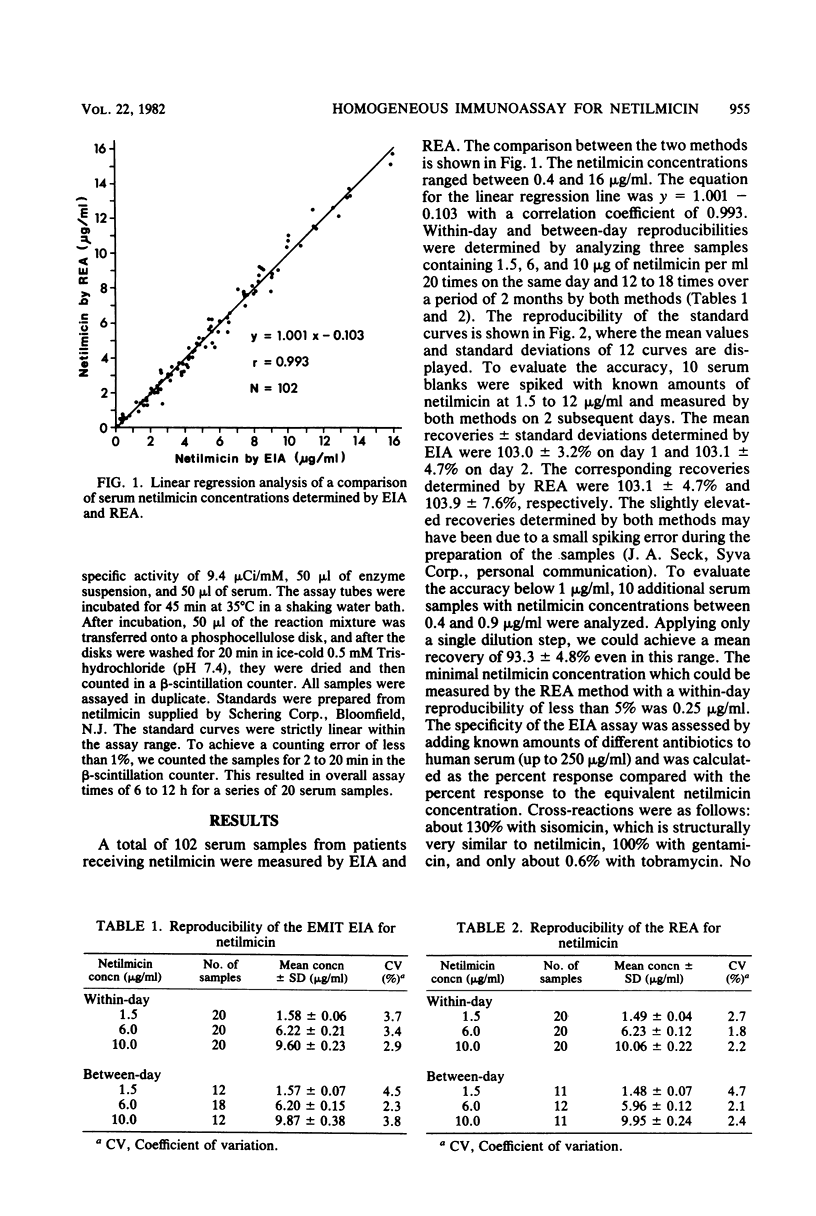
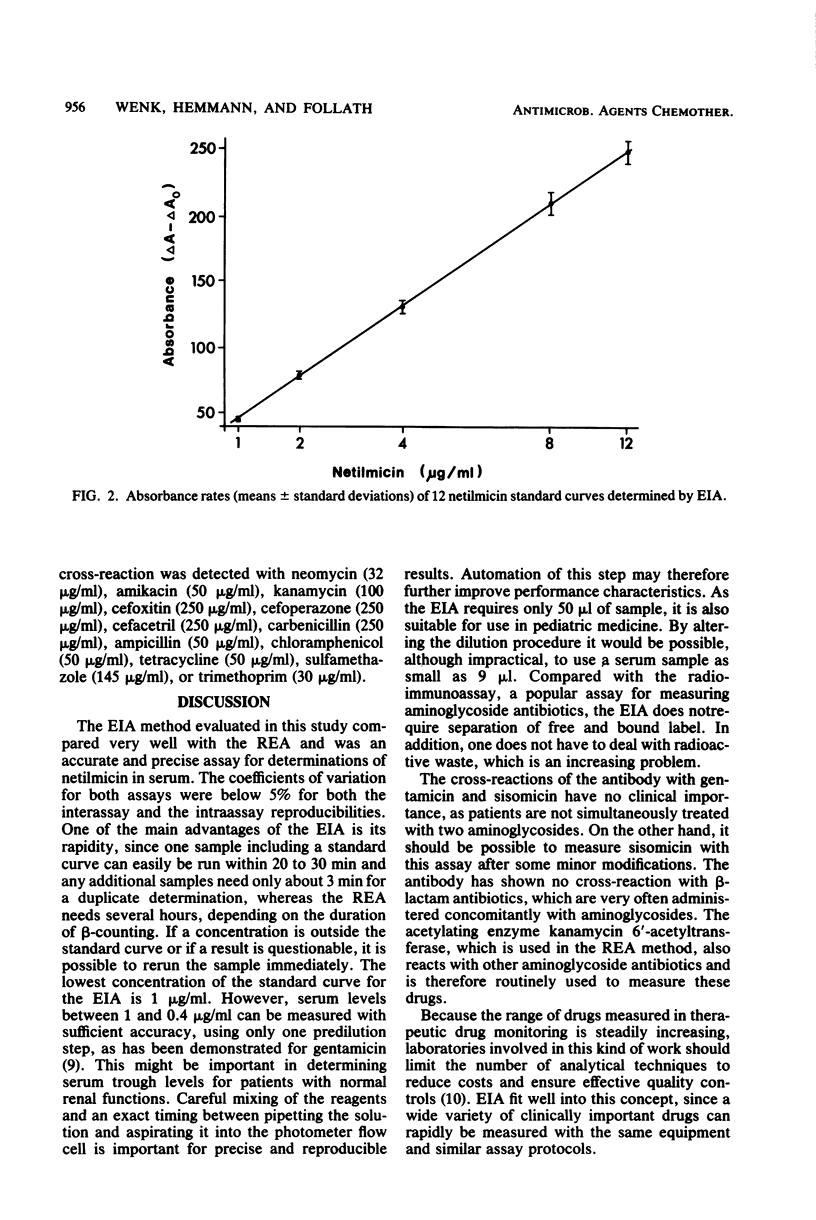
Abstract
A newly developed homogeneous enzyme immunoassay for the determination of netilmicin in serum was evaluated and compared with a radioenzymatic assay. A total of 102 serum samples from patients treated with netilmicin were measured by both methods. This comparison showed an excellent correlation (r = 0.993). The enzyme immunoassay has proved to be precise, accurate, and specific. Because of its rapidity and the ease of performance, this method is a useful alternative to current assays for monitoring serum netilmicin concentrations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broughall J. M., Reeves D. S. The acetyltransferase enzyme method for the assay of serum gentamicon concentrations and a comparison with other methods. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Feb;28(2):140–145. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.2.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummett R. E., Fox K. E., Brown R. T., Himes D. L. Comparative ototoxic liability of netilmicin and gentamicin. Arch Otolaryngol. 1978 Oct;104(10):579–584. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1978.00790100033007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follath F., Wenk M., Vozeh S. Plasma concentration monitoring of aminoglycosides. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jul;8 (Suppl A):37–43. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_a.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke E. L., Srinivasan S., Labthavikul P., Neu H. C. Rapid, reproducible enzyme immunoassay for tobramycin. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):93–96. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.93-96.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Yum M. N., Kleit S. A. Comparative nephrotoxicities of netilmicin and gentamicin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):845–849. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra S. K., Yoshikawa T. T., Guze L. B., Schotz M. C. Determination of aminoglycoside antibiotics in biological fluids: a review. Clin Chem. 1979 Aug;25(8):1361–1367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary T. D., Ratcliff R. M., Geary T. D. Evaluation of an enzyme immunoassay for serum gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 May;17(5):776–778. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.5.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D., Bodey G. P., LeBlanc B. In vitro studies on netilmicin, a new aminoglycoside antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):1017–1020. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voegeli C. J., Vurckart G. J. Improving the sensitivity of gentamicin enzyme immunoassay. Clin Chem. 1982 Jan;28(1):248–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenk M. Concepts for aminoglycoside serum level monitoring. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Mar;9(3):168–169. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.3.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenk M., Spring P., Vozeh S., Follath F. Multicompartment pharmacokinetics of netilmicin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;16(5):331–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00605631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


