Abstract
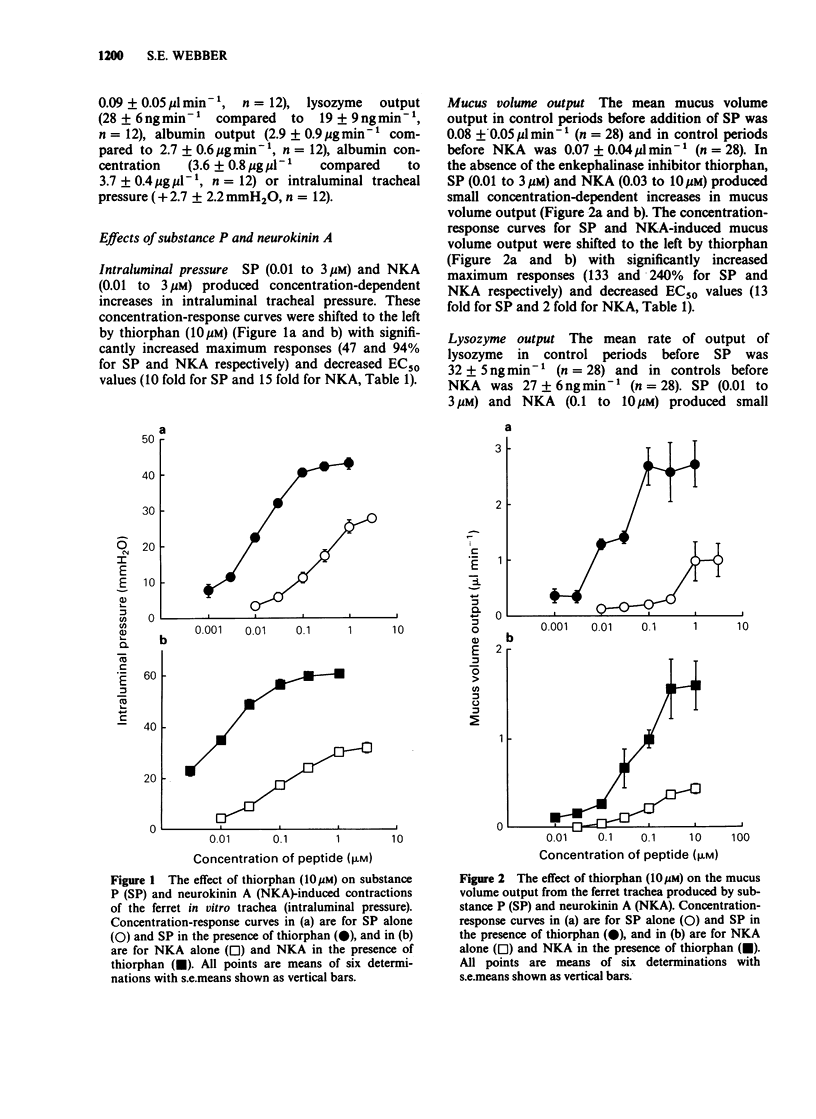
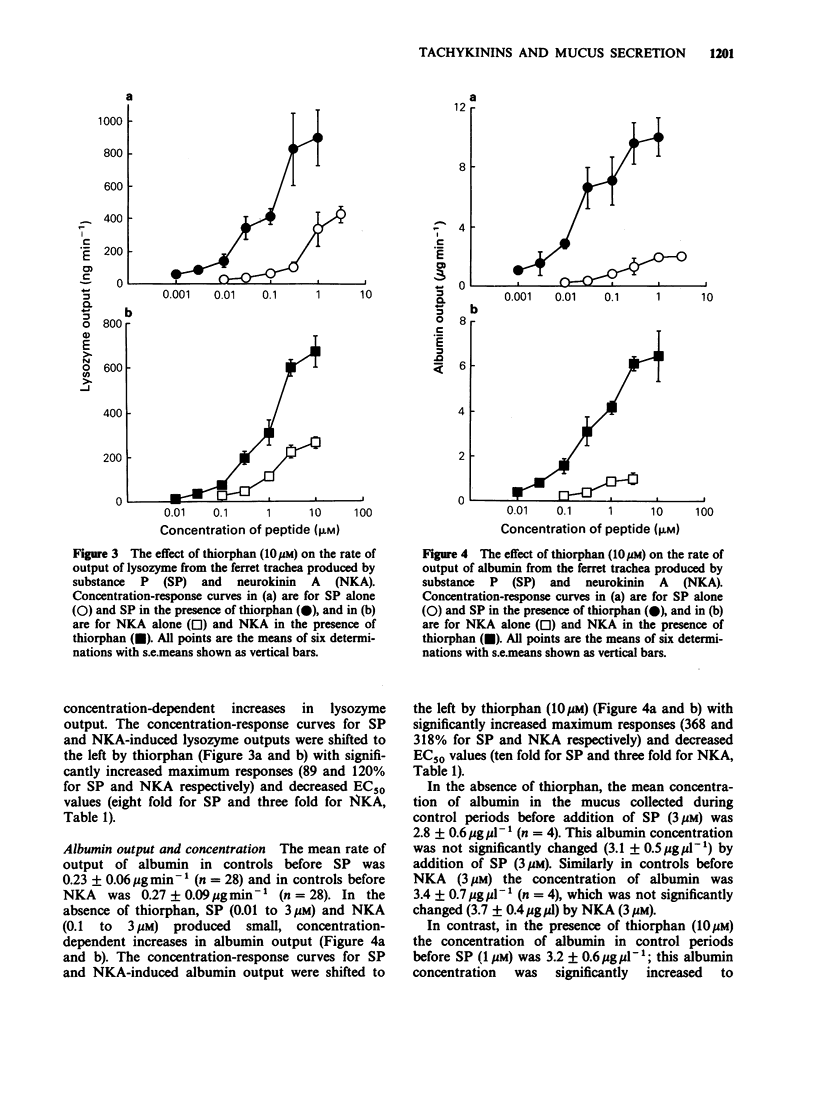
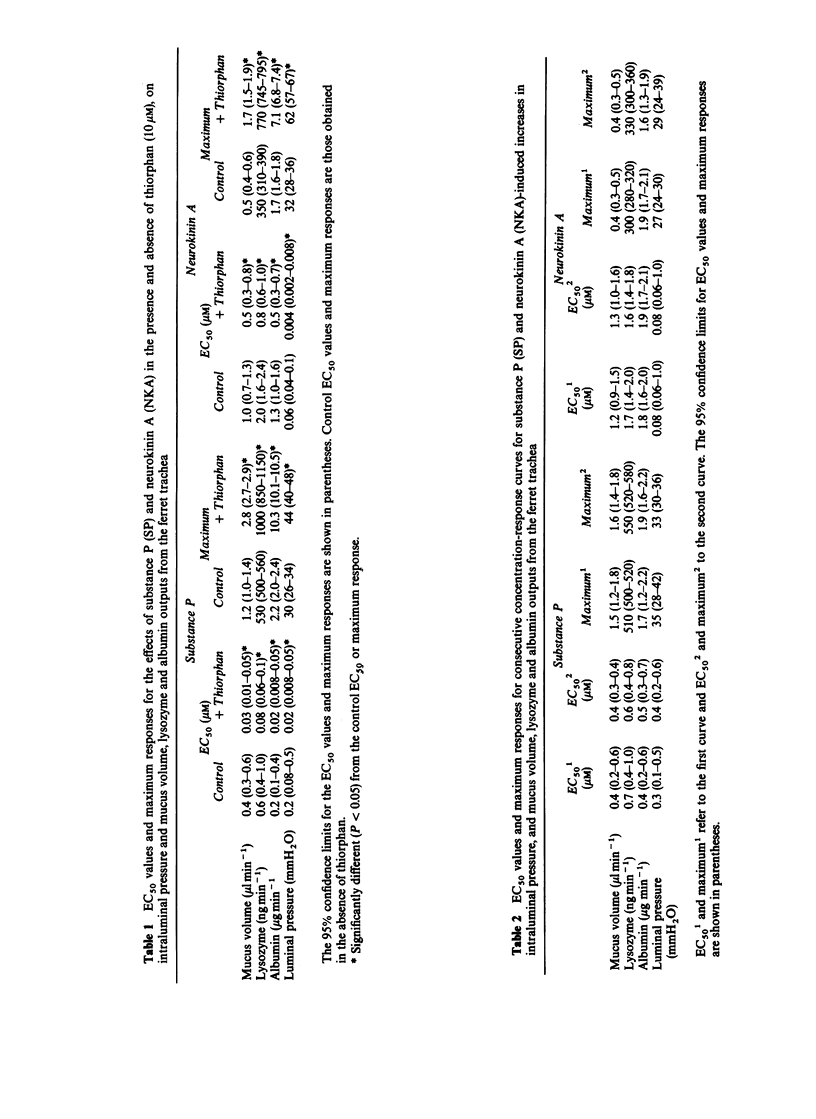
1. The effects of substance P (SP) and neurokinin A (NKA) were examined on tracheal smooth muscle tone, mucus volume output, lysozyme output and albumin transport across the ferret in vitro whole trachea in the presence and absence of the enkephalinase inhibitor, thiorphan. 2. SP (0.001-3 microM) and NKA (0.01-10 microM) contracted the tracheal smooth muscle and increased mucus volume, lysozyme and albumin outputs into the tracheal lumen. The EC50 values for SP and NKA for all of the variables measured were significantly reduced, and all of the maximum responses were significantly enhanced by thiorphan (10 microM). 3. In the presence of thiorphan, SP (1 microM) and NKA (10 microM) produced albumin concentrations in the secreted mucus (8.9 and 7.2 micrograms microliters-1) which were greater than those in the submucosal buffer (4.2 micrograms microliters-1). 4. In the presence of thiorphan, NKA was approximately 5 times more potent than SP at contracting the tracheal smooth muscle. Conversely SP was 23, 15 and 22 times more potent than NKA at stimulating mucus volume, lysozyme and albumin outputs respectively. 5. Thus, there is neutral endopeptidase in the ferret trachea in vitro which cleaves exogenously applied SP and NKA, thereby reducing the magnitude and potency of their actions. SP and NKA contract the ferret tracheal muscle probably by an action at NK2 (or NK3)-receptors but stimulate mucus volume output, lysozyme output and albumin transport across the tracheal wall probably by an action on NK1 receptors.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Advenier C., Naline E., Drapeau G., Regoli D. Relative potencies of neurokinins in guinea pig trachea and human bronchus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 9;139(2):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90244-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Bazzaz F. J., Kelsey J. G., Kaage W. D. Substance P stimulation of chloride secretion by canine tracheal mucosa. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Jan;131(1):86–89. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. L., Johnson P. R., Armour C. L. Potentiation of the contractile effects of neuropeptides in human bronchus by an enkephalinase inhibitor. Pulm Pharmacol. 1988;1(1):21–23. doi: 10.1016/0952-0600(88)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borson D. B., Corrales R., Varsano S., Gold M., Viro N., Caughey G., Ramachandran J., Nadel J. A. Enkephalinase inhibitors potentiate substance P-induced secretion of 35SO4-macromolecules from ferret trachea. Exp Lung Res. 1987;12(1):21–36. doi: 10.3109/01902148709068812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castairs J. R., Barnes P. J. Autoradiographic mapping of substance P receptors in lung. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Aug 15;127(3):295–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles S. J., Neill K. H., Reid L. M. Potent stimulation of glycoprotein secretion in canine trachea by substance P. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Nov;57(5):1323–1327. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.5.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusser D. J., Umeno E., Graf P. D., Djokic T., Borson D. B., Nadel J. A. Airway neutral endopeptidase-like enzyme modulates tachykinin-induced bronchoconstriction in vivo. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Dec;65(6):2585–2591. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.6.2585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D., Levison M. J., Feldman C. H., Clark N. M., Wasilewski Y., Levin B., Mellins R. B. The impact of passive smoking on emergency room visits of urban children with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Mar;135(3):567–572. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.3.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gashi A. A., Borson D. B., Finkbeiner W. E., Nadel J. A., Basbaum C. B. Neuropeptides degranulate serous cells of ferret tracheal glands. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 1):C223–C229. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.2.C223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghatei M. A., Springall D. R., Richards I. M., Oostveen J. A., Griffin R. L., Cadieux A., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Regulatory peptides in the respiratory tract of Macaca fascicularis. Thorax. 1987 Jun;42(6):431–439. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.6.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover D. B., Hancock J. C. Autoradiographic localization of substance P binding sites in guinea-pig airways. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1987 May;19(2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(87)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgin R. L., Charleson S. E., Zimmerman M., Mumford R., Wood P. L. Enkephalinase: selective peptide inhibitors. Life Sci. 1981 Dec 21;29(25):2593–2601. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90632-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. R., Ashton J., Schulz W. W., Erdös E. G. Neutral metalloendopeptidase in human lung tissue and cultured cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):564–568. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Campbell N. J., Williams B. J., Iversen L. L. Multiple tachykinin binding sites in peripheral tissues and in brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 4;130(3):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llorens C., Schwartz J. C. Enkephalinase activity in rat peripheral organs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 5;69(1):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90609-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Franco-Cereceda A., Hua X., Hökfelt T., Fischer J. A. Co-existence of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivities in sensory nerves in relation to cardiovascular and bronchoconstrictor effects of capsaicin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 5;108(3):315–319. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90456-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Saria A., Cuello C. Substance P-immunoreactive sensory nerves in the lower respiratory tract of various mammals including man. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;235(2):251–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00217848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A. Polypeptide-containing neurons in airway smooth muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:557–572. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.003013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzini S., Conti S., Maggi C. A., Rovero P., Ballati L. Neurokinin A-(4-10): a potent bronchospastic agent virtually devoid of sialologic properties in anaesthetized guinea-pigs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 13;148(3):475–478. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martling C. R., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Lundberg J. M. Occurrence and effects of multiple tachykinins; substance P, neurokinin A and neuropeptide K in human lower airways. Life Sci. 1987 Apr 20;40(16):1633–1643. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangachari P. K., McWade D. Effects of tachykinins on the electrical activity of isolated canine tracheal epithelium: an exploratory study. Regul Pept. 1985 Sep;12(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(85)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Drapeau G., Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P. Pharmacological receptors for substance P and neurokinins. Life Sci. 1987 Jan 12;40(2):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90349-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. F., Belvisi M. G., Aursudkij B., Evans T. W., Barnes P. J. Effects and interactions of sensory neuropeptides on airway microvascular leakage in guinea-pigs. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1109–1116. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11745.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen R. O., Webber S. E., Widdicombe J. G. Effects of neuropeptides and capsaicin on the canine tracheal vasculature in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1262–1270. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11763.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekizawa K., Tamaoki J., Nadel J. A., Borson D. B. Enkephalinase inhibitor potentiates substance P- and electrically induced contraction in ferret trachea. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Oct;63(4):1401–1405. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.4.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimura S., Sasaki T., Okayama H., Sasaki H., Takishima T. Effect of substance P on mucus secretion of isolated submucosal gland from feline trachea. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Aug;63(2):646–653. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.2.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki J., Ueki I. F., Widdicombe J. H., Nadel J. A. Stimulation of Cl secretion by neurokinin A and neurokinin B in canine tracheal epithelium. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):899–902. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tom-Moy M., Basbaum C. B., Nadel J. A. Localization and release of lysozyme from ferret trachea: effects of adrenergic and cholinergic drugs. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;228(3):549–562. doi: 10.1007/BF00211475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida Y., Nomura A., Ohtsuka M., Hasegawa S., Goto K., Kimura S., Sugita Y., Uchiyama Y. Neurokinin A as a potent bronchoconstrictor. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Sep;136(3):718–721. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.3.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber S. E., Widdicombe J. G. The effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide on smooth muscle tone and mucus secretion from the ferret trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 May;91(1):139–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08992.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber S. E., Widdicombe J. G. The transport of albumin across the ferret in vitro whole trachea. J Physiol. 1989 Jan;408:457–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


