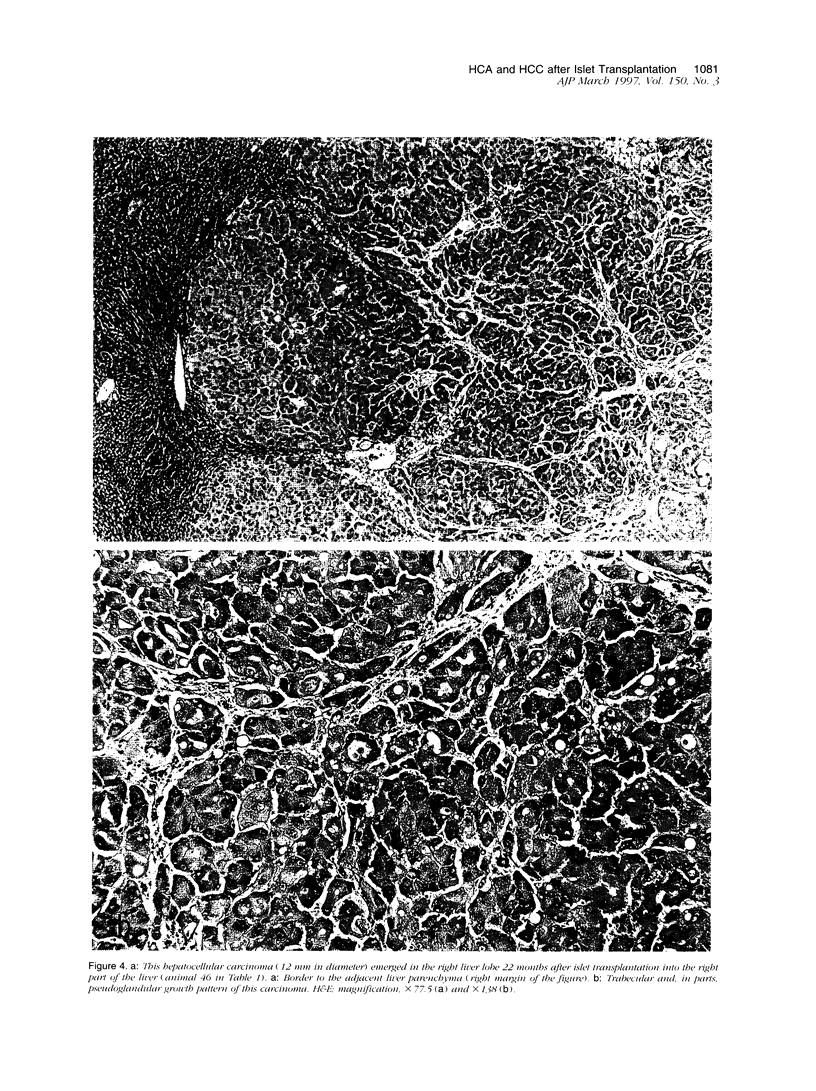
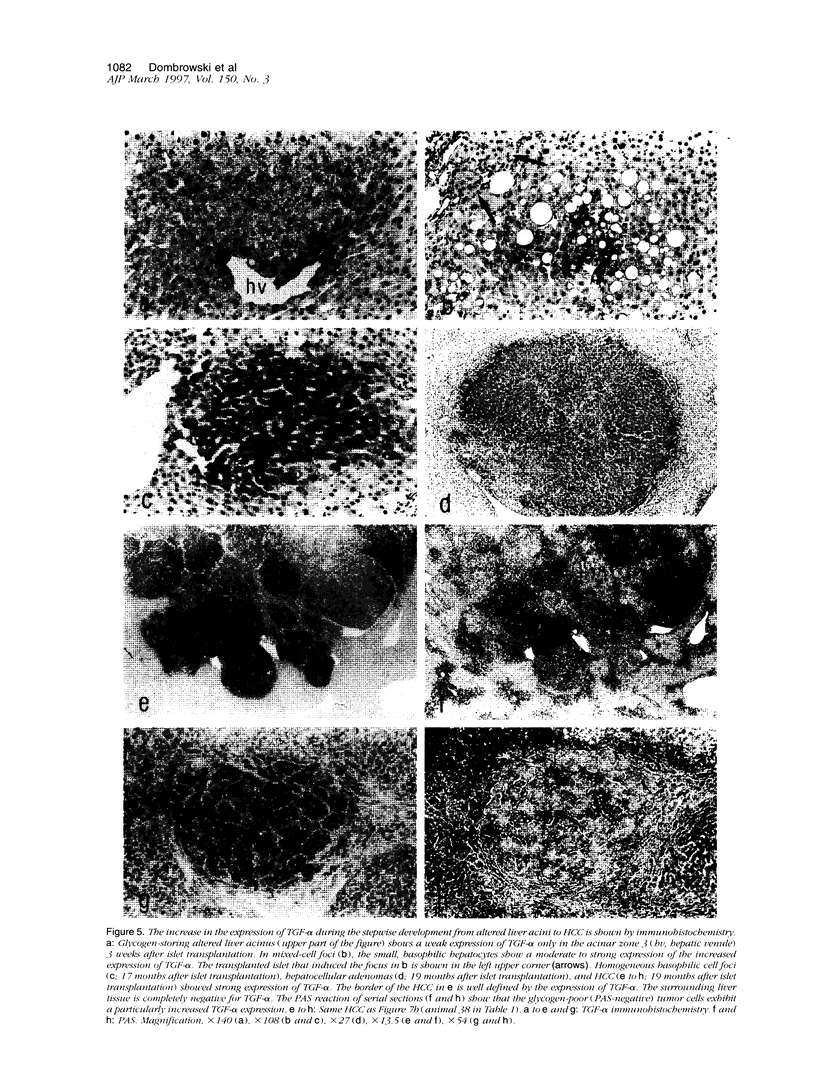
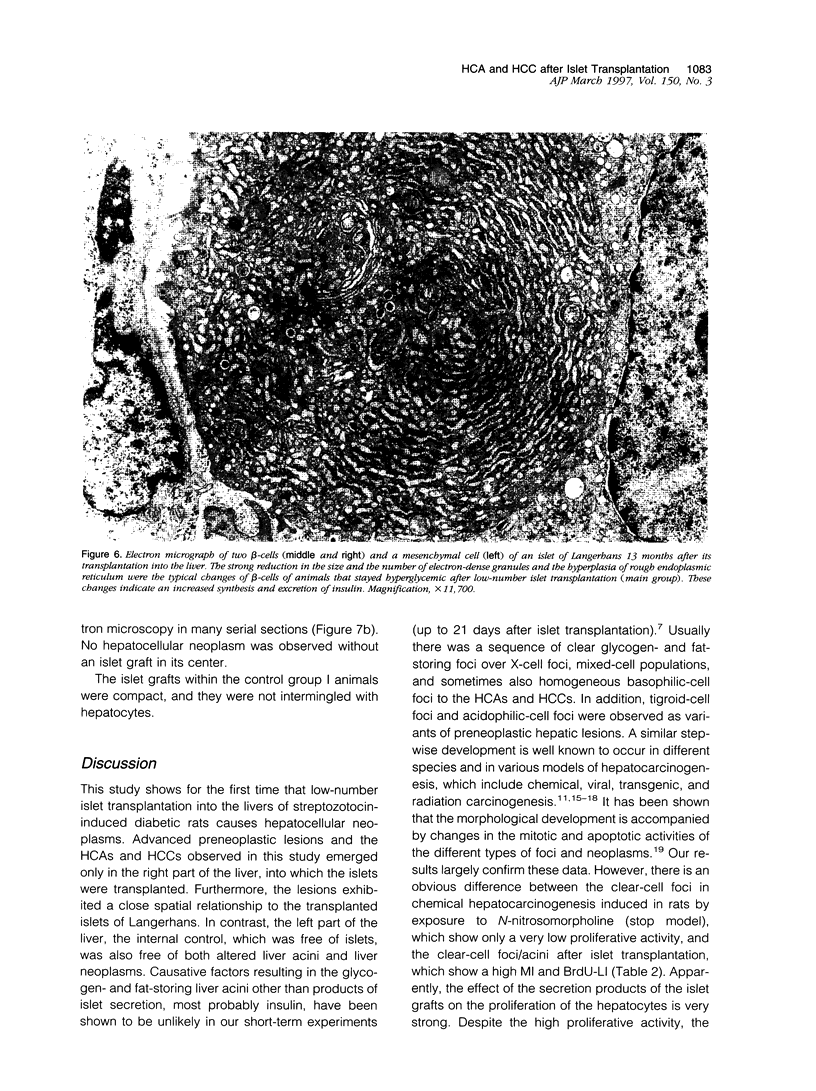
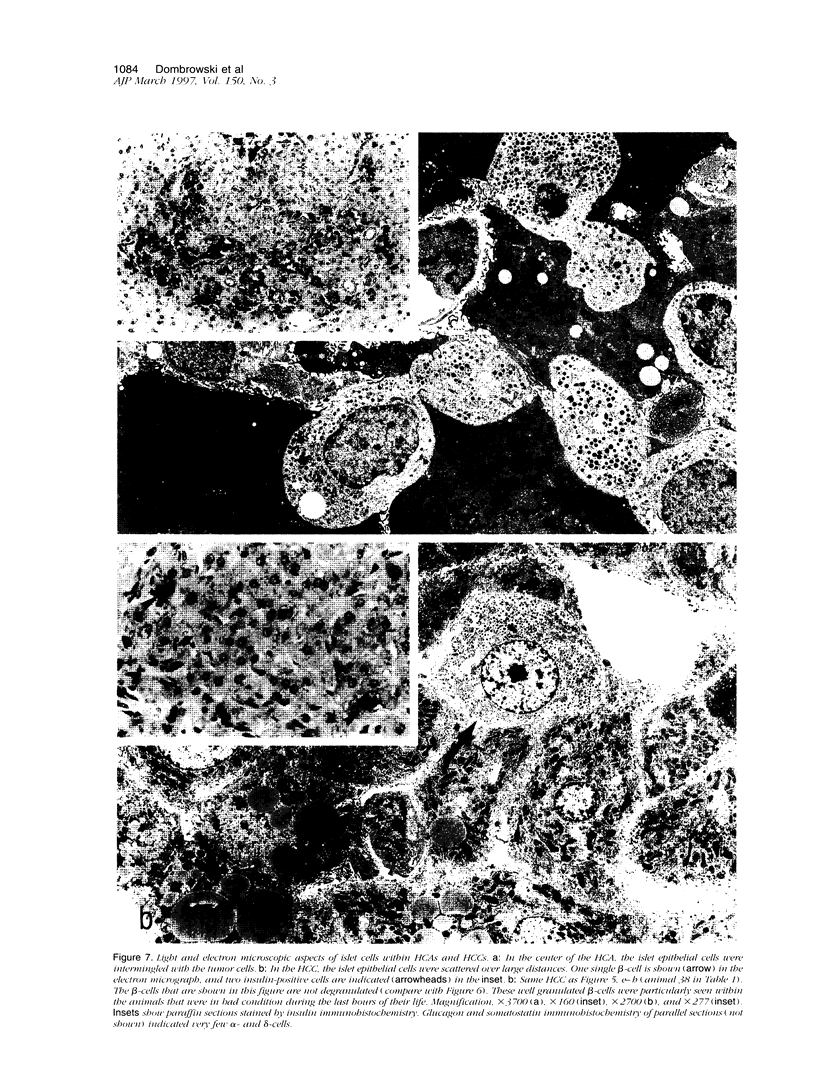
Abstract
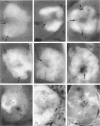
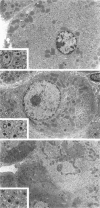
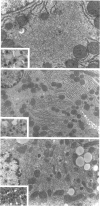
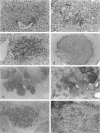
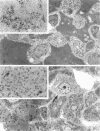
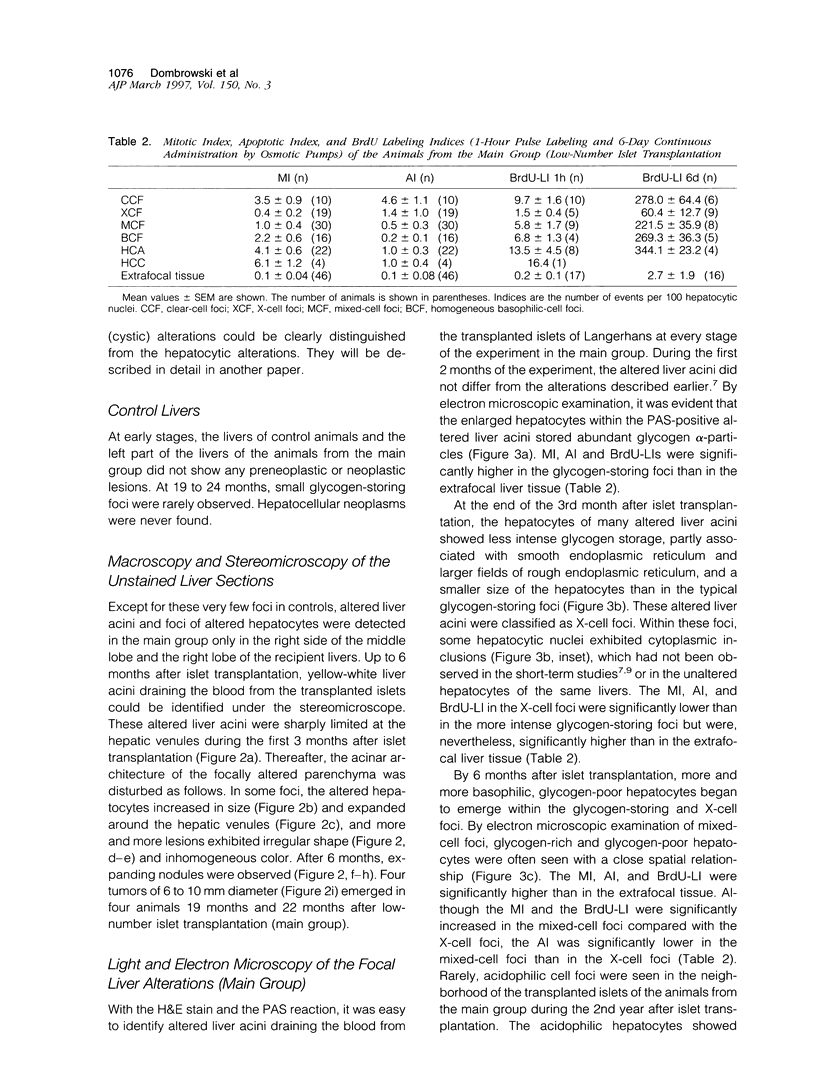
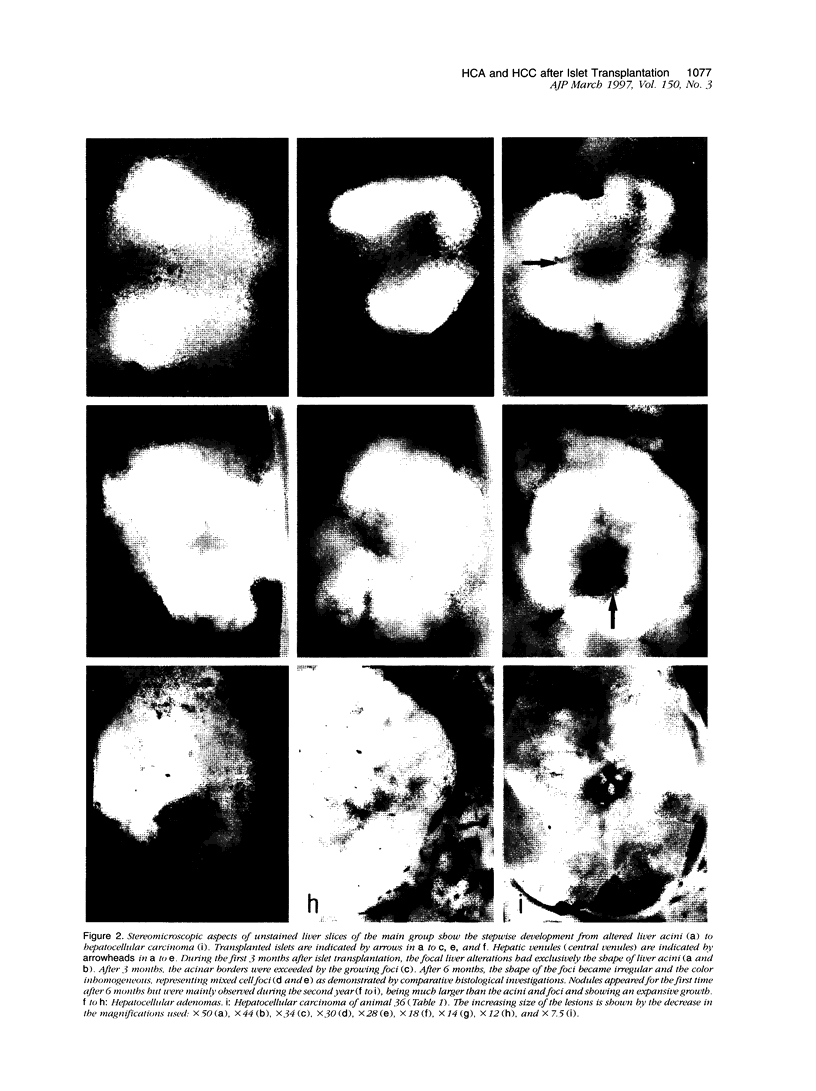
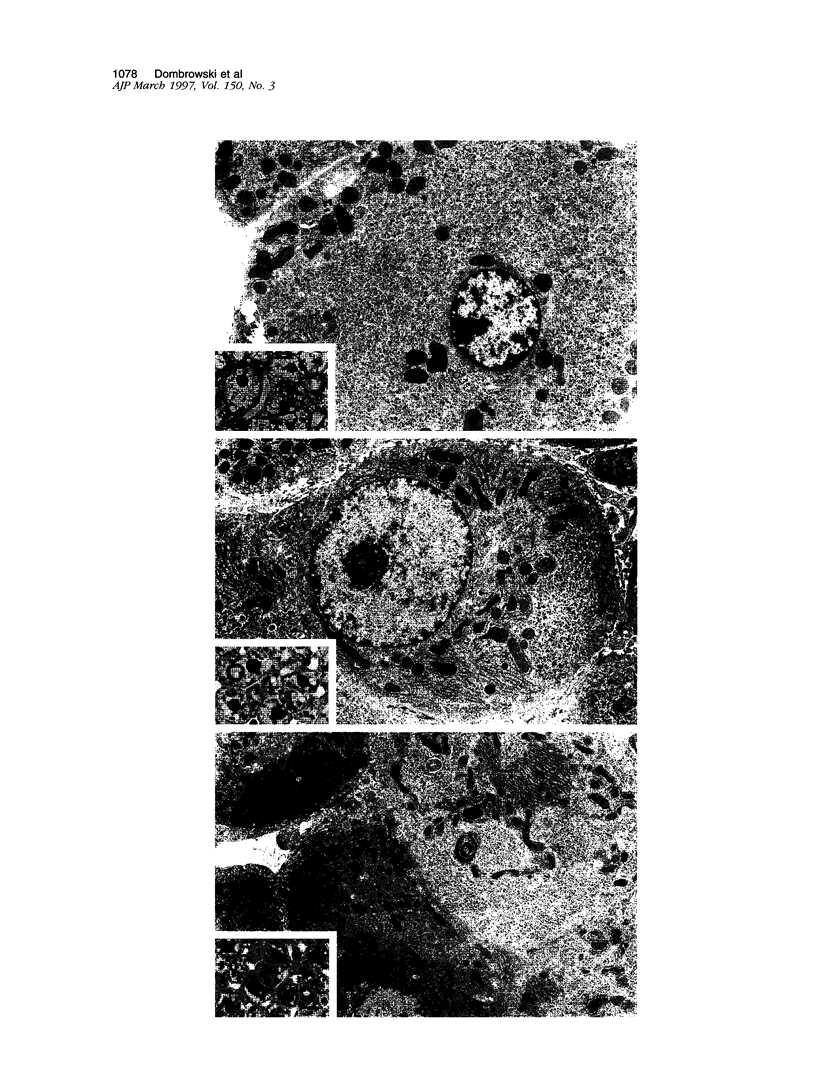
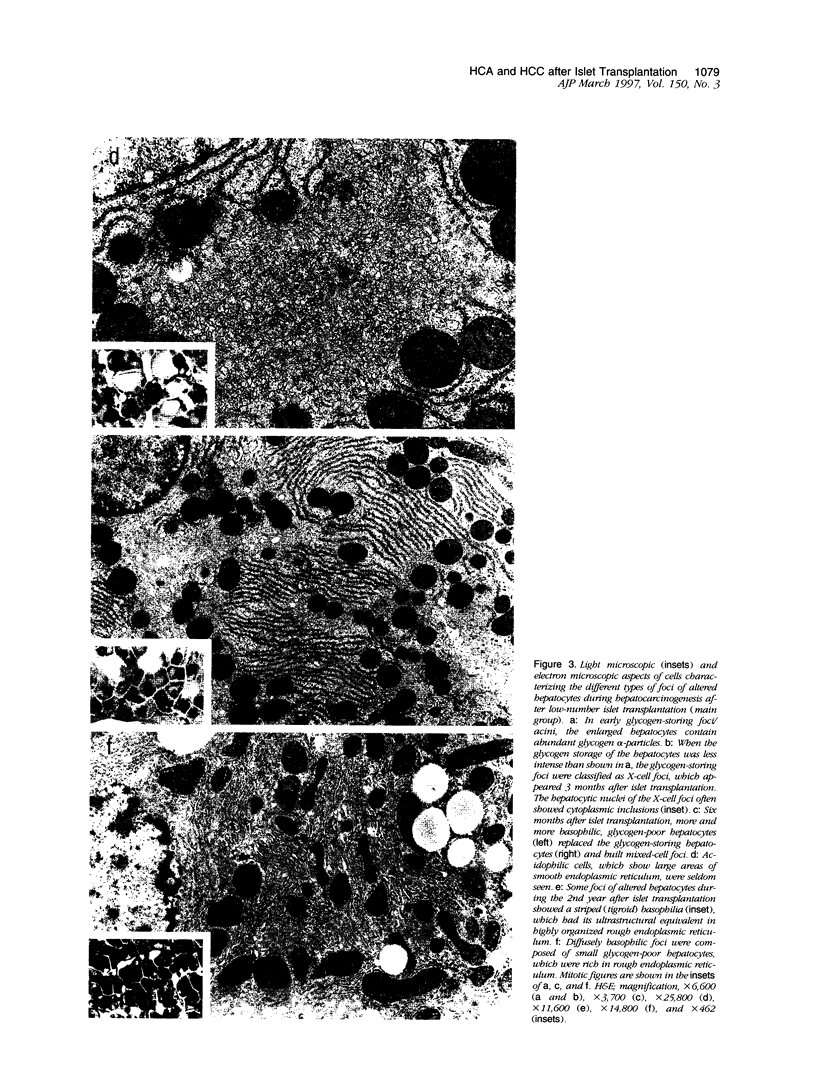
We have previously demonstrated in short-term experiments that altered hepatocytes in liver acini draining the blood from intraportally transplanted pancreatic islets in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats with mild persisting diabetes resemble those in preneoplastic foci of altered hepatocytes. We now present the results of long-term studies (up to 22 months) in this animal model. Glycogen-storing foci (which were the first parenchymal alteration observed some days after transplantation) persisted at least for 6 months, when the first mixed-cell foci and the first hepatocellular adenoma emerged. After 15 to 22 months, 86% of the animals exhibited at least one hepatocellular adenoma and four animals (19%) showed a hepatocellular carcinoma. The transplants were found in a close spatial relationship with the preneoplastic foci and the hepatocellular neoplasms. The mitotic indices, the 5-bromo-2'-desoxyuridine labeling indices and the apoptotic indices showed significant differences between the unaltered liver parenchyma, different types of preneoplastic foci, and hepatocellular neoplasms. The immunohistochemical expression of transforming growth factor-alpha increased during the stepwise development from glycogen-storing liver acini to hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatocarcinogenesis in this new animal model is probably due to the hormonal and growth-stimulating effects of insulin secreted by the intraportally transplanted islets of Langerhans in diabetic rats.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bannasch P., Mayer D., Hacker H. J. Hepatocellular glycogenosis and hepatocarcinogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 6;605(2):217–245. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannasch P., Papenburg J., Ross W. Cytomorphologische und morphometrische Studien der Hepatocarcinogenese. I. Reversible und irreversible Veränderungen am cytoplasma der Leberparenchymzellen bei Nitrosomorpholin-vergifteten Ratten. Z Krebsforsch Klin Onkol Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1972;77(2):108–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00304050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. H., Jr, Pour P. M. Pancreatic carcinogenicity of N-nitrosobis(2-oxopropyl)-amine in diabetic and non-diabetic Chinese hamsters. Cancer Lett. 1987 Feb;34(2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(87)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher M. L., Swaffield M. N. Regulation of hepatic regeneration in rats by synergistic action of insulin and glucagon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1157–1160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossel L., Wohlrab F., Blech W., Hahn H. J. Morphological findings in the liver of diabetic rats after intraportal transplantation of neonatal isologous pancreatic islets. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1990;59(2):65–77. doi: 10.1007/BF02899389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Paepe M. E., Keymeulen B., Pipeleers D., Klöppel G. Proliferation and hypertrophy of liver cells surrounding islet grafts in diabetic recipient rats. Hepatology. 1995 Apr;21(4):1144–1153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
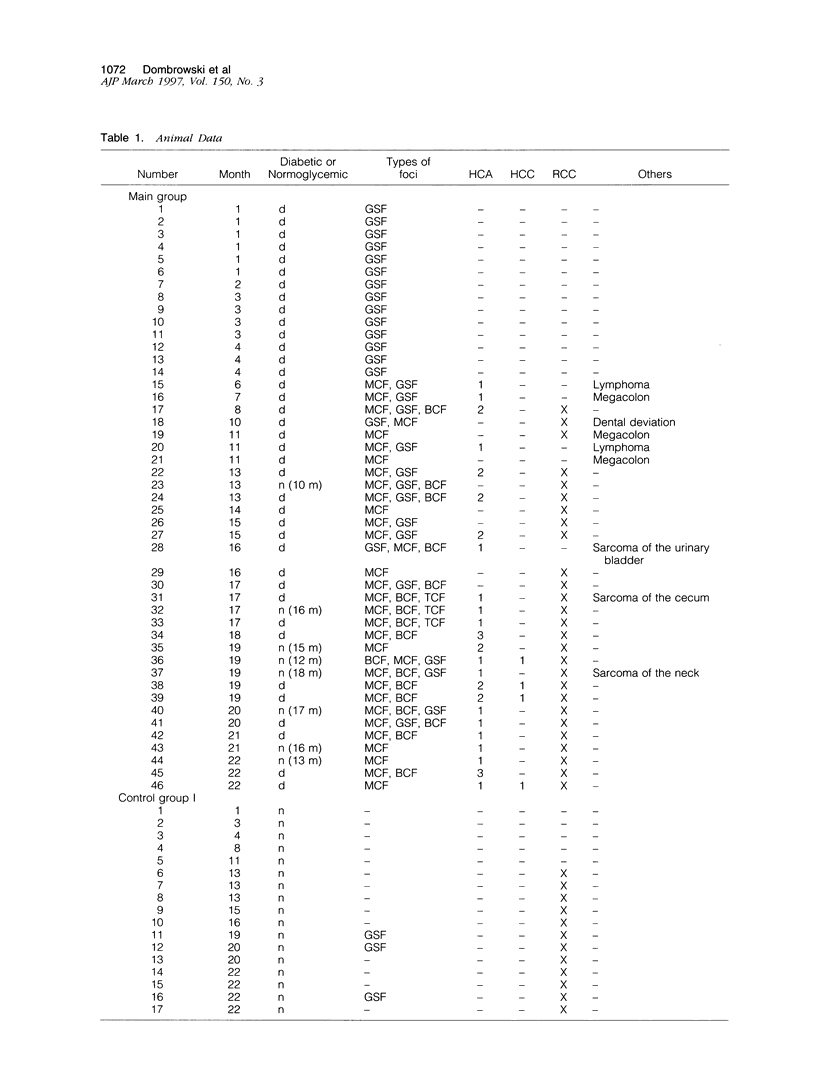
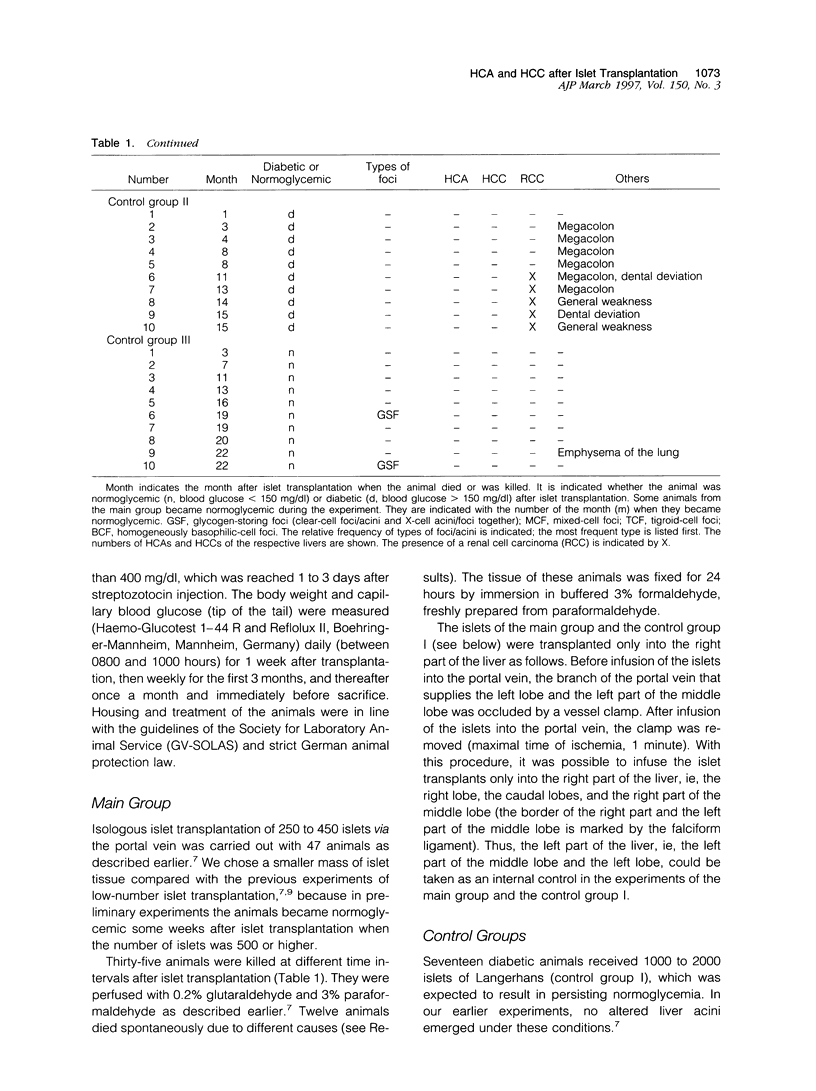
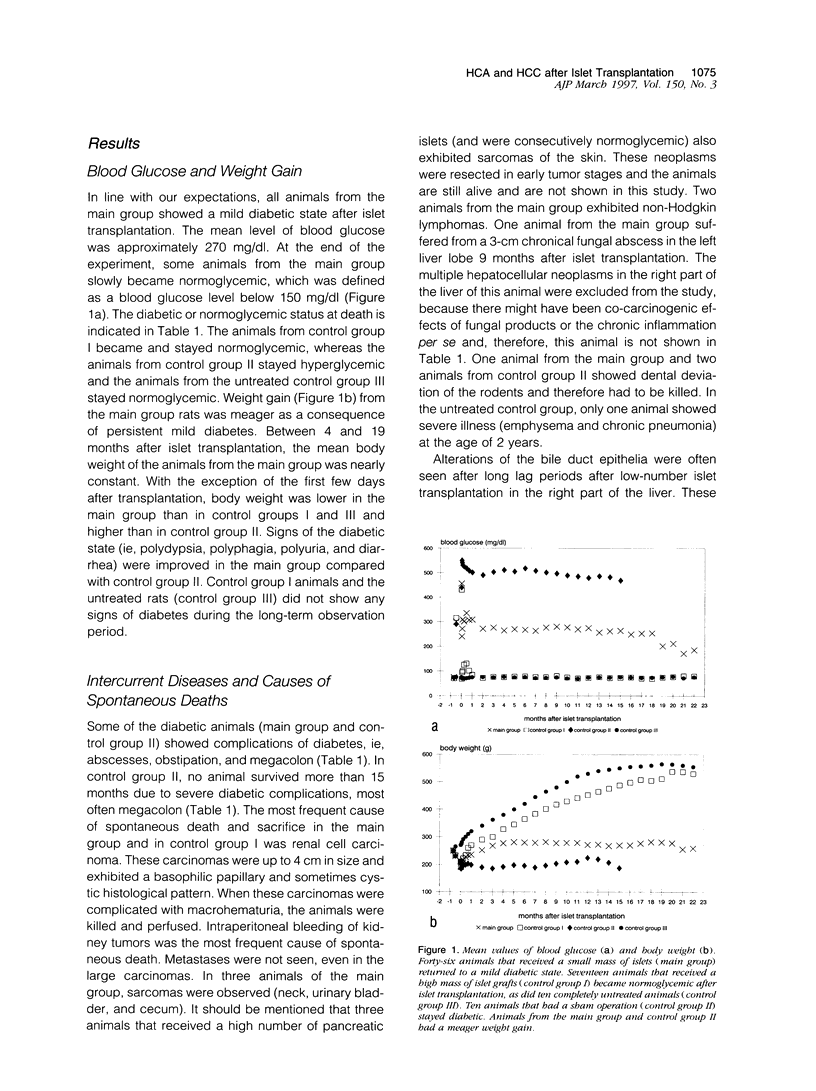
- Dombrowski F., Filsinger E., Bannasch P., Pfeifer U. Altered liver acini induced in diabetic rats by portal vein islet isografts resemble preneoplastic hepatic foci in their enzymic pattern. Am J Pathol. 1996 Apr;148(4):1249–1256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrowski F., Lehringer-Polzin M., Pfeifer U. Hyperproliferative liver acini after intraportal islet transplantation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Lab Invest. 1994 Nov;71(5):688–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragan Y., Teeguarden J., Campbell H., Hsia S., Pitot H. The quantitation of altered hepatic foci during multistage hepatocarcinogenesis in the rat: transforming growth factor alpha expression as a marker for the stage of progression. Cancer Lett. 1995 Jun 29;93(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(95)03789-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge S. R., Tilbury L. F., Goldsworthy T. L., Butterworth B. E. Measurement of chemically induced cell proliferation in rodent liver and kidney: a comparison of 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine and [3H]thymidine administered by injection or osmotic pump. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Dec;11(12):2245–2251. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.12.2245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francavilla A., Starzl T. E., Porter K., Foglieni C. S., Michalopoulos G. K., Carrieri G., Trejo J., Azzarone A., Barone M., Zeng Q. H. Screening for candidate hepatic growth factors by selective portal infusion after canine Eck's fistula. Hepatology. 1991 Oct;14(4 Pt 1):665–670. doi: 10.1016/0270-9139(91)90055-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith R. C., Scharp D. W., Hartman B. K., Ballinger W. F., Lacy P. E. A morphologic study of intrahepatic portal-vein islet isografts. Diabetes. 1977 Mar;26(3):201–214. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.3.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotting J. C., Rosai J., Matas A. J., Frenzel E. M., Payne W. D., Sutherland D. E., Najarian J. S. The fate of intraportally transplanted islets in diabetic rats. A morphologic and immunohistochemical study. Am J Pathol. 1978 Sep;92(3):653–670. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhappan C., Stahle C., Harkins R. N., Fausto N., Smith G. H., Merlino G. T. TGF alpha overexpression in transgenic mice induces liver neoplasia and abnormal development of the mammary gland and pancreas. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1137–1146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90076-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann W. K., Zhang Y., Kaufman D. G. Association between expression of transforming growth factor-alpha and progression of hepatocellular foci to neoplasms. Carcinogenesis. 1992 Aug;13(8):1481–1483. doi: 10.1093/carcin/13.8.1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazumi T., Yoshino G., Fujii S., Baba S. Tumorigenic action of streptozotocin on the pancreas and kidney in male Wistar rats. Cancer Res. 1978 Jul;38(7):2144–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp C. B., Knight M. J., Scharp D. W., Ballinger W. F., Lacy P. E. Effect of transplantation site on the results of pancreatic islet isografts in diabetic rats. Diabetologia. 1973 Dec;9(6):486–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00461694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimek F., Bannasch P. Isoenzyme shift from glucokinase to hexokinase is not an early but a late event in hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1993 Sep;14(9):1857–1861. doi: 10.1093/carcin/14.9.1857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. H., Merlino G., Fausto N. Development of liver tumors in transforming growth factor alpha transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 1;52(19):5162–5170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger C., Mayer D., Hoffmann H., Bocker T., Hobe G., Benner A., Bannasch P. Sequential appearance and ultrastructure of amphophilic cell foci, adenomas, and carcinomas in the liver of male and female rats treated with dehydroepiandrosterone. Toxicol Pathol. 1995 Sep-Oct;23(5):591–605. doi: 10.1177/019262339502300505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orian J. M., Tamakoshi K., Mackay I. R., Brandon M. R. New murine model for hepatocellular carcinoma: transgenic mice expressing metallothionein-ovine growth hormone fusion gene. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Mar 7;82(5):393–398. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.5.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer U. Inhibition by insulin of the formation of autophagic vacuoles in rat liver. A morphometric approach to the kinetics of intracellular degradation by autophagy. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jul;78(1):152–167. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer U. Methods in laboratory investigation. Application of test substances to the surface of rat liver in situ: opposite effects of insulin and isoproterenol on cellular autophagy. Lab Invest. 1984 Mar;50(3):348–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers-Marichal M. A., Pipeleers D. G., Cutler J., Lacy P. E., Kipnis D. M. Metabolic and morphologic studies in intraportal-islet-transplanted rats. Diabetes. 1976 Nov;25(11):1041–1051. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.11.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed G. B., Grisham J. W. Insulin and hydrocortisone effects on viability and glycogen stores of postnatal rat liver organ culture. Lab Invest. 1975 Sep;33(3):298–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Porter K. A., Kashiwagi N. Portal hepatotrophic factors, diabetes mellitus and acute liver atrophy, hypertrophy and regeneration. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1975 Dec;141(6):843–858. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Watanabe K., Porter K. A., Putnam C. W. Effects of insulin, glucagon, and insuling/glucagon infusions on liver morphology and cell division after complete portacaval shunt in dogs. Lancet. 1976 Apr 17;1(7964):821–825. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90477-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi H., Sharp R., Hammermeister C., Goodrow T., Bradley M. O., Fausto N., Merlino G. Molecular and genetic analysis of liver oncogenesis in transforming growth factor alpha transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 1;52(19):5171–5177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toshkov I., Chisari F. V., Bannasch P. Hepatic preneoplasia in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Hepatology. 1994 Nov;20(5):1162–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerban H., Radig S., Kopp-Schneider A., Bannasch P. Cell proliferation and cell death (apoptosis) in hepatic preneoplasia and neoplasia are closely related to phenotypic cellular diversity and instability. Carcinogenesis. 1994 Nov;15(11):2467–2473. doi: 10.1093/carcin/15.11.2467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]