Abstract
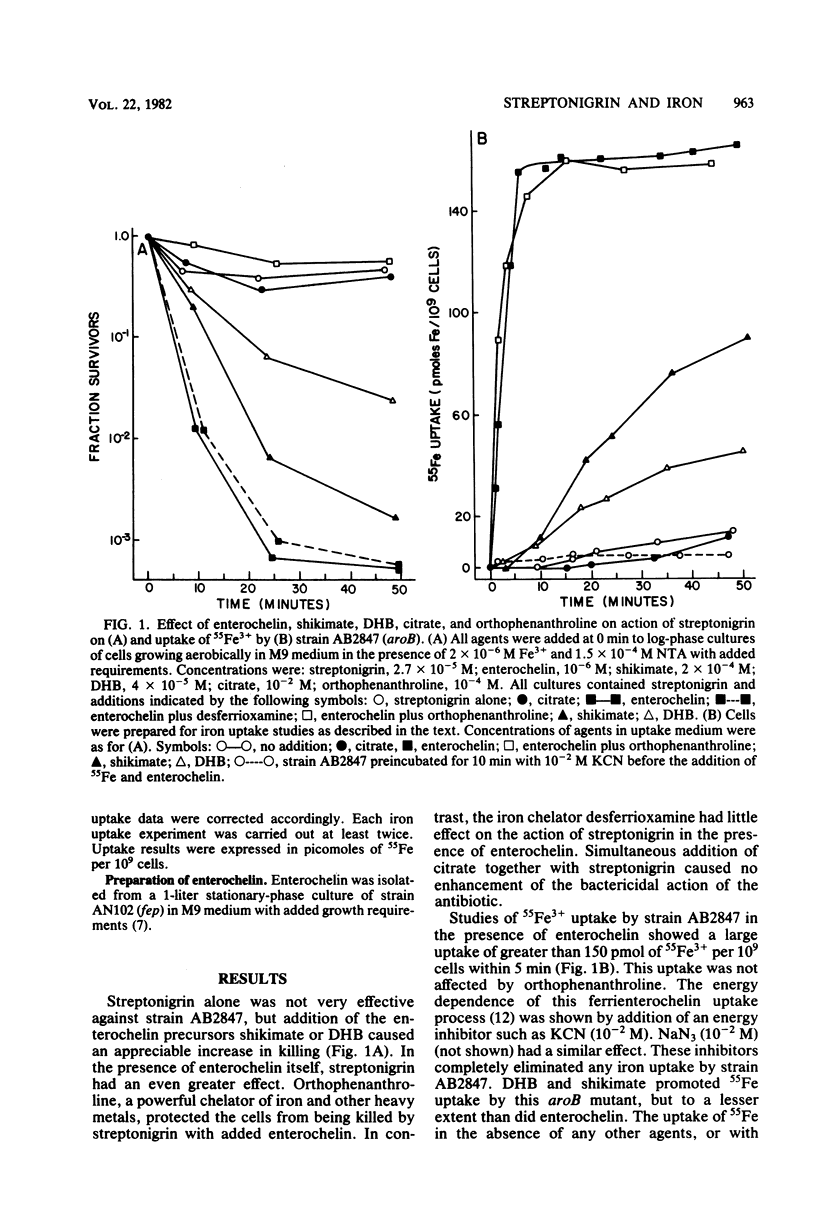
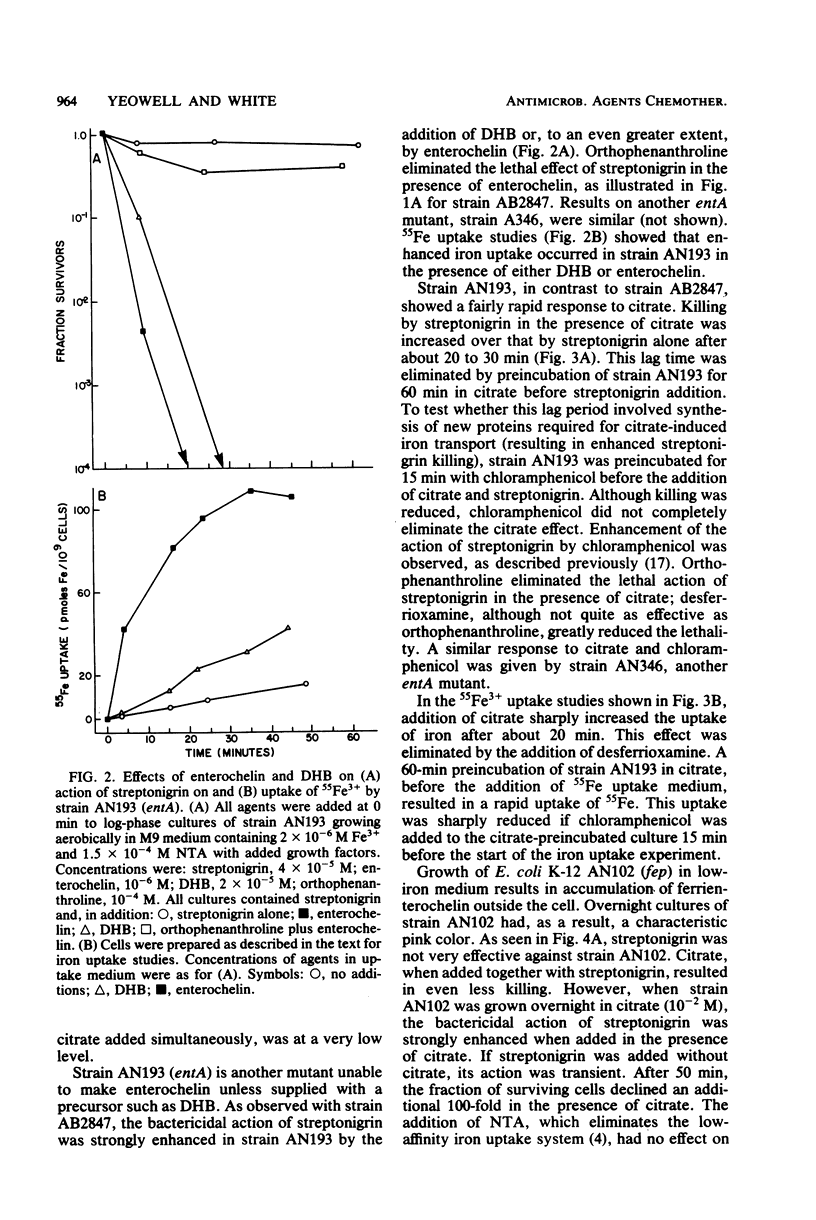
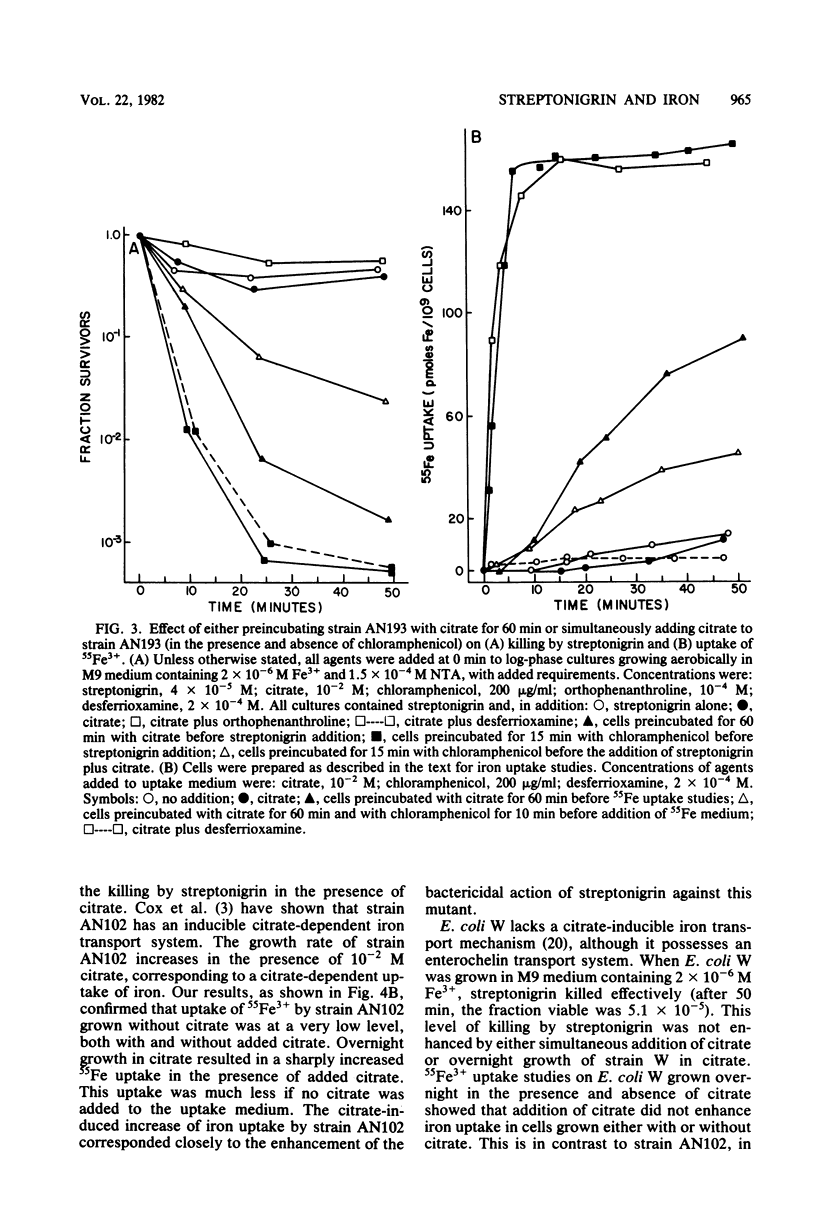
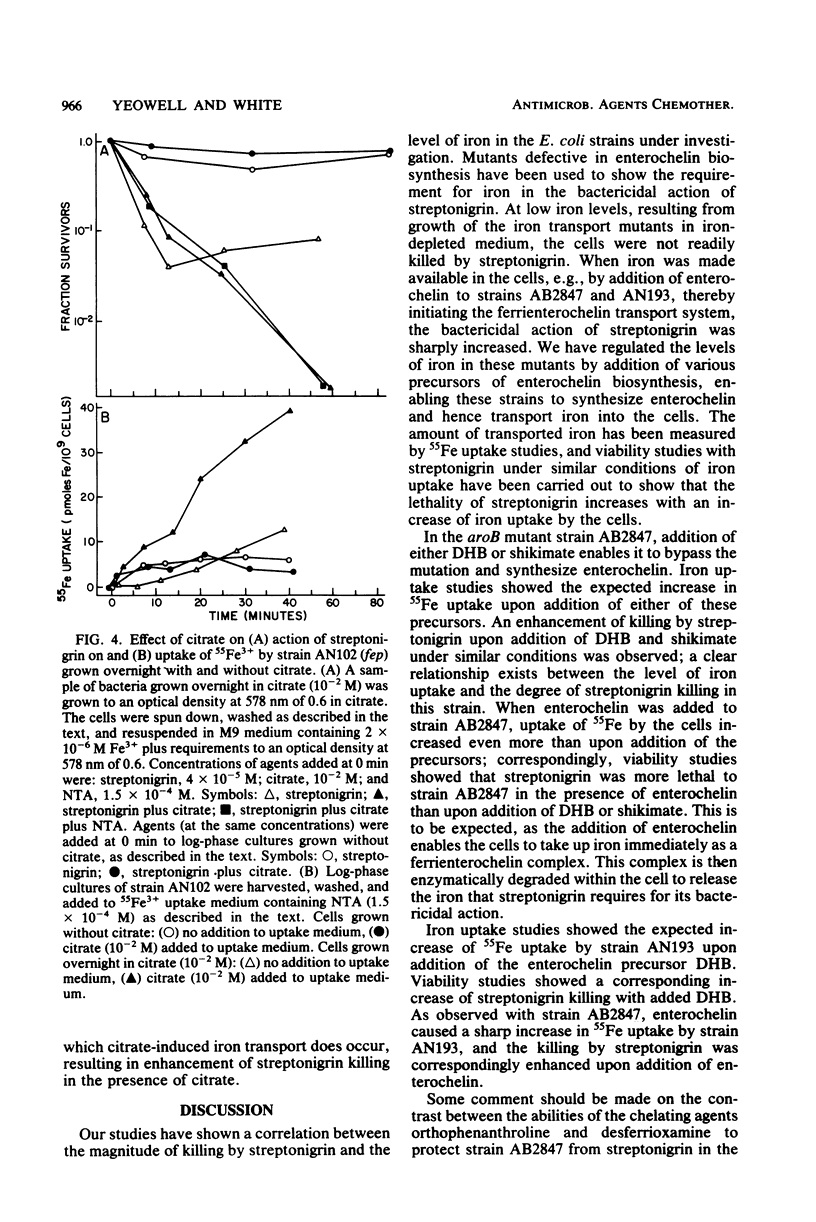
Mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 that are unable to make use of the enterochelin transport system were used to confirm that streptonigrin requires iron for its bactericidal action. Correlation of viability studies and 55Fe3+ uptake experiments showed that killing by streptonigrin increased with an increase in 55Fe3+ uptake by the cells. Streptonigrin did not kill iron-starved mutants that were unable to import iron. The level of iron uptake by these mutants was manipulated by agents such as (i) the enterochelin biosynthetic precursors 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid (2 x 10(-5) M) and shikimic acid (2 x 10(-4) M), (ii) citrate (10(-2) M), which promotes iron uptake by an independent pathway, and (iii) the chelating agents desferrioxamine (2 x 10(-4) M) and orthophenanthroline (10(-4) M). Addition of the precursors shikimate and dihydroxybenzoate to strain AB2847 (aroB) and dihydroxybenzoate to strain AN193 (entA), allowing these strains to make enterochelin, resulted in an increase in Fe3+ uptake and a corresponding sharp increase in killing by streptonigrin. Addition of enterochelin itself (10(-6) M) caused an even more pronounced effect. Studies on the effect of citrate in strain AN102 (fep) showed that this mutant was not killed by streptonigrin (4 x 10(-5) M), even in the presence of citrate; however, overnight growth in citrate induced Fe3+ uptake by means of the ferric citrate transport system and resulted in killing by streptonigrin. These studies showed a clear correlation between the change in levels of intracellular iron and the bactericidal effectiveness of streptonigrin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 6. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Mar;44(1):1–56. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.1.1-56.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. B., Gibson F., Luke R. K., Newton N. A., O'Brien I. G., Rosenberg H. Mutations affecting iron transport in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):219–226. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.219-226.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost G. E., Rosenberg H. The inducible citrate-dependent iron transport system in Escherichia coli K12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 30;330(1):90–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley J. B., Fetterolf C. J., Bello C. A., Flaks J. G. Streptonigrin toxicity in Escherichia coli: oxygen dependence and the role of the intracellular oxidation--reduction state. Can J Microbiol. 1982 May;28(5):545–552. doi: 10.1139/m82-082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Fridovich I. Enzymatic defenses against the toxicity of oxygen and of streptonigrin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1574–1583. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1574-1583.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langman L., Young I. G., Frost G. E., Rosenberg H., Gibson F. Enterochelin system of iron transport in Escherichia coli: mutations affecting ferric-enterochelin esterase. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1142–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1142-1149.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Day E. D., Jr Superoxide-dependent production of hydroxyl radical catalyzed by iron-EDTA complex. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 1;86(1):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh M. A., Earhart C. F. Coordinate regulation by iron of the synthesis of phenolate compounds and three outer membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):331–339. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.331-339.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellencamp M. W., McCabe M. A., Kochan I. The growth-promoting effect of bacterial iron for serum-exposed bacteria. Immunology. 1981 Jul;43(3):483–491. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Reeves P. Uptake of ferrienterochelin by Escherichia coli: energy dependent stage of uptake. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.26-36.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Role of iron and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid in the bactericidal activity of a superoxide anion-generating system. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 May;208(2):512–519. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90539-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagegg W., Braun V. Ferric citrate transport in Escherichia coli requires outer membrane receptor protein fecA. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):156–163. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.156-163.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. L., White J. R. Lethal action and metabolic effects of streptonigrin on Escherichia coli. Mol Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;4(6):549–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. R. Streptonigrin-transition metal complexes: binding to DNA and biological activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):387–391. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. R., Yeowell H. N. Iron enhances the bactericidal action of streptonigrin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):407–411. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91125-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. G., Cox G. B., Gibson F. 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoate as a bacterial growth factor and its route of biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jul 25;141(2):319–331. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90106-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


