Abstract
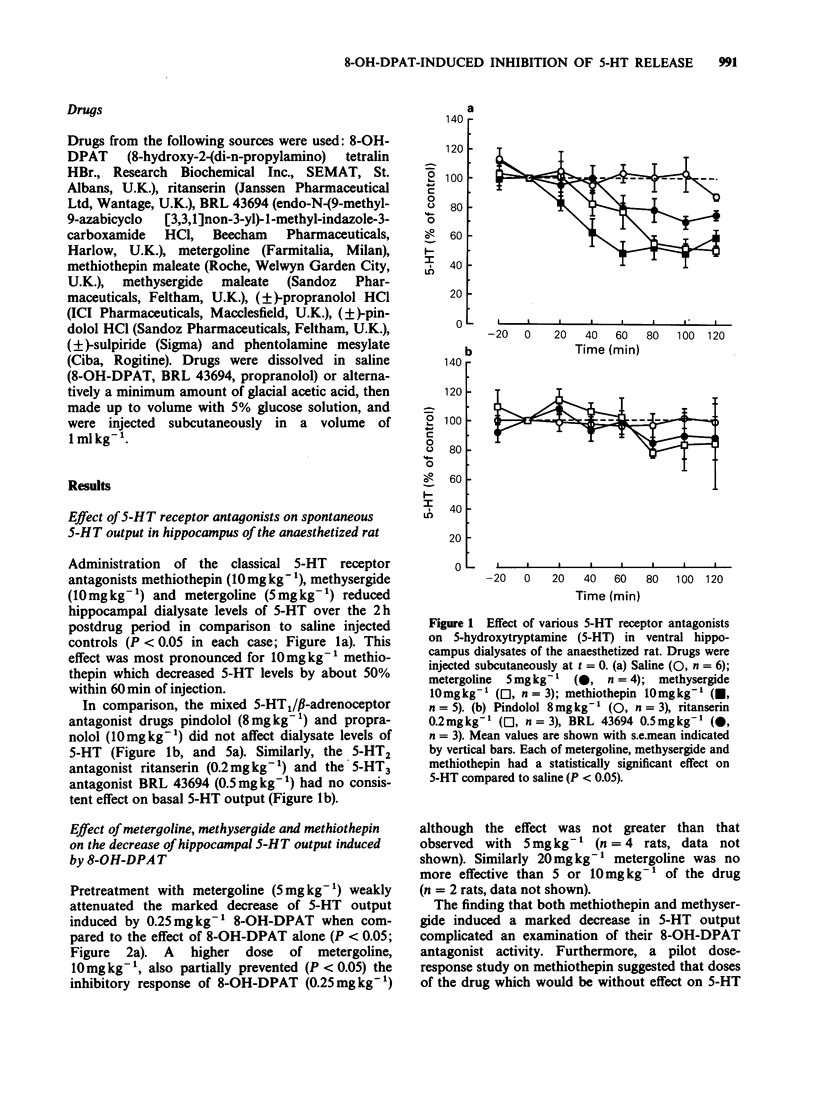
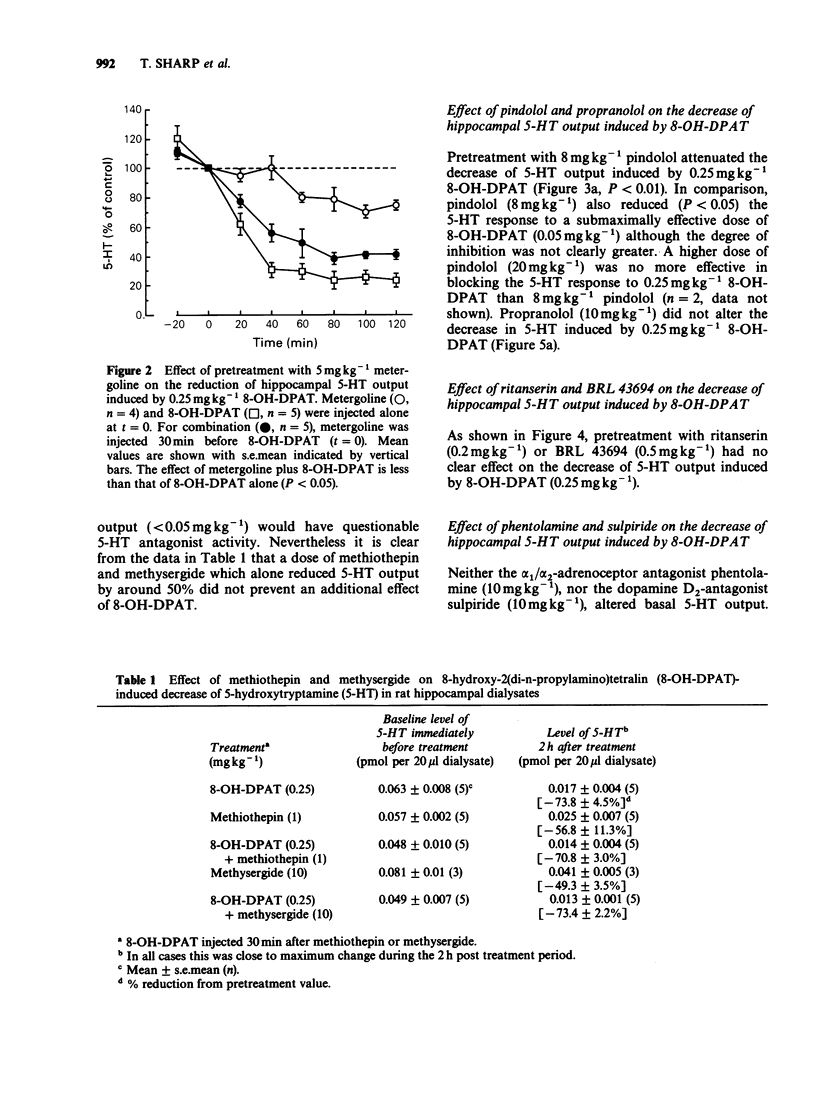
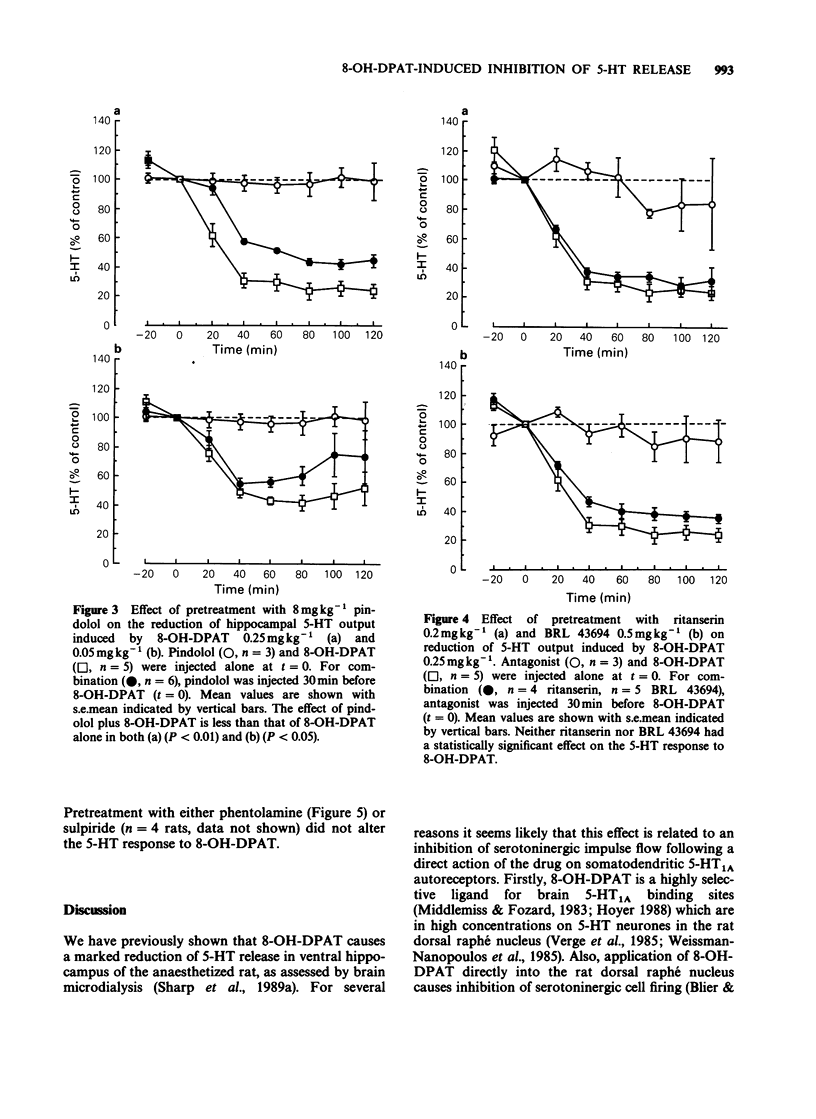
1. We have previously found that the putative 5-HT1A agonist 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) decreases hippocampal 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) release in the anaesthetized rat, as measured by brain microdialysis. The present study attempted to characterize the receptor involved in this response using a range of monoamine receptor antagonists. 2. The classical 5-HT receptor antagonists, metergoline (5 mg kg-1 s.c.), methysergide (10 mg kg-1 s.c.) and methiothepin (10 mg kg-1 s.c.) each reduced dialysate levels of 5-HT which complicated their use as antagonists in these experiments. Nevertheless, pretreatment with metergoline but not methiothepin and methysergide partially reduced the 5-HT response to a maximally effective dose of 8-OH-DPAT (0.25 mg kg-1 s.c.). 3. The mixed 5-HT 1/beta-adrenoceptor antagonist pindolol (8 mg kg-1 s.c.) was without effect on spontaneous 5-HT output but attenuated the effect of both maximally (0.25 mg kg-1 s.c.) and submaximally (0.05 mg kg-1 s.c.) effective dose of 8-OH-DPAT. In comparison, propranolol (10 mg kg-1 s.c.) did not affect 5-HT output when injected alone and did not alter the response to 8-OH-DPAT (0.25 mg kg-1 s.c.). 4. The 5-HT2 receptor antagonist ritanserin (0.2 mg kg-1 s.c.) and the 5-HT3 receptor antagonist BRL 43694 (0.5 mg kg-1 s.c.) neither altered 5-HT output alone nor significantly changed the response to 8-OH-DPAT (0.25 mg kg-1 s.c.).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

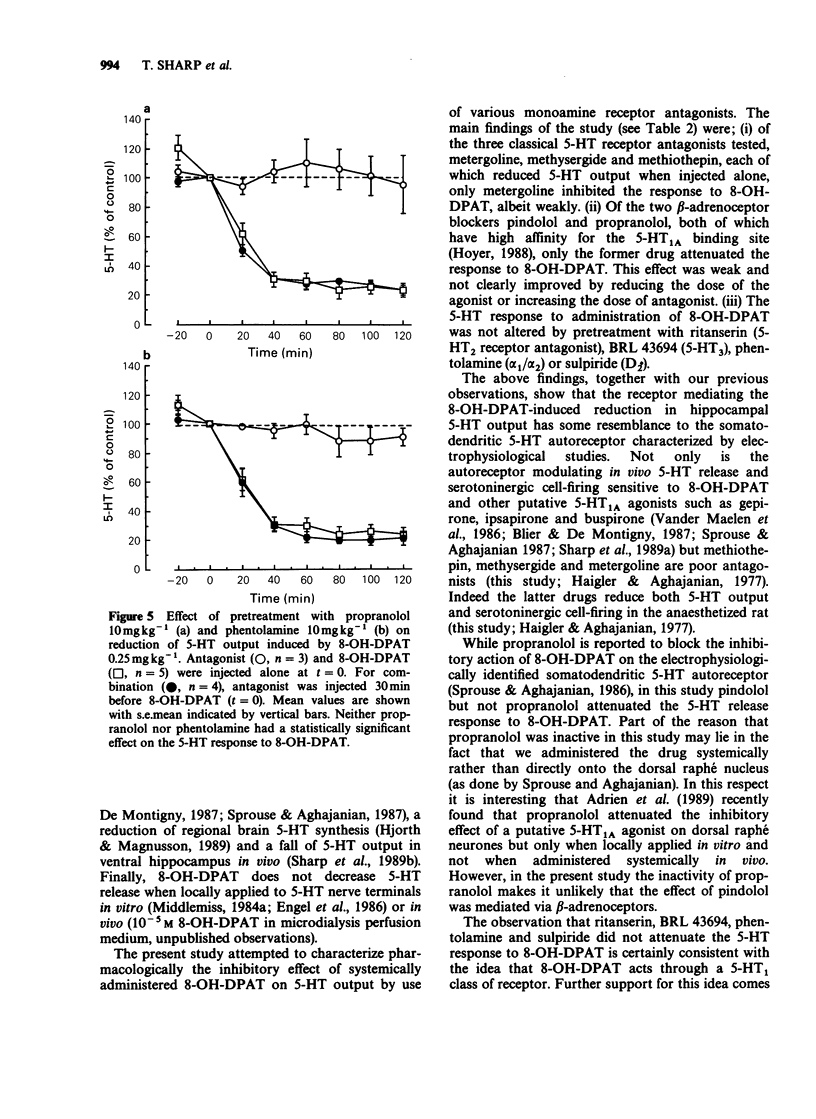



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrien J., Lanfumey L., Gozlan H., Fattaccini C. M., Hamon M. Biochemical and electrophysiological evidence for an agonist action of CM 57493 at pre- and postsynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptors in brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Mar;248(3):1222–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blier P., de Montigny C. Modification of 5-HT neuron properties by sustained administration of the 5-HT1A agonist gepirone: electrophysiological studies in the rat brain. Synapse. 1987;1(5):470–480. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgoin S., Artaud F., Bockaert J., Héry F., Glowinski J., Hamon M. Paradoxical decrease of brain 5-HT turnover by metergoline, a central 5-HT receptor blocker. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1978 May;302(3):313–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00508301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerrito F., Raiteri M. Serotonin release is modulated by presynaptic autoreceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Aug 15;57(4):427–430. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90506-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Roach A. G., Smith C. F. Studies on RX 781094: a selective, potent and specific antagonist of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;78(3):489–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb08809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel G., Göthert M., Hoyer D., Schlicker E., Hillenbrand K. Identity of inhibitory presynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) autoreceptors in the rat brain cortex with 5-HT1B binding sites. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;332(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00633189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnebo L. O., Hamberger B. Regulation of (3H)5-hydroxytryptamine release from rat brain slices. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1974 Aug;26(8):642–644. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1974.tb10680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert F., Brazell C., Tricklebank M. D., Stahl S. M. Activation of the 5-HT1A receptor subtype increases rat plasma ACTH concentration. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 15;147(3):431–439. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. M., Green A. R. A behavioural and biochemical study in mice and rats of putative selective agonists and antagonists for 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Mar;84(3):743–753. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb16157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudelsky G. A., Koenig J. I., Meltzer H. Y. Thermoregulatory responses to serotonin (5-HT) receptor stimulation in the rat. Evidence for opposing roles of 5-HT2 and 5-HT1A receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Dec;25(12):1307–1313. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göthert M., Weinheimer G. Extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine inhibits 5-hydroxytryptamine release from rat brain cortex slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;310(1):93–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00499879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. J., Aghajanian G. K. Serotonin receptors in the brain. Fed Proc. 1977 Jul;36(8):2159–2164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamon M., Bourgoin S., Jagger J., Glowinski J. Effects of LSD on synthesis and release of 5-HT in rat brain slices. Brain Res. 1974 Apr 5;69(2):265–280. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjorth S., Carlsson A. Is pindolol a mixed agonist-antagonist at central serotonin (5-HT) receptors? Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep 23;129(1-2):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90344-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjorth S., Magnusson T. The 5-HT 1A receptor agonist, 8-OH-DPAT, preferentially activates cell body 5-HT autoreceptors in rat brain in vivo. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;338(5):463–471. doi: 10.1007/BF00179315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer D. Functional correlates of serotonin 5-HT1 recognition sites. J Recept Res. 1988;8(1-4):59–81. doi: 10.3109/10799898809048978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. F., Tackett R. L. Interaction of propranolol with central serotonergic neurons. Life Sci. 1988;43(26):2249–2255. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90418-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leysen J. E., Awouters F., Kennis L., Laduron P. M., Vandenberk J., Janssen P. A. Receptor binding profile of R 41 468, a novel antagonist at 5-HT2 receptors. Life Sci. 1981 Mar 2;28(9):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90747-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long J. B., Youngblood W. Y., Kizer J. S. Regional differences in the response of serotonergic neurons in rat CNS to drugs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar 18;88(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90395-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin L. L., Sanders-Bush E. Comparison of the pharmacological characteristics of 5 HT1 and 5 HT2 binding sites with those of serotonin autoreceptors which modulate serotonin release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Dec;321(3):165–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00505480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemiss D. N. 8-Hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin is devoid of activity at the 5-hydroxytryptamine autoreceptor in rat brain. Implications for the proposed link between the autoreceptor and the [3H] 5-HT recognition site. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Aug;327(1):18–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00504986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemiss D. N., Fozard J. R. 8-Hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)-tetralin discriminates between subtypes of the 5-HT1 recognition site. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 May 20;90(1):151–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90230-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemiss D. N. Stereoselective blockade at [3H]5-HT binding sites and at the 5-HT autoreceptor by propranolol. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jun 1;101(3-4):289–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90173-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemiss D. N. The putative 5-HT1 receptor agonist, RU 24969, inhibits the efflux of 5-hydroxytryptamine from rat frontal cortex slices by stimulation of the 5-HT autoreceptor. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;37(6):434–437. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1985.tb03032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounsey I., Brady K. A., Carroll J., Fisher R., Middlemiss D. N. K+-evoked [3H]-5-HT release from rat frontal cortex slices: the effect of 5-HT agonists and antagonists. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Jan 1;31(1):49–53. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicker E., Göthert M., Hillenbrand K. Cyanopindolol is a highly potent and selective antagonist at the presynaptic serotonin autoreceptor in the rat brain cortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Dec;331(4):398–401. doi: 10.1007/BF00500826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeffter P., Hoyer D. Centrally acting hypotensive agents with affinity for 5-HT1A binding sites inhibit forskolin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in calf hippocampus. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):975–985. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11728.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp T., Bramwell S. R., Clark D., Grahame-Smith D. G. In vivo measurement of extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine in hippocampus of the anaesthetized rat using microdialysis: changes in relation to 5-hydroxytryptaminergic neuronal activity. J Neurochem. 1989 Jul;53(1):234–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp T., Bramwell S. R., Grahame-Smith D. G. 5-HT1 agonists reduce 5-hydroxytryptamine release in rat hippocampus in vivo as determined by brain microdialysis. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):283–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11815.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinton C. M., Fallon S. L. Electrophysiological evidence for a functional differentiation between subtypes of the 5-HT1 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov 22;157(2-3):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprouse J. S., Aghajanian G. K. (-)-Propranolol blocks the inhibition of serotonergic dorsal raphe cell firing by 5-HT1A selective agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep 9;128(3):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90782-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprouse J. S., Aghajanian G. K. Electrophysiological responses of serotoninergic dorsal raphe neurons to 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists. Synapse. 1987;1(1):3–9. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tricklebank M. D., Forler C., Fozard J. R. The involvement of subtypes of the 5-HT1 receptor and of catecholaminergic systems in the behavioural response to 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Nov 13;106(2):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90714-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanderMaelen C. P., Matheson G. K., Wilderman R. C., Patterson L. A. Inhibition of serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons by systemic and iontophoretic administration of buspirone, a non-benzodiazepine anxiolytic drug. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep 23;129(1-2):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90343-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verge D., Daval G., Patey A., Gozlan H., el Mestikawy S., Hamon M. Presynaptic 5-HT autoreceptors on serotonergic cell bodies and/or dendrites but not terminals are of the 5-HT1A subtype. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 31;113(3):463–464. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocca F. D., Hyslop D. K., Smith D. W., Maayani S. BMY 7378, a buspirone analog with high affinity, selectivity and low intrinsic activity at the 5-HT1A receptor in rat and guinea pig hippocampal membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 4;137(2-3):293–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterström T., Sharp T., Ungerstedt U. Effect of dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptor selective drugs on dopamine release and metabolism in rat striatum in vivo. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;334(2):117–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00505810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


