Abstract
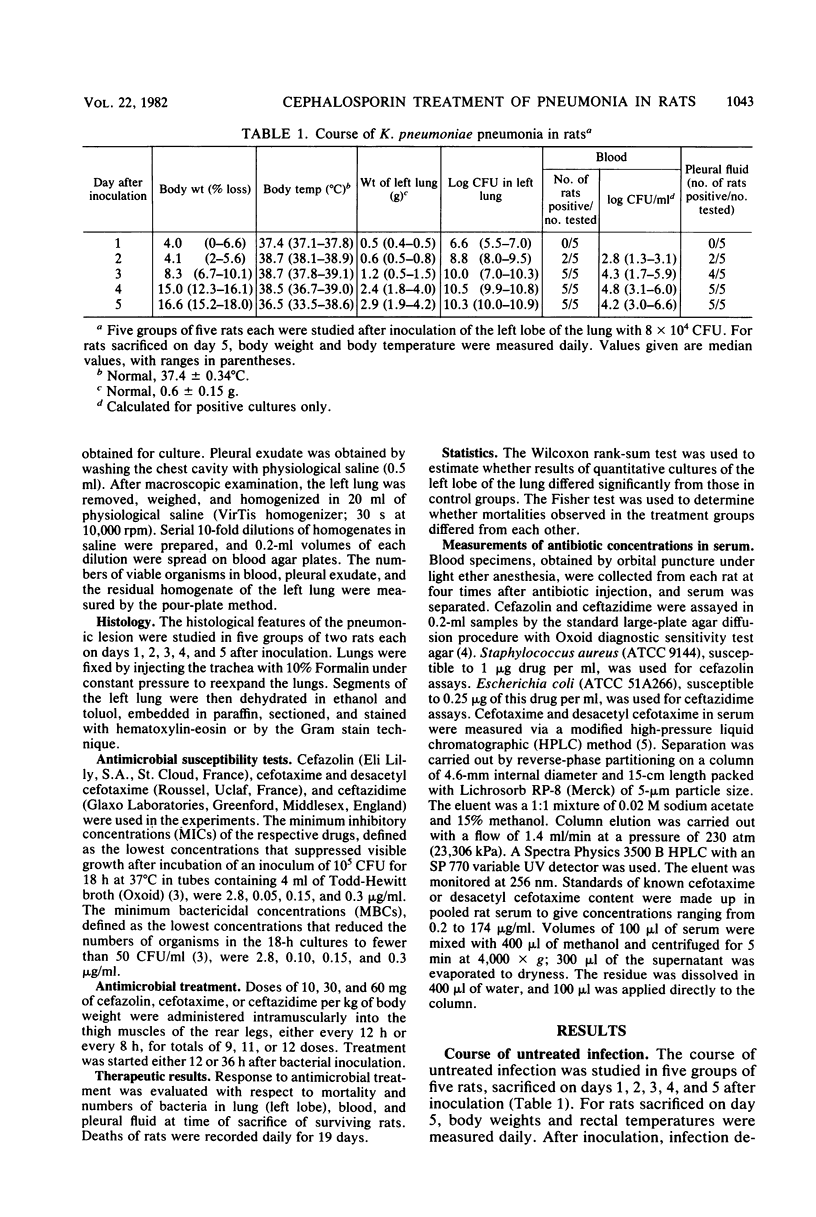
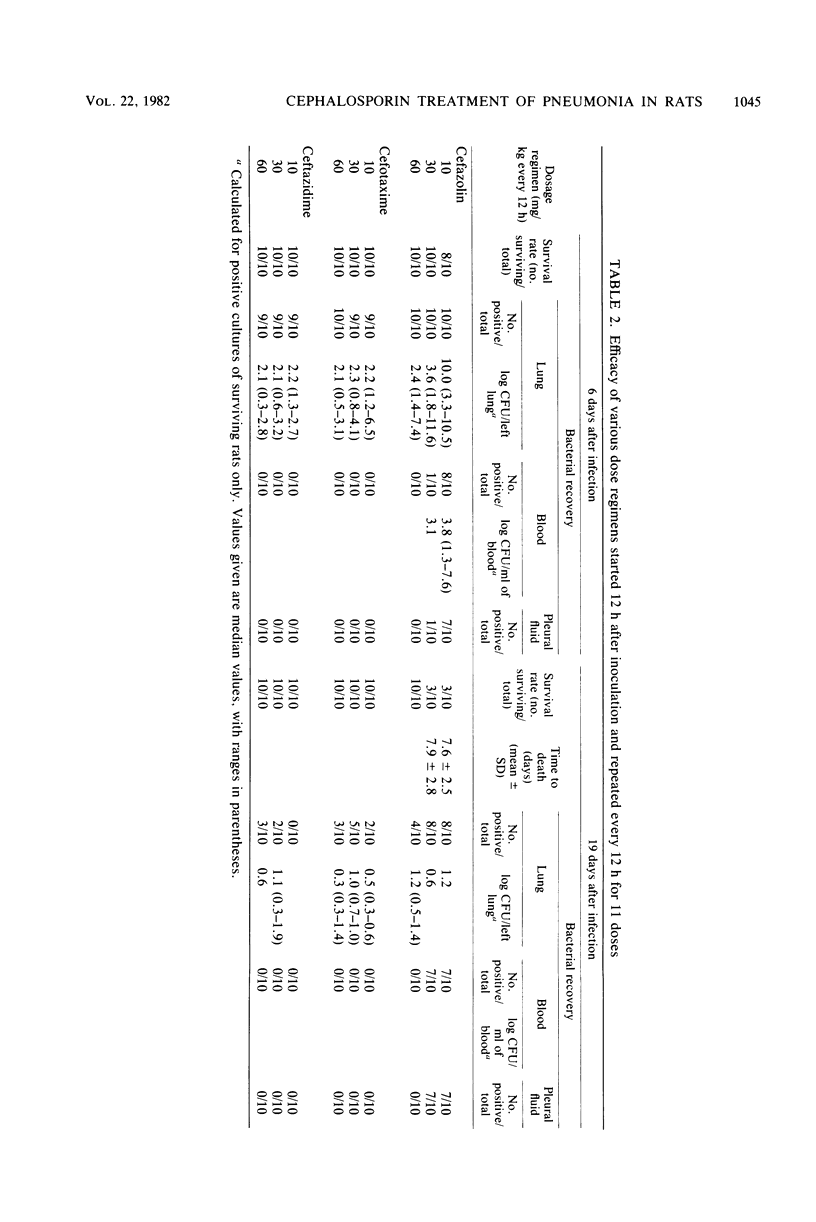
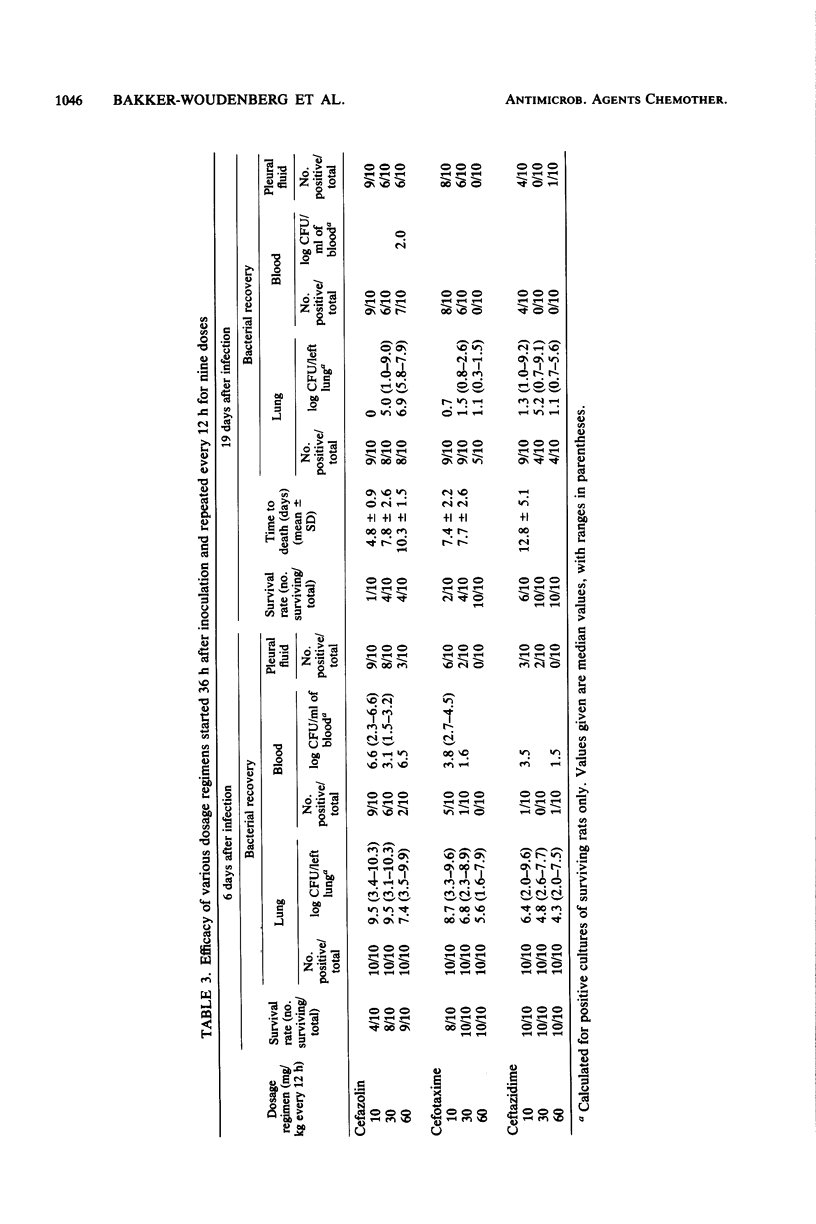
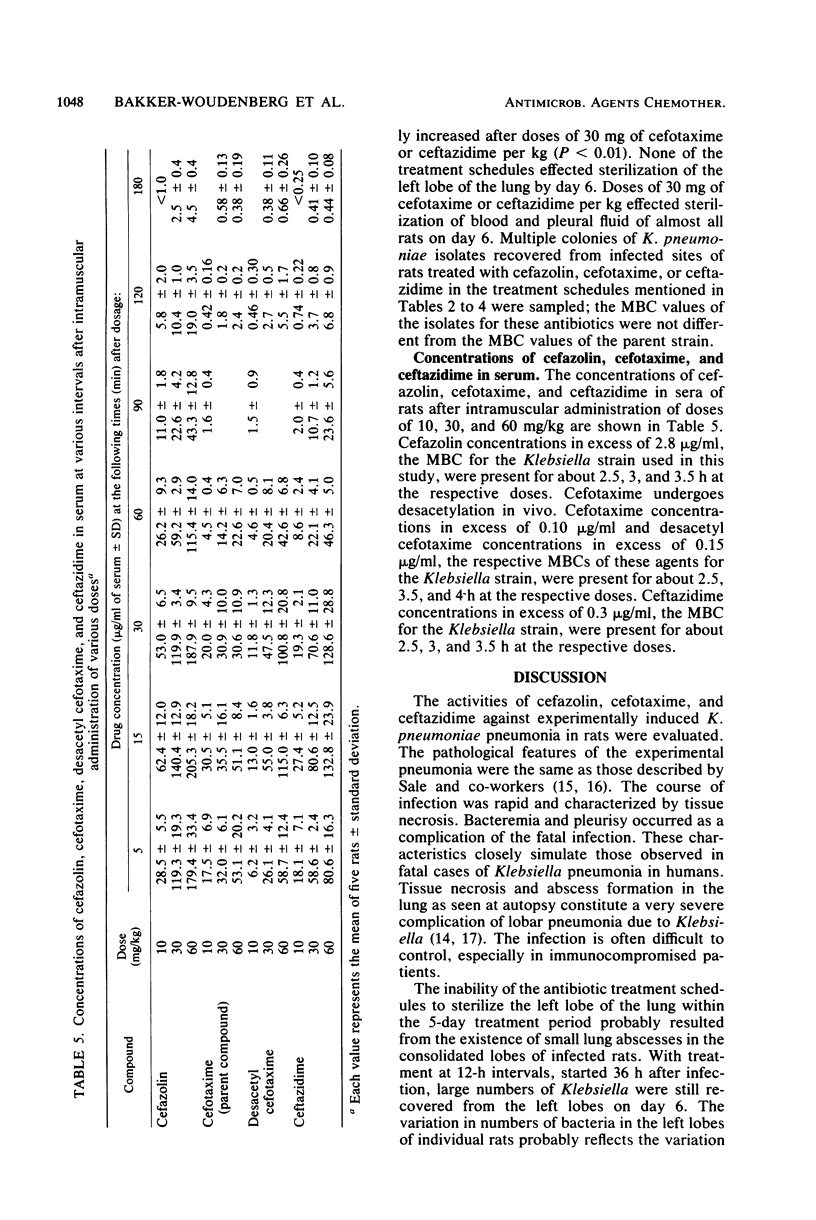
The efficacies of several dosage schedules of cefazolin, cefotaxime, and ceftazidime, started 12 or 36 h after infection, were examined in experimental pneumonia caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae in rats. The therapeutic activities of the cephalosporins were compared with the antibacterial activities in vitro and the serum concentration curves. The course of experimental pneumonia was rapid and characterized by tissue necrosis. Response to antimicrobial treatment was evaluated with respect to mortality and numbers of bacteria in lung (left lobe), blood, and pleural fluid. When antibiotic treatment was started early, i.e., 12 h after bacterial inoculation, cefotaxime and ceftazidime were equally effective and superior to cefazolin. Eleven doses of 10 mg of cefotaxime or ceftazidime per kg or 11 doses of 60 mg of cefazolin per kg were required to improve the survival rate. With a delay in administration to 36 h after inoculation, the efficacy of the cephalosporins decreased markedly. In the three dosages tested, cefazolin was ineffective. Survival improved with the administration of nine doses of 60 mg of cefotaxime per kg or nine doses of 10 mg of ceftazidime per kg. These results are not in accordance with the ratio of in vitro activities of cefotaxime and ceftazidime or the serum concentration curves.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., de Jong-Hoenderop J. Y., Michel M. F. Efficacy of antimicrobial therapy in experimental rat pneumonia: effects of impaired phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):366–375. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.366-375.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. V., Brodie J. L., Benner E. J., Kirby W. M. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):170–177. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergan T., Solberg R. Assay of cefotaxime by high-pressure-liquid chromatography. Chemotherapy. 1981;27(3):155–165. doi: 10.1159/000237972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P. Infections in cancer patients. Cancer Treat Rev. 1975 Jun;2(2):89–128. doi: 10.1016/s0305-7372(75)80005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Rodriguez V., Chang H. Y., Narboni Fever and infection in leukemic patients: a study of 494 consecutive patients. Cancer. 1978 Apr;41(4):1610–1622. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197804)41:4<1610::aid-cncr2820410452>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaya H., Tattersall M. H., Hutchinson R. M., Spiers A. S. Changing patterns of infection in cancer patients. Eur J Cancer. 1973 Jun;9(6):401–406. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(73)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes A. M. Antibiotics and travellers' diarrhoea. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Oct;8(4):247–248. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.4.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kees F., Strehl E., Seeger K., Seidel G., Dominiak P., Grobecker H. Comparative determination of cefotaxime and desacetyl cefotaxime in serum and bile by bioassay and high-performance liquid chromatography. Arzneimittelforschung. 1981;31(2):362–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Weerts D. Recent experience with bacteremia in patients presenting cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1973 Jan;9(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(73)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi T., Tsuchiya K. Therapeutic effects of cefotiam and cefazolin on experimental pneumonia caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae DT-S in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Oct;18(4):549–556. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.4.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. P. Indolent pulmonary abscess associated with Klebsiella and Enterobacter. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Jun;107(6):1055–1059. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.6.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotimi V. O., Turk D. C. Transferable multiple antibiotic resistance in Haemophilus influenzae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Sep;8(3):187–192. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.3.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schamaun M., von Büren U., Pirozynski W. Ausgedehnte Lungennekrose bei Klebsiellen-Pneumonie (sogenannte massive Gangrän der Lunge). Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1980 Feb 9;110(6):223–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrinner E., Limbert M., Penasse L., Lutz A. Antibacterial activity of cefotaxime and other newer cephalosporins (in vitro and in vivo). J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Sep;6 (Suppl A):25–30. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.suppl_a.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umsawasdi T., Middleman E. A., Luna M., Bodey G. P. Klebsiella bacteremia in cancer patients. Am J Med Sci. 1973 Jun;265(6):473–482. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197306000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdivieso M., Gil-extremera B., Zornoza J., Rodriquez V., Bodey G. P. Gram-negative bacillary pneumonia in the compromised host. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 May;56(3):241–254. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197705000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L., Verhaegen J. GR-20263: a new aminothiazolyl cephalosporin with high activity against Pseudomonas and Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 May;17(5):807–812. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.5.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Bedford K. A. Comparison of in vitro activity of GR 20263, a novel cephalosporin derivative, with activities of other beta-lactam compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 May;17(5):884–889. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.5.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Wills P. J., Andrews J. M., Bedford K. A. Activity of the cefotaxime (HR756) desacetyl metabolite compared with those of cefotaxime and other cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jan;17(1):84–86. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]