Abstract
1. The activity profiles of opioid agonists and non-steroidal analgesic agents have been compared against different nociceptive stimuli in the mouse and rat. 2. Opioid agonists, but not non-steroidal analgesic agents, inhibited reflex depressor responses evoked by visceral distension in anaesthetized rats. The ranked order of potency of opioids in the visceral distension reflex was identical to that observed in the mouse writhing assay. 3. Opioid-induced inhibition of reflex depressor responses and writhing was observed with ligands acting on mu- and kappa-, but not delta-receptors. Antinociceptive activity of opioids in the rat cold water tail-flick assay was restricted to mu-receptor agonists. 4. Morphine- and ethylketocyclazocine (EKC)-induced inhibition of the visceral distension reflex was blocked by naloxone, but not by the quaternary opioid antagonist N-methylnalorphine. 5. Direct cardiovascular effects were observed with ligands for the mu- and kappa-receptor. Blood pressure changes induced by morphine and Tyr.D-Ala.Gly.MePhe.Gly-ol (DAGOL), but not EKC, were blocked by N-methylnalorphine. Pretreatment with 16-methylcyprenorphine (M8008) antagonized morphine-, DAGOL- and EKC-induced cardiovascular effects, but not those of dynorphin-(1-13) or U50488. 6. It is concluded that reflex circulatory responses evoked by visceral distension in anaesthetized rats are a valid index for the evaluation of opioid-induced antinociception. A simultaneous assessment of cardiovascular effects of opioids was achieved.
Full text
PDF


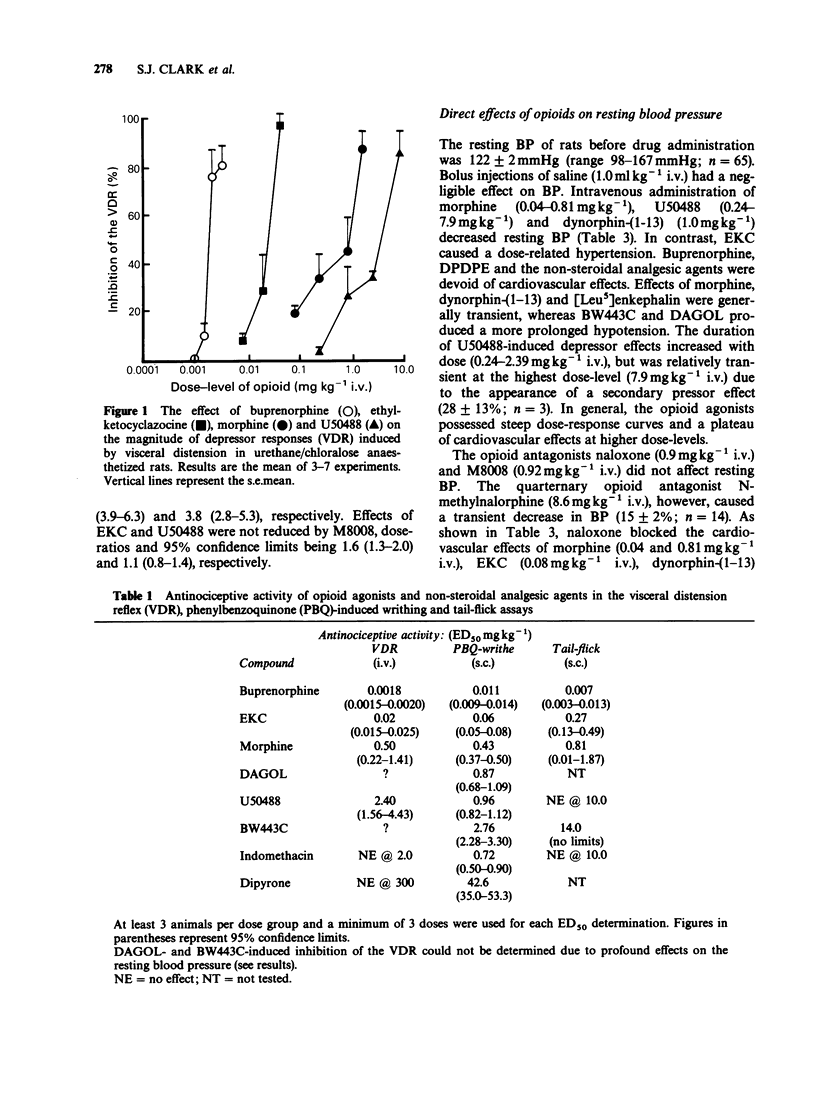
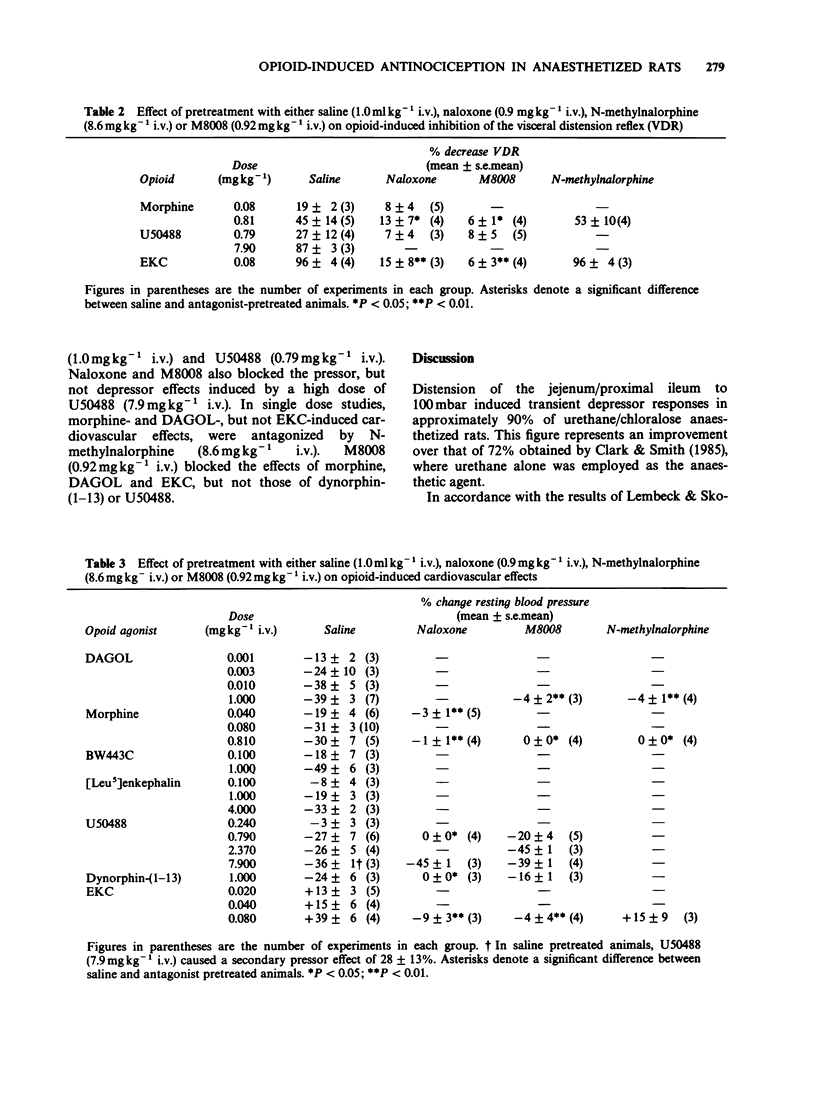




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brasch H., Zetler G. Caerulein and morphine in a model of visceral pain. Effects on the hypotensive response to renal pelvis distension in the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 May;319(2):161–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00503931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaillet P., Coulaud A., Zajac J. M., Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Costentin J., Roques B. P. The mu rather than the delta subtype of opioid receptors appears to be involved in enkephalin-induced analgesia. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 May 18;101(1-2):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. J., Smith T. W. Opiate-induced inhibition of the visceral distension reflex by peripheral and central mechanisms. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;330(3):179–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00572431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett A. D., Gillan M. G., Kosterlitz H. W., McKnight A. T., Paterson S. J., Robson L. E. Selectivities of opioid peptide analogues as agonists and antagonists at the delta-receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;83(1):271–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R., Giles M. G., Miller L., Shaw J. S., Timms D. ICI 174864: a highly selective antagonist for the opioid delta-receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jan 27;97(3-4):331–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downman C. B., McSwiney B. A., Vass C. C. Sensitivity of the small intestine. J Physiol. 1948 Jan 1;107(1):97–106. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1948.sp004253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensinger H., Hedler L., Schurr C., Starke K. Ethylketocyclazocine decreases noradrenaline release and blood pressure in the rabbit at a peripheral opioid receptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;328(1):20–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00496099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins and the mechanism of analgesia produced by aspirin-like drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;49(1):86–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follenfant R. L., Hardy G. W., Lowe L. A., Schneider C., Smith T. W. Antinociceptive effects of the novel opioid peptide BW443C compared with classical opiates; peripheral versus central actions. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;93(1):85–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Given M. B., Sander G. E., Giles T. D. Non-opiate and peripheral-opiate cardiovascular effects of morphine in conscious dogs. Life Sci. 1986 Apr 7;38(14):1299–1303. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDERSHOT L. C., FORSAITH J. Antagonism of the frequency of phenylquinone-induced writhing in the mouse by weak analgesics and nonanalgesics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 Mar;125(3):237–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa B. K., Land A. C., Lord J. A., Morgan B. A., Rance M. J., Smith C. F. Analogues of beta-LPH61-64 possessing selective agonist activity at mu-opiate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 9;70(4):531–540. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90364-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHANSSON B. Circulatory responses to stimulation of somatic afferents with special reference to depressor effects from muscle nerves. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1962;198:1–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajiwara M., Aoki K., Ishii K., Numata H., Matsumiya T., Oka T. Agonist and antagonist actions of buprenorphine on three types of opioid receptor in isolated preparations. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;40(1):95–101. doi: 10.1254/jjp.40.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobylecki R. J., Lane A. C., Smith C. F., Wakelin L. P., Cruse W. B., Egert E., Kennard O. N-Methylnalorphine: definition of N-allyl conformation for antagonism at the opiate receptor. J Med Chem. 1982 Nov;25(11):1278–1280. doi: 10.1021/jm00353a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent S., Schmitt H. Central cardiovascular effects of kappa agonists dynorphin-(1-13) and ethylketocyclazocine in the anaesthetized rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec 9;96(1-2):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90547-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnan J., Paterson S. J., Tavani A., Kosterlitz H. W. The binding spectrum of narcotic analgesic drugs with different agonist and antagonist properties. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Jun;319(3):197–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00495865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Ferreira S. H., Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis as the mechanism of analgesia of aspirin-like drugs in the dog knee joint. Eur J Pharmacol. 1975 Apr;31(2):250–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(75)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Gee K., Yamamura H. I., Galligan J. J., Burks T. F. Bis-penicillamine enkephalins possess highly improved specificity toward delta opioid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5871–5874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Negishi K., Suda M., Sawa A., Fujino M., Wakimasu M. Evidence that dynorphin-(1-13) acts as an agonist on opioid kappa-receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan 22;77(2-3):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson S. J., Robson L. E., Kosterlitz H. W. Classification of opioid receptors. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):31–36. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peets J. M., Pomeranz B. Studies in suppression of nocifensive reflexes measured with tail flick electromyograms and using intrathecal drugs in barbiturate anesthetized rats. Brain Res. 1987 Jul 28;416(2):301–307. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90910-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizziketti R. J., Pressman N. S., Geller E. B., Cowan A., Adler M. W. Rat cold water tail-flick: a novel analgesic test that distinguishes opioid agonists from mixed agonist-antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Dec 10;119(1-2):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Procacci P., Zoppi M., Maresca M. Experimental pain in man. Pain. 1979 Apr;6(2):123–140. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(79)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez R. E., Leighton G., Hill R. G., Hughes J. In vivo evidence for spinal delta-opiate receptor operated antinociception. Neuropeptides. 1986 Oct;8(3):221–241. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(86)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. F. 16-Me cyprenorphine (RX 8008M): a potent opioid antagonist with some delta selectivity. Life Sci. 1987 Jan 19;40(3):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90342-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Buchan P., Parsons D. N., Wilkinson S. Peripheral antinociceptive effects of N-methyl morphine. Life Sci. 1982 Sep 20;31(12-13):1205–1208. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90343-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Follenfant R. L., Ferreira S. H. Antinociceptive models displaying peripheral opioid activity. Int J Tissue React. 1985;7(1):61–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarbrick E. T., Hegarty J. E., Bat L., Williams C. B., Dawson A. M. Site of pain from the irritable bowel. Lancet. 1980 Aug 30;2(8192):443–446. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91885-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo B., Hedler L., Ensinger H., Starke K. Opioid peptides decrease noradrenaline release and blood pressure in the rabbit at peripheral receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;332(1):50–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00633196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallarida R. J., Cowan A., Adler M. W. pA2 and receptor differentiation: a statistical analysis of competitive antagonism. Life Sci. 1979 Aug 20;25(8):637–654. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90505-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M. B. A classification of opiate receptors that mediate antinociception in animals. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;69(3):503–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb07041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonvoigtlander P. F., Lahti R. A., Ludens J. H. U-50,488: a selective and structurally novel non-Mu (kappa) opioid agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. J., Takemori A. E. Relative involvement of mu, kappa and delta receptor mechanisms in opiate-mediated antinociception in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Mar;224(3):525–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Rudy T. A. Studies on the direct spinal action of narcotics in the production of analgesia in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Aug;202(2):411–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


