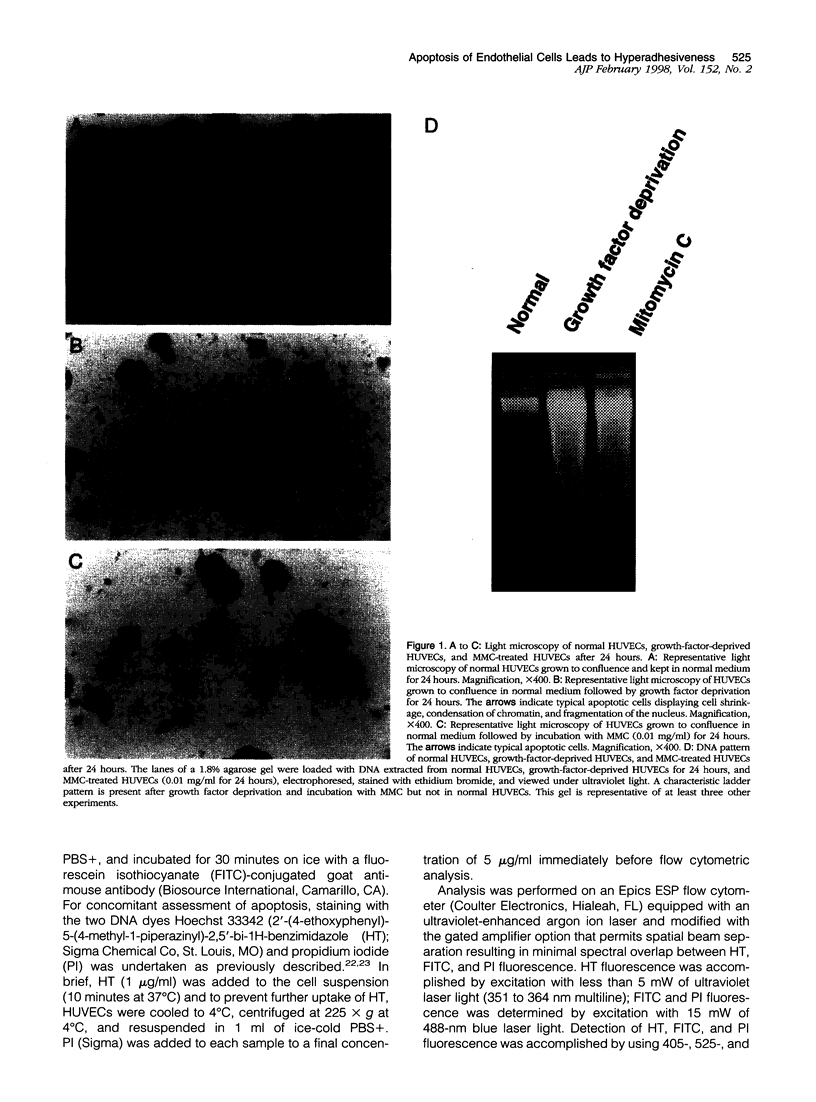
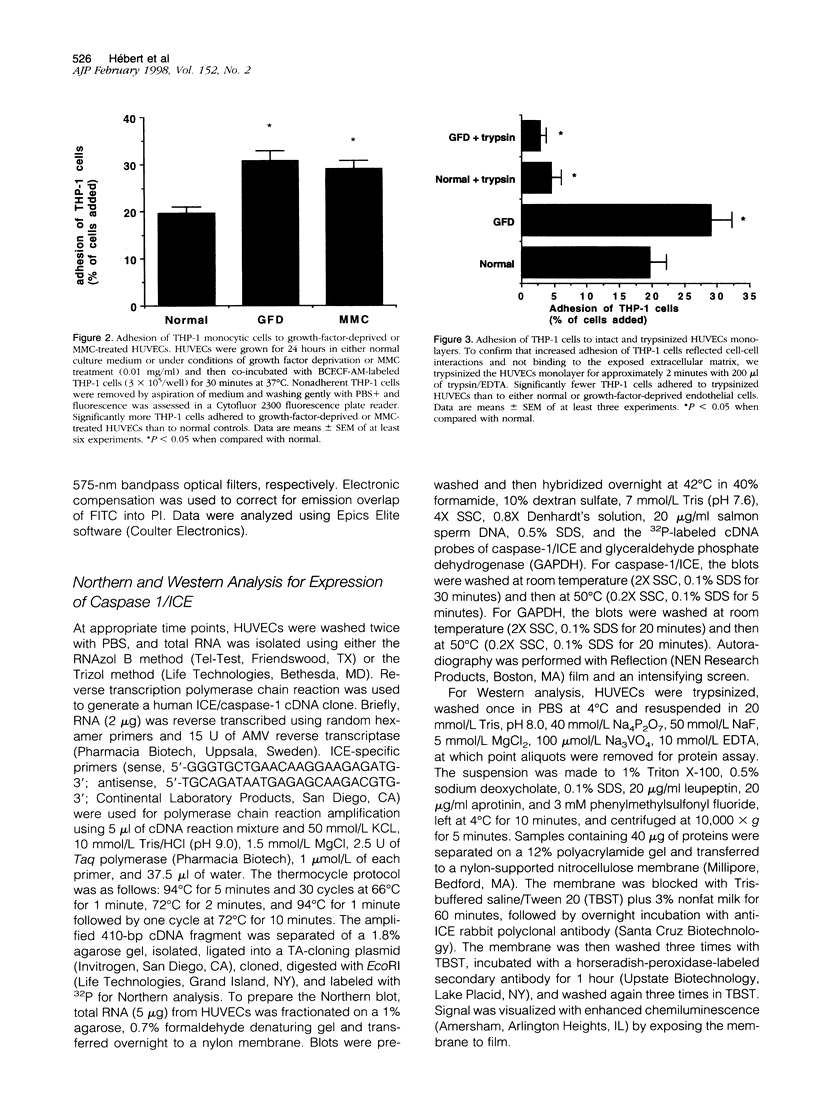
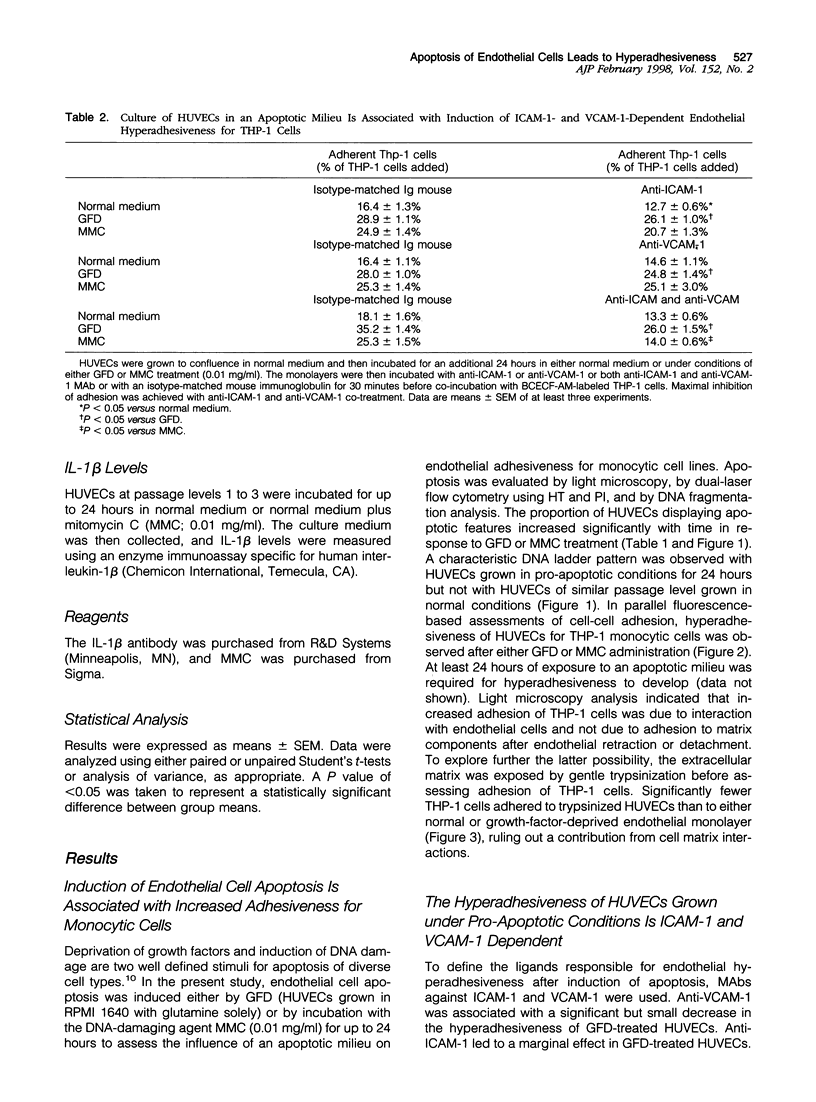
Abstract
Monocytic infiltration of the vessel wall is a hallmark of injury in a variety of vascular diseases. In the present study, we explored the relationship between endothelial apoptosis and hyperadhesiveness for monocytic cells. Apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) was induced by either growth factor deprivation (GFD) for 24 hours or by incubation with mitomycin C (MMC) at 0.01 mg/ml for 24 hours and confirmed by light microscopy and DNA laddering. In parallel assessments of cell-cell adhesion, GFD and MMC induced hyperadhesiveness of HUVECs for the THP-1 monocytic cell line. Hyperadhesiveness developed in association with induction of intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1 on HUVECs and was attenuated by monoclonal antibodies directed against these ligands. Culture medium conditioned by apoptotic HUVECs up-regulated the expression of adhesion molecules on normal HUVECs, suggesting that paracrine factors in the apoptotic milieu led to induction of adhesion molecules. Interleukin (IL)-1beta was implicated as a putative mediator in this setting because 1) exogenous IL-1beta up-regulates ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 with kinetics similar to those noted during endothelial cell apoptosis, 2) endothelial apoptosis was associated with increased expression of IL-1beta converting enzyme, and 3) the adhesion-promoting actions of GFD and MMC were attenuated by an anti-IL-1beta antibody.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abello P. A., Fidler S. A., Bulkley G. B., Buchman T. G. Antioxidants modulate induction of programmed endothelial cell death (apoptosis) by endotoxin. Arch Surg. 1994 Feb;129(2):134–141. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1994.01420260030003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alnemri E. S., Livingston D. J., Nicholson D. W., Salvesen G., Thornberry N. A., Wong W. W., Yuan J. Human ICE/CED-3 protease nomenclature. Cell. 1996 Oct 18;87(2):171–171. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner-Parzer S. M., Wagner L., Pettermann M., Grillari J., Gessl A., Waldhäusl W. High-glucose--triggered apoptosis in cultured endothelial cells. Diabetes. 1995 Nov;44(11):1323–1327. doi: 10.2337/diab.44.11.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady H. R. Leukocyte adhesion molecules and kidney diseases. Kidney Int. 1994 May;45(5):1285–1300. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady H. R., Spertini O., Jimenez W., Brenner B. M., Marsden P. A., Tedder T. F. Neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes bind to cytokine-activated kidney glomerular endothelial cells through L-selectin (LAM-1) in vitro. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2437–2444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casciola-Rosen L., Rosen A., Petri M., Schlissel M. Surface blebs on apoptotic cells are sites of enhanced procoagulant activity: implications for coagulation events and antigenic spread in systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Feb 20;93(4):1624–1629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.4.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissner G., Kohlhuber F., Grell M., Ueffing M., Scheurich P., Hieke A., Multhoff G., Bornkamm G. W., Holler E. Critical involvement of transmembrane tumor necrosis factor-alpha in endothelial programmed cell death mediated by ionizing radiation and bacterial endotoxin. Blood. 1995 Dec 1;86(11):4184–4193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fadok V. A., Savill J. S., Haslett C., Bratton D. L., Doherty D. E., Campbell P. A., Henson P. M. Different populations of macrophages use either the vitronectin receptor or the phosphatidylserine receptor to recognize and remove apoptotic cells. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 15;149(12):4029–4035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fadok V. A., Voelker D. R., Campbell P. A., Cohen J. J., Bratton D. L., Henson P. M. Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the surface of apoptotic lymphocytes triggers specific recognition and removal by macrophages. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2207–2216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser A., Evan G. A license to kill. Cell. 1996 Jun 14;85(6):781–784. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr Vascular endothelium: an integrator of pathophysiologic stimuli in atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 1995 Feb 23;75(6):67B–70B. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(95)80016-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb R. A., Burleson K. O., Kloner R. A., Babior B. M., Engler R. L. Reperfusion injury induces apoptosis in rabbit cardiomyocytes. J Clin Invest. 1994 Oct;94(4):1621–1628. doi: 10.1172/JCI117504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y., Kuida K., Tsutsui H., Ku G., Hsiao K., Fleming M. A., Hayashi N., Higashino K., Okamura H., Nakanishi K. Activation of interferon-gamma inducing factor mediated by interleukin-1beta converting enzyme. Science. 1997 Jan 10;275(5297):206–209. doi: 10.1126/science.275.5297.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. ICE family proteases: mediators of all apoptotic cell death? Immunity. 1996 Mar;4(3):195–201. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80428-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert M. J., Takano T., Holthöfer H., Brady H. R. Sequential morphologic events during apoptosis of human neutrophils. Modulation by lipoxygenase-derived eicosanoids. J Immunol. 1996 Oct 1;157(7):3105–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Wyllie A. H., Currie A. R. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 1972 Aug;26(4):239–257. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo S., Kondo Y., Yin D., Barnett G. H., Kaakaji R., Peterson J. W., Morimura T., Kubo H., Takeuchi J., Barna B. P. Involvement of interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme in apoptosis of bFGF-deprived murine aortic endothelial cells. FASEB J. 1996 Aug;10(10):1192–1197. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.10.10.8751721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuida K., Lippke J. A., Ku G., Harding M. W., Livingston D. J., Su M. S., Flavell R. A. Altered cytokine export and apoptosis in mice deficient in interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme. Science. 1995 Mar 31;267(5206):2000–2003. doi: 10.1126/science.7535475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li P., Allen H., Banerjee S., Franklin S., Herzog L., Johnston C., McDowell J., Paskind M., Rodman L., Salfeld J. Mice deficient in IL-1 beta-converting enzyme are defective in production of mature IL-1 beta and resistant to endotoxic shock. Cell. 1995 Feb 10;80(3):401–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90490-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lizard G., Deckert V., Dubrez L., Moisant M., Gambert P., Lagrost L. Induction of apoptosis in endothelial cells treated with cholesterol oxides. Am J Pathol. 1996 May;148(5):1625–1638. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loffing J., Loffing-Cueni D., Hegyi I., Kaplan M. R., Hebert S. C., Le Hir M., Kaissling B. Thiazide treatment of rats provokes apoptosis in distal tubule cells. Kidney Int. 1996 Oct;50(4):1180–1190. doi: 10.1038/ki.1996.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooney A., Jobson T., Bacon R., Kitamura M., Savill J. Cytokines promote glomerular mesangial cell survival in vitro by stimulus-dependent inhibition of apoptosis. J Immunol. 1997 Oct 15;159(8):3949–3960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polunovsky V. A., Wendt C. H., Ingbar D. H., Peterson M. S., Bitterman P. B. Induction of endothelial cell apoptosis by TNF alpha: modulation by inhibitors of protein synthesis. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Oct;214(2):584–594. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):801–809. doi: 10.1038/362801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savill J. Apoptosis and the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1994 Jul;5(1):12–21. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V5112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savill J., Fadok V., Henson P., Haslett C. Phagocyte recognition of cells undergoing apoptosis. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H. Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1445–1449. doi: 10.1126/science.7878463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. M., Snowden R. T., Skilleter D. N., Dinsdale D., Ormerod M. G., Cohen G. M. A flow-cytometric method for the separation and quantitation of normal and apoptotic thymocytes. Anal Biochem. 1992 Aug 1;204(2):351–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90251-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata S., Matsubara M., Allen P. G., Janmey P. A., Serhan C. N., Brady H. R. Remodeling of neutrophil phospholipids with 15(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid inhibits leukotriene B4-induced neutrophil migration across endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1994 Feb;93(2):499–508. doi: 10.1172/JCI116999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1456–1462. doi: 10.1126/science.7878464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton S. C., Mueller S. N., Levine E. M. Human endothelial cells: use of heparin in cloning and long-term serial cultivation. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):623–625. doi: 10.1126/science.6635659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Haecker G., Strasser A. An evolutionary perspective on apoptosis. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):777–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Strasser A. The molecular biology of apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Mar 19;93(6):2239–2244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.6.2239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):555–556. doi: 10.1038/284555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zychlinsky A., Fitting C., Cavaillon J. M., Sansonetti P. J. Interleukin 1 is released by murine macrophages during apoptosis induced by Shigella flexneri. J Clin Invest. 1994 Sep;94(3):1328–1332. doi: 10.1172/JCI117452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]