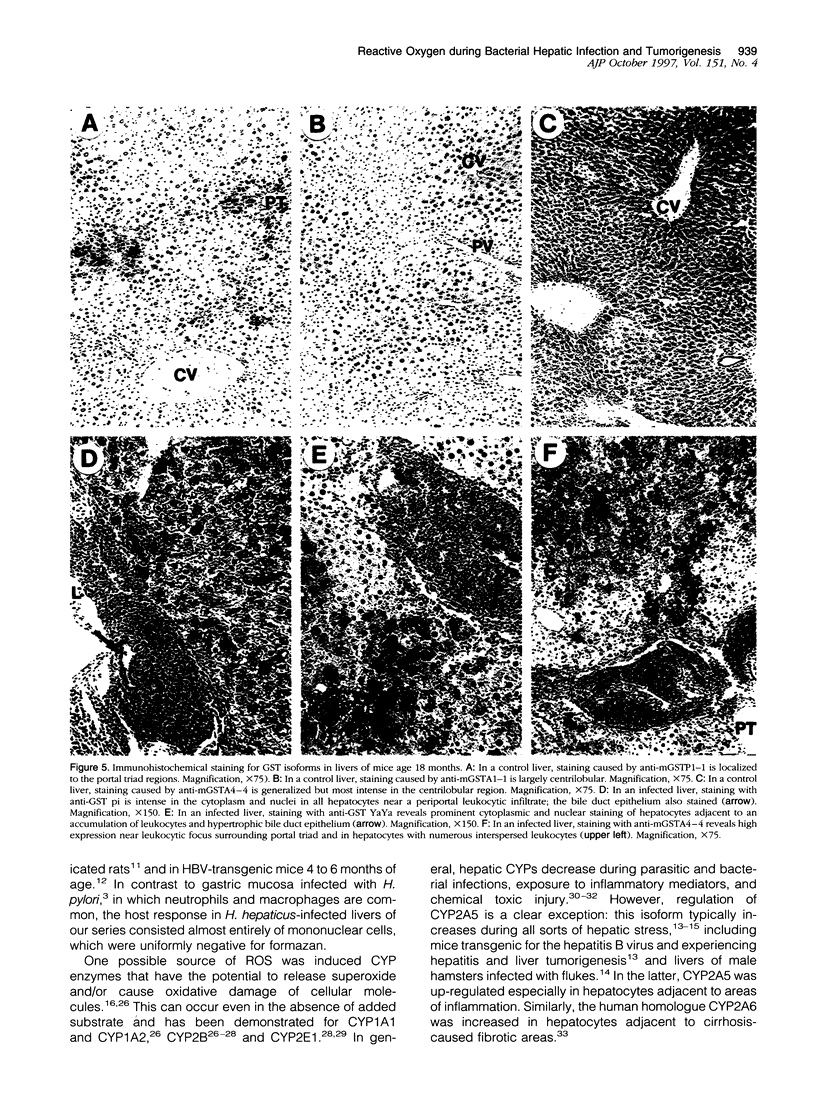
Abstract
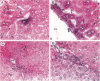
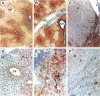
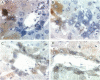
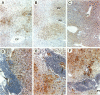
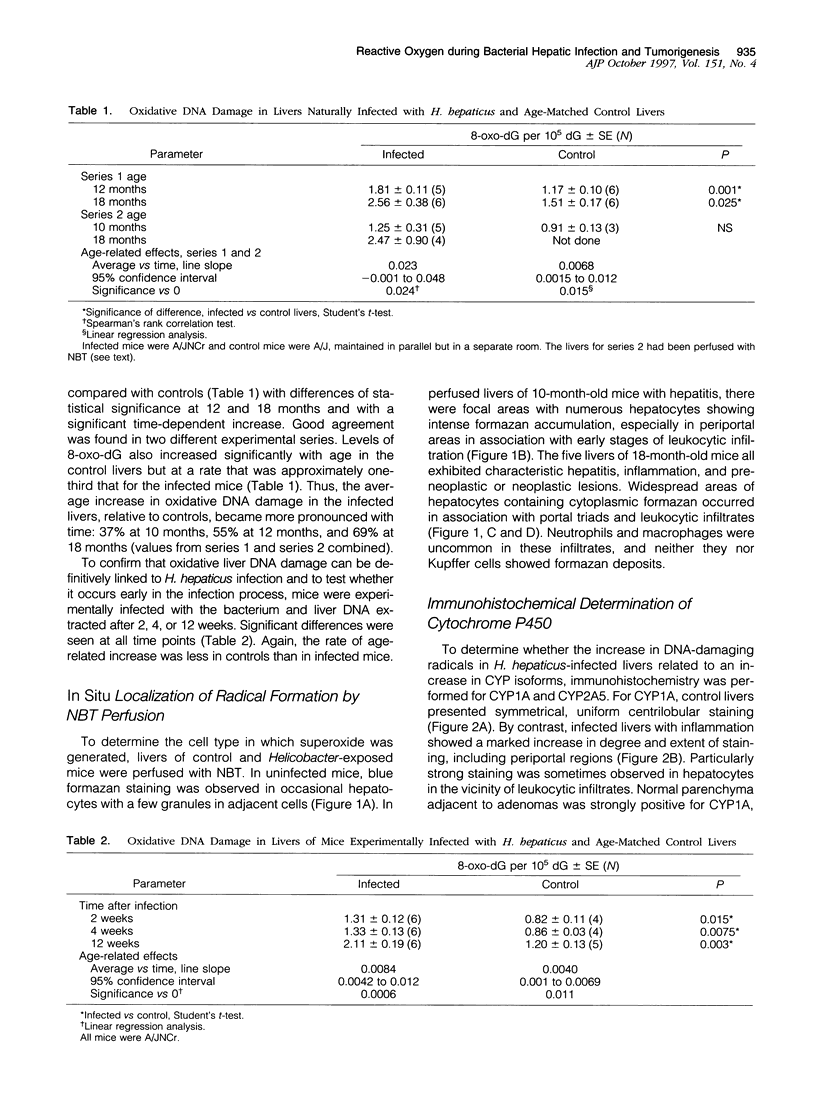
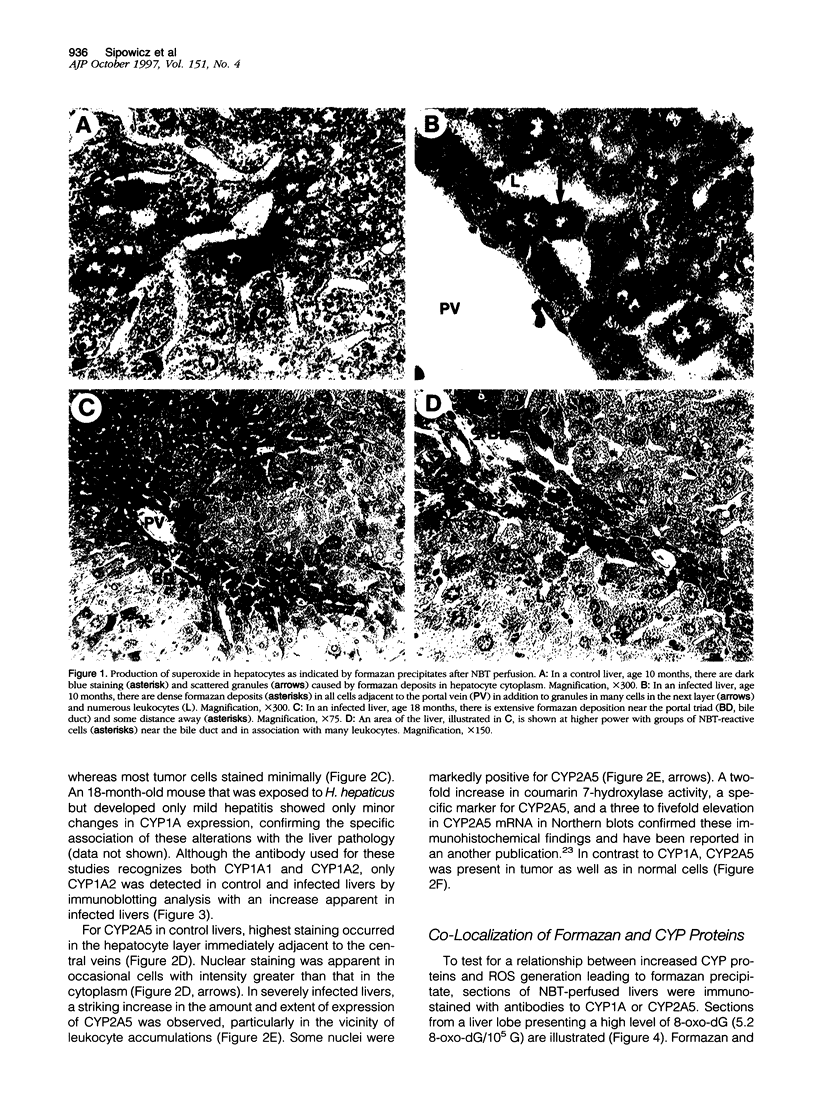
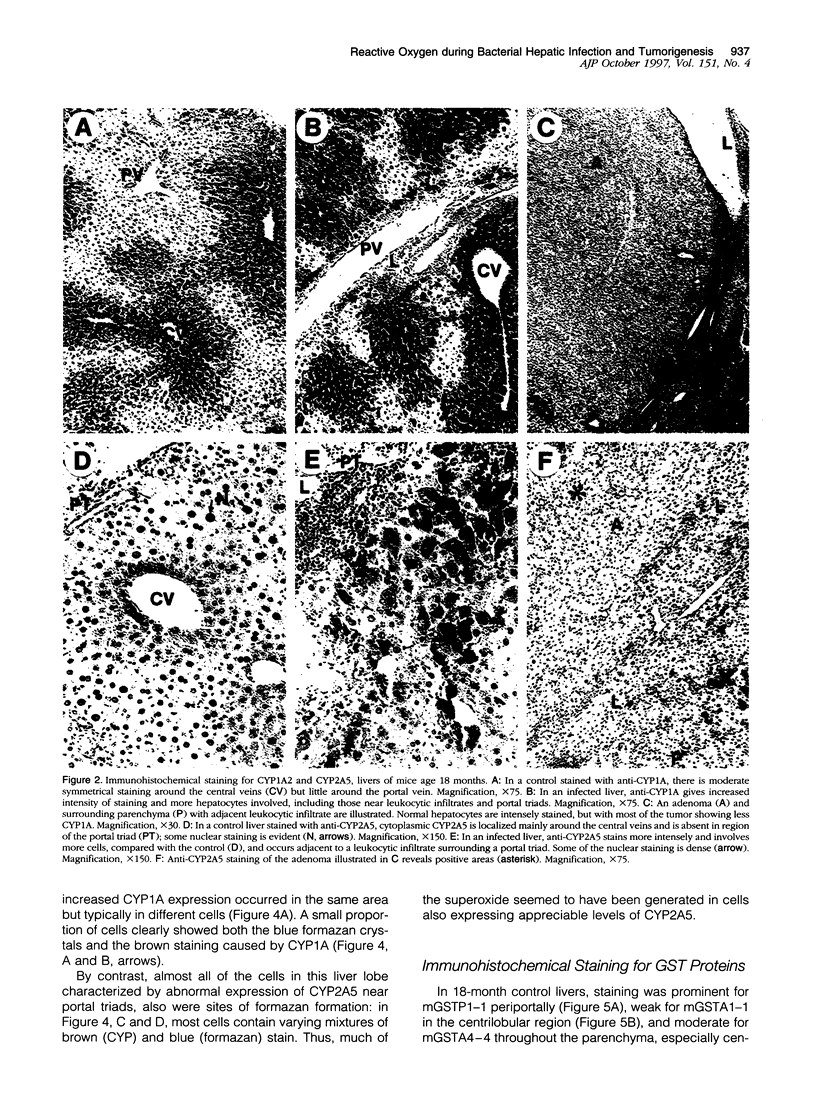
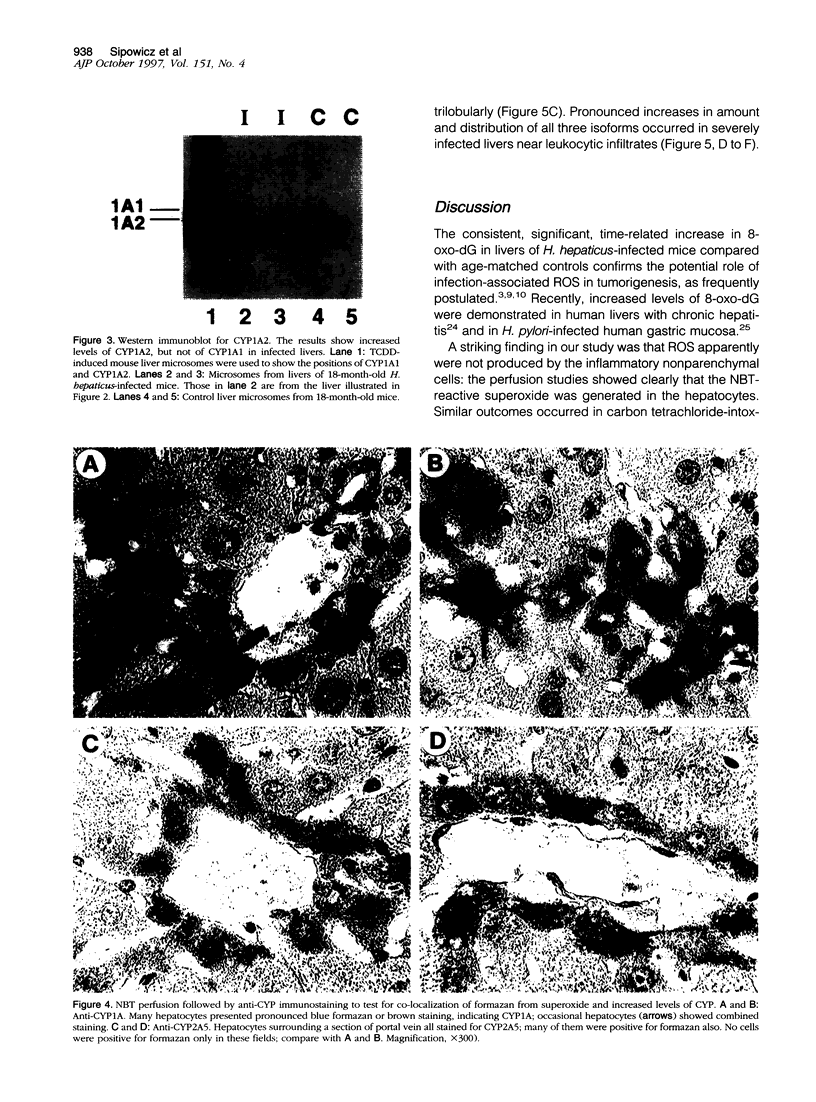
A recently discovered bacterium, Helicobacter hepaticus, infects the intrahepatic bile canaliculi of mice, causing a severe chronic hepatitis culminating in liver cancer. Thus, it affords an animal model for study of bacteria-associated tumorigenesis including H. pylori-related gastric cancer. Reactive oxygen species are often postulated to contribute to this process. We now report that hepatitis of male mice infected with H. hepaticus show significant increases in the oxidatively damaged DNA deoxynucleoside 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine, with the degree of damage increasing with progression of the disease. Perfusion of infected livers with nitro blue tetrazolium revealed that superoxide was produced in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes, especially in association with plasmacytic infiltrates near portal triads. Contrary to expectations, Kupffer cells, macrophages, and neutrophils were rarely involved. However, levels of cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms 1A2 and 2A5 in hepatocytes appeared to be greatly increased, as indicated by the number of cells positive in immunohistochemistry and the intensity of staining in many cells, concomitant with severe hepatitis. The CYP2A5 immunohistochemical staining co-localized with formazan deposits resulting from nitro blue tetrazolium reduction and occurred in nuclei as well as cytoplasm. These findings suggest that CYP2A5 contributes to the superoxide production and 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine formation, although reactive oxygen species from an unknown source in the hepatocytes leading to CYP2A5 induction or coincidental occurrence of these events are also possibilities. Three glutathione S-transferase isoforms, mGSTP1-1 (pi), mGSTA1-1 (YaYa), and mGSTA4-4, also showed striking increases evidencing major oxidative stress in these livers.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Razzak Z., Loyer P., Fautrel A., Gautier J. C., Corcos L., Turlin B., Beaune P., Guillouzo A. Cytokines down-regulate expression of major cytochrome P-450 enzymes in adult human hepatocytes in primary culture. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;44(4):707–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi S., Zeisig M., Möller L. Improvements in the analytical method for 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine in nuclear DNA. Carcinogenesis. 1995 Feb;16(2):253–258. doi: 10.1093/carcin/16.2.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baik S. C., Youn H. S., Chung M. H., Lee W. K., Cho M. J., Ko G. H., Park C. K., Kasai H., Rhee K. H. Increased oxidative DNA damage in Helicobacter pylori-infected human gastric mucosa. Cancer Res. 1996 Mar 15;56(6):1279–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy S. C., Naderi S. Contribution of hepatic cytochrome P450 systems to the generation of reactive oxygen species. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Jul 5;48(1):155–159. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E. Nuclear activation of polycyclic hydrocarbons. Drug Metab Rev. 1979;10(2):209–223. doi: 10.3109/03602537908997469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camus-Randon A. M., Raffalli F., Béréziat J. C., McGregor D., Konstandi M., Lang M. A. Liver injury and expression of cytochromes P450: evidence that regulation of CYP2A5 is different from that of other major xenobiotic metabolizing CYP enzymes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1996 May;138(1):140–148. doi: 10.1006/taap.1996.0107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canella K. A., Diwan B. A., Gorelick P. L., Donovan P. J., Sipowicz M. A., Kasprzak K. S., Weghorst C. M., Snyderwine E. G., Davis C. D., Keefer L. K. Liver tumorigenesis by Helicobacter hepaticus: considerations of mechanism. In Vivo. 1996 May-Jun;10(3):285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carubelli R., Graham S. A., McCay P. B., Friedman F. K. Prevention of 2-acetylaminofluorene-induced loss of nuclear envelope cytochrome P450 by the simultaneous administration of 3-methylcholanthrene. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 May 1;41(9):1331–1334. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90105-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chemin I., Takahashi S., Belloc C., Lang M. A., Ando K., Guidotti L. G., Chisari F. V., Wild C. P. Differential induction of carcinogen metabolizing enzymes in a transgenic mouse model of fulminant hepatitis. Hepatology. 1996 Sep;24(3):649–656. doi: 10.1002/hep.510240330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa P. Helicobacter pylori and gastric carcinogenesis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995;19 (Suppl 1):S37–S43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai Y., Rashba-Step J., Cederbaum A. I. Stable expression of human cytochrome P4502E1 in HepG2 cells: characterization of catalytic activities and production of reactive oxygen intermediates. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 13;32(27):6928–6937. doi: 10.1021/bi00078a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekström G., Ingelman-Sundberg M. Rat liver microsomal NADPH-supported oxidase activity and lipid peroxidation dependent on ethanol-inducible cytochrome P-450 (P-450IIE1). Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Apr 15;38(8):1313–1319. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90338-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Dewhirst F. E., Tully J. G., Paster B. J., Yan L., Taylor N. S., Collins M. J., Jr, Gorelick P. L., Ward J. M. Helicobacter hepaticus sp. nov., a microaerophilic bacterium isolated from livers and intestinal mucosal scrapings from mice. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 May;32(5):1238–1245. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.5.1238-1245.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Li X., Yan L., Cahill R. J., Hurley R., Lewis R., Murphy J. C. Chronic proliferative hepatitis in A/JCr mice associated with persistent Helicobacter hepaticus infection: a model of helicobacter-induced carcinogenesis. Infect Immun. 1996 May;64(5):1548–1558. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.5.1548-1558.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraga C. G., Shigenaga M. K., Park J. W., Degan P., Ames B. N. Oxidative damage to DNA during aging: 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine in rat organ DNA and urine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen T. M., Huang S., Curnutte J., Fowler P., Martinez V., Wehr C. M., Ames B. N., Chisari F. V. Extensive oxidative DNA damage in hepatocytes of transgenic mice with chronic active hepatitis destined to develop hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12808–12812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D., Pulford D. J. The glutathione S-transferase supergene family: regulation of GST and the contribution of the isoenzymes to cancer chemoprotection and drug resistance. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1995;30(6):445–600. doi: 10.3109/10409239509083491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honkakoski P., Lang M. A. Mouse liver phenobarbital-inducible P450 system: purification, characterization, and differential inducibility of four cytochrome P450 isozymes from D2 mouse. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Aug 15;273(1):42–57. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90160-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. F., Srivastava S. K., Singhal S. S., Chaubey M., Awasthi S., Petersen D. R., Ansari G. A., Awasthi Y. C. Iron-induced lipid peroxidation in rat liver is accompanied by preferential induction of glutathione S-transferase 8-8 isozyme. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1995 Mar;131(1):63–72. doi: 10.1006/taap.1995.1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby G. M., Chemin I., Montesano R., Chisari F. V., Lang M. A., Wild C. P. Induction of specific cytochrome P450s involved in aflatoxin B1 metabolism in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Mol Carcinog. 1994 Oct;11(2):74–80. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940110204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby G. M., Pelkonen P., Vatanasapt V., Camus A. M., Wild C. P., Lang M. A. Association of liver fluke (Opisthorchis viverrini) infestation with increased expression of cytochrome P450 and carcinogen metabolism in male hamster liver. Mol Carcinog. 1994 Oct;11(2):81–89. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940110205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobliakov V., Kulikova L., Samoilov D., Lang M. A. High expression of cytochrome P450 2a-5 (coumarin 7-hydroxylase) in mouse hepatomas. Mol Carcinog. 1993;7(4):276–280. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940070411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokohchi K., Matsuo Y., Yoneyama H., Nishioka M., Ichikawa Y. Interleukin 2 induction of cytochrome P450-linked monooxygenase systems of rat liver microsomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Feb 9;45(3):585–592. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90131-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang M. A., Juvonen R., Järvinen P., Honkakoski P., Raunio H. Mouse liver P450Coh: genetic regulation of the pyrazole-inducible enzyme and comparison with other P450 isoenzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 May 15;271(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90264-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langouet S., Corcos L., Abdel-Razzak Z., Loyer P., Ketterer B., Guillouzo A. Up-regulation of glutathione S-transferases alpha by interleukin 4 in human hepatocytes in primary culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Nov 22;216(3):793–800. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madra S., Mann F., Francis J. E., Manson M. M., Smith A. G. Modulation by iron of hepatic microsomal and nuclear cytochrome P450, and cytosolic glutathione S-transferase and peroxidase in C57BL/10ScSn mice induced with polychlorinated biphenyls (Aroclor 1254). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1996 Jan;136(1):79–86. doi: 10.1006/taap.1996.0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle T. J. The glutathione S-transferase multigene family: a paradigm for xenobiotic interactions. Biochem Soc Trans. 1995 May;23(2):423–425. doi: 10.1042/bst0230423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marnett L. J. Peroxyl free radicals: potential mediators of tumor initiation and promotion. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Oct;8(10):1365–1373. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.10.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochida S., Masaki N., Ohta Y., Matsui A., Ogata I., Fujiwara K. In situ detection of oxidative stress in rat hepatocytes. J Pathol. 1992 May;167(1):83–89. doi: 10.1002/path.1711670114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morehouse L. A., Aust S. D. Generation of superoxide by the microsomal mixed-function oxidase system. Basic Life Sci. 1988;49:517–521. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5568-7_80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer C. N., Coates P. J., Davies S. E., Shephard E. A., Phillips I. R. Localization of cytochrome P-450 gene expression in normal and diseased human liver by in situ hybridization of wax-embedded archival material. Hepatology. 1992 Sep;16(3):682–687. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proulx M., du Souich P. Inflammation-induced decrease in hepatic cytochrome P450 in conscious rabbits is accompanied by an increase in hepatic oxidative stress. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 1995 Feb;87(2):221–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puntarulo S., Cederbaum A. I. Effect of phenobarbital and 3-methylcholanthrene treatment on NADPH- and NADH-dependent production of reactive oxygen intermediates by rat liver nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Mar 5;1116(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(92)90122-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puntarulo S., Cederbaum A. I. Role of cytochrome P-450 in the stimulation of microsomal production of reactive oxygen species by ferritin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996 Mar 15;1289(2):238–246. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(95)00157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn B. A., Crane T. L., Kocal T. E., Best S. J., Cameron R. G., Rushmore T. H., Farber E., Hayes M. A. Protective activity of different hepatic cytosolic glutathione S-transferases against DNA-binding metabolites of aflatoxin B1. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1990 Sep 15;105(3):351–363. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(90)90139-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice J. M. Helicobacter hepaticus, a recently recognized bacterial pathogen, associated with chronic hepatitis and hepatocellular neoplasia in laboratory mice. Emerg Infect Dis. 1995 Oct-Dec;1(4):129–131. doi: 10.3201/eid0104.950404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda R., Nagashima M., Sakamoto M., Yamaguchi N., Hirohashi S., Yokota J., Kasai H. Increased formation of oxidative DNA damage, 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine, in human livers with chronic hepatitis. Cancer Res. 1994 Jun 15;54(12):3171–3172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinel M., Robin M. A., Doostzadeh J., Maratrat M., Ballet F., Fardel N., el Kahwaji J., Beaune P., Daujat M., Labbe G. The interleukin-2 receptor down-regulates the expression of cytochrome P450 in cultured rat hepatocytes. Gastroenterology. 1995 Nov;109(5):1589–1599. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90648-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., Anver M. R., Haines D. C., Benveniste R. E. Chronic active hepatitis in mice caused by Helicobacter hepaticus. Am J Pathol. 1994 Oct;145(4):959–968. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., Fox J. G., Anver M. R., Haines D. C., George C. V., Collins M. J., Jr, Gorelick P. L., Nagashima K., Gonda M. A., Gilden R. V. Chronic active hepatitis and associated liver tumors in mice caused by a persistent bacterial infection with a novel Helicobacter species. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Aug 17;86(16):1222–1227. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.16.1222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimniak P., Singhal S. S., Srivastava S. K., Awasthi S., Sharma R., Hayden J. B., Awasthi Y. C. Estimation of genomic complexity, heterologous expression, and enzymatic characterization of mouse glutathione S-transferase mGSTA4-4 (GST 5.7). J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):992–1000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]