Abstract
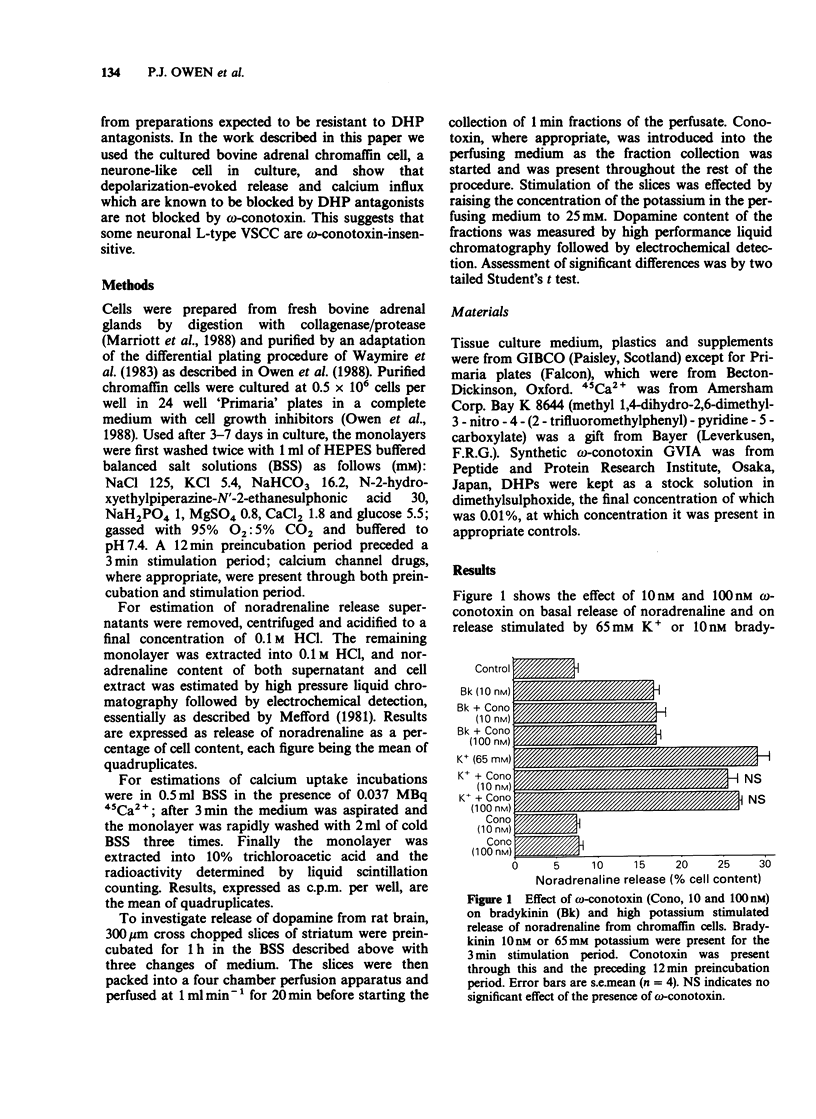
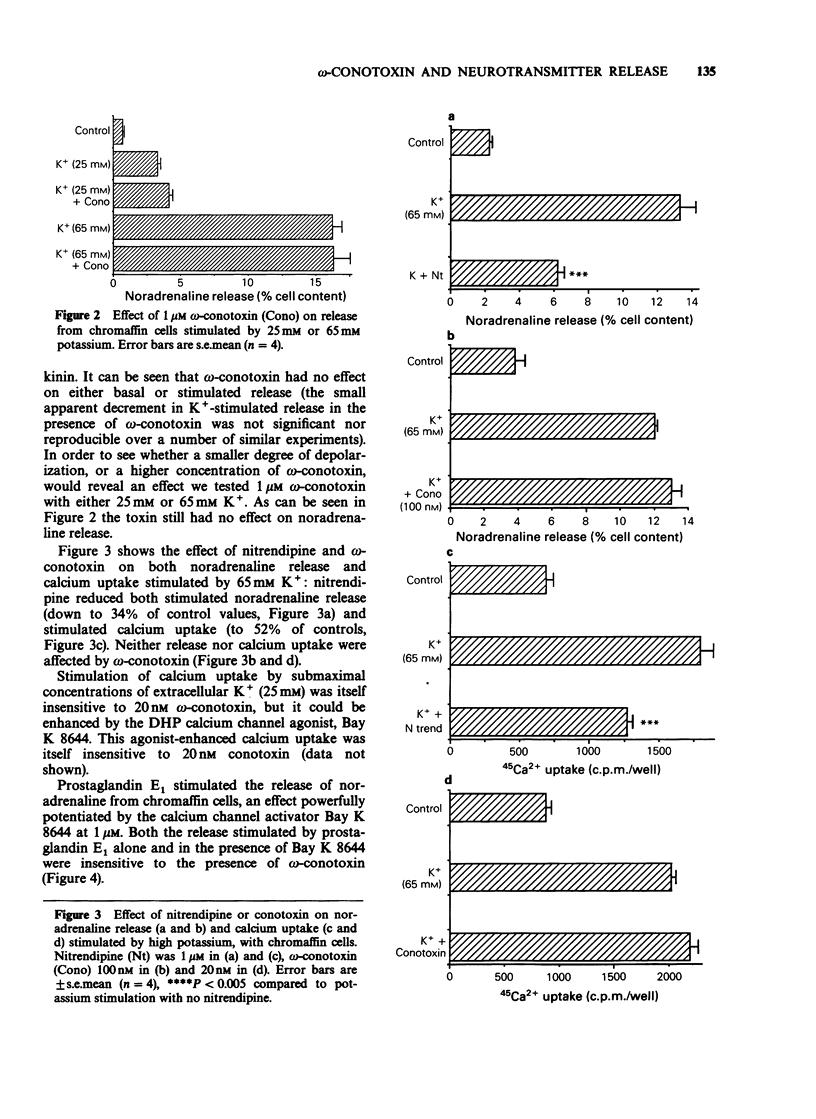
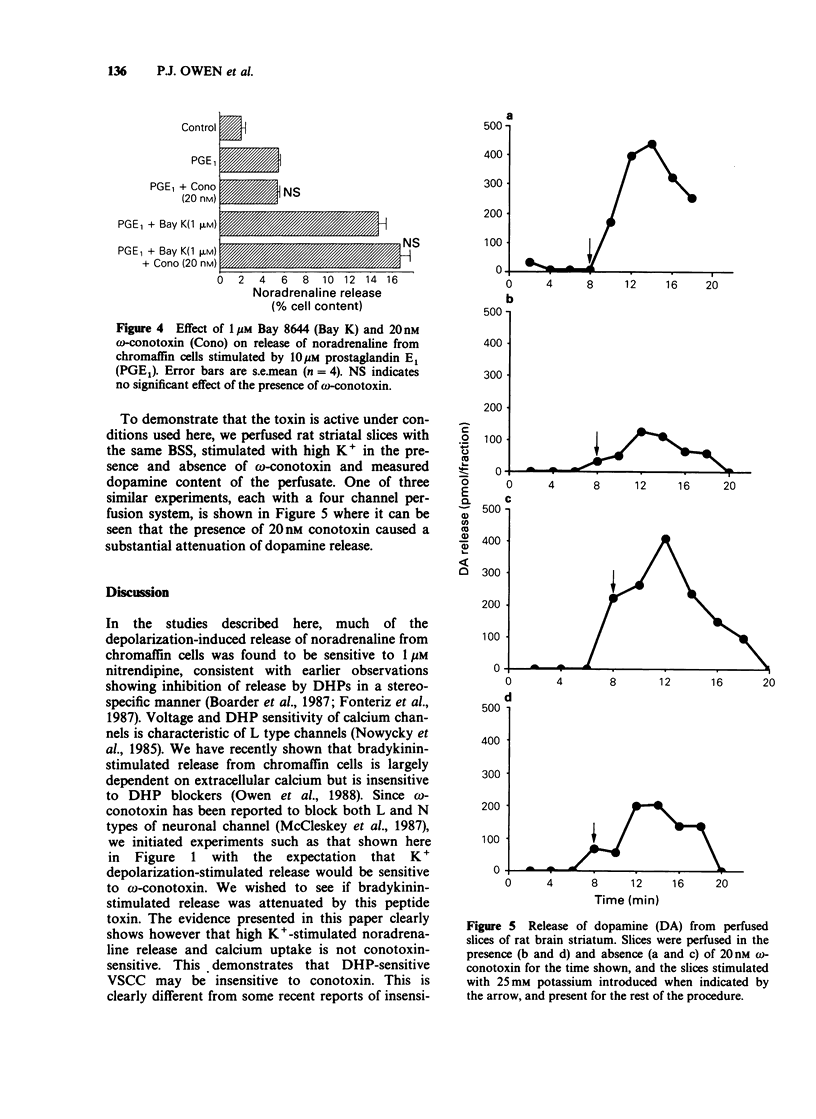
1. It has been suggested that neuronal voltage-sensitive calcium channels (VSCC) may be divided into dihydropyridine (DHP)-sensitive (L) and DHP-insensitive (N and T), and that both the L and the N type channels are attenuated by the peptide blocker omega-conotoxin. Here the effects of omega-conotoxin on release of noradrenaline and uptake of calcium in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells were investigated. 2. Release of noradrenaline in response to 25 mM K+, 65 mM K+, 10 nM bradykinin or 10 microM prostaglandin E1 was not affected by omega-conotoxin in the range 10 nM-1 microM. 3. 45Ca2+ uptake stimulated by high K+ and prostaglandin was attenuated by 1 microM nitrendipine and enhanced by 1 microM Bay K 8644; these calcium fluxes were not modified by 20 nM omega-conotoxin. 4. With superfused rat brain striatal slices in the same medium as the above cell studies, release of dopamine in response to 25 mM K+ was attenuated by 20 nM omega-conotoxin. 5. These results show that in these neurone-like cells, release may be effected by calcium influx through DHP-sensitive but omega-conotoxin-insensitive VSCC, a result inconsistent with the suggestion that omega-conotoxin blocks both L-type and N-type neuronal calcium channels.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson A. J., Harvey A. L. Omega-conotoxin does not block the verapamil-sensitive calcium channels at mouse motor nerve terminals. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Nov 23;82(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barhanin J., Schmid A., Lazdunski M. Properties of structure and interaction of the receptor for omega-conotoxin, a polypeptide active on Ca2+ channels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):1051–1062. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90736-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boarder M. R., Marriott D., Adams M. Stimulus secretion coupling in cultured chromaffin cells. Dependency on external sodium and on dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 1;36(1):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90394-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz L. J., Johnson D. S., Olivera B. M. Characterization of the omega-conotoxin target. Evidence for tissue-specific heterogeneity in calcium channel types. Biochemistry. 1987 Feb 10;26(3):820–824. doi: 10.1021/bi00377a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley D. J., Lupp A., Hertting G. Inhibition of central neurotransmitter release by omega-conotoxin GVIA, a peptide modulator of the N-type voltage-sensitive calcium channel. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;336(4):467–470. doi: 10.1007/BF00164885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonteriz R. I., Gandia L., Lopez M. G., Artalejo C. R., García A. G. Dihydropyridine chirality at the chromaffin cell calcium channel. Brain Res. 1987 Apr 7;408(1-2):359–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90405-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Dunlap K., Kream R. M. Characterization of the electrically evoked release of substance P from dorsal root ganglion neurons: methods and dihydropyridine sensitivity. J Neurosci. 1988 Feb;8(2):463–471. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-02-00463.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. M., Yoshikami D. A venom peptide with a novel presynaptic blocking action. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):282–284. doi: 10.1038/308282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama Y., Kitayama S., Dohi T., Tsujimoto A. Evidence that prostaglandins activate calcium channels to enhance basal and stimulation-evoked catecholamine release from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells in culture. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 May 1;37(9):1725–1730. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90435-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Santicioli P., Lippe I. T., Giuliani S., Geppetti P., Del Bianco E., Selleri S., Meli A. The effect of omega conotoxin GVIA, a peptide modulator of the N-type voltage sensitive calcium channels, on motor responses produced by activation of efferent and sensory nerves in mammalian smooth muscle. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;338(2):107–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00174856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott D., Adams M., Boarder M. R. Effect of forskolin and prostaglandin E1 on stimulus secretion coupling in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1988 Feb;50(2):616–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb02955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleskey E. W., Fox A. P., Feldman D. H., Cruz L. J., Olivera B. M., Tsien R. W., Yoshikami D. Omega-conotoxin: direct and persistent blockade of specific types of calcium channels in neurons but not muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4327–4331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mefford I. N. Application of high performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection to neurochemical analysis: measurement of catecholamines, serotonin and metabolites in rat brain. J Neurosci Methods. 1981 Feb;3(3):207–224. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(81)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. Multiple calcium channels and neuronal function. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):46–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2432656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachshen D. A., Blaustein M. P. The effects of some organic "calcium antagonists" on calcium influx in presynaptic nerve terminals. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;16(2):576–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., McIntosh J. M., Cruz L. J., Luque F. A., Gray W. R. Purification and sequence of a presynaptic peptide toxin from Conus geographus venom. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 23;23(22):5087–5090. doi: 10.1021/bi00317a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perney T. M., Hirning L. D., Leeman S. E., Miller R. J. Multiple calcium channels mediate neurotransmitter release from peripheral neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6656–6659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampe D., Janis R. A., Triggle D. J. BAY K 8644, a 1,4-dihydropyridine Ca2+ channel activator: dissociation of binding and functional effects in brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1984 Dec;43(6):1688–1692. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb06096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rane S. G., Holz G. G., 4th, Dunlap K. Dihydropyridine inhibition of neuronal calcium current and substance P release. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Aug;409(4-5):361–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00583789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds I. J., Wagner J. A., Snyder S. H., Thayer S. A., Olivera B. M., Miller R. J. Brain voltage-sensitive calcium channel subtypes differentiated by omega-conotoxin fraction GVIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8804–8807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier J., Galyean R., Gray W. R., Azimi-Zonooz A., McIntosh J. M., Cruz L. J., Olivera B. M. Neuronal calcium channel inhibitors. Synthesis of omega-conotoxin GVIA and effects on 45Ca uptake by synaptosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1194–1198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Enomoto K., Maeno T. Effects of synthetic omega-conotoxin, a new type Ca2+ antagonist, on frog and mouse neuromuscular transmission. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 11;141(2):235–241. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90268-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher E., Pandiella A., Clementi F. Omega-conotoxin binding and effects on calcium channel function in human neuroblastoma and rat pheochromocytoma cell lines. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):178–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81258-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium channels in rat brain synaptosomes: identification and pharmacological characterization. High affinity blockade by organic Ca2+ channel blockers. J Neurosci. 1985 Mar;5(3):841–849. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-03-00841.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waymire J. C., Bennett W. F., Boehme R., Hankins L., Gilmer-Waymire K., Haycock J. W. Bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: high-yield purification and viability in suspension culture. J Neurosci Methods. 1983 Apr;7(4):329–351. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(83)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager R. E., Yoshikami D., Rivier J., Cruz L. J., Miljanich G. P. Transmitter release from presynaptic terminals of electric organ: inhibition by the calcium channel antagonist omega Conus toxin. J Neurosci. 1987 Aug;7(8):2390–2396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Din M. M., Malik K. U. Differential effect of omega-conotoxin on release of the adrenergic transmitter and the vasoconstrictor response to noradrenaline in the rat isolated kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):355–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


