Abstract
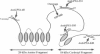
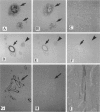
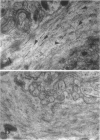
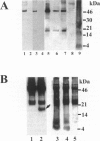
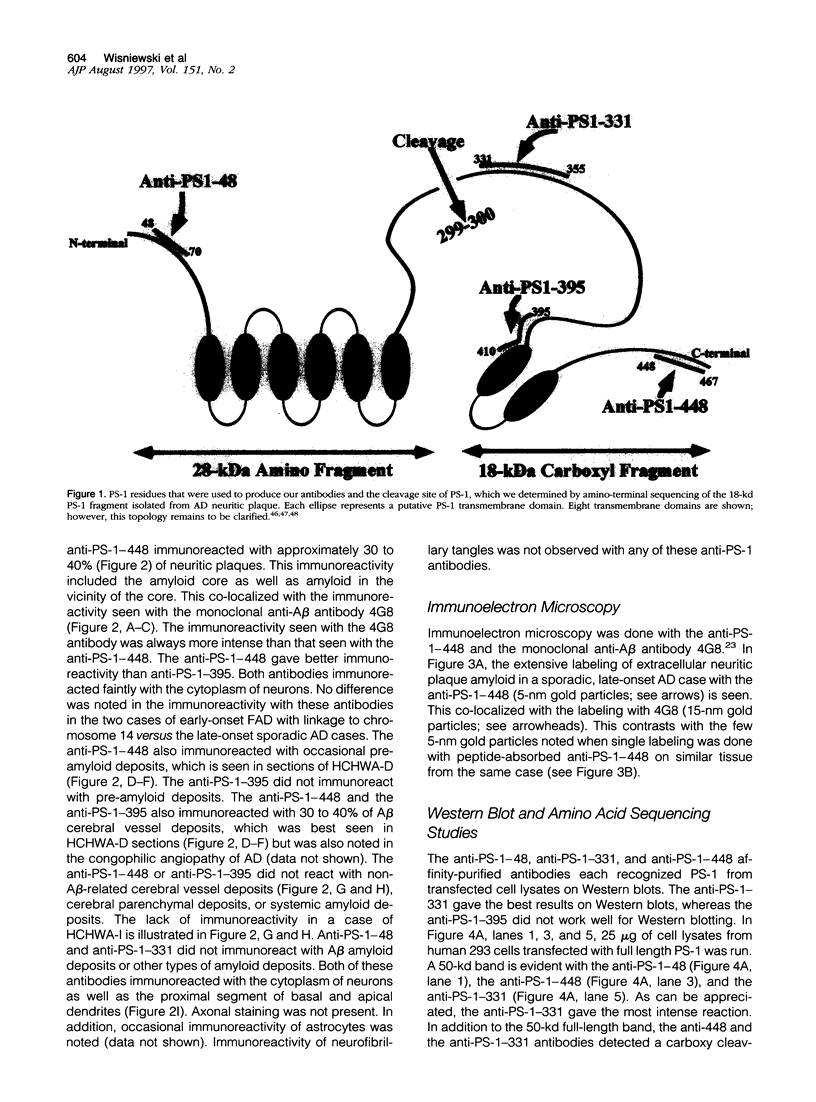
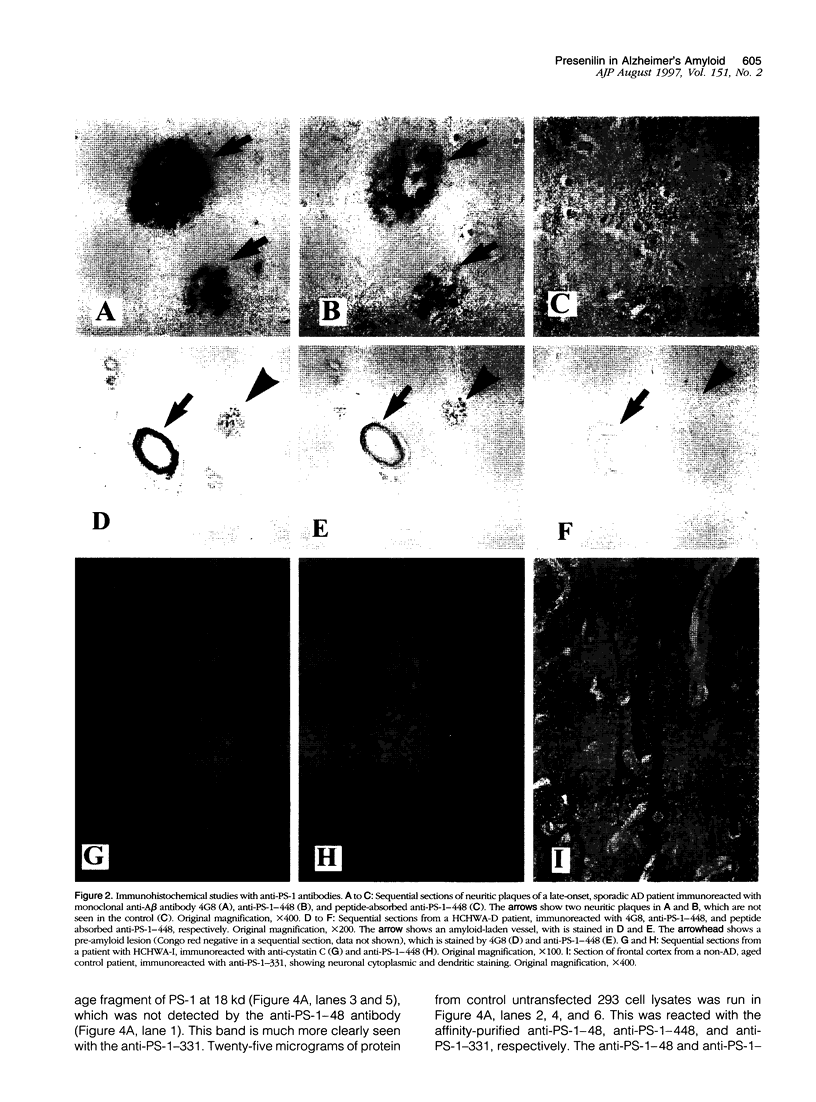
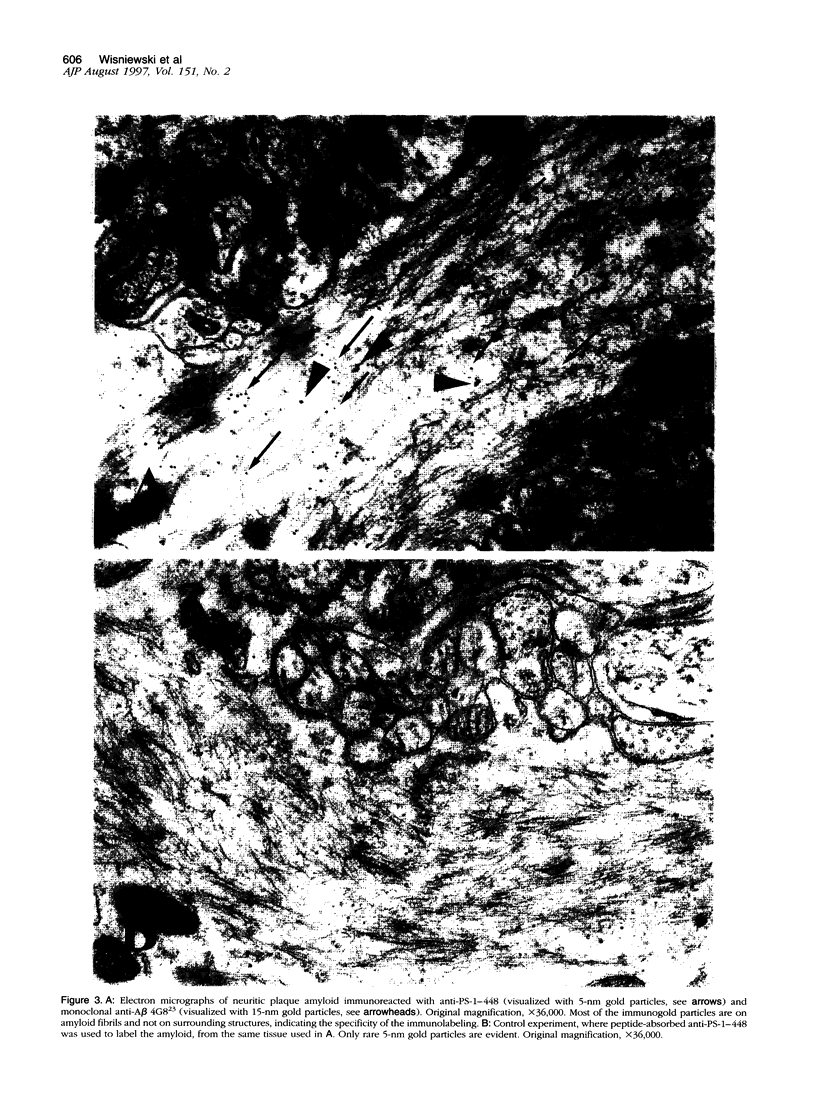
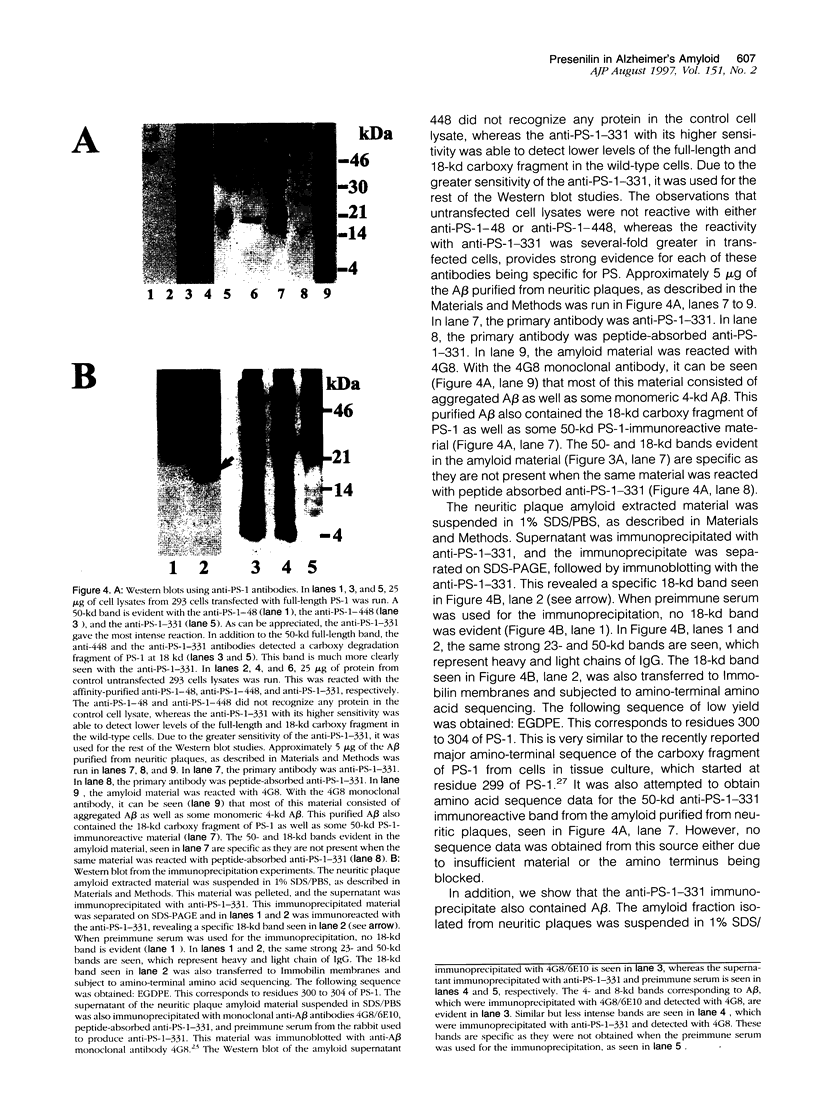
Mutations in presenilin (PS)-1 and -2, located on chromosome 14 and 1 respectively, are the major association with early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD). FAD has also been linked to mutations in the amyloid beta precursor protein (beta PP), and the presence of the apolipoprotein E4 allele is a risk factor for late-onset AD. The role of PS in FAD and in sporadic AD is unclear. We previously reported the presence of a PS-1 carboxyl-terminal epitope in neuritic plaques (Wisniewski T, Palha JA, Ghiso J, Frangione B: S182 protein in Alzheimer's disease neuritic plaques. Lancet 1995, 346:1366). In the present study, we examined a number of biochemically different cerebral and systemic amyloidoses, finding the PS-1 carboxy epitope only in association with amyloid beta (A beta) lesions. We confirm the presence of this epitope ultrastructurally in neuritic plaques. In addition, biochemical and amino acid sequence data are presented for an association of the 18-kd carboxy fragment of PS-1 with neuritic plaques with a start at residue 300. Three of the proteins with linkage to AD have now been found as components of neuritic plaques. It remains to be determined whether all of these proteins are involved in the same or different pathological pathway(s) and which of these proteins is the most important for the common, late-onset form of AD.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham C. R., Selkoe D. J., Potter H. Immunochemical identification of the serine protease inhibitor alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in the brain amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):487–501. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90462-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borchelt D. R., Thinakaran G., Eckman C. B., Lee M. K., Davenport F., Ratovitsky T., Prada C. M., Kim G., Seekins S., Yager D. Familial Alzheimer's disease-linked presenilin 1 variants elevate Abeta1-42/1-40 ratio in vitro and in vivo. Neuron. 1996 Nov;17(5):1005–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouras C., Giannakopoulos P., Schioi J., Tezapsidis N., Robakis N. K. Presenilin-1 polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1996 Apr 27;347(9009):1185–1186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño E. M., Prelli F., Soto C., Beavis R., Matsubara E., Shoji M., Frangione B. The length of amyloid-beta in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis, Dutch type. Implications for the role of amyloid-beta 1-42 in Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Chem. 1996 Dec 13;271(50):32185–32191. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.50.32185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron M., Westaway D., Xia W., Carlson G., Diehl T., Levesque G., Johnson-Wood K., Lee M., Seubert P., Davis A. Mutant presenilins of Alzheimer's disease increase production of 42-residue amyloid beta-protein in both transfected cells and transgenic mice. Nat Med. 1997 Jan;3(1):67–72. doi: 10.1038/nm0197-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coria F., Castaño E., Prelli F., Larrondo-Lillo M., van Duinen S., Shelanski M. L., Frangione B. Isolation and characterization of amyloid P component from Alzheimer's disease and other types of cerebral amyloidosis. Lab Invest. 1988 Apr;58(4):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cribbs D. H., Chen L. S., Bende S. M., LaFerla F. M. Widespread neuronal expression of the presenilin-1 early-onset Alzheimer's disease gene in the murine brain. Am J Pathol. 1996 Jun;148(6):1797–1806. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doan A., Thinakaran G., Borchelt D. R., Slunt H. H., Ratovitsky T., Podlisny M., Selkoe D. J., Seeger M., Gandy S. E., Price D. L. Protein topology of presenilin 1. Neuron. 1996 Nov;17(5):1023–1030. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff K., Eckman C., Zehr C., Yu X., Prada C. M., Perez-tur J., Hutton M., Buee L., Harigaya Y., Yager D. Increased amyloid-beta42(43) in brains of mice expressing mutant presenilin 1. Nature. 1996 Oct 24;383(6602):710–713. doi: 10.1038/383710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eikelenboom P., Stam F. C. Immunoglobulins and complement factors in senile plaques. An immunoperoxidase study. Acta Neuropathol. 1982;57(2-3):239–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00685397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder G. A., Tezapsidis N., Carter J., Shioi J., Bouras C., Li H. C., Johnston J. M., Efthimiopoulos S., Friedrich V. L., Jr, Robakis N. K. Identification and neuron specific expression of the S182/presenilin I protein in human and rodent brains. J Neurosci Res. 1996 Aug 1;45(3):308–320. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19960801)45:3<308::AID-JNR13>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiso J., Jensson O., Frangione B. Amyloid fibrils in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis of Icelandic type is a variant of gamma-trace basic protein (cystatin C). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2974–2978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiso J., Wisniewski T., Frangione B. Unifying features of systemic and cerebral amyloidosis. Mol Neurobiol. 1994 Feb;8(1):49–64. doi: 10.1007/BF02778007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannakopoulos P., Bouras C., Kövari E., Shioi J., Tezapsidis N., Hof P. R., Robakis N. K. Presenilin-1-immunoreactive neurons are preserved in late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1997 Feb;150(2):429–436. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A., Chartier-Harlin M. C., Mullan M., Brown J., Crawford F., Fidani L., Giuffra L., Haynes A., Irving N., James L. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):704–706. doi: 10.1038/349704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltia M., Ghiso J., Wisniewski T., Kiuru S., Miller D., Frangione B. Gelsolin variant and beta-amyloid co-occur in a case of Alzheimer's with Lewy bodies. Neurobiol Aging. 1991 Jul-Aug;12(4):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(91)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs D. M., Fausett H. J., Page K. J., Kim T. W., Moir R. D., Merriam D. E., Hollister R. D., Hallmark O. G., Mancini R., Felsenstein K. M. Alzheimer-associated presenilins 1 and 2: neuronal expression in brain and localization to intracellular membranes in mammalian cells. Nat Med. 1996 Feb;2(2):224–229. doi: 10.1038/nm0296-224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalowski M., Golabek A., Lemere C. A., Selkoe D. J., Wisniewski H. M., Beavis R. C., Frangione B., Wisniewski T. The "nonamyloidogenic" p3 fragment (amyloid beta17-42) is a major constituent of Down's syndrome cerebellar preamyloid. J Biol Chem. 1996 Dec 27;271(52):33623–33631. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.52.33623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann S., Chiesa R., Harris D. A. Evidence for a six-transmembrane domain structure of presenilin 1. J Biol Chem. 1997 May 2;272(18):12047–12051. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.18.12047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemere C. A., Lopera F., Kosik K. S., Lendon C. L., Ossa J., Saido T. C., Yamaguchi H., Ruiz A., Martinez A., Madrigal L. The E280A presenilin 1 Alzheimer mutation produces increased A beta 42 deposition and severe cerebellar pathology. Nat Med. 1996 Oct;2(10):1146–1150. doi: 10.1038/nm1096-1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Lahad E., Wasco W., Poorkaj P., Romano D. M., Oshima J., Pettingell W. H., Yu C. E., Jondro P. D., Schmidt S. D., Wang K. Candidate gene for the chromosome 1 familial Alzheimer's disease locus. Science. 1995 Aug 18;269(5226):973–977. doi: 10.1126/science.7638622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Lahad E., Wijsman E. M., Nemens E., Anderson L., Goddard K. A., Weber J. L., Bird T. D., Schellenberg G. D. A familial Alzheimer's disease locus on chromosome 1. Science. 1995 Aug 18;269(5226):970–973. doi: 10.1126/science.7638621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Carman M. D., Fernandez-Madrid I. J., Power M. D., Lieberburg I., van Duinen S. G., Bots G. T., Luyendijk W., Frangione B. Mutation of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid gene in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage, Dutch type. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1124–1126. doi: 10.1126/science.2111584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Greenwald I. Membrane topology of the C. elegans SEL-12 presenilin. Neuron. 1996 Nov;17(5):1015–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80231-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maury C. P., Nurmiaho-Lassila E. L., Liljeström M. Alzheimer's disease-associated presenilins 1 and 2: accelerated amyloid fibril formation of mutant 410 Cys-->Tyr and 141 Asn-->Ile peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997 Jun 9;235(1):249–252. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1997.6336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercken M., Takahashi H., Honda T., Sato K., Murayama M., Nakazato Y., Noguchi K., Imahori K., Takashima A. Characterization of human presenilin 1 using N-terminal specific monoclonal antibodies: Evidence that Alzheimer mutations affect proteolytic processing. FEBS Lett. 1996 Jul 8;389(3):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00608-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. M., Jr, Forno L. S., Ellis W. G., Nochlin D., Levy-Lahad E., Poorkaj P., Bird T. D., Jiang Z., Cordell B. Antibodies to presenilin proteins detect neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1996 Dec;149(6):1839–1846. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Näslund J., Thyberg J., Tjernberg L. O., Wernstedt C., Karlström A. R., Bogdanovic N., Gandy S. E., Lannfelt L., Terenius L., Nordstedt C. Characterization of stable complexes involving apolipoprotein E and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer's disease brain. Neuron. 1995 Jul;15(1):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phend K. D., Weinberg R. J., Rustioni A. Techniques to optimize post-embedding single and double staining for amino acid neurotransmitters. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Jul;40(7):1011–1020. doi: 10.1177/40.7.1376741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podlisny M. B., Citron M., Amarante P., Sherrington R., Xia W., Zhang J., Diehl T., Levesque G., Fraser P., Haass C. Presenilin proteins undergo heterogeneous endoproteolysis between Thr291 and Ala299 and occur as stable N- and C-terminal fragments in normal and Alzheimer brain tissue. Neurobiol Dis. 1997;3(4):325–337. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.1997.0129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogaev E. I., Sherrington R., Rogaeva E. A., Levesque G., Ikeda M., Liang Y., Chi H., Lin C., Holman K., Tsuda T. Familial Alzheimer's disease in kindreds with missense mutations in a gene on chromosome 1 related to the Alzheimer's disease type 3 gene. Nature. 1995 Aug 31;376(6543):775–778. doi: 10.1038/376775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuner D., Eckman C., Jensen M., Song X., Citron M., Suzuki N., Bird T. D., Hardy J., Hutton M., Kukull W. Secreted amyloid beta-protein similar to that in the senile plaques of Alzheimer's disease is increased in vivo by the presenilin 1 and 2 and APP mutations linked to familial Alzheimer's disease. Nat Med. 1996 Aug;2(8):864–870. doi: 10.1038/nm0896-864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrington R., Rogaev E. I., Liang Y., Rogaeva E. A., Levesque G., Ikeda M., Chi H., Lin C., Li G., Holman K. Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1995 Jun 29;375(6534):754–760. doi: 10.1038/375754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow A. D., Willmer J., Kisilevsky R. Sulfated glycosaminoglycans: a common constituent of all amyloids? Lab Invest. 1987 Jan;56(1):120–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini F., Giaccone G., Frangione B., Bugiani O. Preamyloid deposits in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease and nondemented individuals. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Nov 11;93(2-3):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Kovacs D. M., Kim T. W., Moir R. D., Guenette S. Y., Wasco W. The gene defects responsible for familial Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 1996;3(3):159–168. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.1996.0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thinakaran G., Borchelt D. R., Lee M. K., Slunt H. H., Spitzer L., Kim G., Ratovitsky T., Davenport F., Nordstedt C., Seeger M. Endoproteolysis of presenilin 1 and accumulation of processed derivatives in vivo. Neuron. 1996 Jul;17(1):181–190. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers W. F., Tagliavini F., Haan J., Frangione B. Parenchymal preamyloid and amyloid deposits in the brains of patients with hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis--Dutch type. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Oct 16;118(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90632-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchihara T., el Hachimi H. K., Duyckaerts C., Foncin J. F., Fraser P. E., Levesque L., St George-Hyslop P. H., Hauw J. J. Widespread immunoreactivity of presenilin in neurons of normal and Alzheimer's disease brains: double-labeling immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol. 1996 Oct;92(4):325–330. doi: 10.1007/s004010050526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal R., Garzuly F., Budka H., Lalowski M., Linke R. P., Brittig F., Frangione B., Wisniewski T. Meningocerebrovascular amyloidosis associated with a novel transthyretin mis-sense mutation at codon 18 (TTRD 18G) Am J Pathol. 1996 Feb;148(2):361–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber L. L., Leissring M. A., Yang A. J., Glabe C. G., Cribbs D. H., LaFerla F. M. Presenilin-1 immunoreactivity is localized intracellularly in Alzheimer's disease brain, but not detected in amyloid plaques. Exp Neurol. 1997 Jan;143(1):37–44. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1996.6348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Frangione B. Molecular biology of brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1996;56(1):267–279. doi: 10.55782/ane-1996-1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Lalowski M., Baumann M., Rauvala H., Raulo E., Nolo R., Frangione B. HB-GAM is a cytokine present in Alzheimer's and Down's syndrome lesions. Neuroreport. 1996 Jan 31;7(2):667–671. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199601310-00068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Lalowski M., Bobik M., Russell M., Strosznajder J., Frangione B. Amyloid beta 1-42 deposits do not lead to Alzheimer's neuritic plaques in aged dogs. Biochem J. 1996 Jan 15;313(Pt 2):575–580. doi: 10.1042/bj3130575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Lalowski M., Golabek A., Vogel T., Frangione B. Is Alzheimer's disease an apolipoprotein E amyloidosis? Lancet. 1995 Apr 15;345(8955):956–958. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)90701-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Palha J. A., Ghiso J., Frangione B. S182 protein in Alzheimer's disease neuritic plaques. Lancet. 1995 Nov 18;346(8986):1366–1366. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)92379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. C., Zheng H., Chen H., Becher M. W., Sirinathsinghji D. J., Trumbauer M. E., Chen H. Y., Price D. L., Van der Ploeg L. H., Sisodia S. S. Presenilin 1 is required for Notch1 and DII1 expression in the paraxial mesoderm. Nature. 1997 May 15;387(6630):288–292. doi: 10.1038/387288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]