Abstract
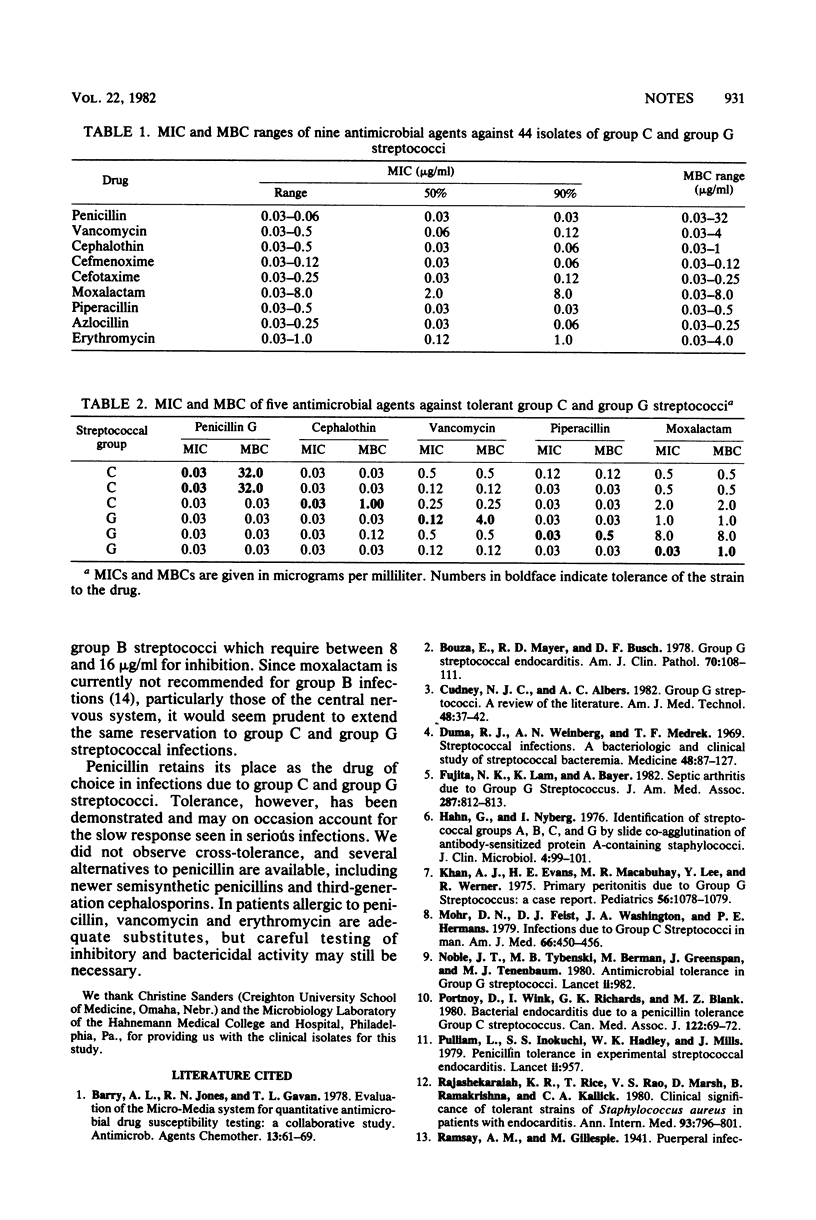
The activity of nine antimicrobial agents against 44 strains of group C and group G streptococci was studied using a microtiter broth dilution technique. Several antimicrobial agents, including third-generation cephalosporins, the newer semisynthetic penicillins, and erythromycin, exhibited good activity against the organisms. Occasional tolerance to various agents was observed. No cross-tolerance was observed in this study.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Jones R. N., Gavan T. L. Evaluation of the micro-media system for quantitative antimicrobial drug susceptibility testing: a collaborative study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):61–69. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouza E., Meyer R. D., Busch D. F. Group G streptococcal endocarditis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jul;70(1):108–111. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/70.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudney N. J., Albers A. C. Group G streptococci: a review of the literature. Am J Med Technol. 1982 Jan;48(1):37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita N. K., Lam K., Bayer A. S. Septic arthritis due to group G streptococcus. JAMA. 1982 Feb 12;247(6):812–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn G., Nyberg I. Identification of streptococcal groups A,B,C, and G by slide co-agglutination of antibody-sensitized protein A-containing staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):99–101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.99-101.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. J., Evans H. E., Macabuhay M. R., Lee Y., Werner R. Primary peritonitis due to group G Streptococcus: A case report. Pediatrics. 1975 Dec;56(6):1078–1079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr D. N., Feist D. J., Washington J. A., 2nd, Hermans P. E. Infections due to group C streptococci in man. Am J Med. 1979 Mar;66(3):450–456. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)91067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble J. T., Tyburski M. B., Berman M., Greenspan J., Tenenbaum M. J. Antimicrobial tolerance in group G streptococci. Lancet. 1980 Nov 1;2(8201):982–982. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92143-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D., Wink I., Richards G. K., Blanc M. Z. Bacterial endocarditis due to a penicillin-tolerant group C streptococcus. Can Med Assoc J. 1980 Jan 12;122(1):69-70, 75. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulliam L., Inokuchi S., Hadley W. K., Mills J. Penicillin tolerance in experimental streptococcal endocarditis. Lancet. 1979 Nov 3;2(8149):957–957. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92649-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajashekaraiah K. R., Rice T., Rao V. S., Marsh D., Ramakrishna B., Kallick C. A. Clinical significance of tolerant strains of Staphylococcus aureus in patients with endocarditis. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Dec;93(6):796–801. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-6-796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed M. D., Bertino J. S., Jr, Aronoff S. C., Speck W. T., Blumer J. L. Evaluation of moxalactam. Clin Pharm. 1982 Mar-Apr;1(2):124–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewardson-Krieger P., Gotoff S. P. Neonatal meningitis due to group C beta hemolytic streptococcus. J Pediatr. 1977 Jan;90(1):103–104. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80780-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon C. U. Group G streptococcus. Am J Med Sci. 1980 Mar-Apr;279(2):121–124. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198003000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


