Abstract
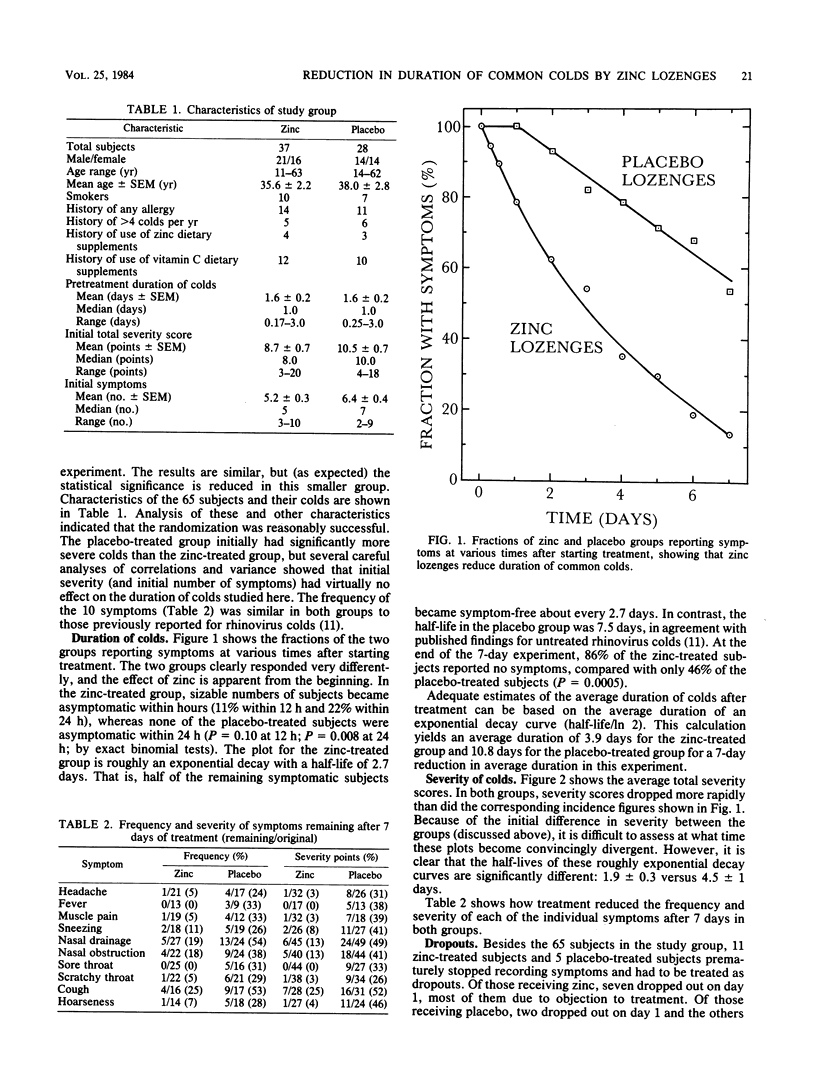
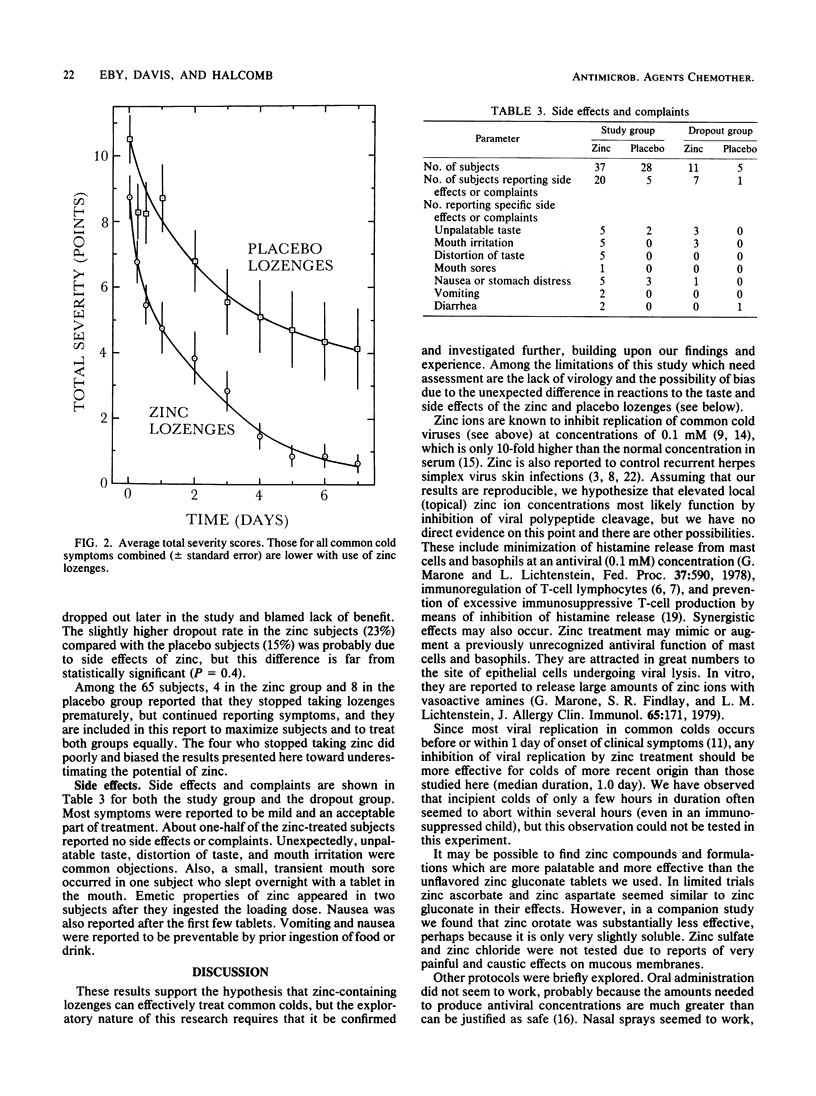
As a possible treatment for common colds, we tested zinc gluconate lozenges in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. One 23-mg zinc lozenge or matched placebo was dissolved in the mouth every 2 wakeful h after an initial double dose. After 7 days, 86% of 37 zinc-treated subjects were asymptomatic, compared with only 46% of 28 placebo-treated subjects (P = 0.0005). Side effects or complaints were usually minor and consisted mainly of objectionable taste and mouth irritation. Zinc lozenges shortened the average duration of common colds by about 7 days.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki F. Y., Crowley J. C. Distribution and removal of human serum albumin-technetium 99m instilled intranasally. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;3(5):869–878. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1976.tb00640.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogomolova G. G., Karlinskii V. M. Pokazateli obmena tsinka pri leikozakh. Vrach Delo. 1977 Dec;(12):57–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody I. Topical treatment of recurrent herpes simplex and post-herpetic erythema multiforme with low concentrations of zinc sulphate solution. Br J Dermatol. 1981 Feb;104(2):191–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1981.tb00044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Grunert R. R., Korant B. D., Lonberg-Holm K., Yin F. H. Replication of rhinoviruses. Arch Virol. 1976;51(3):169–189. doi: 10.1007/BF01318022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Korant B. D. Characterization of the large picornaviral polypeptides produced in the presence of zinc ion. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):282–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.282-291.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchateau J., Delepesse G., Vrijens R., Collet H. Beneficial effects of oral zinc supplementation on the immune response of old people. Am J Med. 1981 May;70(5):1001–1004. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90849-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchateau J., Delespesse G., Vereecke P. Influence of oral zinc supplementation on the lymphocyte response to mitogens of normal subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Jan;34(1):88–93. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.1.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahim M. S., Brawner T. A., Hall D. G. New treatment for herpes simplex virus type 2 [ultrasound and zinc, urea and tannic acid ointment]. Part II: Female patients. J Med. 1980;11(2-3):143–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridlender B., Chejanovsky N., Becker Y. Selective inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase by zinc ions. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):551–554. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90274-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., Rapp F. Effect of zinc ions on synthesis of herpes simplex virus type 2-induced polypeptides. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Jul;152(3):455–458. doi: 10.3181/00379727-152-39417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D., Butterworth B. E. Inhibition by zinc of rhinovirus protein cleavage: interaction of zinc with capsid polypeptides. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):298–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.298-306.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D., Kauer J. C., Butterworth B. E. Zinc ions inhibit replication of rhinoviruses. Nature. 1974 Apr 12;248(449):588–590. doi: 10.1038/248588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pories W. J., Henzel J. H., Rob C. G., Strain W. H. Acceleration of wound healing in man with zinc sulphate given by mouth. Lancet. 1967 Jan 21;1(7482):121–124. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E., Haberek-Davidson A. Histamine activates suppressor cells in vitro using a coculture technique. J Clin Immunol. 1981 Jan;1(1):73–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00915479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahba A. Topical application of zinc-solutions: a new treatment for herpes simplex infections of the skin? Acta Derm Venereol. 1980;60(2):175–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wazewska-Czyzewska M., Wesierska-Gadek J., Legutko L. Immunostimulatory effect of zinc in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1978;105(6):727–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


