Abstract
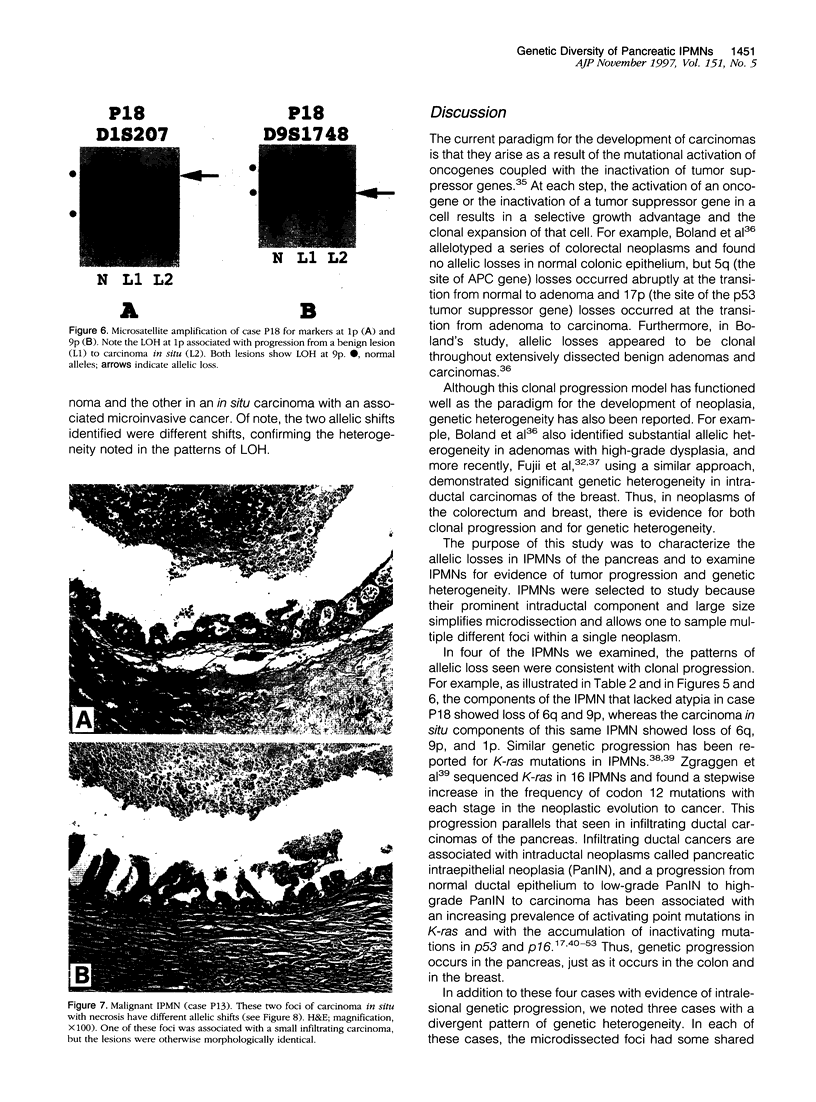
Intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) of the pancreas are ideal neoplasms to study clonal progression and genetic diversity because of their large size and prominent intraductal component. We microdissected 55 histologically defined areas from 13 IPMNs, extracted the DNA from each, and performed polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based microsatellite analysis to detect loss of heterozygosity on chromosome arms 1p, 3p, 6q, 8p, 9p, 17p, 18q, and 22q. LOH was identified at 1p in two cases, at 3p in four cases, at 6q in seven cases, at 8p in four cases, at 9p in eight cases, at 17p in five cases, at 18q in five cases, and at 22q in one of the IPMNs examined. In one of the IPMNs, the allelic losses were uniform throughout multiple microdissected areas, and in four of the IPMNs, there was evidence of clonal progression. In contrast, in three of the IPMNs, substantial allelic heterogeneity was seen. This remarkable heterogeneity may, in part, be due to the slow growth rate of these neoplasms.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardi G., Sukhikh T., Pandis N., Fenger C., Kronborg O., Heim S. Karyotypic characterization of colorectal adenocarcinomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1995 Feb;12(2):97–109. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870120204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthet M., Spinosa S., Bernard J. P., Payan M. J., Berthier J., Sahel J. An association between villous adenomas and mucinous ductal ectasia of the pancreas. Endoscopy. 1995 Oct;27(8):601–603. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch D., Shevlin D. W., Tung W. S., Kisker O., Wells S. A., Jr, Goodfellow P. J. Frequent mutations of CDKN2 in primary pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1995 Nov;14(3):189–195. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870140306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block K. P., Mahvi D., Voytovich M., Watkins J. L., Mosley R., Reichelderfer M. Mucinous ductal ectasia in an octogenarian: successful treatment with the Whipple procedure. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996 Feb;91(2):388–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boland C. R., Sato J., Appelman H. D., Bresalier R. S., Feinberg A. P. Microallelotyping defines the sequence and tempo of allelic losses at tumour suppressor gene loci during colorectal cancer progression. Nat Med. 1995 Sep;1(9):902–909. doi: 10.1038/nm0995-902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschman C. R., Stryker S., Reddy J. K., Rao M. S. Expression of p53 protein in precursor lesions and adenocarcinoma of human pancreas. Am J Pathol. 1994 Dec;145(6):1291–1295. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldas C., Hahn S. A., Hruban R. H., Redston M. S., Yeo C. J., Kern S. E. Detection of K-ras mutations in the stool of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and pancreatic ductal hyperplasia. Cancer Res. 1994 Jul 1;54(13):3568–3573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldas C., Hahn S. A., da Costa L. T., Redston M. S., Schutte M., Seymour A. B., Weinstein C. L., Hruban R. H., Yeo C. J., Kern S. E. Frequent somatic mutations and homozygous deletions of the p16 (MTS1) gene in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Nat Genet. 1994 Sep;8(1):27–32. doi: 10.1038/ng0994-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerny W. L., Mangold K. A., Scarpelli D. G. K-ras mutation is an early event in pancreatic duct carcinogenesis in the Syrian golden hamster. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 15;52(16):4507–4513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubilla A. L., Fitzgerald P. J. Morphological lesions associated with human primary invasive nonendocrine pancreas cancer. Cancer Res. 1976 Jul;36(7 Pt 2):2690–2698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiGiuseppe J. A., Hruban R. H., Goodman S. N., Polak M., van den Berg F. M., Allison D. C., Cameron J. L., Offerhaus G. J. Overexpression of p53 protein in adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994 Jun;101(6):684–688. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/101.6.684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiGiuseppe J. A., Redston M. S., Yeo C. J., Kern S. E., Hruban R. H. p53-independent expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 in pancreatic carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1995 Oct;147(4):884–888. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii H., Marsh C., Cairns P., Sidransky D., Gabrielson E. Genetic divergence in the clonal evolution of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1996 Apr 1;56(7):1493–1497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii H., Szumel R., Marsh C., Zhou W., Gabrielson E. Genetic progression, histological grade, and allelic loss in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Cancer Res. 1996 Nov 15;56(22):5260–5265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Chiba R., Kobari M., Matsuno S., Nagura H., Takahashi T. Varying grades of epithelial atypia in the pancreatic ducts of humans. Classification based on morphometry and multivariate analysis and correlated with positive reactions of carcinoembryonic antigen. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1994 Mar;118(3):227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorunova L., Johansson B., Dawiskiba S., Andrén-Sandberg A., Jin Y., Mandahl N., Heim S., Mitelman F. Massive cytogenetic heterogeneity in a pancreatic carcinoma: fifty-four karyotypically unrelated clones. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1995 Dec;14(4):259–266. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870140404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorunova L., Johansson B., Dawiskiba S., Andrén-Sandberg A., Mandahl N., Heim S., Mitelman F. Cytogenetically detected clonal heterogeneity in a duodenal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1995 Jul 15;82(2):146–150. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(95)00032-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S. A., Hoque A. T., Moskaluk C. A., da Costa L. T., Schutte M., Rozenblum E., Seymour A. B., Weinstein C. L., Yeo C. J., Hruban R. H. Homozygous deletion map at 18q21.1 in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 1996 Feb 1;56(3):490–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S. A., Schutte M., Hoque A. T., Moskaluk C. A., da Costa L. T., Rozenblum E., Weinstein C. L., Fischer A., Yeo C. J., Hruban R. H. DPC4, a candidate tumor suppressor gene at human chromosome 18q21.1. Science. 1996 Jan 19;271(5247):350–353. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5247.350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S. A., Seymour A. B., Hoque A. T., Schutte M., da Costa L. T., Redston M. S., Caldas C., Weinstein C. L., Fischer A., Yeo C. J. Allelotype of pancreatic adenocarcinoma using xenograft enrichment. Cancer Res. 1995 Oct 15;55(20):4670–4675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heim S., Jin Y., Mandahl N., Biörklund A., Wennerberg J., Jonsson N., Mitelman F. Multiple unrelated clonal chromosome abnormalities in an in situ squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Dec;36(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heim S., Mandahl N., Mitelman F. Genetic convergence and divergence in tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1988 Nov 1;48(21):5911–5916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Imai M., Ogawa K. Frequent K-ras mutations and absence of p53 mutations in mucin-producing tumors of the pancreas. J Surg Oncol. 1994 Feb;55(2):84–91. doi: 10.1002/jso.2930550205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruban R. H., van Mansfeld A. D., Offerhaus G. J., van Weering D. H., Allison D. C., Goodman S. N., Kensler T. W., Bose K. K., Cameron J. L., Bos J. L. K-ras oncogene activation in adenocarcinoma of the human pancreas. A study of 82 carcinomas using a combination of mutant-enriched polymerase chain reaction analysis and allele-specific oligonucleotide hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):545–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Goodrow T. L., Zhang S. Y., Klein-Szanto A. J., Chang H., Ruggeri B. A. Deletion and mutation analyses of the P16/MTS-1 tumor suppressor gene in human ductal pancreatic cancer reveals a higher frequency of abnormalities in tumor-derived cell lines than in primary ductal adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1996 Mar 1;56(5):1137–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itai Y., Ohhashi K., Nagai H., Murakami Y., Kokubo T., Makita K., Ohtomo K. "Ductectatic" mucinous cystadenoma and cystadenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Radiology. 1986 Dec;161(3):697–700. doi: 10.1148/radiology.161.3.3786719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin Y., Mertens F., Mandahl N., Heim S., Olegård C., Wennerberg J., Biörklund A., Mitelman F. Chromosome abnormalities in eighty-three head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: influence of culture conditions on karyotypic pattern. Cancer Res. 1993 May 1;53(9):2140–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawarada Y., Yano T., Yamamoto T., Yokoi H., Imai T., Ogura Y., Mizumoto R. Intraductal mucin-producing tumors of the pancreas. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992 May;87(5):634–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozuka S., Sassa R., Taki T., Masamoto K., Nagasawa S., Saga S., Hasegawa K., Takeuchi M. Relation of pancreatic duct hyperplasia to carcinoma. Cancer. 1979 Apr;43(4):1418–1428. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197904)43:4<1418::aid-cncr2820430431>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengauer C., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. DNA methylation and genetic instability in colorectal cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Mar 18;94(6):2545–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.6.2545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengauer C., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Genetic instability in colorectal cancers. Nature. 1997 Apr 10;386(6625):623–627. doi: 10.1038/386623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftus E. V., Jr, Olivares-Pakzad B. A., Batts K. P., Adkins M. C., Stephens D. H., Sarr M. G., DiMagno E. P. Intraductal papillary-mucinous tumors of the pancreas: clinicopathologic features, outcome, and nomenclature. Members of the Pancreas Clinic, and Pancreatic Surgeons of Mayo Clinic. Gastroenterology. 1996 Jun;110(6):1909–1918. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8964418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker D. S. Intraductal papillary-mucinous tumors of the pancreas. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1995 Mar;119(3):197–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskaluk C. A., Hruban R. H., Kern S. E. p16 and K-ras gene mutations in the intraductal precursors of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1997 Jun 1;57(11):2140–2143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumann M., Savitskaia N., Eilert C., Schramm A., Kalthoff H., Schmiegel W. Frequent codeletion of p16/MTS1 and p15/MTS2 and genetic alterations in p16/MTS1 in pancreatic tumors. Gastroenterology. 1996 Apr;110(4):1215–1224. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8613012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara T., Maguchi H., Saitoh Y., Sohma M., Tsuji K., Koike Y., Takemura K., Ura H., Namiki M. Intraductal papillary neoplasms of the pancreas: diagnosis by endoscopic pancreatic biopsy. Endoscopy. 1993 May;25(4):290–293. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Nagakawa T., Akiyama T., Fukushima W., Ueno K., Miyazaki I., Suzuki M., Matsui O., Terada T., Nakanuma Y. The "duct-ectatic" variant of mucinous cystic neoplasm of the pancreas: clinical and radiologic studies of seven cases. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992 Mar;87(3):300–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pour P. M., Sayed S., Sayed G. Hyperplastic, preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions found in 83 human pancreases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Feb;77(2):137–152. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/77.2.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redston M. S., Caldas C., Seymour A. B., Hruban R. H., da Costa L., Yeo C. J., Kern S. E. p53 mutations in pancreatic carcinoma and evidence of common involvement of homocopolymer tracts in DNA microdeletions. Cancer Res. 1994 Jun 1;54(11):3025–3033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickaert F., Cremer M., Devière J., Tavares L., Lambilliotte J. P., Schröder S., Wurbs D., Klöppel G. Intraductal mucin-hypersecreting neoplasms of the pancreas. A clinicopathologic study of eight patients. Gastroenterology. 1991 Aug;101(2):512–519. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90032-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblum E., Schutte M., Goggins M., Hahn S. A., Panzer S., Zahurak M., Goodman S. N., Sohn T. A., Hruban R. H., Yeo C. J. Tumor-suppressive pathways in pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1997 May 1;57(9):1731–1734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santini D., Campione O., Salerno A., Gullo L., Mazzoleni G., Leone O., Martinelli G., Marrano D. Intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. A clinicopathologic entity. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1995 Mar;119(3):209–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa A., Capelli P., Mukai K., Zamboni G., Oda T., Iacono C., Hirohashi S. Pancreatic adenocarcinomas frequently show p53 gene mutations. Am J Pathol. 1993 May;142(5):1534–1543. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutte M., Hruban R. H., Hedrick L., Cho K. R., Nadasdy G. M., Weinstein C. L., Bova G. S., Isaacs W. B., Cairns P., Nawroz H. DPC4 gene in various tumor types. Cancer Res. 1996 Jun 1;56(11):2527–2530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessa F., Solcia E., Capella C., Bonato M., Scarpa A., Zamboni G., Pellegata N. S., Ranzani G. N., Rickaert F., Klöppel G. Intraductal papillary-mucinous tumours represent a distinct group of pancreatic neoplasms: an investigation of tumour cell differentiation and K-ras, p53 and c-erbB-2 abnormalities in 26 patients. Virchows Arch. 1994;425(4):357–367. doi: 10.1007/BF00189573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seymour A. B., Hruban R. H., Redston M., Caldas C., Powell S. M., Kinzler K. W., Yeo C. J., Kern S. E. Allelotype of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1994 May 15;54(10):2761–2764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyr Y. M., Su C. H., Tsay S. H., Lui W. Y. Mucin-producing neoplasms of the pancreas. Intraductal papillary and mucinous cystic neoplasms. Ann Surg. 1996 Feb;223(2):141–146. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199602000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M., Ohashi M., Shiratori Y., Okudaira T., Komatsu Y., Kawabe T., Yoshida H., Machinami R., Kishi K., Omata M. Analysis of K-ras gene mutation in hyperplastic duct cells of the pancreas without pancreatic disease. Gastroenterology. 1996 Jan;110(1):227–231. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8536861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M., Omata M., Ohto M. Ras gene mutations in intraductal papillary neoplasms of the pancreas. Analysis in five cases. Cancer. 1991 Feb 1;67(3):634–637. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910201)67:3<634::aid-cncr2820670318>3.0.co;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner S., Carr-Locke D. L., Banks P. A., Brooks D. C., Van Dam J., Farraye F. A., Turner J. R., Lichtenstein D. R. Intraductal mucin-hypersecreting neoplasm "mucinous ductal ectasia": endoscopic recognition and management. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996 Dec;91(12):2548–2554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian F. Z., Myles J., Howard J. M. Mucinous pancreatic ductal ectasia of latent malignancy: an emerging clinicopathologic entity. Surgery. 1992 Jan;111(1):109–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyrer K., Feichtinger H., Haun M., Weiss G., Ofner D., Weger A. R., Umlauft F., Grünewald K. p53, Ki-ras, and DNA ploidy in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Lab Invest. 1996 Jan;74(1):279–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Ogawa Y., Chijiiwa K., Tanaka M. Mucin-hypersecreting tumors of the pancreas: assessing the grade of malignancy preoperatively. Am J Surg. 1996 Apr;171(4):427–431. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(97)89624-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa A., Ohtake K., Ohashi K., Hori M., Kitagawa T., Sugano H., Kato Y. Frequent c-Ki-ras oncogene activation in mucous cell hyperplasias of pancreas suffering from chronic inflammation. Cancer Res. 1993 Mar 1;53(5):953–956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]










