Abstract
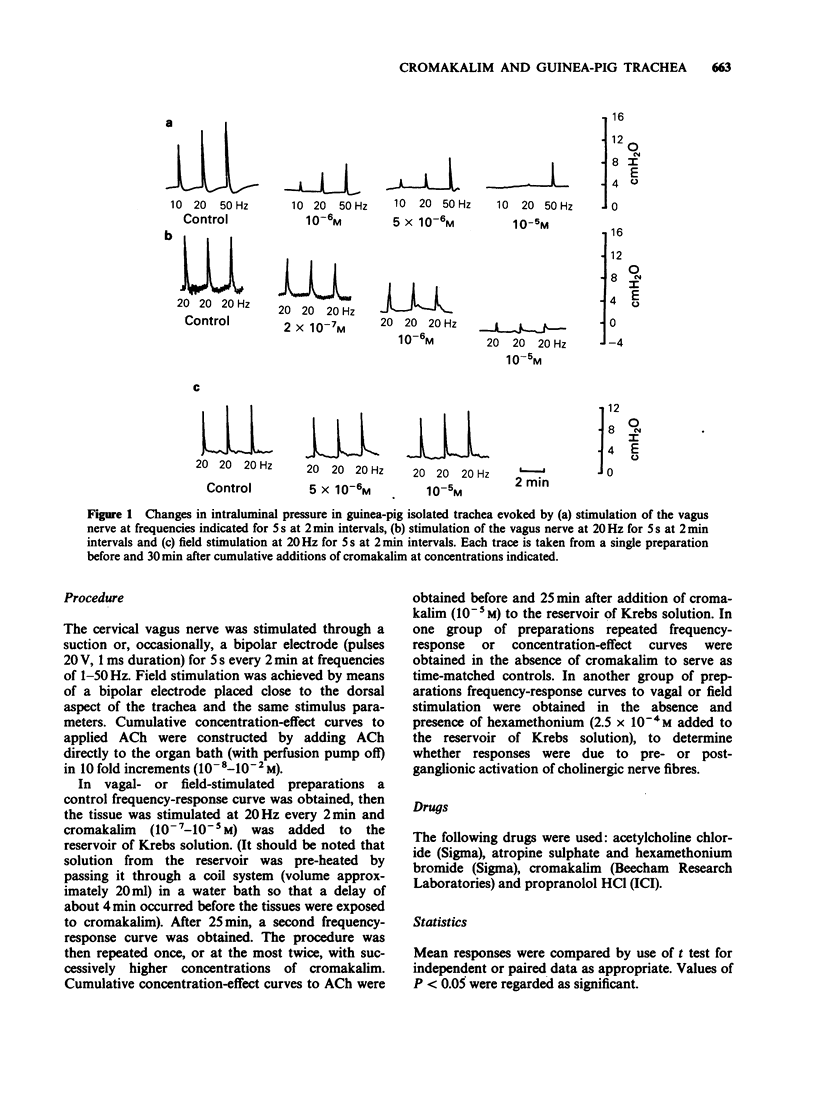
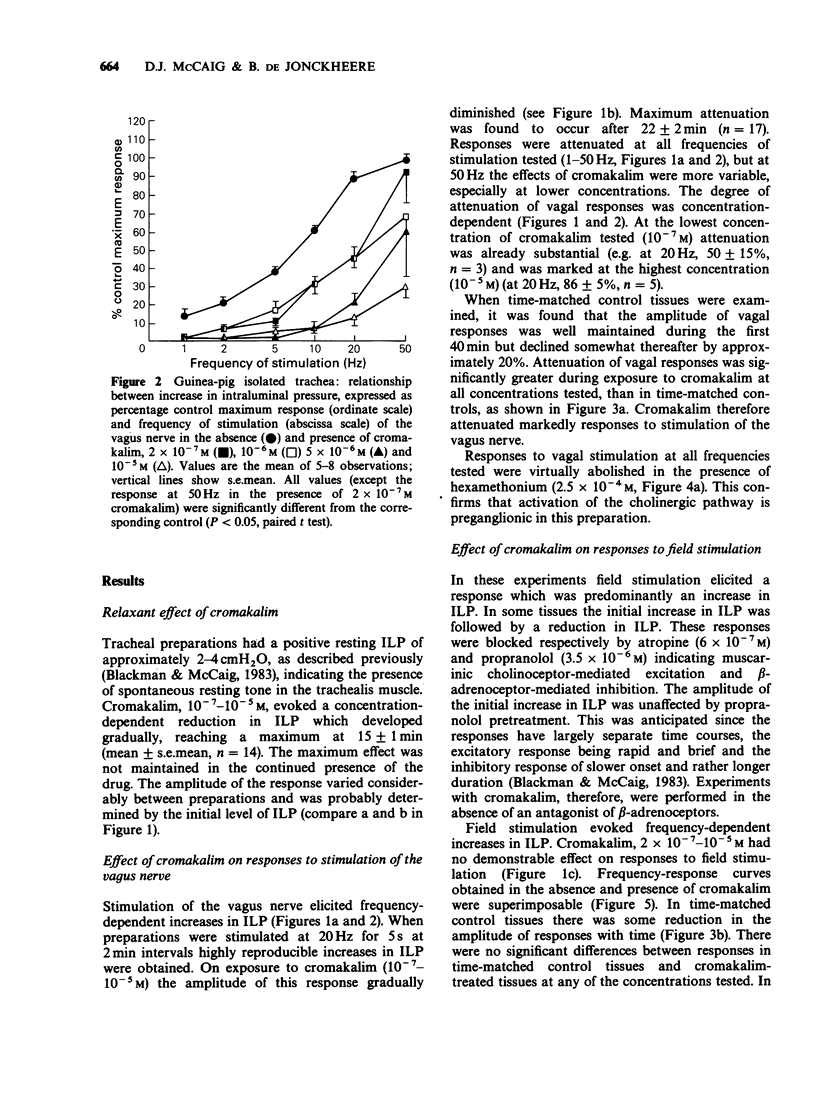
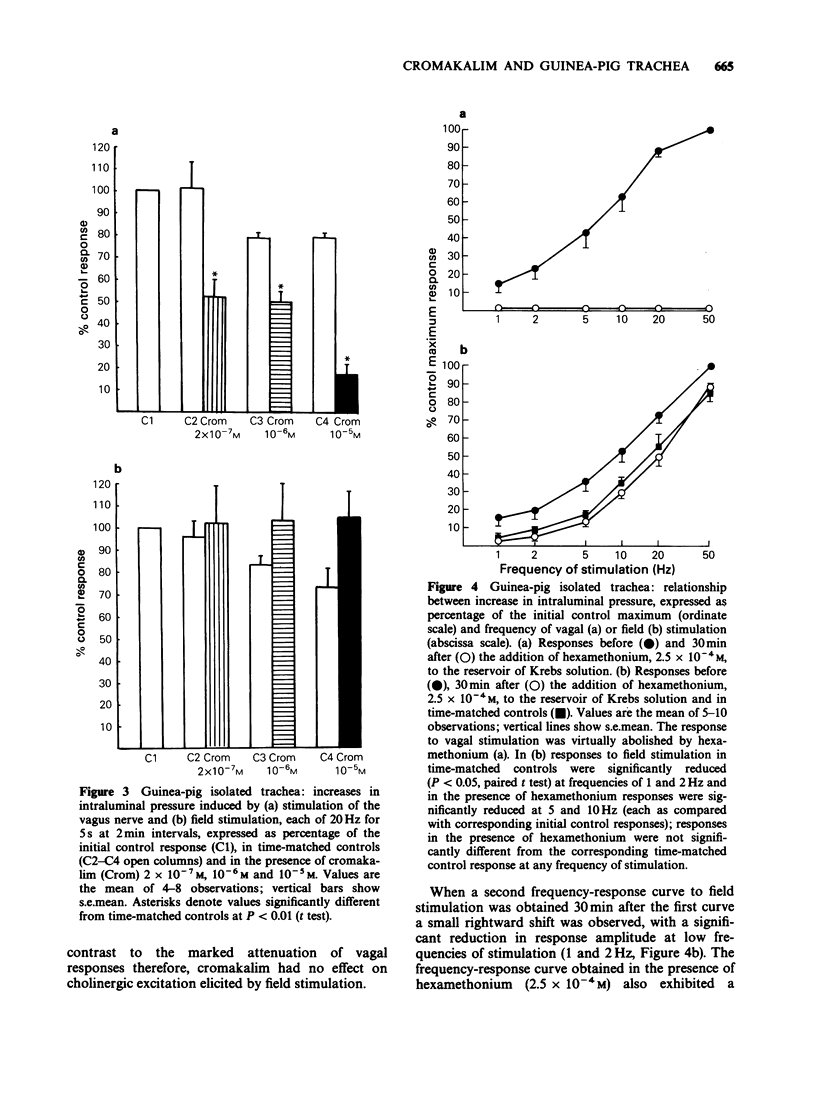
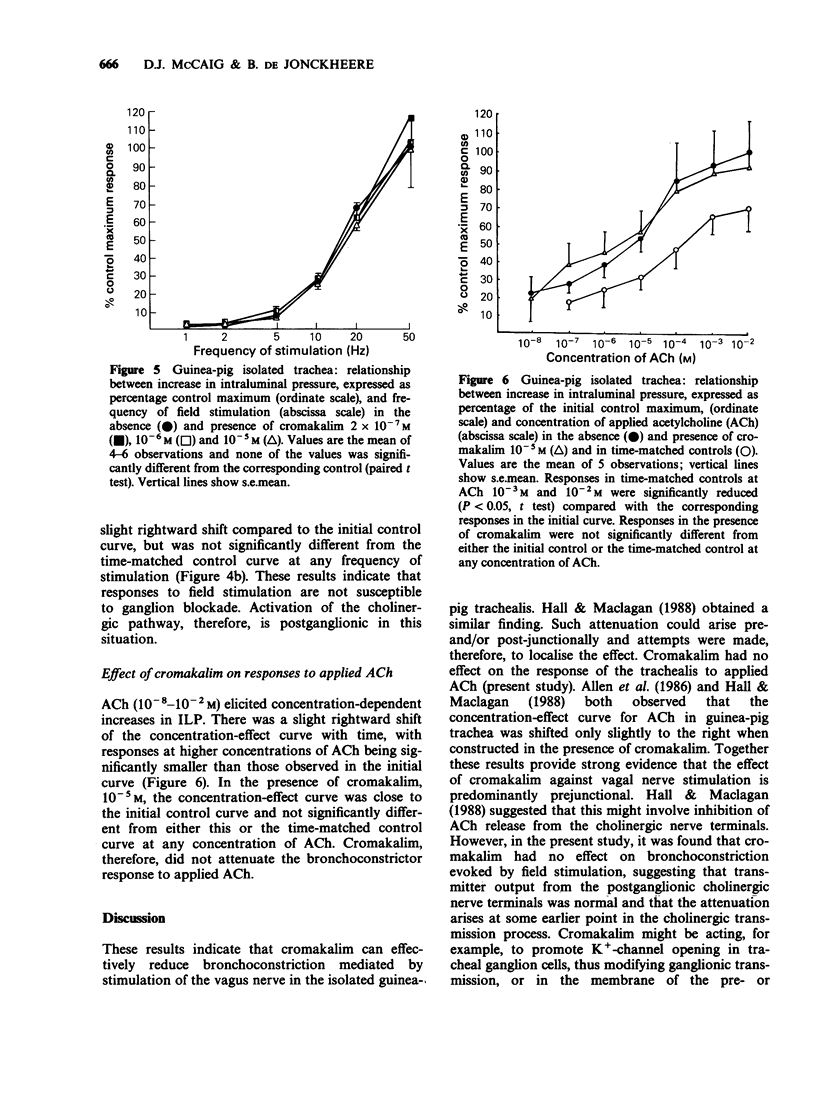
1. Cromakalim reduced intraluminal pressure in the guinea-pig isolated, innervated trachea. 2. Preganglionic stimulation of the cervical vagus nerve elicited a frequency-dependent increase in intraluminal pressure. Cromakalim attenuated responses to vagal stimulation in a concentration-dependent manner at all frequencies tested. 3. Field stimulation caused a frequency-dependent increase in intraluminal pressure mediated by muscarinic cholinoceptors. Cromakalim did not affect the amplitude of responses at any frequency of stimulation, even at high concentrations. 4. Acetylcholine, added to the Krebs solution bathing the adventitial surface of the trachea, evoked a concentration-dependent increase in intraluminal pressure. The concentration-effect curve for acetylcholine was unaltered in the presence of cromakalim. 5. It is concluded that cromakalim modulates cholinergic neuroeffector transmission in the trachea chiefly by a prejunctional mechanism. However, cromakalim probably does not interfere with acetylcholine release from postganglionic cholinergic neurones.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed F., Foster R. W., Small R. C. Some effects of nifedipine in guinea-pig isolated trachealis. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr;84(4):861–869. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb17380.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen S. L., Boyle J. P., Cortijo J., Foster R. W., Morgan G. P., Small R. C. Electrical and mechanical effects of BRL34915 in guinea-pig isolated trachealis. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;89(2):395–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman J. G., McCaig D. J. Studies on an isolated innervated preparation of guinea-pig trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec;80(4):703–710. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B., Large W. A. Are junction potentials essential? Dual mechanism of smooth muscle cell activation by transmitter released from autonomic nerves. Q J Exp Physiol. 1986 Jan;71(1):1–28. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1986.sp002960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J. M., Miles P. R. Role of depolarization in acetylcholine-induced contractions of dog trachealis muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Apr;201(1):199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J. M., Miles P. R. The sources of calcium for acetylcholine-induced contractions of dog tracheal smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Nov;207(2):340–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R. W., Small R. C., Weston A. H. Evidence that the spasmogenic action of tetraethylammonium in guinea-pig trachealis is both direct and dependent on the cellular influx of calcium ion. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 May;79(1):255–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. C., Weir S. W., Weston A. H. Comparison of the effects of BRL 34915 and verapamil on electrical and mechanical activity in rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaig D. J. Effects of sympathetic stimulation and applied catecholamines on mechanical and electrical responses to stimulation of the vagus nerve in guinea-pig isolated trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun;91(2):385–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb10293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaig D. J. Electrophysiology of neuroeffector transmission in the isolated, innervated trachea of the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;89(4):793–801. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11184.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Okabe K., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H., Weston A. H. Characteristics of cromakalim-induced relaxations in the smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig mesenteric artery and vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):795–804. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small R. C. Electrical slow waves and tone of guinea-pig isolated trachealis muscle: effects of drugs and temperature changes. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;77(1):45–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir S. W., Weston A. H. Effect of apamin on responses to BRL 34915, nicorandil and other relaxants in the guinea-pig taenia caeci. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):113–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir S. W., Weston A. H. The effects of BRL 34915 and nicorandil on electrical and mechanical activity and on 86Rb efflux in rat blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):121–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09478.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


