Abstract
An association between pancreatic microcystic (serous) adenomas (MCAs) and von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease has been suggested. However, genetic alterations of the VHL gene in MCAs of the pancreas have never been reported. In this study, we performed genetic analysis of 12 pancreatic MCAs. In 2 cases, VHL disease was documented clinically, and 10 cases were sporadic. For LOH analysis, tumor and normal pancreatic cells were procured from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded material using tissue microdissection. After DNA extraction, the samples were amplified by polymerase chain reaction using the polymorphic markers D3S2452, D3S1110, D3S192, and D3S656. In addition, the sporadic tumors were analyzed for VHL gene mutations using probes 3b/10b and K55/K56. Both MCAs associated with VHL disease showed LOH with at least one of the microsatellite markers tested. Among the 10 sporadic cases, 7 tumors showed LOH at the VHL gene locus. A somatic VHL gene mutation on exon 2 was documented in one sporadic case. The study provides the first direct genetic evidence for the role of the VHL gene in MCA tumorigenesis. Furthermore, VHL gene alterations may be detected in both VHL-associated and sporadic pancreatic MCAs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert L. C., Truong L. D., Bossart M. I., Spjut H. J. Microcystic adenoma (serous cystadenoma) of the pancreas. A study of 14 cases with immunohistochemical and electron-microscopic correlation. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Apr;12(4):251–263. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198804000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTOFERSON L. A., GUSTAFSON M. B., PETERSEN A. G. Von Hippel-Lindau's disease. JAMA. 1961 Oct 21;178:280–282. doi: 10.1001/jama.1961.03040420020005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choyke P. L., Glenn G. M., Walther M. M., Patronas N. J., Linehan W. M., Zbar B. von Hippel-Lindau disease: genetic, clinical, and imaging features. Radiology. 1995 Mar;194(3):629–642. doi: 10.1148/radiology.194.3.7862955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compagno J., Oertel J. E. Microcystic adenomas of the pancreas (glycogen-rich cystadenomas): a clinicopathologic study of 34 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Mar;69(3):289–298. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.1.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossey P. A., Foster K., Richards F. M., Phipps M. E., Latif F., Tory K., Jones M. H., Bentley E., Kumar R., Lerman M. I. Molecular genetic investigations of the mechanism of tumourigenesis in von Hippel-Lindau disease: analysis of allele loss in VHL tumours. Hum Genet. 1994 Jan;93(1):53–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00218913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster K., Prowse A., van den Berg A., Fleming S., Hulsbeek M. M., Crossey P. A., Richards F. M., Cairns P., Affara N. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Somatic mutations of the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumour suppressor gene in non-familial clear cell renal carcinoma. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Dec;3(12):2169–2173. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.12.2169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilcrease M. Z., Schmidt L., Zbar B., Truong L., Rutledge M., Wheeler T. M. Somatic von Hippel-Lindau mutation in clear cell papillary cystadenoma of the epididymis. Hum Pathol. 1995 Dec;26(12):1341–1346. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnarra J. R., Tory K., Weng Y., Schmidt L., Wei M. H., Li H., Latif F., Liu S., Chen F., Duh F. M. Mutations of the VHL tumour suppressor gene in renal carcinoma. Nat Genet. 1994 May;7(1):85–90. doi: 10.1038/ng0594-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman J. G., Latif F., Weng Y., Lerman M. I., Zbar B., Liu S., Samid D., Duan D. S., Gnarra J. R., Linehan W. M. Silencing of the VHL tumor-suppressor gene by DNA methylation in renal carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):9700–9704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton W. A., Wong V., Eldridge R. Von Hippel-Lindau disease: clinical and pathological manifestations in nine families with 50 affected members. Arch Intern Med. 1976 Jul;136(7):769–777. doi: 10.1001/archinte.136.7.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno H., Kondo K., Ito S., Yamamoto I., Fujii S., Torigoe S., Sakai N., Hosaka M., Shuin T., Yao M. Somatic mutations of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene in sporadic central nervous system hemangioblastomas. Cancer Res. 1994 Sep 15;54(18):4845–4847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson A. G., Jr Genetics of human cancer. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:231–251. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamiell J. M., Salazar F. G., Hsia Y. E. von Hippel-Lindau disease affecting 43 members of a single kindred. Medicine (Baltimore) 1989 Jan;68(1):1–29. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198901000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latif F., Tory K., Gnarra J., Yao M., Duh F. M., Orcutt M. L., Stackhouse T., Kuzmin I., Modi W., Geil L. Identification of the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1317–1320. doi: 10.1126/science.8493574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J. The tumor suppressor genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:623–651. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.003203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher E. R. Von Hippel-Lindau disease. Eur J Cancer. 1994;30A(13):1987–1990. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(94)00391-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
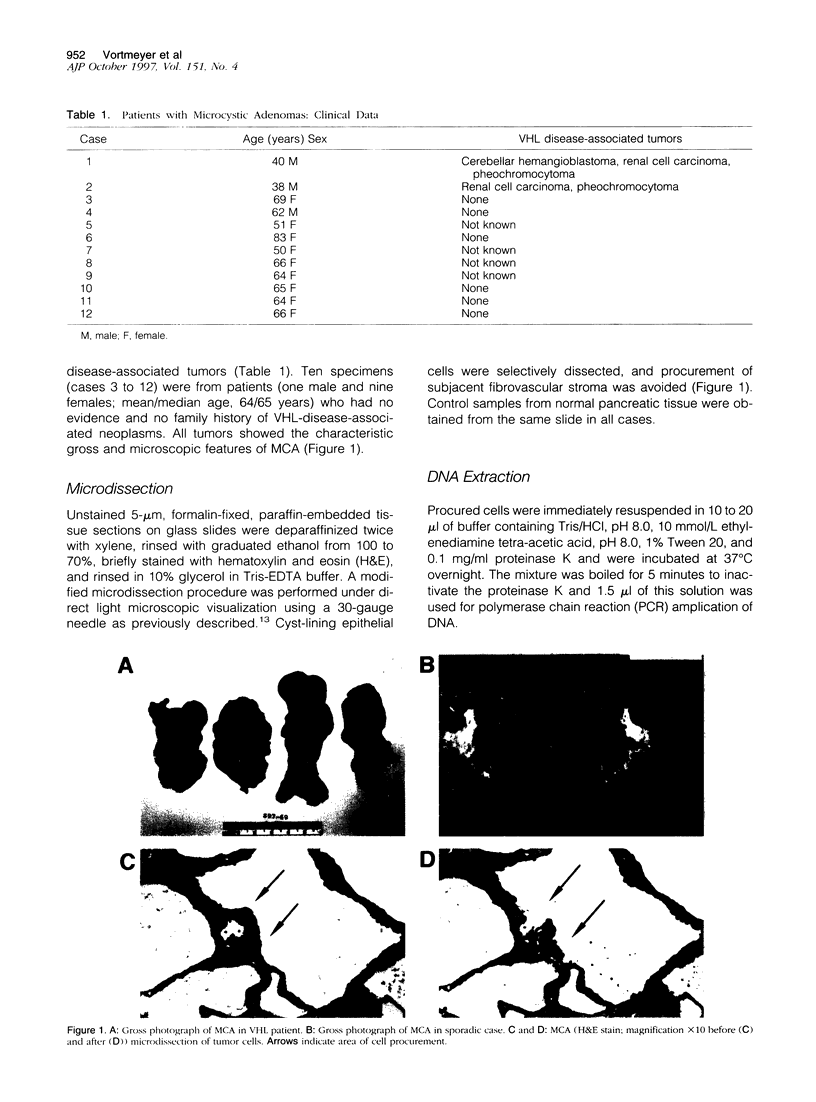
- Morohoshi T., Held G., Klöppel G. Exocrine pancreatic tumours and their histological classification. A study based on 167 autopsy and 97 surgical cases. Histopathology. 1983 Sep;7(5):645–661. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1983.tb02277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann H. P., Dinkel E., Brambs H., Wimmer B., Friedburg H., Volk B., Sigmund G., Riegler P., Haag K., Schollmeyer P. Pancreatic lesions in the von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1991 Aug;101(2):465–471. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90026-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyongo A., Huntrakoon M. Microcystic adenoma of the pancreas with myoepithelial cells. A hitherto undescribed morphologic feature. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jul;84(1):114–120. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/84.1.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberstrass J., Reifenberger G., Reifenberger J., Wechsler W., Collins V. P. Mutation of the Von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor gene in capillary haemangioblastomas of the central nervous system. J Pathol. 1996 Jun;179(2):151–156. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9896(199606)179:2<151::aid-path556>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seizinger B. R., Rouleau G. A., Ozelius L. J., Lane A. H., Farmer G. E., Lamiell J. M., Haines J., Yuen J. W., Collins D., Majoor-Krakauer D. Von Hippel-Lindau disease maps to the region of chromosome 3 associated with renal cell carcinoma. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):268–269. doi: 10.1038/332268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
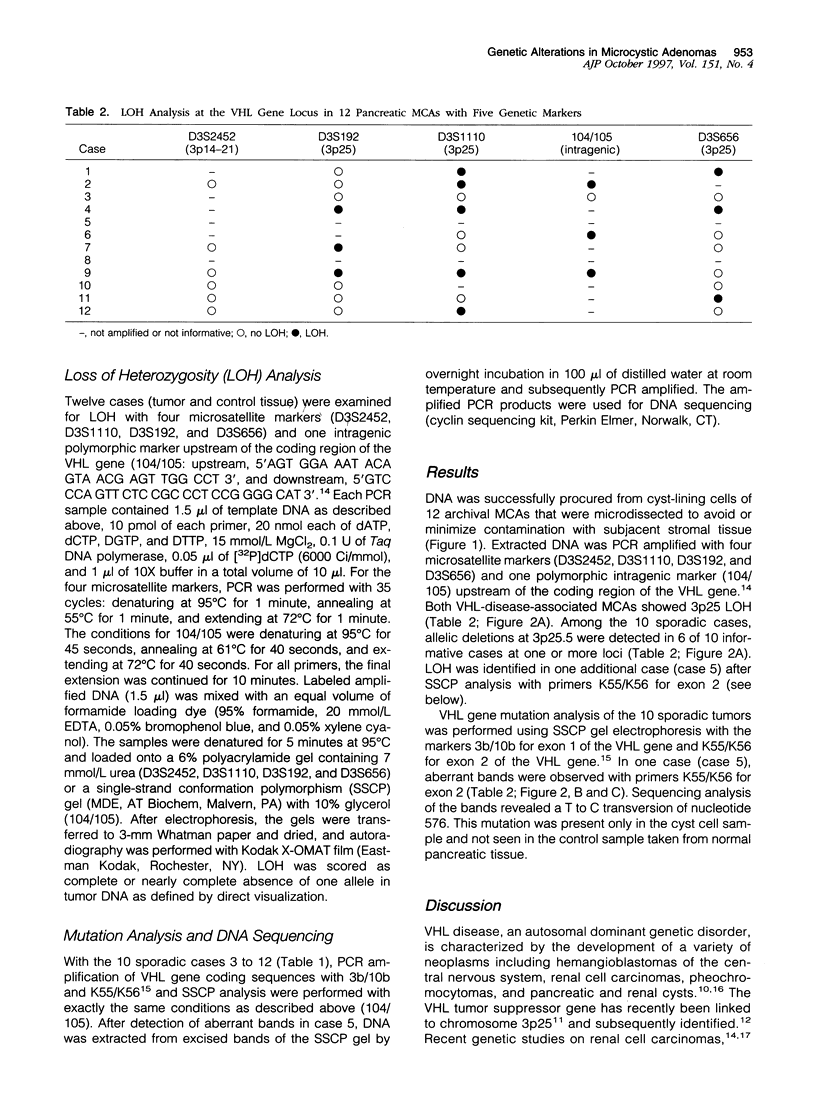
- Sheffield V. C., Beck J. S., Kwitek A. E., Sandstrom D. W., Stone E. M. The sensitivity of single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis for the detection of single base substitutions. Genomics. 1993 May;16(2):325–332. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorten S. D., Hart W. R., Petras R. E. Microcystic adenomas (serous cystadenomas) of pancreas. A clinicopathologic investigation of eight cases with immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies. Am J Surg Pathol. 1986 Jun;10(6):365–372. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198606000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuin T., Kondo K., Torigoe S., Kishida T., Kubota Y., Hosaka M., Nagashima Y., Kitamura H., Latif F., Zbar B. Frequent somatic mutations and loss of heterozygosity of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene in primary human renal cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1994 Jun 1;54(11):2852–2855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tory K., Brauch H., Linehan M., Barba D., Oldfield E., Filling-Katz M., Seizinger B., Nakamura Y., White R., Marshall F. F. Specific genetic change in tumors associated with von Hippel-Lindau disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Jul 19;81(14):1097–1101. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.14.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse J. Y., Wong J. H., Lo K. W., Poon W. S., Huang D. P., Ng H. K. Molecular genetic analysis of the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene in familial and sporadic cerebellar hemangioblastomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1997 Apr;107(4):459–466. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/107.4.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger M. A., Zbar B., Keiser H., Linehan W. M., Gnarra J. R. Loss of heterozygosity on the short arm of chromosome 3 in sporadic, von Hippel-Lindau disease-associated, and familial pheochromocytoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1995 Jul;13(3):151–156. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870130303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Z., Bertheau P., Emmert-Buck M. R., Liotta L. A., Gnarra J., Linehan W. M., Lubensky I. A. A microdissection technique for archival DNA analysis of specific cell populations in lesions < 1 mm in size. Am J Pathol. 1995 Mar;146(3):620–625. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]