Abstract
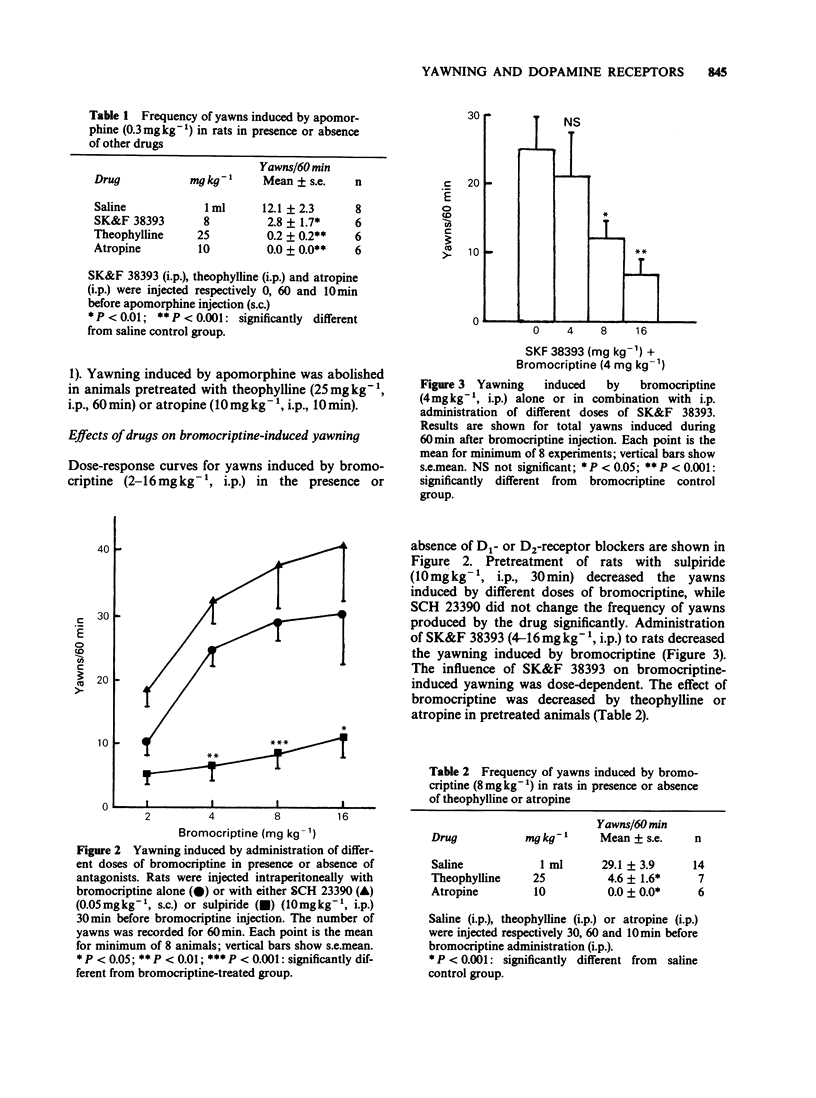
1. Yawning was induced by subcutaneous (s.c.) injection of low doses of apomorphine to rats. This effect decreased with increasing doses of the drug. 2. Intraperitoneal (i.p.) pretreatment of animals with sulpiride (D2-receptor blocker) reduced the frequency of the yawns induced by apomorphine, while SCH 23390 (D1-receptor blocker, s.c.) pretreatment increased the small number of yawns which was induced by higher doses of apomorphine. Administration of SCH 23390 alone to rats also produced a low degree of yawning. 3. Apomorphine-induced yawning was decreased in animals treated with SK&F 38393 (D1-agonist, i.p.), atropine (i.p.) or theophylline (i.p.). 4. Intraperitoneal injection of bromocriptine (D2-agonist) in rats also induced dose-dependent yawning. The effect was decreased in animals pretreated with sulpiride, while SCH 23390 pretreatment did not change bromocriptine-induced yawning significantly. Pretreatment of animals with SK&F 38393, atropine or theophylline reduced the number of yawns induced by bromocriptine. 5. Physostigmine (i.p.) but not neostigmine (i.p.) also induced yawning. The effect was antagonized by atropine or theophylline but not by sulpiride. Administration of SK&F 38393 decreased yawning induced by physostigmine. This inhibitory influence of SK&F 38393 was reduced by SCH 23390 in pretreated animals. Treatment of animals with SCH 23390 or bromocriptine increased the frequency of yawns induced by physostigmine. 6. It is concluded that D2-receptor activation elicits yawning through influence on cholinergic mechanisms, whereas D1-receptor stimulation decreases yawning behaviour by a negative influence on the cholinergic system.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altar C. A., O'Neil S., Walter R. J., Jr, Marshall J. F. Brain dopamine and serotonin receptor sites revealed by digital subtraction autoradiography. Science. 1985 May 3;228(4699):597–600. doi: 10.1126/science.2580352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTCHER R. W., SUTHERLAND E. W. Adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in biological materials. I. Purification and properties of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase and use of this enzyme to characterize adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in human urine. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1244–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggio G., Ferrari F. The role of dopaminergic receptors in the behavioral effects induced by lisuride in male rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1983;80(1):38–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00427492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costall B., Fortune D. H., Hui S. C., Naylor R. J. Neuroleptic antagonism of the motor inhibitory effects of apomorphine within the nucleus accumbens: drug interaction at presynaptic receptors? Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 May 16;63(4):347–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson T. M., Gehlert D. R., Yamamura H. I., Barnett A., Wamsley J. K. D-1 dopamine receptors in the rat brain: autoradiographic localization using [3H]SCH 23390. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 5;108(3):323–325. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90458-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Chiara G., Porceddu M. L., Vargiu L., Argiolas A., Gessa G. L. Evidence for dopamine receptors mediating sedation in the mouse brain. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):564–567. doi: 10.1038/264564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Chiara G., Vargiu L., Porceddu M. L., Gessa G. L. Bromocriptine: a rather specific stimulant of dopamine receptors regulating dopamine metabolism. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1977;16:443–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dourish C. T., Cooper S. J., Philips S. R. Yawning elicited by systemic and intrastriatal injection of piribedil and apomorphine in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1985;86(1-2):175–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00431705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubuc I., Protais P., Colboc O., Costentin J. Antagonism of the apomorphine-induced yawning by "atypical" neuroleptics. Neuropharmacology. 1982 Nov;21(11):1203–1206. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(82)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumbrille-Ross A., Niznik H., Seeman P. Separation of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Mar 26;110(1):151–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fage D., Scatton B. Opposing effects of D-1 and D-2 receptor antagonists on acetylcholine levels in the rat striatum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 7;129(3):359–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90447-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garau L., Govoni S., Stefanini E., Trabucchi M., Spano P. F. Dopamine receptors: pharmacological and anatomical evidences indicate that two distinct dopamine receptor populations are present in rat striatum. Life Sci. 1978 Oct 30;23(17-18):1745–1750. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90102-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianutsos G., Moore K. E. Differential behavioral and biochemical effects of four dopaminergic agonists. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1980;68(2):139–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00432131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren B., Urbá-Holmgren R. Interaction of cholinergic and dopaminergic influences on yawning behavior. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1980;40(3):633–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyttel J. Functional evidence for selective dopamine D-1 receptor blockade by SCH 23390. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Dec;23(12A):1395–1401. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Calne D. B. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. doi: 10.1038/277093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendler K. S., Bracha H. S., Davis K. L. Dopamine autoreceptor and postsynaptic receptor blocking potency of neuroleptics. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Apr 23;79(3-4):217–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90627-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martres M. P., Bouthenet M. L., Sales N., Sokoloff P., Schwartz J. C. Widespread distribution of brain dopamine receptors evidenced with [125I]iodosulpride, a highly selective ligand. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):752–755. doi: 10.1126/science.3838821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogilnicka E., Klimek V. Drugs affecting dopamine neurons and yawning behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1977 Oct;7(4):303–305. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(77)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morelli M., Longoni R., Spina L., Di Chiara G. Antagonism of apomorphine-induced yawning by SCH 23390: evidence against the autoreceptor hypothesis. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1986;89(2):259–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00310640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M., Klimek V., Hyttel J. Distinct target size of dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptors in rat striatum. Life Sci. 1984 Jul 16;35(3):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90116-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onali P., Olianas M. C., Gessa G. L. Characterization of dopamine receptors mediating inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity in rat striatum. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Aug;28(2):138–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onali P., Olianas M. C., Gessa G. L. Selective blockade of dopamine D-1 receptors by SCH 23390 discloses striatal dopamine D-2 receptors mediating the inhibition of adenylate cyclase in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Mar 16;99(1):127–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90445-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protais P., Dubuc I., Costentin J. Pharmacological characteristics of dopamine receptors involved in the dual effect of dopamine agonists on yawning behaviour in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Oct 28;94(3-4):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90416-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scatton B., Dubois A. Autoradiographic localization of D1 dopamine receptors in the rat brain with [3H]SKF 38393. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr 23;111(1):145–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. Brain dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Sep;32(3):229–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethy V. H., Roth R. H., Kuhar M. J., Van Woert M. H. Choline and acetylcholine: regional distribution and effect of degeneration of cholinergic nerve terminals in the rat hippocampus. Neuropharmacology. 1973 Sep;12(9):819–823. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(73)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethy V. H., Van Woert M. H. Regulation of striatal acetylcholine concentration by dopamine receptors. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):529–530. doi: 10.1038/251529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setler P. E., Sarau H. M., Zirkle C. L., Saunders H. L. The central effects of a novel dopamine agonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Aug 15;50(4):419–430. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoof J. C., Kebabian J. W. Independent in vitro regulation by the D-2 dopamine receptor of dopamine-stimulated efflux of cyclic AMP and K+-stimulated release of acetylcholine from rat neostriatum. Brain Res. 1982 Nov 4;250(2):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90420-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoof J. C., Kebabian J. W. Opposing roles for D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptors in efflux of cyclic AMP from rat neostriatum. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):366–368. doi: 10.1038/294366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoof J. C., Kebabian J. W. Two dopamine receptors: biochemistry, physiology and pharmacology. Life Sci. 1984 Dec 3;35(23):2281–2296. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90519-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuruta K., Frey E. A., Grewe C. W., Cote T. E., Eskay R. L., Kebabian J. W. Evidence that LY-141865 specifically stimulates the D-2 dopamine receptor. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):463–465. doi: 10.1038/292463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urba-Holmgren R., Holmgren B., Anias J. Pre- and post-synaptic dopaminergic receptors involved in apomorphine-induced yawning. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1982;42(2):115–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbá-Holmgren R., González R. M., Holmgren B. Is yawning a cholinergic response? Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):261–262. doi: 10.1038/267261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushijima I., Yamada K., Inoue T., Tokunaga T., Furukawa T., Noda Y. Muscarinic and nicotinic effects on yawning and tongue protruding in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1984 Aug;21(2):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(84)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S., Sebben M., Garcia-Sainz J. A., Bockaert J. D2-dopamine receptor-mediated inhibition of cyclic AMP formation in striatal neurons in primary culture. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;27(6):595–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Furukawa T. Direct evidence for involvement of dopaminergic inhibition and cholinergic activation in yawning. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1980 Jan;67(1):39–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00427593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Tanaka M., Shibata K., Furukawa T. Involvement of septal and striatal dopamine D-2 receptors in yawning behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1986;90(1):9–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00172863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


