Abstract
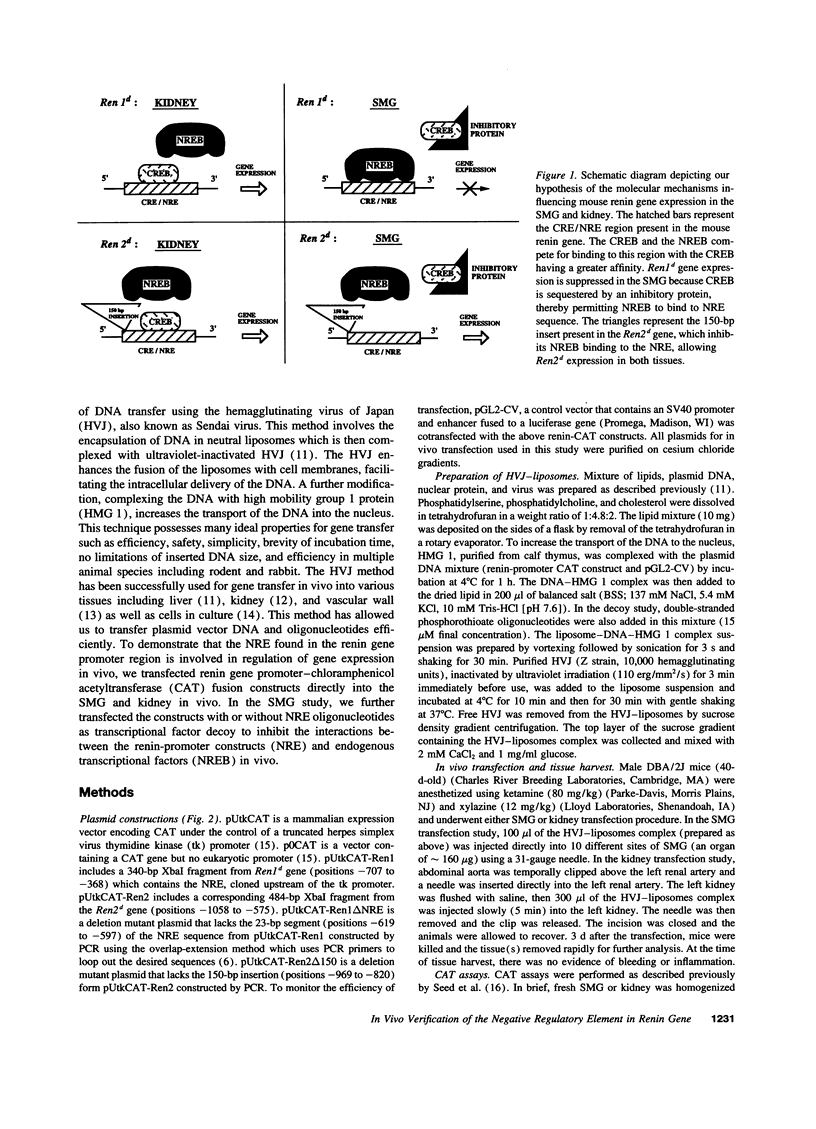
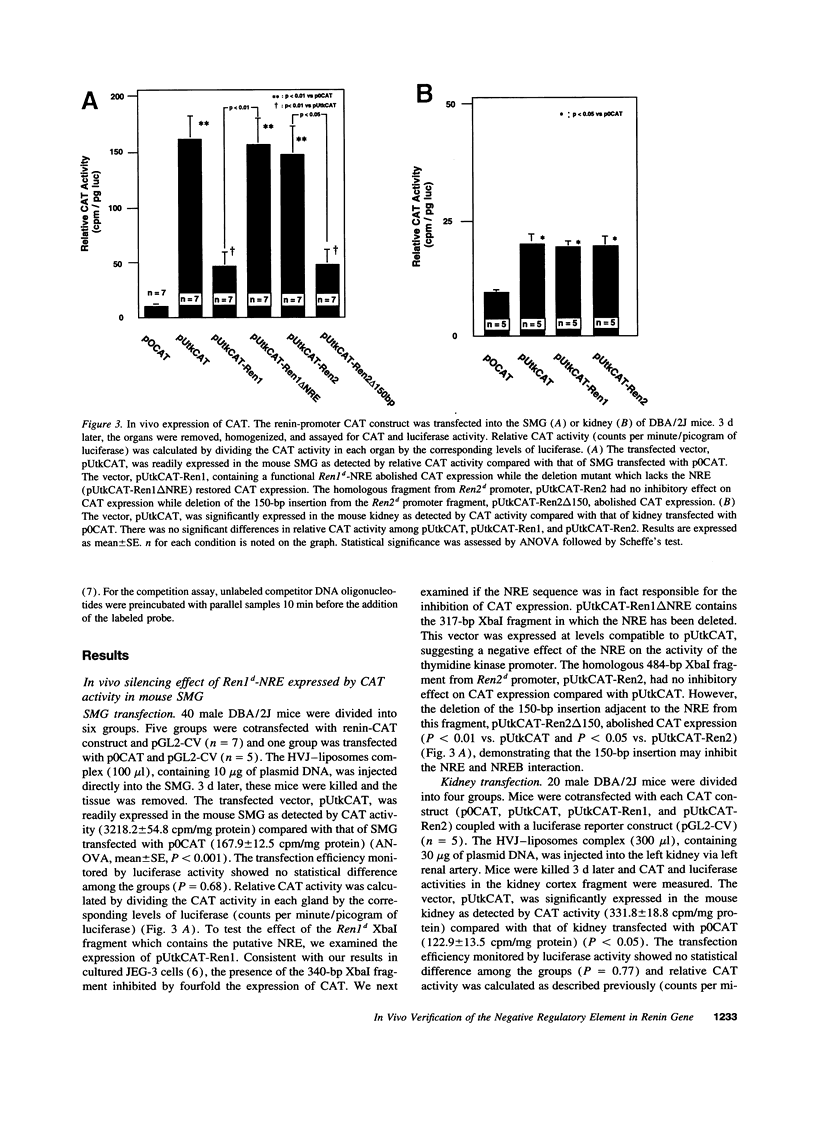
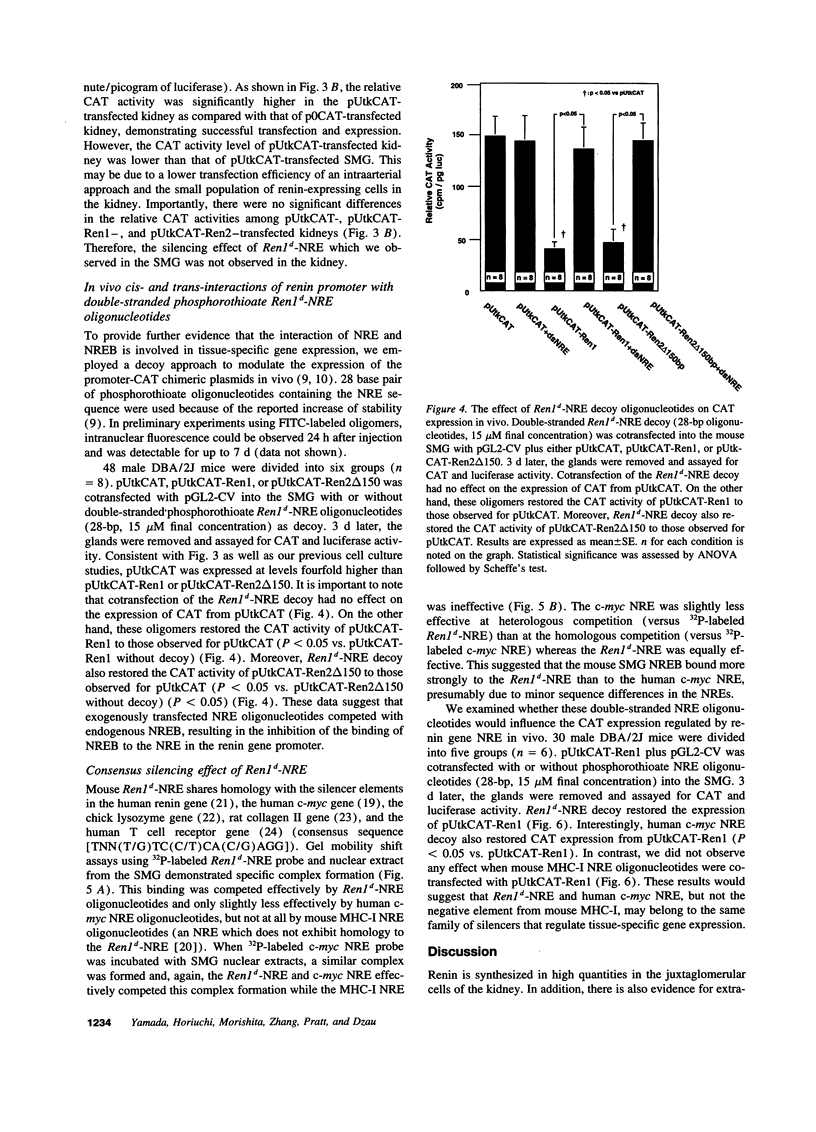
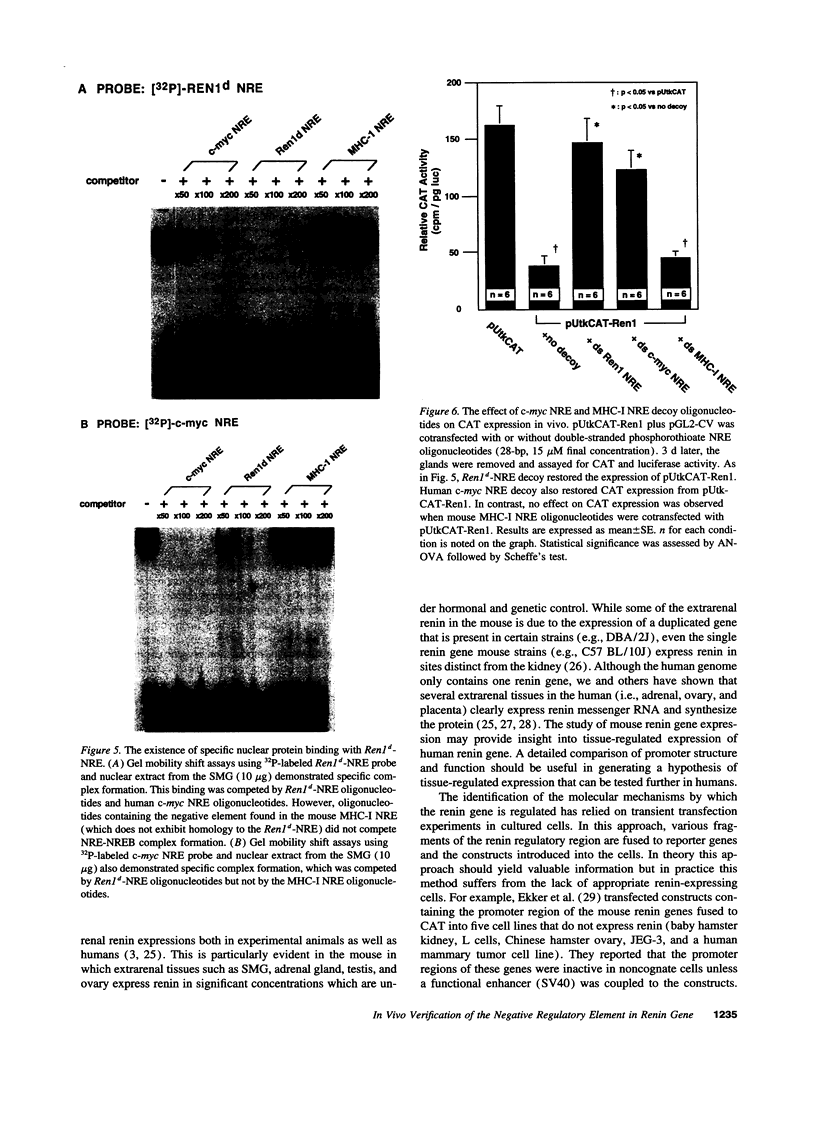
DBA/2J mouse contains two renin gene loci (Ren1d and Ren2d). Ren2d but not Ren1d is expressed in submandibular gland (SMG) while both are expressed in the kidney. Based on vitro studies, we have postulated that a negative regulatory element (NRE) in the renin gene promoter is involved in its tissue-specific expression. In this study, we examined the molecular mechanism at the in vivo level using direct gene transfer. Fragments of the Ren1d or Ren2d promoter were fused to a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene expression vector. These constructs complexed in fusogenic liposomes were injected directly into the mouse SMG or intraarterially into the mouse kidney via the renal artery. The vector containing the CAT exhibited readily detectable in vivo expressions in both SMG and kidney. In the SMG, Ren1d fragment containing the NRE abolished CAT expression while deletion of the NRE restored CAT expression. The homologous fragment from the Ren2d promoter did not inhibit CAT expression while deletion of the 150-bp insertion resulted in the inhibition. Cotransfection of Ren1d construct with Ren1d-NRE oligonucleotides as transcriptional factor decoy restored CAT expression. Contrary to the SMG, transfection with Ren1d fragment-CAT construct or Ren2d fragment-CAT construct into the kidney resulted in similar levels of CAT expression. Interestingly, human c-myc NRE oligonucleotides which share homology with Ren1d-NRE competed effectively with these oligonucleotides for the regulation of Ren1d gene expression in vivo. This NRE sequence is also homologous to silencer elements found in multiple mammalian genes, suggesting the presence of a family of NRE/NRE binding proteins regulating expression of diverse genes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard D. W., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Sista P., Molitor J. A., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene encodes a kappa B enhancer binding protein that inhibits NF-kappa B function. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Muller M., Steiner C., Renkawitz R. Activity of two different silencer elements of the chicken lysozyme gene can be compensated by enhancer elements. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2297–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02504.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
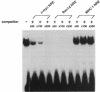
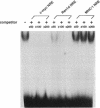
- Barrett G., Horiuchi M., Paul M., Pratt R. E., Nakamura N., Dzau V. J. Identification of a negative regulatory element involved in tissue-specific expression of mouse renin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):885–889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Duncan K., Chu W., James M. N., Russell R. B., Haidar M. A., DeNoto F. M., Hsueh W., Reudelhuber T. L. Molecular biology of human renin and its gene. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1991;47:211–258. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571147-0.50011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielinska A., Shivdasani R. A., Zhang L. Q., Nabel G. J. Regulation of gene expression with double-stranded phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):997–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.2237444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. Optimized use of the firefly luciferase assay as a reporter gene in mammalian cell lines. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1116–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt D. W., Nakamura N., Kelley P., Dzau V. J. Identification of negative and positive regulatory elements in the human renin gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7357–7362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttrick P. M., Kass A., Kitsis R. N., Kaplan M. L., Leinwand L. A. Behavior of genes directly injected into the rat heart in vivo. Circ Res. 1992 Jan;70(1):193–198. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.1.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzau V. J., Burt D. W., Pratt R. E. Molecular biology of the renin-angiotensin system. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):F563–F573. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.4.F563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker M., Tronik D., Rougeon F. Extra-renal transcription of the renin genes in multiple tissues of mice and rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5155–5158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. J., Gross K. W. Ren-1 and Ren-2 loci are expressed in mouse kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6196–6200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. R., Murata M., Burke P. A., Shirayoshi Y., Appella E., Sharp P. A., Ozato K. Negative regulation of the major histocompatibility complex class I promoter in embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3145–3149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Takimoto M., Bishop J. M. A FOS protein is present in a complex that binds a negative regulator of MYC. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):293–303. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi M., Pratt R. E., Nakamura N., Dzau V. J. Distinct nuclear proteins competing for an overlapping sequence of cyclic adenosine monophosphate and negative regulatory elements regulate tissue-specific mouse renin gene expression. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):1805–1811. doi: 10.1172/JCI116770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaka Y., Fujiwara Y., Ueda N., Kaneda Y., Kamada T., Imai E. Glomerulosclerosis induced by in vivo transfection of transforming growth factor-beta or platelet-derived growth factor gene into the rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2597–2601. doi: 10.1172/JCI116874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda Y., Iwai K., Uchida T. Increased expression of DNA cointroduced with nuclear protein in adult rat liver. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):375–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2911748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitsis R. N., Buttrick P. M., McNally E. M., Kaplan M. L., Leinwand L. A. Hormonal modulation of a gene injected into rat heart in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4138–4142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M. Transcriptional regulation of T cell receptor genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:539–570. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.002543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz T., James G. D., Laragh J. H., Sealey J. E. Prorenin secretion from human placenta perfused in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 1):E876–E882. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.260.6.E876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire J. E., Frels W. I., Richardson J. C., Weissman J. D., Singer D. S. In vivo function of regulatory DNA sequence elements of a major histocompatibility complex class I gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3078–3086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita R., Gibbons G. H., Ellison K. E., Nakajima M., Zhang L., Kaneda Y., Ogihara T., Dzau V. J. Single intraluminal delivery of antisense cdc2 kinase and proliferating-cell nuclear antigen oligonucleotides results in chronic inhibition of neointimal hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8474–8478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita R., Gibbons G. H., Kaneda Y., Ogihara T., Dzau V. J. Novel and effective gene transfer technique for study of vascular renin angiotensin system. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2580–2585. doi: 10.1172/JCI116496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. J., Burt D. W., Windass J. D., McTurk P., George H., Brammar W. J. Molecular cloning of two distinct renin genes from the DBA/2 mouse. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1461–1466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. J., Sigmund C. D., Kane-Haas C., Wu C. Z., Pacholec F., Zeng Q., Gross K. W. Studies on the regulation of renin genes using transgenic mice. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1988;10(6):1157–1167. doi: 10.1080/07300077.1988.11878808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel E. G., Plautz G., Boyce F. M., Stanley J. C., Nabel G. J. Recombinant gene expression in vivo within endothelial cells of the arterial wall. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1342–1344. doi: 10.1126/science.2499928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura N., Burt D. W., Paul M., Dzau V. J. Negative control elements and cAMP responsive sequences in the tissue-specific expression of mouse renin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):56–59. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul M., Wagner J., Dzau V. J. Gene expression of the renin-angiotensin system in human tissues. Quantitative analysis by the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):2058–2064. doi: 10.1172/JCI116428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prost E., Moore D. D. CAT vectors for analysis of eukaryotic promoters and enhancers. Gene. 1986;45(1):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savagner P., Miyashita T., Yamada Y. Two silencers regulate the tissue-specific expression of the collagen II gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6669–6674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada S., Scarborough J. D., Killeen N., Littman D. R. A lineage-specific transcriptional silencer regulates CD4 gene expression during T lymphocyte development. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):917–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund C. D., Gross K. W. Structure, expression, and regulation of the murine renin genes. Hypertension. 1991 Oct;18(4):446–457. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.18.4.446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sola C., Tronik D., Dreyfus M., Babinet C., Rougeon F. Renin-promoter SV40 large T-antigen transgenes induce tumors irrespective of normal cellular expression of renin genes. Oncogene Res. 1989;5(2):149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullenger B. A., Gallardo H. F., Ungers G. E., Gilboa E. Overexpression of TAR sequences renders cells resistant to human immunodeficiency virus replication. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90455-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronik D., Dreyfus M., Babinet C., Rougeon F. Regulated expression of the Ren-2 gene in transgenic mice derived from parental strains carrying only the Ren-1 gene. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):983–987. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04848.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. M., Moolten D., Burlein J., Romano J., Bhaerman R., Godillot A., Mellon M., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Kant J. A. Identification of a zinc finger protein that inhibits IL-2 gene expression. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1791–1794. doi: 10.1126/science.1840704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Baltimore D. Alpha beta lineage-specific expression of the alpha T cell receptor gene by nearby silencers. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):649–655. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Harsdorf R., Schott R. J., Shen Y. T., Vatner S. F., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Gene injection into canine myocardium as a useful model for studying gene expression in the heart of large mammals. Circ Res. 1993 Mar;72(3):688–695. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.3.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]