Abstract
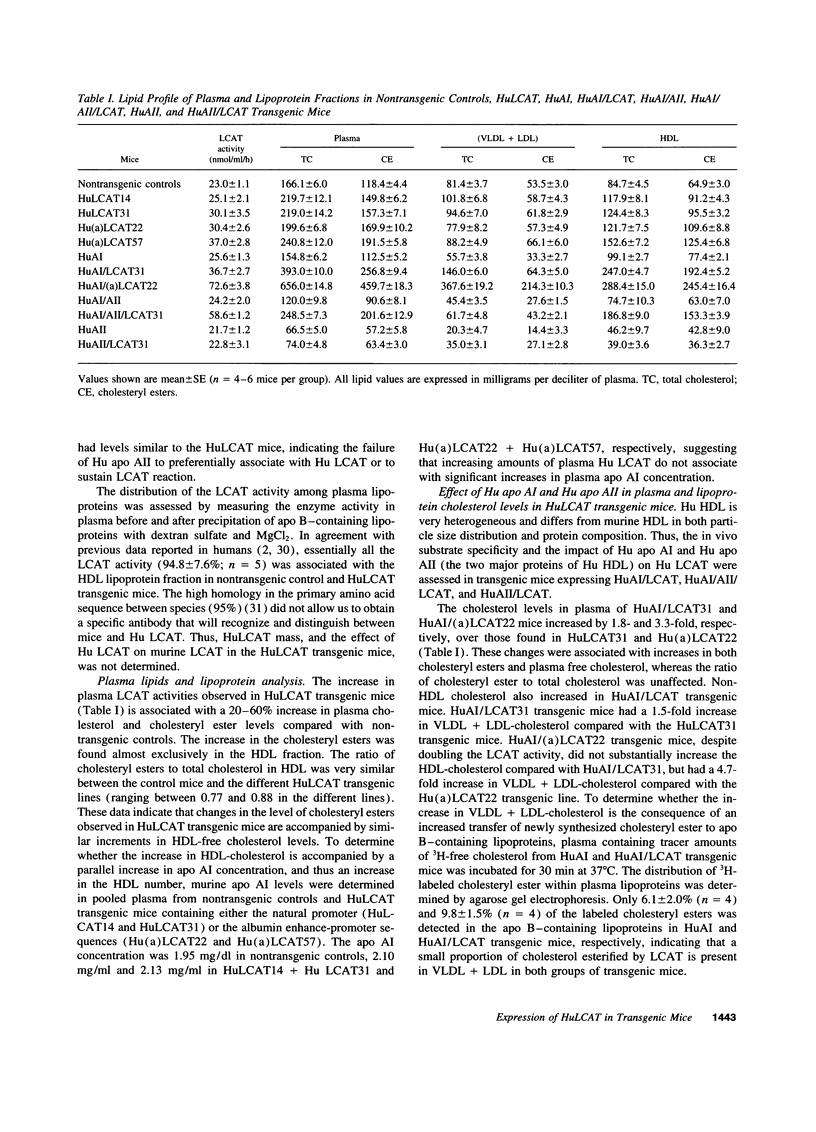
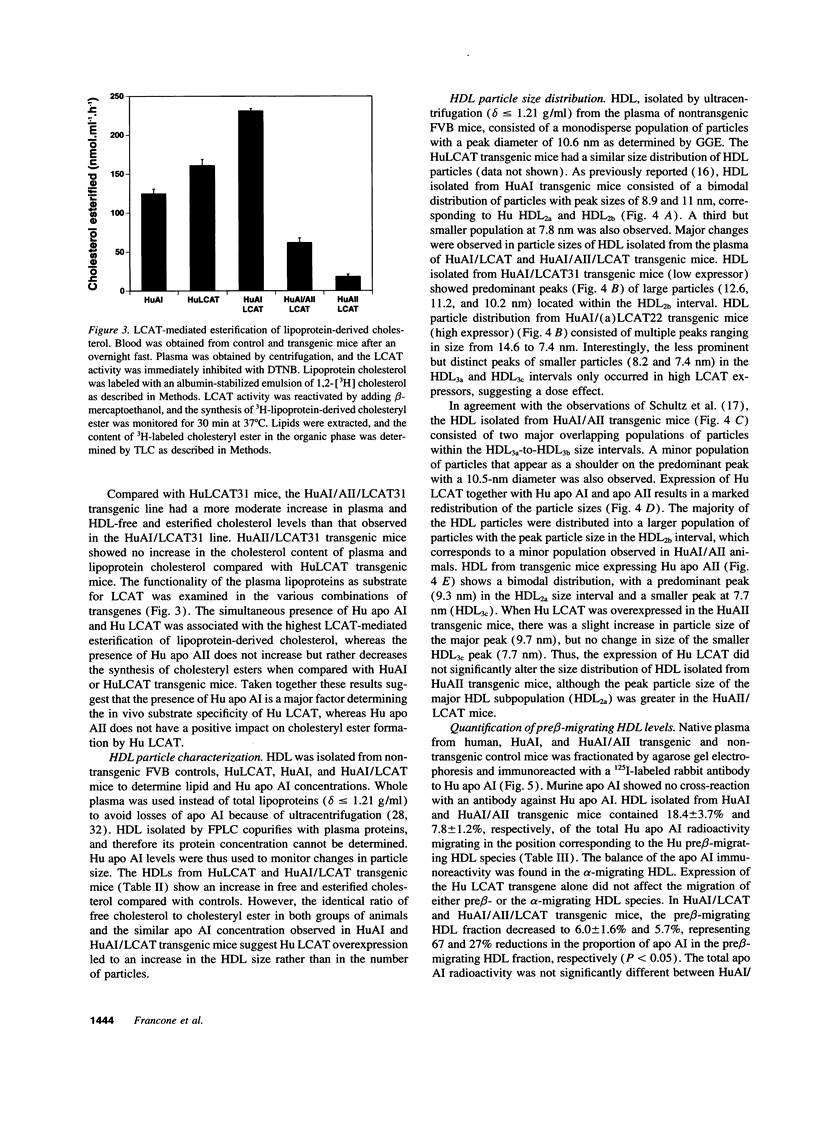
Human (Hu) lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) is a key enzyme in the plasma metabolism of cholesterol. To assess the effects of increased plasma levels of LCAT, four lines of transgenic mice were created expressing a Hu LCAT gene driven by either its natural or the mouse albumin enhancer promoter. Plasma LCAT activity increased from 1.2- to 1.6-fold higher than that found in control mouse plasma. Lipid profiles, upon comparing Hu LCAT transgenics to control animals, revealed a 20 t0 60% increase in total and cholesteryl esters that were mainly present in HDL. The in vivo substrate specificity of Hu LCAT was assessed by creating animals expressing Hu apo AI + Hu LCAT (HuAI/ LCAT), Hu apo AI + Hu apo AII + Hu LCAT (HuAI/ AII/LCAT), and Hu apo AII + Hu LCAT (HuAII/LCAT). Plasma cholesterol was increased up to 4.2-fold in HuAI/ LCAT transgenic mice and twofold in the HuAI/AII/LCAT transgenic mice, compared with HuAI and HuAI/AII transgenic mice. HDL cholesteryl ester levels were increased more than twofold in both the HuAI/LCAT and HuAI/AII/LCAT mice compared with the HuAI, HuAI/AII, and HuLCAT animals. The HDL particles were predominantly larger in the HuAI/LCAT and the HuAI/AII/LCAT mice compared with those in HuAI, HuAII/LCAT, and HuLCAT animals. The increase in LCAT activity in the HuAI/LCAT and HuAI/AII/LCAT mice was associated with 62 and 27% reductions respectively, in the proportion of Hu apo AI in the pre beta-HDL fraction, when compared with HuAI and HuAI/AII transgenic mice. These data demonstrate that moderate increases in LCAT activity are associated with significant changes in lipoprotein cholesterol levels and that Hu LCAT has a significant preference for HDL containing Hu apo AI.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain C. C., Poon L. S., Chan C. S., Richmond W., Fu P. C. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem. 1974 Apr;20(4):470–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asztalos B. F., Sloop C. H., Wong L., Roheim P. S. Two-dimensional electrophoresis of plasma lipoproteins: recognition of new apo A-I-containing subpopulations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Sep 8;1169(3):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(93)90253-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:243–255. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanche P. J., Gong E. L., Forte T. M., Nichols A. V. Characterization of human high-density lipoproteins by gradient gel electrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 24;665(3):408–419. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. A., Holmquist L. Evidence for deficiency of high density lipoprotein lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase activity (alpha-LCAT) in fish eye disease. Acta Med Scand. 1985;218(2):189–196. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1985.tb08846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle C. K., Pape M. E., Marotti K. R., Melchior G. W. Secretion of pre-beta-migrating apoA-I by cynomolgus monkey hepatocytes in culture. J Lipid Res. 1991 Mar;32(3):439–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro G. R., Fielding C. J. Early incorporation of cell-derived cholesterol into pre-beta-migrating high-density lipoprotein. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):25–29. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. H., Albers J. J. Distribution of lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) in human plasma lipoprotein fractions. Evidence for the association of active LCAT with low density lipoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1091–1096. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90633-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. H., Albers J. J. Interspecies activation of lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase by apolipoprotein A-I isolated from the plasma of humans, horses, sheep, goats and rabbits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 29;753(1):40–46. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Applegate K., King W. C., Glomset J. A., Norum K. R., Gjone E. A study of the small spherical high density lipoproteins of patients afflicted with familial lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency. J Lipid Res. 1984 Mar;25(3):269–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung M. C., Albers J. J. Characterization of lipoprotein particles isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography. Particles containing A-I and A-II and particles containing A-I but no A-II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12201–12209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung M. C., Segrest J. P., Albers J. J., Cone J. T., Brouillette C. G., Chung B. H., Kashyap M., Glasscock M. A., Anantharamaiah G. M. Characterization of high density lipoprotein subspecies: structural studies by single vertical spin ultracentrifugation and immunoaffinity chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1987 Aug;28(8):913–929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong K. S., Jahani M., Hara S., Lacko A. G. Characterization of lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase from human plasma. 3. Chemical properties of the enzyme. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;61(8):875–881. doi: 10.1139/o83-112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duverger N., Rader D., Duchateau P., Fruchart J. C., Castro G., Brewer H. B., Jr Biochemical characterization of the three major subclasses of lipoprotein A-I preparatively isolated from human plasma. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 23;32(46):12372–12379. doi: 10.1021/bi00097a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E. A protein cofactor of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 25;46(4):1493–1498. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90776-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francone O. L., Fielding C. J. Structure-function relationships in human lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Site-directed mutagenesis at serine residues 181 and 216. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 22;30(42):10074–10077. doi: 10.1021/bi00106a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francone O. L., Gurakar A., Fielding C. Distribution and functions of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase and cholesteryl ester transfer protein in plasma lipoproteins. Evidence for a functional unit containing these activities together with apolipoproteins A-I and D that catalyzes the esterification and transfer of cell-derived cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):7066–7072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L. S., Hamilton R. L., Kane J. P., Fielding C. J., Chen G. C. Characterization and quantitation of apolipoproteins A-I and E of normal and cholesterol-fed guinea pigs. J Lipid Res. 1982 May;23(4):531–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Jr, Goerke J., Guo L. S., Williams M. C., Havel R. J. Unilamellar liposomes made with the French pressure cell: a simple preparative and semiquantitative technique. J Lipid Res. 1980 Nov;21(8):981–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayek T., Chajek-Shaul T., Walsh A., Agellon L. B., Moulin P., Tall A. R., Breslow J. L. An interaction between the human cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) and apolipoprotein A-I genes in transgenic mice results in a profound CETP-mediated depression of high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):505–510. doi: 10.1172/JCI115887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida B. Y., Albee D., Paigen B. Interconversion of prebeta-migrating lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein A-I and HDL. J Lipid Res. 1990 Feb;31(2):227–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Januzzi J. L., Azrolan N., O'Connell A., Aalto-Setälä K., Breslow J. L. Characterization of the mouse apolipoprotein Apoa-1/Apoc-3 gene locus: genomic, mRNA, and protein sequences with comparisons to other species. Genomics. 1992 Dec;14(4):1081–1088. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiao S., Cole T. G., Kitchens R. T., Pfleger B., Schonfeld G. Genetic heterogeneity of lipoproteins in inbred strains of mice: analysis by gel-permeation chromatography. Metabolism. 1990 Feb;39(2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90069-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas A., Kézdy K. E., Wald J. H. Defined apolipoprotein A-I conformations in reconstituted high density lipoprotein discs. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4818–4824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunitake S. T., Kane J. P. Factors affecting the integrity of high density lipoproteins in the ultracentrifuge. J Lipid Res. 1982 Aug;23(6):936–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matz C. E., Jonas A. Micellar complexes of human apolipoprotein A-I with phosphatidylcholines and cholesterol prepared from cholate-lipid dispersions. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4535–4540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall M. R., Nichols A. V., Blanche P. J., Shore V. G., Forte T. M. Lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase-induced transformation of HepG2 lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1989 Oct;30(10):1579–1589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J., Wion K., Drayna D., Fielding C., Lawn R. Human lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase gene: complete gene sequence and sites of expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9397–9406. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng Q. H., Calabresi L., Fruchart J. C., Marcel Y. L. Apolipoprotein A-I domains involved in the activation of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Importance of the central domain. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):16966–16973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miida T., Kawano M., Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. Regulation of the concentration of pre beta high-density lipoprotein in normal plasma by cell membranes and lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase activity. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 17;31(45):11112–11117. doi: 10.1021/bi00160a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida H. I., Nakanishi T., Yen E. A., Arai H., Yen F. T., Nishida T. Nature of the enhancement of lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase reaction by various apolipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12028–12035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patsch W., Schonfeld G., Gotto A. M., Jr, Patsch J. R. Characterization of human high density lipoproteins by zonal ultracentrifugation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3178–3185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkert C. A., Ornitz D. M., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. An albumin enhancer located 10 kb upstream functions along with its promoter to direct efficient, liver-specific expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):268–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn D., Shirai K., Jackson R. L. Lipoprotein lipase: mechanism of action and role in lipoprotein metabolism. Prog Lipid Res. 1983;22(1):35–78. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(83)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rader D. J., Castro G., Zech L. A., Fruchart J. C., Brewer H. B., Jr In vivo metabolism of apolipoprotein A-I on high density lipoprotein particles LpA-I and LpA-I,A-II. J Lipid Res. 1991 Nov;32(11):1849–1859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. M., Ishida B. Y., Clift S. M., Krauss R. M. Expression of human apolipoprotein A-I in transgenic mice results in reduced plasma levels of murine apolipoprotein A-I and the appearance of two new high density lipoprotein size subclasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):434–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J. R., Gong E. L., McCall M. R., Nichols A. V., Clift S. M., Rubin E. M. Expression of human apolipoprotein A-II and its effect on high density lipoproteins in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21630–21636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. M., Lawn R. M., Wilcox J. N. Cellular localization of apolipoprotein D and lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase mRNA in rhesus monkey tissues by in situ hybridization. J Lipid Res. 1990 Jun;31(6):995–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokke K. T., Norum K. R. Determination of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransfer in human blood plasma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Feb;27(1):21–27. doi: 10.3109/00365517109080184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh A., Ito Y., Breslow J. L. High levels of human apolipoprotein A-I in transgenic mice result in increased plasma levels of small high density lipoprotein (HDL) particles comparable to human HDL3. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6488–6494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warden C. H., Langner C. A., Gordon J. I., Taylor B. A., McLean J. W., Lusis A. J. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and chromosomal mapping of the lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase gene. Evidence for expression in brain and testes as well as liver. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21573–21581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Tilbeurgh H., Sarda L., Verger R., Cambillau C. Structure of the pancreatic lipase-procolipase complex. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):159–162. doi: 10.1038/359159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]