Abstract
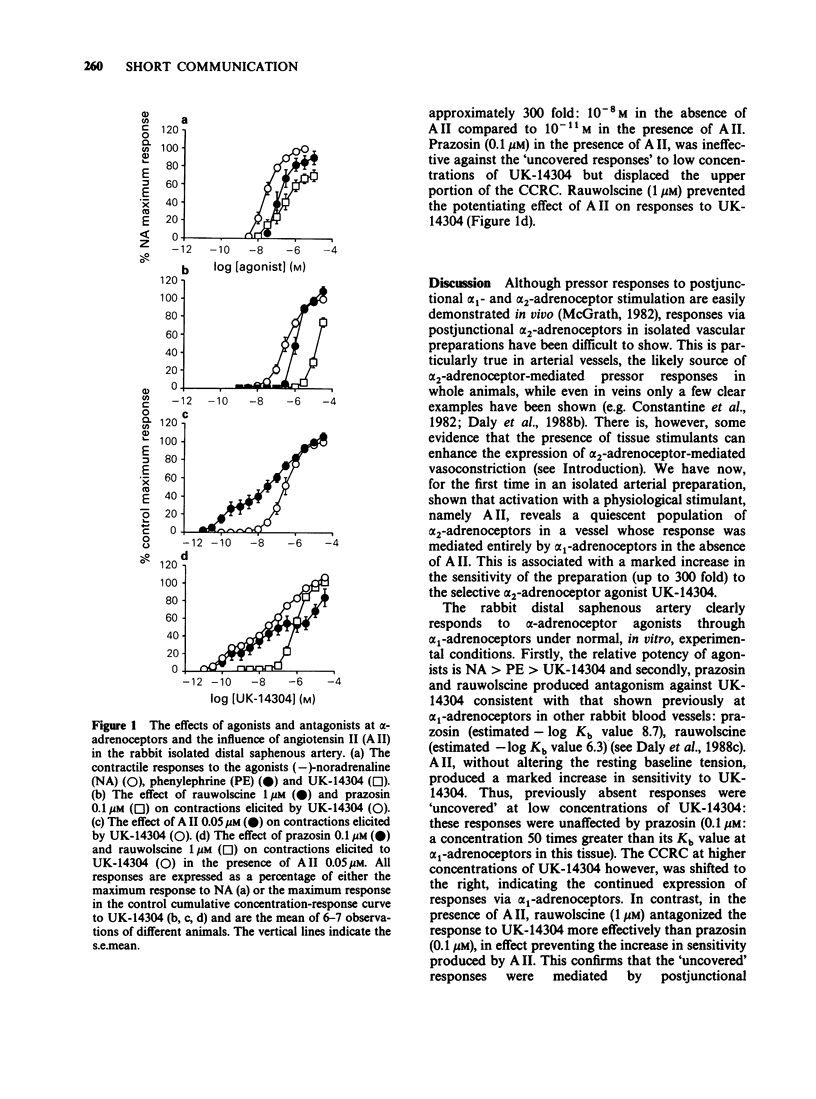
In the rabbit isolated distal saphenous artery, the population of postjunctional adrenoceptors is of the alpha 1 variety under normal in vitro experimental conditions, based on the potency order of selective agonists and on the effects of the antagonists prazosin and rauwolscine against responses to UK-14304. Angiotensin II (A II, 0.05 microM) however, without affecting resting baseline tension, markedly enhanced responses to UK-14304, particularly at low concentrations. This previously unseen component of the response to UK-14304 was resistant to prazosin (0.1 microM) but susceptible to rauwolscine (1 microM). A II would therefore appear to have a permissive role for the expression of a quiescent population of postjunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the rabbit distal saphenous artery.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Constantine J. W., Lebel W., Archer R. Functional postsynaptic alpha 2- but not alpha 1-adrenoceptors in dog saphenous vein exposed to phenoxybenzamine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 3;85(3-4):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly C. J., Dunn W. R., McGrath J. C., Wilson V. G. An attempt at selective protection from phenoxybenzamine of postjunctional alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes mediating contractions to noradrenaline in the rabbit isolated saphenous vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):501–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11670.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly C. J., McGrath J. C., Wilson V. G. An examination of the postjunctional alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes for (-)-noradrenaline in several isolated blood vessels from the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):473–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta T. Precontraction-induced contractile response of isolated canine portal vein to alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonists. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 May;337(5):525–530. doi: 10.1007/BF00182726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Evidence for more than one type of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):467–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schümann H. J., Lues I. Postjunctional alpha-adrenoceptors in the isolated saphenous vein of the rabbit. Characterization and influence of angiotensin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Aug;323(4):328–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00512471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulpizio A., Hieble J. P. Demonstration of alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated contraction in the isolated canine saphenous artery treated with Bay K 8644. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 3;135(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90765-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


