Abstract
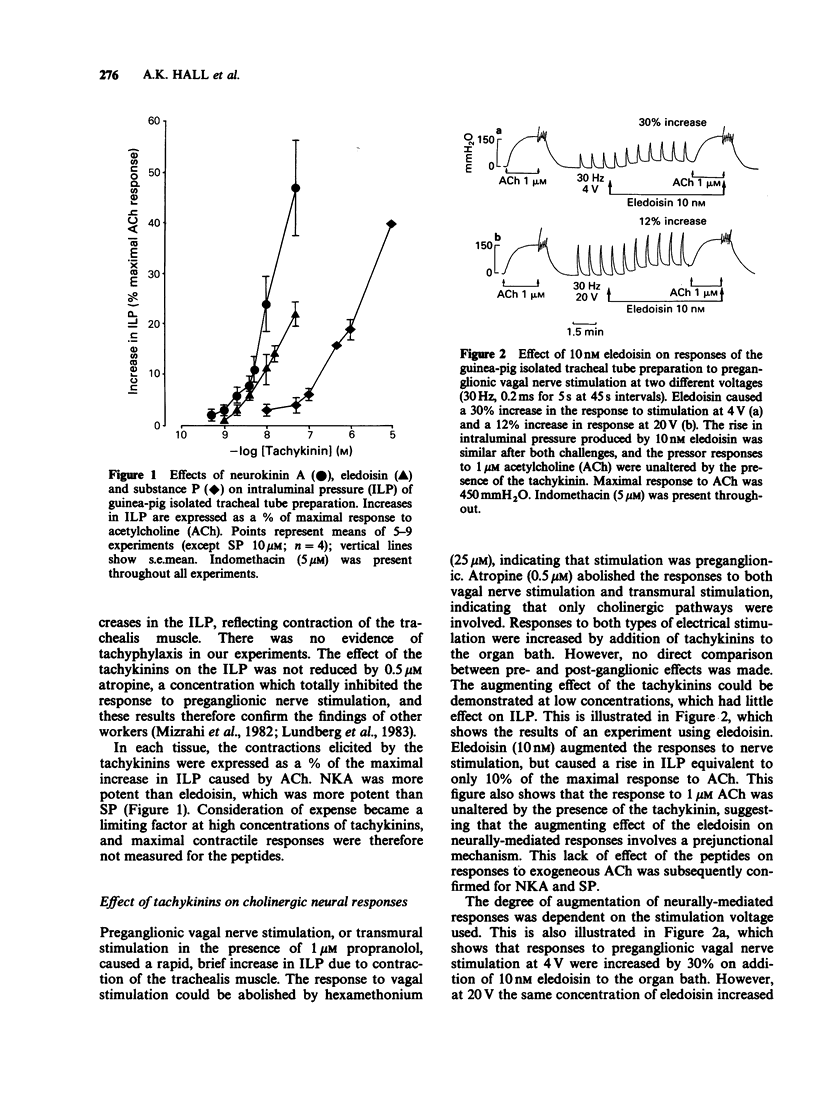
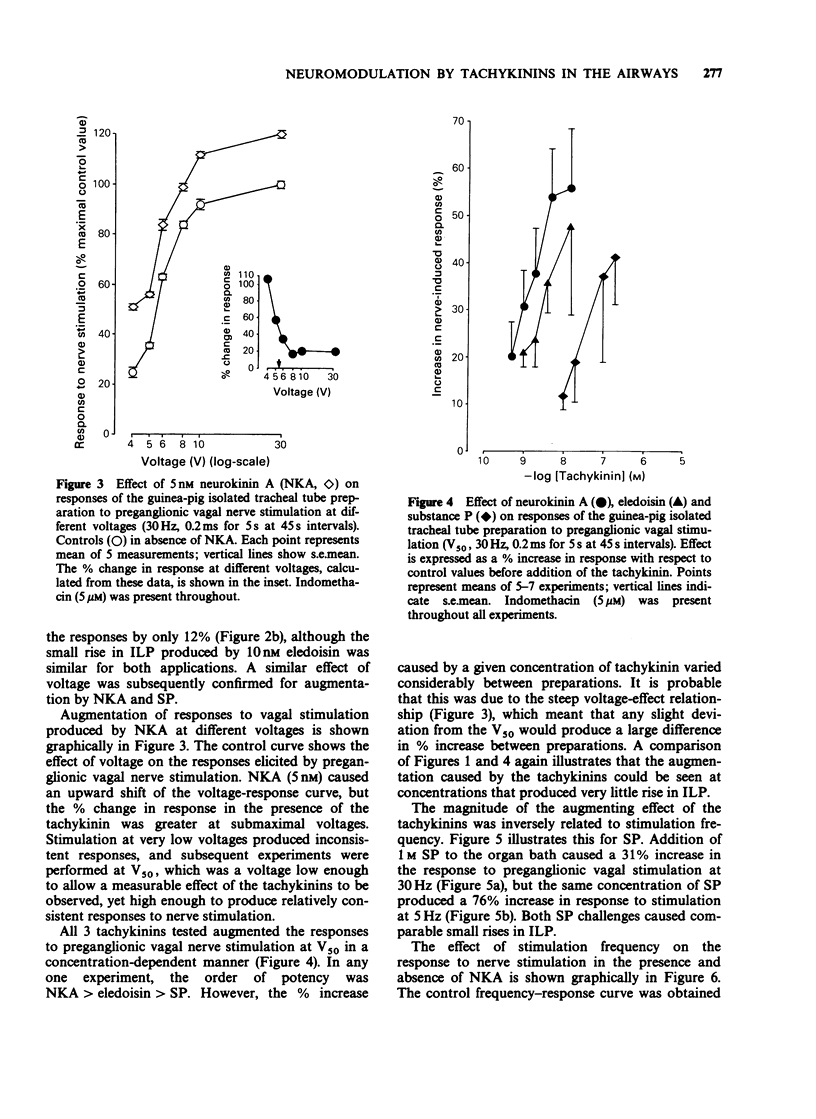
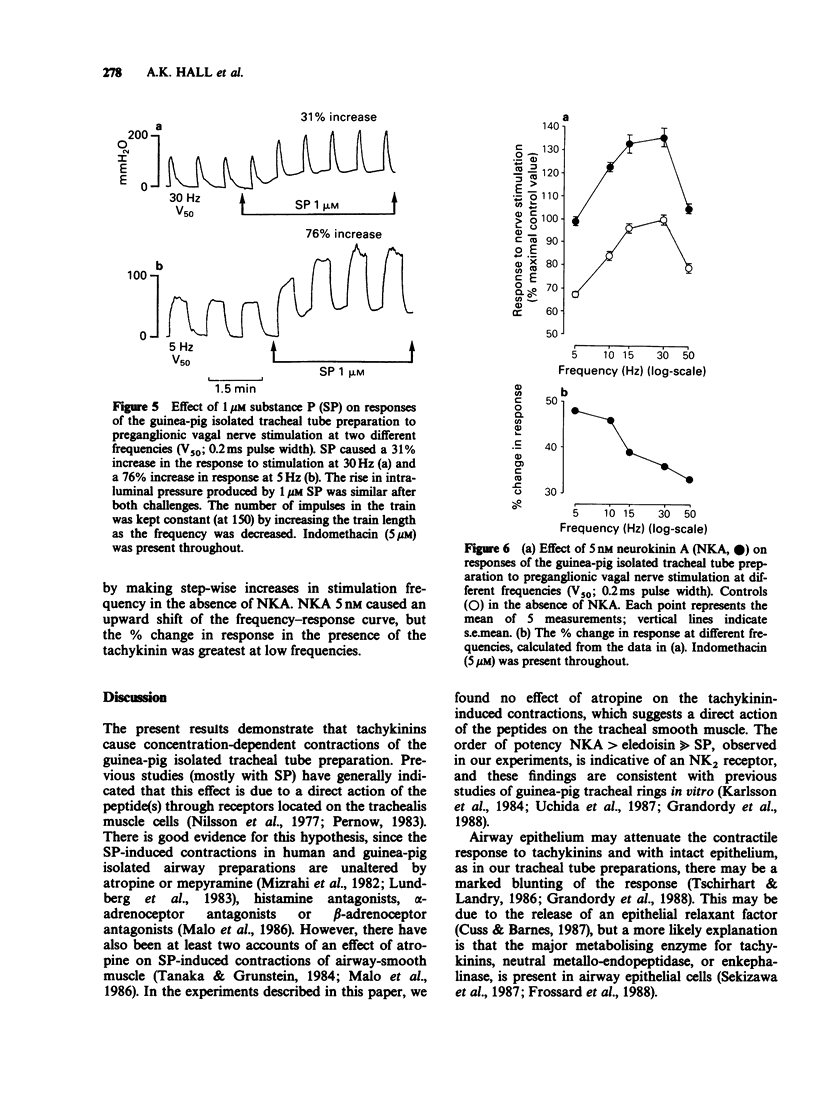
1. The effect of tachykinins on cholinergic neurotransmission was studied in an innervated tracheal tube preparation isolated from guinea-pigs anaesthetized with urethane. The tracheal tube was bathed in Krebs-Henseleit solution containing 5 microM indomethacin. 2. Neurokinin A (NKA), eledoisin (El) and substance P (SP) caused concentration-dependent increases in intraluminal pressure (ILP), with an order of potency NKA greater than El much greater than SP. 3. Low concentrations of tachykinins, that had little effect on ILP, caused an increase in the contractions elicited by stimulation of the preganglionic vagal nerve fibres and by postganglionic (transmural) stimulation. The order of potency was NKA greater than or equal to El greater than SP. Contractions induced by exogenous acetylcholine (ACh) were not increased by the tachykinins. 4. The magnitude of the tachykinin-induced augmentation of responses to nerve stimulation was inversely related to stimulation voltage and frequency. 5. These results suggest that tachykinins act on NK2 receptors, both on the trachealis muscle and on postganglionic pulmonary parasympathetic nerve terminals. Activation of the neuronal receptors may increase the probability of transmitter release from the nerve terminals.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson P., Persson H. Effect of substance P on pulmonary resistance and dynamic pulmonary compliance in the anaesthetized cat and guinea-pig. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1977 Nov;41(5):444–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1977.tb02154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J. Asthma as an axon reflex. Lancet. 1986 Feb 1;1(8475):242–245. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90777-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman J. G., McCaig D. J. Studies on an isolated innervated preparation of guinea-pig trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec;80(4):703–710. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock J. A., Cunnane T. C. Relationship between the nerve action potential and transmitter release from sympathetic postganglionic nerve terminals. Nature. 1987 Apr 9;326(6113):605–607. doi: 10.1038/326605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castairs J. R., Barnes P. J. Autoradiographic mapping of substance P receptors in lung. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Aug 15;127(3):295–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuss F. M., Barnes P. J. Airway smooth muscle and disease workshop: epithelial mediators. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Oct;136(4 Pt 2):S32–S35. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.4_Pt_2.S32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. B., Coleman R. A. A new preparation of the isolated intact trachea of the guinea-pig. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;22(1):46–50. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1970.tb08383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone R. L., Fosbraey P., Morton I. K. A comparison of the effects of three substance P antagonists on tachykinin-stimulated [3H]-acetylcholine release in the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;87(1):73–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryer A. D., Maclagan J. Muscarinic inhibitory receptors in pulmonary parasympathetic nerves in the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;83(4):973–978. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16539.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamse R., Lembeck F., Cuello A. C. Substance P in the vagus nerve. Immunochemical and immunohistochemical evidence for axoplasmic transport. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;306(1):37–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00515591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goel V., Biggs D. F. Comparison of the bronchoconstrictor and cardiovascular effects of some tachykinins in guinea pigs. Life Sci. 1987 Mar 9;40(10):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90318-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandordy B. M., Frossard N., Rhoden K. J., Barnes P. J. Tachykinin-induced phosphoinositide breakdown in airway smooth muscle and epithelium: relationship to contraction. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):515–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström N., Andersson R. G., Wikberg J. E. Pharmacological characterization of the autonomous innervation of the guinea pig tracheobronchial smooth muscle. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1981 Aug;49(2):150–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1981.tb00884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua X., Lundberg J. M., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Brodin E. Comparison of cardiovascular and bronchoconstrictor effects of substance P, substance K and other tachykinins. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;328(2):196–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00512072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson J. A., Finney M. J., Persson C. G., Post C. Substance P antagonists and the role of tachykinins in non-cholinergic bronchoconstriction. Life Sci. 1984 Dec 24;35(26):2681–2691. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Campbell N. J., Williams B. J., Iversen L. L. Multiple tachykinin binding sites in peripheral tissues and in brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 4;130(3):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Saria A., Cuello C. Substance P-immunoreactive sensory nerves in the lower respiratory tract of various mammals including man. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;235(2):251–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00217848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Martling C. R., Saria A. Substance P and capsaicin-induced contraction of human bronchi. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Sep;119(1):49–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclagan J. Presynaptic control of airway smooth muscle. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Oct;136(4 Pt 2):S54–S57. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.4_Pt_2.S54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malo P. E., Wasserman M. A., Torphy T. J., Parris D. J., Pfeiffer D. F. Characterization of substance P-induced contractions of guinea-pig trachea. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jun;237(3):782–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi J., Couture R., Caranikas S., Regoli D. Pharmacological effects of peptides on tracheal smooth muscle. Pharmacology. 1982;25(1):39–50. doi: 10.1159/000137722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow B. Substance P. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Jun;35(2):85–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Regulatory peptides of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1986 Apr;280(2 Suppl):16–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekizawa K., Tamaoki J., Nadel J. A., Borson D. B. Enkephalinase inhibitor potentiates substance P- and electrically induced contraction in ferret trachea. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Oct;63(4):1401–1405. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.4.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretton C. D., Barnes P. J. Modulation of cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea-pig trachea by neuropeptide Y. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;93(3):672–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb10325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka D. T., Grunstein M. M. Effect of substance P on neurally mediated contraction of rabbit airway smooth muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Feb;60(2):458–463. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.2.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka D. T., Grunstein M. M. Mechanisms of substance P-induced contraction of rabbit airway smooth muscle. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Nov;57(5):1551–1557. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.5.1551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschirhart E., Landry Y. Airway epithelium releases a relaxant factor: demonstration with substance P. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Dec 2;132(1):103–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida Y., Nomura A., Ohtsuka M., Hasegawa S., Goto K., Kimura S., Sugita Y., Uchiyama Y. Neurokinin A as a potent bronchoconstrictor. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Sep;136(3):718–721. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.3.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau W. M., Youther M. L. Direct evidence for a release of acetylcholine from the myenteric plexus of guinea pig small intestine by substance P. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 30;81(4):665–668. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


