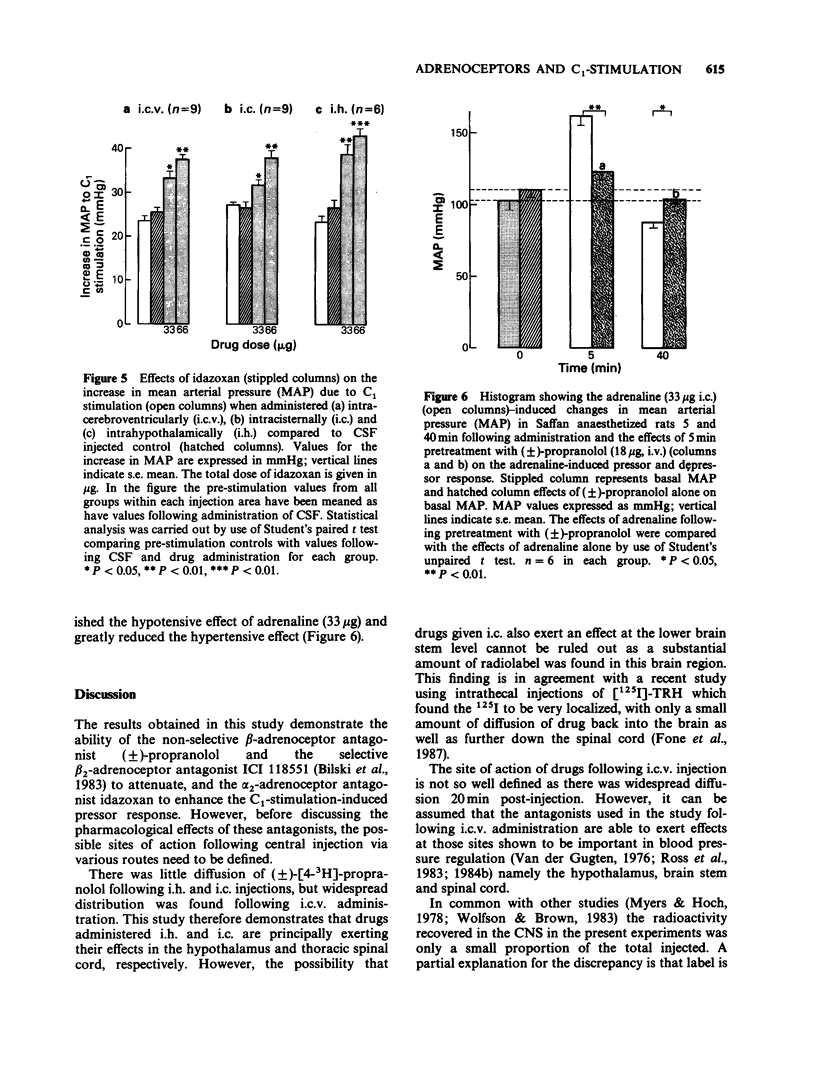
1. Electrical stimulation of the C1 area of the rostral ventrolateral medulla in rats elicits an increase in mean arterial pressure (MAP). 2. This increase in MAP is attenuated by intra-hypothalamic and intracisternal administration of the non-selective beta-adrenoceptor antagonist (+/-)-propranolol and the beta 2-selective antagonist ICI 118551. 3. The selective beta 1-antagonist atenolol and (+)-propranolol, which is inactive on beta-adrenoceptors, did not alter the increase in MAP produced by stimulation of the C1 area. 4. The alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist idazoxan enhanced the effects of C1 stimulation on MAP when administered either into the posterior hypothalamus or intracisternally. 5. The results indicate that beta 2- and alpha 2-receptors both have a role in the mediation of the rise in MAP during stimulation of the C1 area and that the receptors involved are located both within the hypothalamus and the spinal cord.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong D. M., Ross C. A., Pickel V. M., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Distribution of dopamine-, noradrenaline-, and adrenaline-containing cell bodies in the rat medulla oblongata: demonstrated by the immunocytochemical localization of catecholamine biosynthetic enzymes. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Dec 1;212(2):173–187. doi: 10.1002/cne.902120207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson J., Lambas-Senas L., Parker M., Boillat N., Luthi P., Sonnay M., Seccia M., Renaud B. Chronic clonidine treatment and its withdrawal: effects on blood pressure and catecholamine synthesizing enzymes in brain-stem nuclei. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Feb 11;121(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava K. P., Mishra N., Tangri K. K. An analysis of central adrenoceptors for control of cardiovascular function. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Aug;45(4):596–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb08117.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilski A. J., Halliday S. E., Fitzgerald J. D., Wale J. L. The pharmacology of a beta 2-selective adrenoceptor antagonist (ICI 118,551). J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1983 May-Jun;5(3):430–437. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198305000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolme P., Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T., Lidbrink P., Goldstein M. Possible involvement of central adrenaline neurons in vasomotor and respiratory control. Studies with clonidine and its interactions with piperoxane and yohimbine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Sep;28(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dampney R. A., Moon E. A. Role of ventrolateral medulla in vasomotor response to cerebral ischemia. Am J Physiol. 1980 Sep;239(3):H349–H358. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.239.3.H349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day M. D., Poyser R. H., Sempik J. Effects on blood pressure of noradrenaline and isoprenaline administered into the third ventricle of the brain of anaesthetized and conscious cats. J Auton Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;1(1):37–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1980.tb00439.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day M. D., Roach A. G. Central alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors modifying arterial blood pressure and heart rate in conscious cats. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Jul;51(3):325–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb10666.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fone K. C., Bennett G. W., Marsden C. A. Involvement of catecholaminergic neurones and alpha-adrenoceptors in the wet-dog shake and forepaw licking behaviour produced by the intrathecal injection of an analogue of thyrotrophin-releasing hormone (CG 3509). Neuropharmacology. 1987 Aug;26(8):1147–1155. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W. Pharmacology of brain epinephrine neurons. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:31–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giron L. T., Jr, McCann S. A., Crist-Orlando S. G. Pharmacological characterization and regional distribution of alpha-noradrenergic binding sites of rat spinal cord. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep 24;115(2-3):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90701-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goshima Y., Kubo T., Misu Y. Autoregulation of endogenous epinephrine release via presynaptic adrenoceptors in the rat hypothalamic slice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Oct;235(1):248–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe P. R., Lovenberg W., Chalmers J. P. Increased number of PNMT-immunofluorescent nerve cell bodies in the medulla oblongata of stroke-prone hypertensive rats. Brain Res. 1981 Jan 26;205(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90724-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobinger W., Walland A. Evidence for a central activation of a vagal cardiodepressor reflex by clonidine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 Aug;19(2):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Sixth gaddum memorial lecture, National Institute for Medical Research, Mill Hill, January 1977. Presynaptic receptors and their role in the regulation of transmitter release. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;60(4):481–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew J. Y., Hata F., Sauter A., Baba Y., Engel J., Goldstein M. Distribution of PNMT and epinephrine in the medulla oblongata of normotensive and spontaneous hypertensive rats. J Neural Transm. 1979;44(4):309–316. doi: 10.1007/BF01250326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. J., Haeusler G. Reduction in sympathetic nervous activity as a mechanism for hypotensive effect of propranolol. Nature. 1975 Jul 31;256(5516):440–440. doi: 10.1038/256440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz R. G., Saper C. B., Wong D. L., Ciaranello R. D., Loewy A. D. Co-localization of substance P- and phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase-like immunoreactivity in neurons of ventrolateral medulla that project to the spinal cord: potential role in control of vasomotor tone. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Apr 19;55(3):255–260. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90444-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwaha J., Aghajanian G. K. Relative potencies of alpha-1 and alpha-2 antagonists in the locus ceruleus, dorsal raphe and dorsal lateral geniculate nuclei: an electrophysiological study. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Aug;222(2):287–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mefford I. N. Are there epinephrine neurons in rat brain? Brain Res. 1987 Nov;434(4):383–395. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(87)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
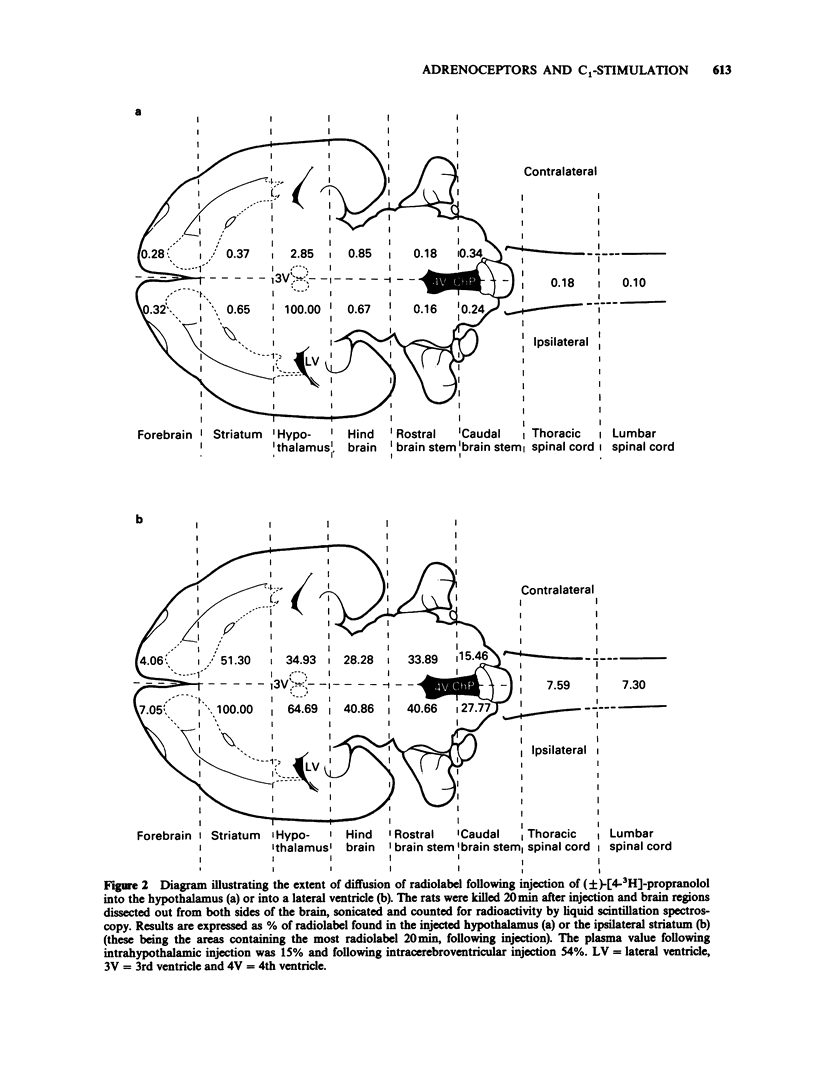
- Myers R. D., Hoch D. B. 14C-dopamine microinjected into the brain-stem of the rat: dispersion kinetics, site content and functional dose. Brain Res Bull. 1978 Nov-Dec;3(6):601–609. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(78)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Armstrong D. M., Ruggiero D. A., Pickel V. M., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Adrenaline neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla innervate thoracic spinal cord: a combined immunocytochemical and retrograde transport demonstration. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Sep 25;25(3):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Ruggiero D. A., Joh T. H., Park D. H., Reis D. J. Adrenaline synthesizing neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla: a possible role in tonic vasomotor control. Brain Res. 1983 Aug 29;273(2):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90862-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Ruggiero D. A., Joh T. H., Park D. H., Reis D. J. Rostral ventrolateral medulla: selective projections to the thoracic autonomic cell column from the region containing C1 adrenaline neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Sep 10;228(2):168–185. doi: 10.1002/cne.902280204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Ruggiero D. A., Park D. H., Joh T. H., Sved A. F., Fernandez-Pardal J., Saavedra J. M., Reis D. J. Tonic vasomotor control by the rostral ventrolateral medulla: effect of electrical or chemical stimulation of the area containing C1 adrenaline neurons on arterial pressure, heart rate, and plasma catecholamines and vasopressin. J Neurosci. 1984 Feb;4(2):474–494. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-02-00474.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouot B. R., Snyder S. H. [3H]Para-amino-clonidine: a novel ligand which binds with high affinity to alpha-adrenergic receptors. Life Sci. 1979 Aug 27;25(9):769–774. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90521-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge C., Marsden C. A. Comparison of the effects of selected drugs on the release of hypothalamic adrenaline and noradrenaline measured in vivo. Brain Res. 1987 Nov 17;426(1):103–111. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90429-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge C., Marsden C. A. Electrical stimulation of the C1 region of the rostral ventrolateral medulla of the rat increases mean arterial pressure and adrenaline release in the posterior hypothalamus. Neuroscience. 1987 Feb;20(2):457–466. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saavedra J. M. Adrenaline levels in brain stem nuclei and effects of a PNMT inhibitor on spontaneously hypertensive rats. Brain Res. 1979 Apr 27;166(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saavedra J. M., Grobecker H., Axelrod J. Adrenaline-forming enzyme in brainstem: elevation in genetic and experimental hypertension. Science. 1976 Feb 6;191(4226):483–484. doi: 10.1126/science.1246633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scatton B., Pelayo F., Dubocovich M. L., Langer S. Z., Bartholini G. Effect of clonidine on utilization and potassium-evoked release of adrenaline in rat brain areas. Brain Res. 1979 Oct 26;176(1):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90887-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H., Fenard S. Evidence for an alpha-sympathomimetic component in the effects of catapresan on vasomotor centres: antagonism by piperoxane. Eur J Pharmacol. 1971;14(1):98–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(71)90130-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha J. N., Gurtu S., Sharma D. K., Bhargava K. P. An analysis of the alpha-adrenoceptor modulation of vasomotor tone at the level of lateral medullary pressor area (LMPA). Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;330(3):163–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00572428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Presynaptic receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:7–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Sawchenko P. E., Bérod A., Hartman B. K., Helle K. B., Vanorden D. E. An immunohistochemical study of the organization of catecholaminergic cells and terminal fields in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Feb 20;196(2):271–285. doi: 10.1002/cne.901960207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tackett R. L., Webb J. G., Privitera P. J. Site and mechanism of the centrally mediated hypotensive action of propranolol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Oct;235(1):66–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Goshima Y., Kubo T., Misu Y. Involvement of epinephrine in the presynaptic beta adrenoceptor mechanism of norepinephrine release from rat hypothalamic slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Feb;232(2):507–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Goshima Y., Misu Y. Presynaptic mediation by alpha 2-, beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors of endogenous noradrenaline and dopamine release from slices of rat hypothalamus. Life Sci. 1983 Jul 25;33(4):371–376. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(83)80011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unnerstall J. R., Kopajtic T. A., Kuhar M. J. Distribution of alpha 2 agonist binding sites in the rat and human central nervous system: analysis of some functional, anatomic correlates of the pharmacologic effects of clonidine and related adrenergic agents. Brain Res. 1984 Mar;319(1):69–101. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(84)90030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Gugten J., Palkovits M., Wijnen H. L., Versteeg D. H. Regional distribution of adrenaline in rat brain. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 30;107(1):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westfall T. C. Local regulation of adrenergic neurotransmission. Physiol Rev. 1977 Oct;57(4):659–728. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.4.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson L. I., Brown L. L. Intrastriatal injection of [3H]dopamine through a chronic cannula to produce rotation: distribution and concentration of the tracer in specific brain regions. Brain Res. 1983 Feb 21;261(2):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90624-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


