Abstract
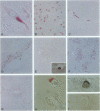
Entry of the type 1 human immunodeficiency virus into most cells requires the presence of the CD4 protein in combination with one of several recently described co-receptors. CXCR-4 (fusin) was the first identified, and it serves as co-receptor for T-cell-line tropic (T-tropic) HIV-1 isolates. To determine the expression of CXCR-4 in the brain, a major target of HIV pathology, we used immunohistochemistry and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction with CXCR-4-specific antibodies and probes. We found that CXCR-4 was expressed in several cell types in brain, but notably in neurons and microglia, a finding that was replicated in tissue culture. The study of the expression of CXCR-4 in the brain, which may be one of many chemokine receptors in the central nervous system, may provide further insight into the interactions between brain cells, pathogens, and the immune system, and help understand the pathogenesis of HIV dementia.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright A. V., Strizki J., Harouse J. M., Lavi E., O'Connor M., González-Scarano F. HIV-1 infection of cultured human adult oligodendrocytes. Virology. 1996 Mar 1;217(1):211–219. doi: 10.1006/viro.1996.0108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkhatib G., Combadiere C., Broder C. C., Feng Y., Kennedy P. E., Murphy P. M., Berger E. A. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996 Jun 28;272(5270):1955–1958. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5270.1955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagasra O., Lavi E., Bobroski L., Khalili K., Pestaner J. P., Tawadros R., Pomerantz R. J. Cellular reservoirs of HIV-1 in the central nervous system of infected individuals: identification by the combination of in situ polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry. AIDS. 1996 Jun;10(6):573–585. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199606000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson J. F., Long D., Doranz B. J., Rucker J., Jirik F. R., Doms R. W. A seven-transmembrane domain receptor involved in fusion and entry of T-cell-tropic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 strains. J Virol. 1996 Sep;70(9):6288–6295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.9.6288-6295.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleul C. C., Farzan M., Choe H., Parolin C., Clark-Lewis I., Sodroski J., Springer T. A. The lymphocyte chemoattractant SDF-1 is a ligand for LESTR/fusin and blocks HIV-1 entry. Nature. 1996 Aug 29;382(6594):829–833. doi: 10.1038/382829a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe H., Farzan M., Sun Y., Sullivan N., Rollins B., Ponath P. D., Wu L., Mackay C. R., LaRosa G., Newman W. The beta-chemokine receptors CCR3 and CCR5 facilitate infection by primary HIV-1 isolates. Cell. 1996 Jun 28;85(7):1135–1148. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81313-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng H., Liu R., Ellmeier W., Choe S., Unutmaz D., Burkhart M., Di Marzio P., Marmon S., Sutton R. E., Hill C. M. Identification of a major co-receptor for primary isolates of HIV-1. Nature. 1996 Jun 20;381(6584):661–666. doi: 10.1038/381661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doranz B. J., Rucker J., Yi Y., Smyth R. J., Samson M., Peiper S. C., Parmentier M., Collman R. G., Doms R. W. A dual-tropic primary HIV-1 isolate that uses fusin and the beta-chemokine receptors CKR-5, CKR-3, and CKR-2b as fusion cofactors. Cell. 1996 Jun 28;85(7):1149–1158. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81314-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endres M. J., Clapham P. R., Marsh M., Ahuja M., Turner J. D., McKnight A., Thomas J. F., Stoebenau-Haggarty B., Choe S., Vance P. J. CD4-independent infection by HIV-2 is mediated by fusin/CXCR4. Cell. 1996 Nov 15;87(4):745–756. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81393-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. G., Gendelman H. E. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of the nervous system: pathogenetic mechanisms. Ann Neurol. 1993 May;33(5):429–436. doi: 10.1002/ana.410330502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. G., Kuiken C., Blumberg B. M., Hartman S., Sharer L. R., Clement M., Goudsmit J. HIV-1 V3 domain variation in brain and spleen of children with AIDS: tissue-specific evolution within host-determined quasispecies. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):583–590. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90072-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantini J., Cook D. G., Nathanson N., Spitalnik S. L., Gonzalez-Scarano F. Infection of colonic epithelial cell lines by type 1 human immunodeficiency virus is associated with cell surface expression of galactosylceramide, a potential alternative gp120 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2700–2704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federsppiel B., Melhado I. G., Duncan A. M., Delaney A., Schappert K., Clark-Lewis I., Jirik F. R. Molecular cloning of the cDNA and chromosomal localization of the gene for a putative seven-transmembrane segment (7-TMS) receptor isolated from human spleen. Genomics. 1993 Jun;16(3):707–712. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y., Broder C. C., Kennedy P. E., Berger E. A. HIV-1 entry cofactor: functional cDNA cloning of a seven-transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptor. Science. 1996 May 10;272(5263):872–877. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5263.872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godiska R., Chantry D., Dietsch G. N., Gray P. W. Chemokine expression in murine experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 1995 May;58(2):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(95)00008-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harouse J. M., Bhat S., Spitalnik S. L., Laughlin M., Stefano K., Silberberg D. H., Gonzalez-Scarano F. Inhibition of entry of HIV-1 in neural cell lines by antibodies against galactosyl ceramide. Science. 1991 Jul 19;253(5017):320–323. doi: 10.1126/science.1857969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horuk R., Martin A., Hesselgesser J., Hadley T., Lu Z. H., Wang Z. X., Peiper S. C. The Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines: structural analysis and expression in the brain. J Leukoc Biol. 1996 Jan;59(1):29–38. doi: 10.1002/jlb.59.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson D. G., Usher D. C., Rader D. J., Lavi E. Apolipoprotein(a) deposition in atherosclerotic plaques of cerebral vessels. A potential role for endothelial cells in lesion formation. Am J Pathol. 1995 Dec;147(6):1567–1574. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapham C. K., Ouyang J., Chandrasekhar B., Nguyen N. Y., Dimitrov D. S., Golding H. Evidence for cell-surface association between fusin and the CD4-gp120 complex in human cell lines. Science. 1996 Oct 25;274(5287):602–605. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5287.602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llanes C., Collman R. G., Hrin R., Kolson D. L. Acetylcholinesterase expression in NTera 2 human neuronal cells: a model for developmental expression in the nervous system. J Neurosci Res. 1995 Dec 15;42(6):791–802. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490420608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher M., Geiser T., O'Reilly T., Zwahlen R., Baggiolini M., Moser B. Cloning of a human seven-transmembrane domain receptor, LESTR, that is highly expressed in leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):232–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitta T., Allegretta M., Okumura K., Sato K., Steinman L. Neoplastic and reactive human astrocytes express interleukin-8 gene. Neurosurg Rev. 1992;15(3):203–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00345934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuovo G. J., Gallery F., MacConnell P., Braun A. In situ detection of polymerase chain reaction-amplified HIV-1 nucleic acids and tumor necrosis factor-alpha RNA in the central nervous system. Am J Pathol. 1994 Apr;144(4):659–666. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlin E., Amara A., Bachelerie F., Bessia C., Virelizier J. L., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Schwartz O., Heard J. M., Clark-Lewis I., Legler D. F. The CXC chemokine SDF-1 is the ligand for LESTR/fusin and prevents infection by T-cell-line-adapted HIV-1. Nature. 1996 Aug 29;382(6594):833–835. doi: 10.1038/382833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleasure S. J., Lee V. M. NTera 2 cells: a human cell line which displays characteristics expected of a human committed neuronal progenitor cell. J Neurosci Res. 1993 Aug 15;35(6):585–602. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490350603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleasure S. J., Page C., Lee V. M. Pure, postmitotic, polarized human neurons derived from NTera 2 cells provide a system for expressing exogenous proteins in terminally differentiated neurons. J Neurosci. 1992 May;12(5):1802–1815. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-05-01802.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransohoff R. M., Hamilton T. A., Tani M., Stoler M. H., Shick H. E., Major J. A., Estes M. L., Thomas D. M., Tuohy V. K. Astrocyte expression of mRNA encoding cytokines IP-10 and JE/MCP-1 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. FASEB J. 1993 Apr 1;7(6):592–600. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.6.8472896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimland J., Xin W., Sweetnam P., Saijoh K., Nestler E. J., Duman R. S. Sequence and expression of a neuropeptide Y receptor cDNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):869–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasseville V. G., Smith M. M., Mackay C. R., Pauley D. R., Mansfield K. G., Ringler D. J., Lackner A. A. Chemokine expression in simian immunodeficiency virus-induced AIDS encephalitis. Am J Pathol. 1996 Nov;149(5):1459–1467. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharer L. R., Saito Y., Da Cunha A., Ung P. C., Gelbard H. A., Epstein L. G., Blumberg B. M. In situ amplification and detection of HIV-1 DNA in fixed pediatric AIDS brain tissue. Hum Pathol. 1996 Jun;27(6):614–617. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(96)90172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strizki J. M., Albright A. V., Sheng H., O'Connor M., Perrin L., González-Scarano F. Infection of primary human microglia and monocyte-derived macrophages with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates: evidence of differential tropism. J Virol. 1996 Nov;70(11):7654–7662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.11.7654-7662.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trkola A., Dragic T., Arthos J., Binley J. M., Olson W. C., Allaway G. P., Cheng-Mayer C., Robinson J., Maddon P. J., Moore J. P. CD4-dependent, antibody-sensitive interactions between HIV-1 and its co-receptor CCR-5. Nature. 1996 Nov 14;384(6605):184–187. doi: 10.1038/384184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Meir E., Ceska M., Effenberger F., Walz A., Grouzmann E., Desbaillets I., Frei K., Fontana A., de Tribolet N. Interleukin-8 is produced in neoplastic and infectious diseases of the human central nervous system. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 15;52(16):4297–4305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westmoreland S. V., Kolson D., González-Scarano F. Toxicity of TNF alpha and platelet activating factor for human NT2N neurons: a tissue culture model for human immunodeficiency virus dementia. J Neurovirol. 1996 Apr;2(2):118–126. doi: 10.3109/13550289609146545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Gerard N. P., Wyatt R., Choe H., Parolin C., Ruffing N., Borsetti A., Cardoso A. A., Desjardin E., Newman W. CD4-induced interaction of primary HIV-1 gp120 glycoproteins with the chemokine receptor CCR-5. Nature. 1996 Nov 14;384(6605):179–183. doi: 10.1038/384179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younkin D. P., Tang C. M., Hardy M., Reddy U. R., Shi Q. Y., Pleasure S. J., Lee V. M., Pleasure D. Inducible expression of neuronal glutamate receptor channels in the NT2 human cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2174–2178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]