Abstract
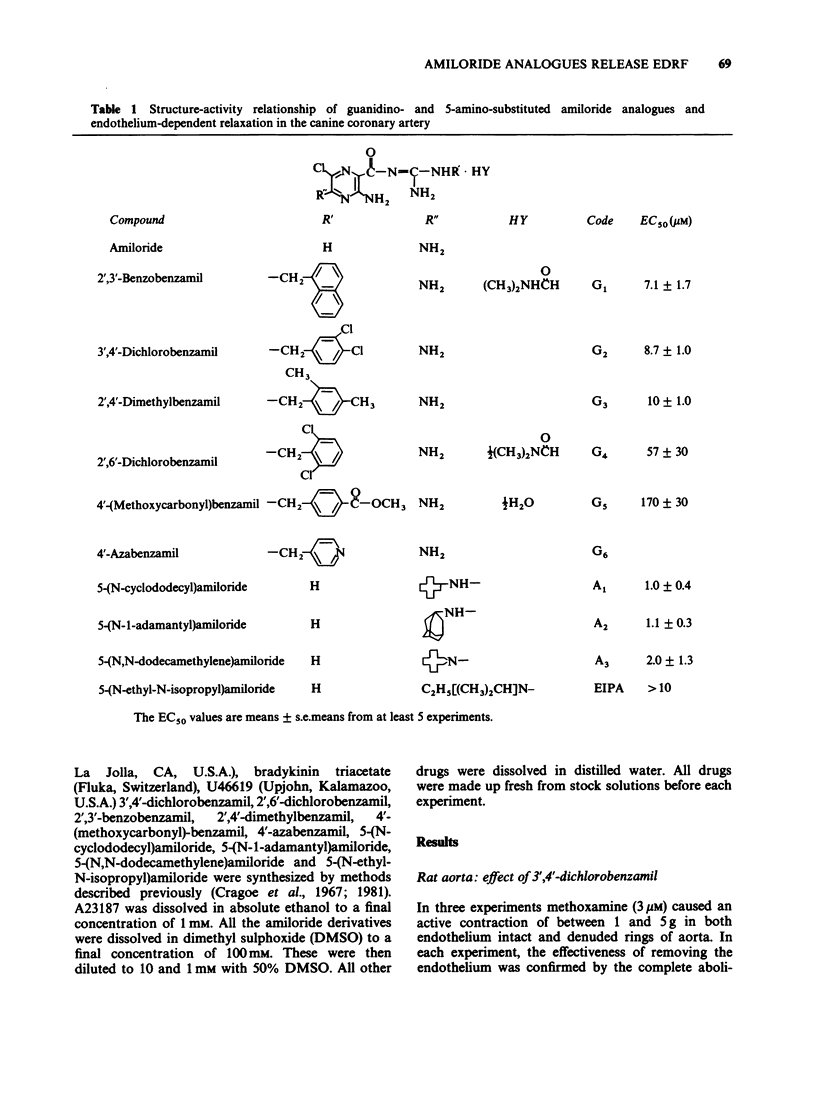
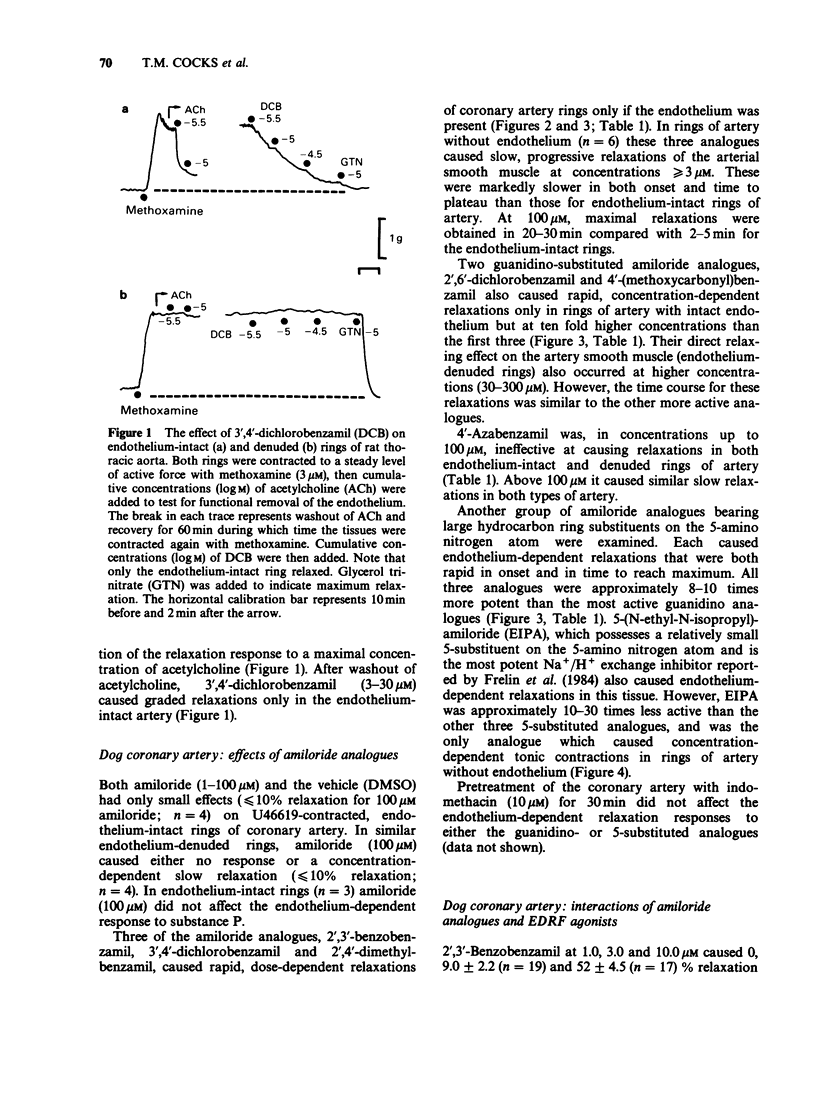
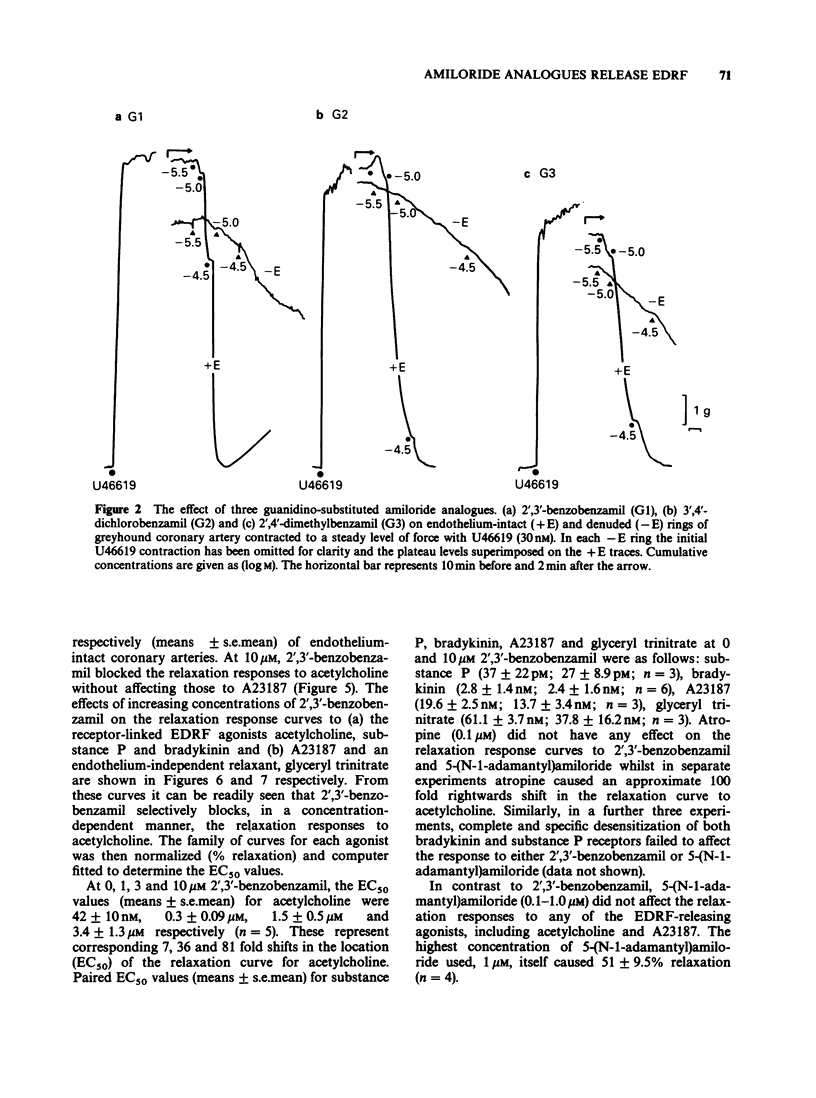
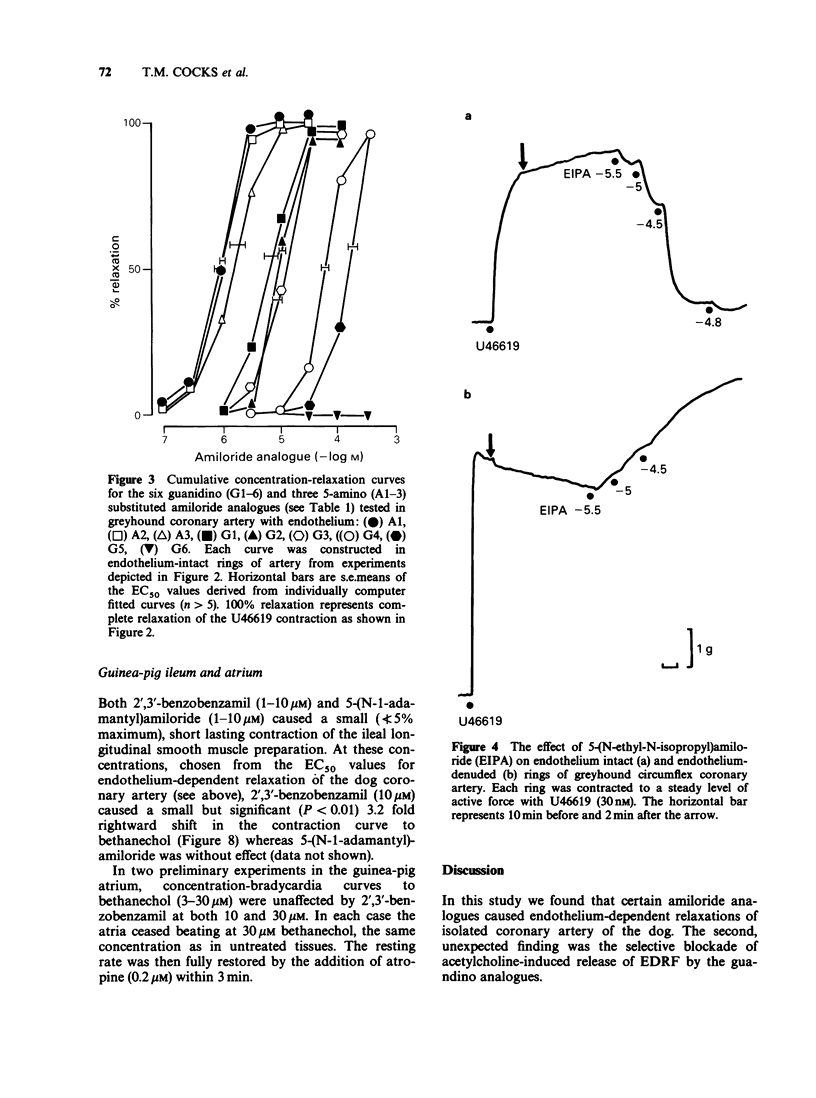
1. A number of amiloride analogues were used to test the proposal that Na+/Ca2+ exchange may play a role in the secretion of endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF). The analogues used were those substituted on either the 5-amino group or the terminal guanidino nitrogen atom. The former block both Na+/Ca2+ and Na+/H+ exchange whilst the latter block the Na+ channel and the Na+/Ca2+ exchange. 2. Both series of compounds caused relaxation in isolated rings of dog coronary artery (EC50 values, 1-10 microM) presumably due to release of EDRF since removal of endothelium greatly attenuated the response. 3. Amiloride (1-100 microM) had little effect on either endothelium-intact or denuded arteries. 4. The guanidino substituted analogues also appeared to block selectively the relaxation response to acetylcholine in the coronary artery, independently of their EDRF-releasing activity. 5. It is proposed that endothelial cells have an active Na+/Ca2+ exchange operating in the forward mode to extrude Ca2+. This mechanism may be important in the control of EDRF release.
Full text
PDF

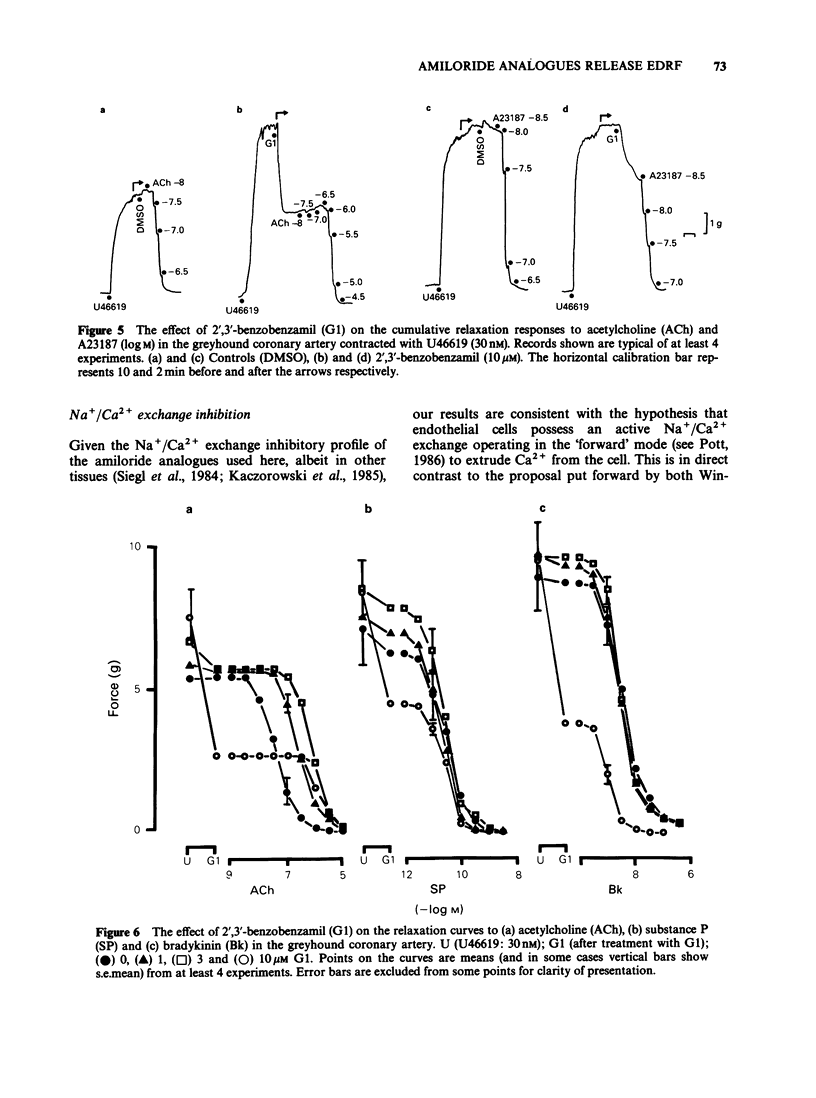
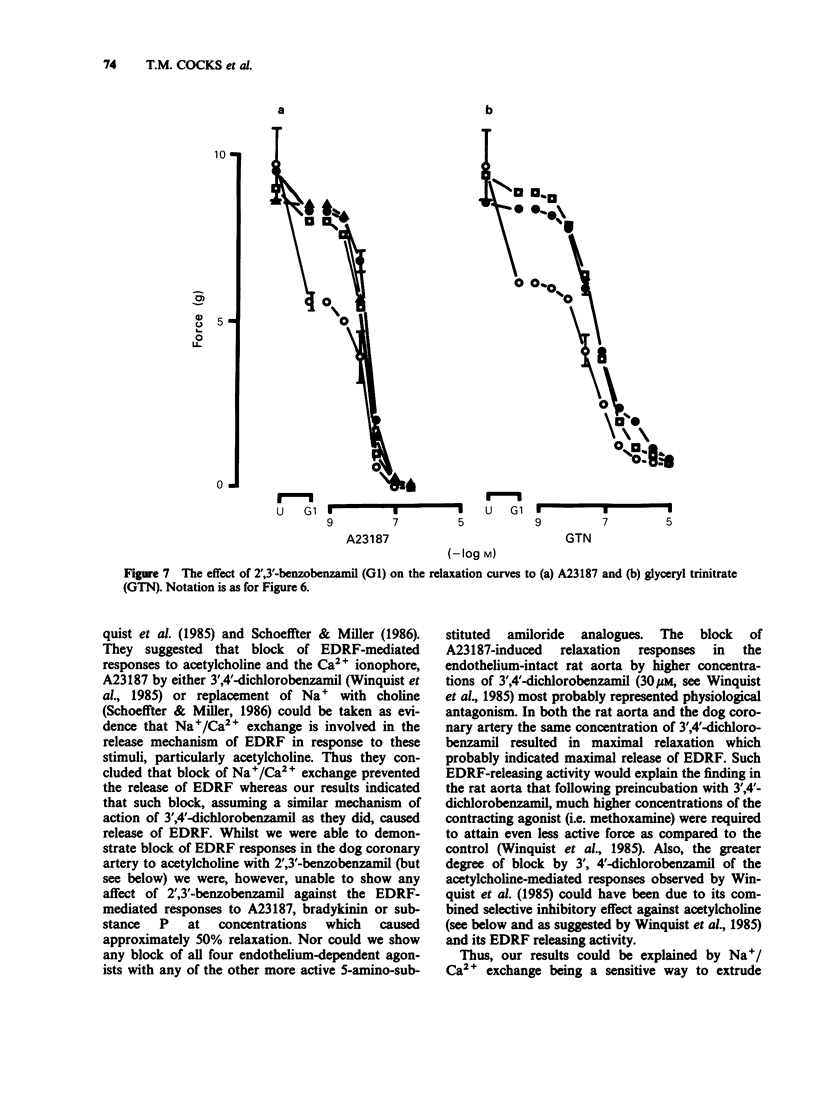
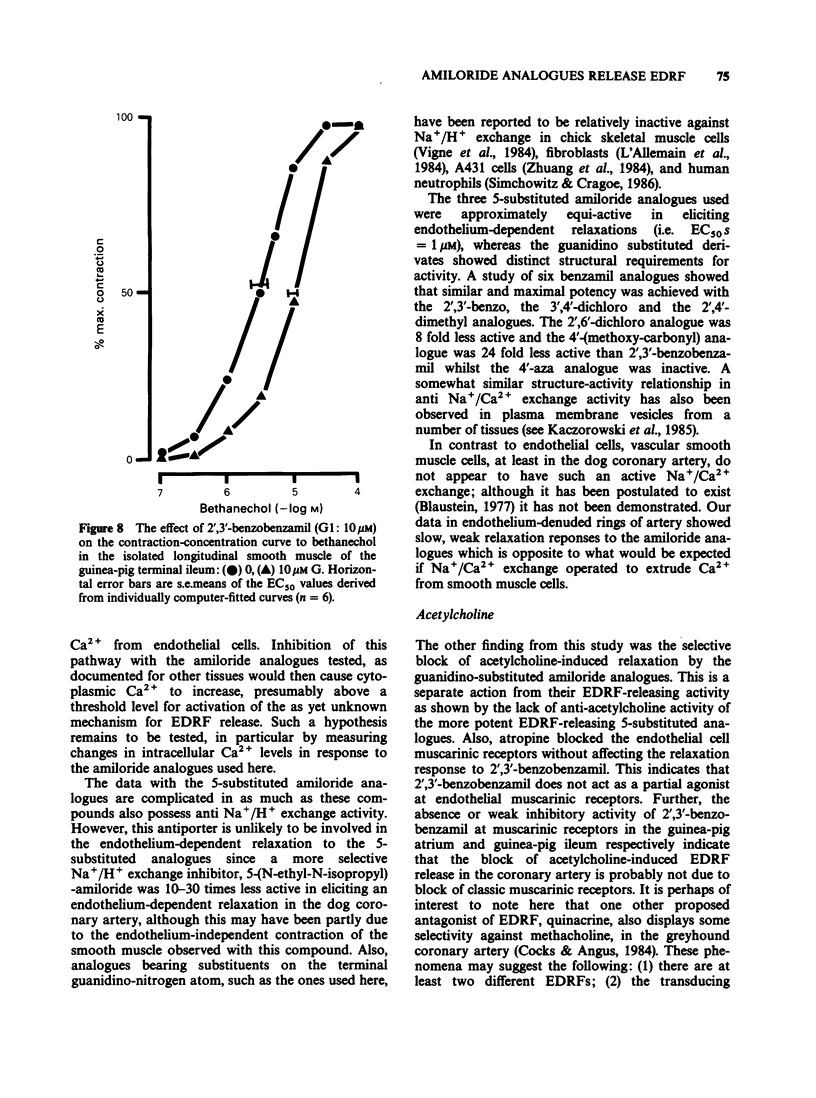

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angus J. A., Harvey K. Refractory period fluid stimulation of right atria: a method for studying presynaptic receptors in cardiac autonomic transmission. J Pharmacol Methods. 1981 Aug;6(1):51–64. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(81)90084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry W. H., Smith T. W. Mechanisms of transmembrane calcium movement in cultured chick embryo ventricular cells. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:243–260. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Sodium ions, calcium ions, blood pressure regulation, and hypertension: a reassessment and a hypothesis. Am J Physiol. 1977 May;232(5):C165–C173. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1977.232.5.C165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks T. M., Angus J. A. Endothelium-dependent relaxation of coronary arteries by noradrenaline and serotonin. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):627–630. doi: 10.1038/305627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cragoe E. J., Jr, Woltersdorf O. W., Jr, Bicking J. B., Kwong S. F., Jones J. H. Pyrazine diuretics. II. N-amidino-3-amino-5-substituted 6-halopyrazinecarboxamides. J Med Chem. 1967 Jan;10(1):66–75. doi: 10.1021/jm00313a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelin C., Vigne P., Lazdunski M. The role of the Na+/H+ exchange system in cardiac cells in relation to the control of the internal Na+ concentration. A molecular basis for the antagonistic effect of ouabain and amiloride on the heart. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8880–8885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F. The role of endothelium in the responses of vascular smooth muscle to drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1984;24:175–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.24.040184.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski G. J., Barros F., Dethmers J. K., Trumble M. J., Cragoe E. J., Jr Inhibition of Na+/Ca2+ exchange in pituitary plasma membrane vesicles by analogues of amiloride. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1394–1403. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kizer J. S., Busby W. H., Jr, Cottle C., Youngblood W. W. Glycine-directed peptide amidation: presence in rat brain of two enzymes that convert p-Glu-His-Pro-Gly-OH into p-Glu-His-Pro-NH2 (thyrotropin-releasing hormone). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3228–3232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Allemain G., Franchi A., Cragoe E., Jr, Pouysségur J. Blockade of the Na+/H+ antiport abolishes growth factor-induced DNA synthesis in fibroblasts. Structure-activity relationships in the amiloride series. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4313–4319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer G. A. Sodium-calcium exchange in the heart. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:435–449. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima A., Angus J. A., Johnston C. I. Comparison of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors captopril and MK421-diacid in guinea pig atria. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 16;81(3):487–492. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90114-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeffter P., Miller R. C. Role of sodium-calcium exchange and effects of calcium entry blockers on endothelial-mediated responses in rat isolated aorta. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Jul;30(1):53–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchowitz L., Cragoe E. J., Jr Inhibition of chemotactic factor-activated Na+/H+ exchange in human neutrophils by analogues of amiloride: structure-activity relationships in the amiloride series. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Aug;30(2):112–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne P., Frelin C., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Lazdunski M. Structure-activity relationships of amiloride and certain of its analogues in relation to the blockade of the Na+/H+ exchange system. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;25(1):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Bunting P. B., Schofield T. L. Blockade of endothelium-dependent relaxation by the amiloride analog dichlorobenzamil: possible role of Na+/Ca++ exchange in the release of endothelium-derived relaxant factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Dec;235(3):644–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Shaikewitz T., Glaser L., Cassel D. Characterization of potent Na+/H+ exchange inhibitors from the amiloride series in A431 cells. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 11;23(19):4481–4488. doi: 10.1021/bi00314a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


