Abstract
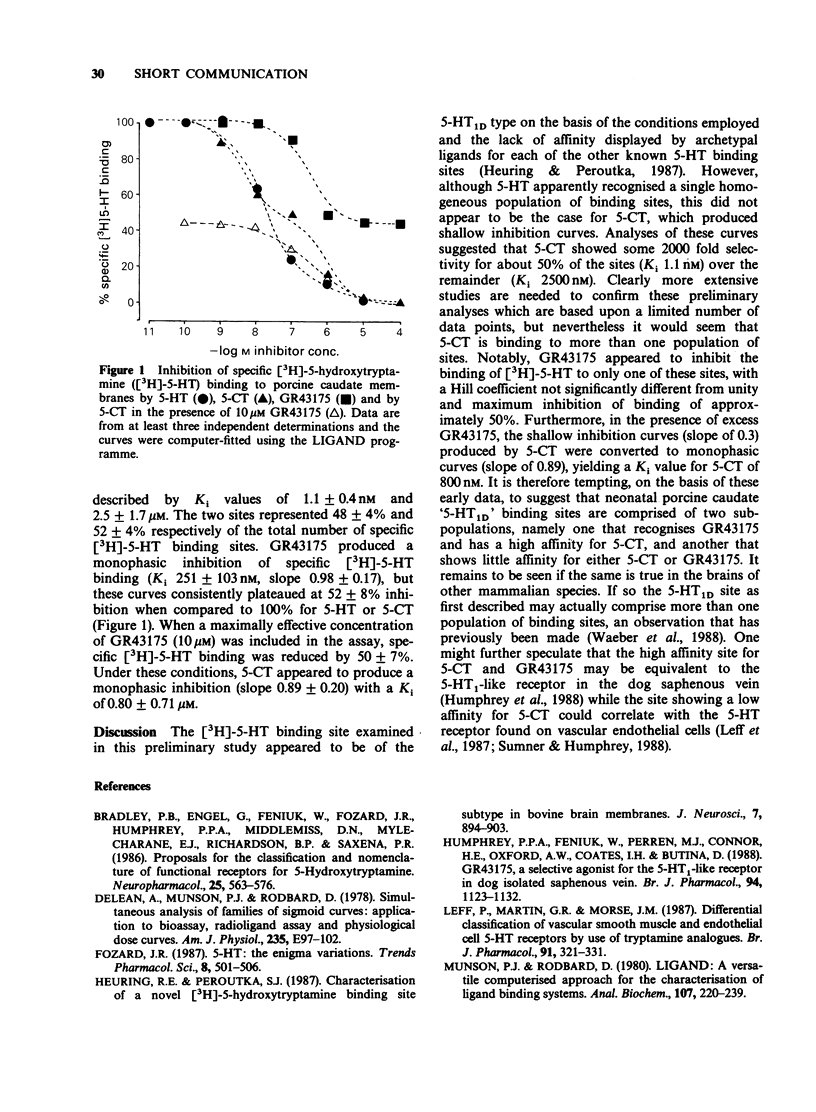
We have examined the binding of 5-carboxamidotryptamine (5-CT) and GR43175 (3-(2-dimethylamino)ethyl-N-methyl-1H-indole-5-methane sulphonamide) to 5-HT1D sites labelled with [3H]-5-hydroxytryptamine [( 3H]-5-HT) in neonatal porcine caudate membranes. In competition studies, 5-CT produced shallow inhibition curves (Ki 138 nM, slope 0.31), indicating binding site heterogeneity, while GR43175 interacted with a single population of binding sites (Ki 251 nM, slope 0.98), producing a maximum of only 52% inhibition of [3H]-5-HT binding compared to 100% for 5-HT or 5-CT. In the presence of excess GR43175 (10 microM), 5-CT produced a monophasic inhibition curve with a Ki value of 800 nM for the remaining sites (slope 0.89). These preliminary data suggest that under the conditions employed, GR43175, and to a lesser extent 5-CT, may discriminate between two sub-populations of 5-HT1D binding sites in porcine brain.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley P. B., Engel G., Feniuk W., Fozard J. R., Humphrey P. P., Middlemiss D. N., Mylecharane E. J., Richardson B. P., Saxena P. R. Proposals for the classification and nomenclature of functional receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Jun;25(6):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuring R. E., Peroutka S. J. Characterization of a novel 3H-5-hydroxytryptamine binding site subtype in bovine brain membranes. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):894–903. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00894.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey P. P., Feniuk W., Perren M. J., Connor H. E., Oxford A. W., Coates L. H., Butina D. GR43175, a selective agonist for the 5-HT1-like receptor in dog isolated saphenous vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;94(4):1123–1132. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11630.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff P., Martin G. R., Morse J. M. Differential classification of vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cell 5-HT receptors by use of tryptamine analogues. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun;91(2):321–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb10287.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waeber C., Schoeffter P., Palacios J. M., Hoyer D. Molecular pharmacology of 5-HT1D recognition sites: radioligand binding studies in human, pig and calf brain membranes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;337(6):595–601. doi: 10.1007/BF00175783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


