Abstract
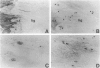
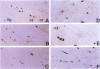
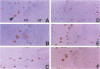
Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) is a pathological ossification in the spinal ligament, with formation of ectopic bone mainly through endochondral ossification. Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) and activins are multifunctional proteins that belong to the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily and that have been implicated in the formation of new bone and cartilage. BMPs and activins signal via type I and type II receptors for BMPs (BMPRs) and activins (ActRs), respectively. OP-1/BMP-7 binds to BMPR-II and ActR-II and forms complexes with BMPR-IA and -IB and ActR-I. We studied the expression of BMPR-IA, -IB, and -II, ActR-I, ActR-II, and OP-1/BMP-7 by immunohistochemistry in ossified ligament tissues of patients with OPLL and control ligament tissues from patients with cervical disc herniation. The expression of BMPRs and ActRs was elevated in OPLL compared with controls. Expressions of BMPR-IA, -IB, and -II were observed not only in chondrocytes at the fibrocartilage tissue around the calcified zone but also in fibroblast-like spindle cells at the nonossified ligament. ActR-I and -II were found co-localized in the hypertrophic chondrocytes near the calcified zone and in the ossified tissue. OP-1/BMP-7 was expressed in chondrocytes near the calcified zone. In the control cases, the BMPRs and ActRs were only weakly expressed in the fibrocartilage tissue at the site of ligament attachments to bone and OP-1/BMP-7 was not detected. Enhanced expression of BMPRs at the nonossified ligament in OPLL patients suggests that these cells have a greater potential to differentiate into osteogenic cells than ligament cells from non-OPLL patients. The high expression of BMPRs and ActRs in the ectopic ossified ligament suggests that BMPs and activin may be tightly involved in the pathological ossification process of OPLL.
Full text
PDF



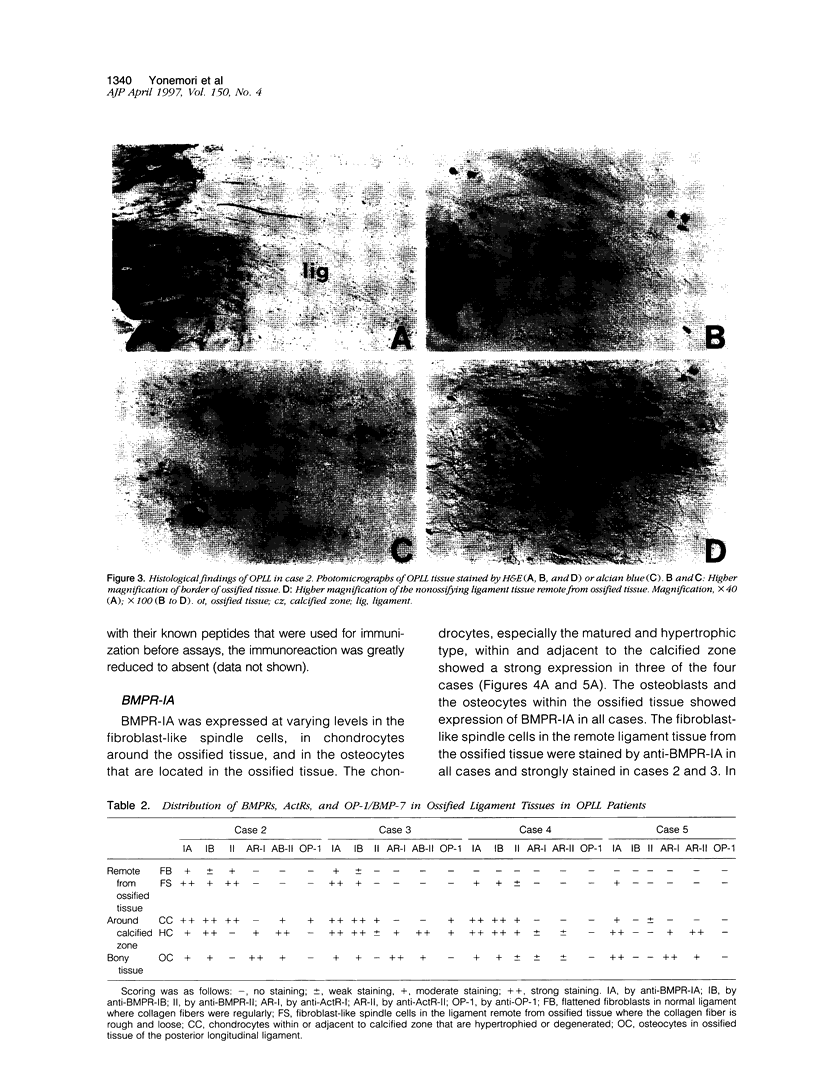
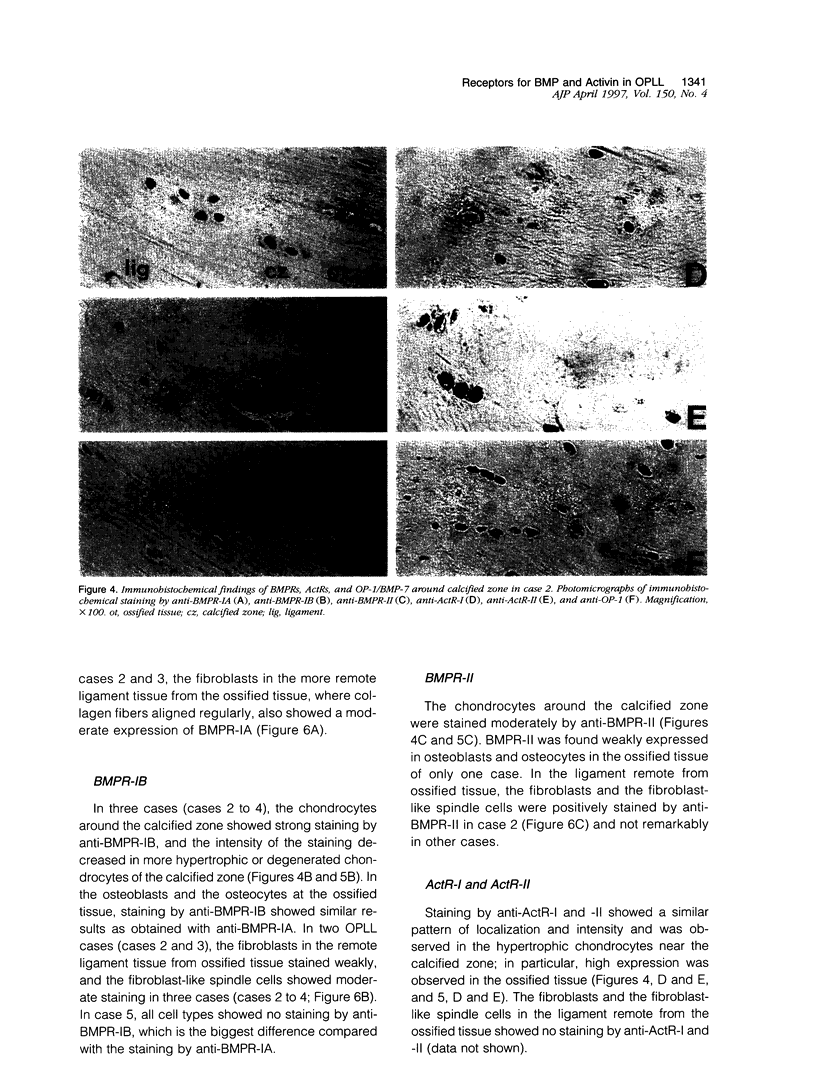
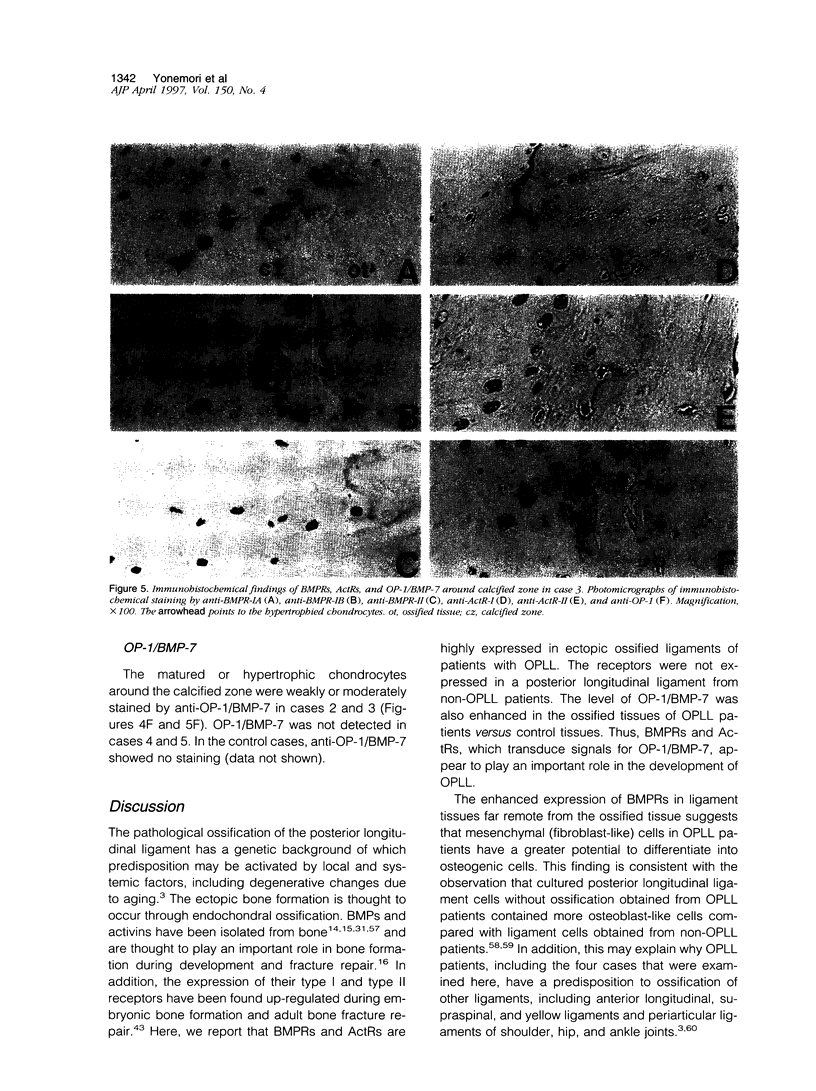





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asahina I., Sampath T. K., Hauschka P. V. Human osteogenic protein-1 induces chondroblastic, osteoblastic, and/or adipocytic differentiation of clonal murine target cells. Exp Cell Res. 1996 Jan 10;222(1):38–47. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.0005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asahina I., Sampath T. K., Nishimura I., Hauschka P. V. Human osteogenic protein-1 induces both chondroblastic and osteoblastic differentiation of osteoprogenitor cells derived from newborn rat calvaria. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):921–933. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attisano L., Cárcamo J., Ventura F., Weis F. M., Massagué J., Wrana J. L. Identification of human activin and TGF beta type I receptors that form heteromeric kinase complexes with type II receptors. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90488-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attisano L., Wrana J. L., Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Novel activin receptors: distinct genes and alternative mRNA splicing generate a repertoire of serine/threonine kinase receptors. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90209-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centrella M., McCarthy T. L., Canalis E. Activin-A binding and biochemical effects in osteoblast-enriched cultures from fetal-rat parietal bone. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):250–258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cárcamo J., Weis F. M., Ventura F., Wieser R., Wrana J. L., Attisano L., Massagué J. Type I receptors specify growth-inhibitory and transcriptional responses to transforming growth factor beta and activin. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):3810–3821. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.3810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewulf N., Verschueren K., Lonnoy O., Morén A., Grimsby S., Vande Spiegle K., Miyazono K., Huylebroeck D., Ten Dijke P. Distinct spatial and temporal expression patterns of two type I receptors for bone morphogenetic proteins during mouse embryogenesis. Endocrinology. 1995 Jun;136(6):2652–2663. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.6.7750489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley A. T., Lyons K. M., Robertson E. J. A requirement for bone morphogenetic protein-7 during development of the mammalian kidney and eye. Genes Dev. 1995 Nov 15;9(22):2795–2807. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.22.2795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feijen A., Goumans M. J., van den Eijnden-van Raaij A. J. Expression of activin subunits, activin receptors and follistatin in postimplantation mouse embryos suggests specific developmental functions for different activins. Development. 1994 Dec;120(12):3621–3637. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.12.3621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichijo H., Yamashita H., ten Dijke P., Eto Y., Heldin C. H., Miyazono K. Characterization of in vivo phosphorylation of activin type II receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Aug 16;194(3):1508–1514. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida Y., Kawai S. Effects of bone-seeking hormones on DNA synthesis, cyclic AMP level, and alkaline phosphatase activity in cultured cells from human posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. J Bone Miner Res. 1993 Nov;8(11):1291–1300. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650081104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishidou Y., Kitajima I., Obama H., Maruyama I., Murata F., Imamura T., Yamada N., ten Dijke P., Miyazono K., Sakou T. Enhanced expression of type I receptors for bone morphogenetic proteins during bone formation. J Bone Miner Res. 1995 Nov;10(11):1651–1659. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650101107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley D. M., Bland A. E., Grubber J. M., Marker P. C., Russell L. B., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. The mouse short ear skeletal morphogenesis locus is associated with defects in a bone morphogenetic member of the TGF beta superfamily. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):399–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90510-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley D. M. The TGF-beta superfamily: new members, new receptors, and new genetic tests of function in different organisms. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig B. B., Cook J. S., Wolsing D. H., Ting J., Tiesman J. P., Correa P. E., Olson C. A., Pecquet A. L., Ventura F., Grant R. A. Characterization and cloning of a receptor for BMP-2 and BMP-4 from NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):5961–5974. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.5961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga H., Hayashi K., Taketomi E., Matsunaga S., Yashiki S., Fujiyoshi T., Sonoda S., Sakou T. Restriction fragment length polymorphism of genes of the alpha 2(XI) collagen, bone morphogenetic protein-2, alkaline phosphatase, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha among patients with ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament and controls from the Japanese population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996 Feb 15;21(4):469–473. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199602150-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Ventura F., Doody J., Massagué J. Human type II receptor for bone morphogenic proteins (BMPs): extension of the two-kinase receptor model to the BMPs. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;15(7):3479–3486. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.7.3479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo G., Hofmann C., Bronckers A. L., Sohocki M., Bradley A., Karsenty G. BMP-7 is an inducer of nephrogenesis, and is also required for eye development and skeletal patterning. Genes Dev. 1995 Nov 15;9(22):2808–2820. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.22.2808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons K. M., Jones C. M., Hogan B. L. The DVR gene family in embryonic development. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):408–412. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90265-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Attisano L., Wrana J. L. The TGF-beta family and its composite receptors. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 May;4(5):172–178. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews L. S., Vale W. W. Expression cloning of an activin receptor, a predicted transmembrane serine kinase. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90549-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga S., Sakou T., Taketomi E., Nakanisi K. Effects of strain distribution in the intervertebral discs on the progression of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligaments. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996 Jan 15;21(2):184–189. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199601150-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzuk M. M., Kumar T. R., Bradley A. Different phenotypes for mice deficient in either activins or activin receptor type II. Nature. 1995 Mar 23;374(6520):356–360. doi: 10.1038/374356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzuk M. M., Kumar T. R., Vassalli A., Bickenbach J. R., Roop D. R., Jaenisch R., Bradley A. Functional analysis of activins during mammalian development. Nature. 1995 Mar 23;374(6520):354–356. doi: 10.1038/374354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto S., Takaoka K., Yonenobu K., Ono K. Ossification of the ligamentum flavum induced by bone morphogenetic protein. An experimental study in mice. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992 Mar;74(2):279–283. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.74B2.1544970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata M., Eto Y., Shibai H., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. Erythroid differentiation factor is encoded by the same mRNA as that of the inhibin beta A chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2434–2438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohno T., Ishikawa T., Saito T., Hosokawa K., Noji S., Wolsing D. H., Rosenbaum J. S. Identification of a human type II receptor for bone morphogenetic protein-4 that forms differential heteromeric complexes with bone morphogenetic protein type I receptors. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 22;270(38):22522–22526. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.38.22522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Schmidt D. K., Nathan R. M., Armstrong R. M., Miller K. L., Sawamura S. J., Ziman J. M., Erickson K. L., de Leon E. R., Rosen D. M. Bovine bone activin enhances bone morphogenetic protein-induced ectopic bone formation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14233–14237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki T., Takuwa Y., Yamamoto M., Matsumoto T., Igarashi T., Kurokawa T., Ogata E. Ossification of the paravertebral ligaments: a frequent complication of hypoparathyroidism. Metabolism. 1984 Aug;33(8):710–713. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(84)90209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddi A. H. Bone and cartilage differentiation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Oct;4(5):737–744. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90141-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick D., Guerra J., Jr, Robinson C. A., Vint V. C. Association of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) and calcification and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978 Dec;131(6):1049–1053. doi: 10.2214/ajr.131.6.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig B. L., Imamura T., Okadome T., Cox G. N., Yamashita H., ten Dijke P., Heldin C. H., Miyazono K. Cloning and characterization of a human type II receptor for bone morphogenetic proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7632–7636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakou T., Taketomi E., Matsunaga S., Yamaguchi M., Sonoda S., Yashiki S. Genetic study of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament in the cervical spine with human leukocyte antigen haplotype. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1991 Nov;16(11):1249–1252. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199111000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampath T. K., Coughlin J. E., Whetstone R. M., Banach D., Corbett C., Ridge R. J., Ozkaynak E., Oppermann H., Rueger D. C. Bovine osteogenic protein is composed of dimers of OP-1 and BMP-2A, two members of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13198–13205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampath T. K., Maliakal J. C., Hauschka P. V., Jones W. K., Sasak H., Tucker R. F., White K. H., Coughlin J. E., Tucker M. M., Pang R. H. Recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 (hOP-1) induces new bone formation in vivo with a specific activity comparable with natural bovine osteogenic protein and stimulates osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20352–20362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Price B. M., Van Nimmen K., Huylebroeck D. Identification of a potent Xenopus mesoderm-inducing factor as a homologue of activin A. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):729–731. doi: 10.1038/345729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Oida S., Ichijo H., Iimura T., Maruoka Y., Amagasa T., Sasaki S. Molecular cloning of rat bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type IA receptor and its expression during ectopic bone formation induced by BMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Oct 14;204(1):203–209. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanno T. [Experimental study on the spinal lesions in hyperostotic mouse (twy/twy): special reference to the pathogenesis of the ossification of the spinal ligaments and to the action of ethane-1-hydroxy-1, 1-diphosphonate (EHDP)]. Nihon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi. 1992 Oct;66(10):1073–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terayama K. Genetic studies on ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1989 Nov;14(11):1184–1191. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198911000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen G., Woolf T., Whitman M., Sokol S., Vaughan J., Vale W., Melton D. A. Activins are expressed early in Xenopus embryogenesis and can induce axial mesoderm and anterior structures. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):485–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90445-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida K., Mathews L. S., Vale W. W. Cloning and characterization of a transmembrane serine kinase that acts as an activin type I receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11242–11246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida K., Vaughan J. M., Wiater E., Gaddy-Kurten D., Vale W. W. Inactivation of activin-dependent transcription by kinase-deficient activin receptors. Endocrinology. 1995 Dec;136(12):5493–5503. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.12.7588300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuyama N. Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984 Apr;(184):71–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli A., Matzuk M. M., Gardner H. A., Lee K. F., Jaenisch R. Activin/inhibin beta B subunit gene disruption leads to defects in eyelid development and female reproduction. Genes Dev. 1994 Feb 15;8(4):414–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.4.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vukicevic S., Latin V., Chen P., Batorsky R., Reddi A. H., Sampath T. K. Localization of osteogenic protein-1 (bone morphogenetic protein-7) during human embryonic development: high affinity binding to basement membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jan 28;198(2):693–700. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vukicevic S., Luyten F. P., Reddi A. H. Stimulation of the expression of osteogenic and chondrogenic phenotypes in vitro by osteogenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8793–8797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltenberger J., Lundin L., Oberg K., Wilander E., Miyazono K., Heldin C. H., Funa K. Involvement of transforming growth factor-beta in the formation of fibrotic lesions in carcinoid heart disease. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jan;142(1):71–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. A., Rosen V., D'Alessandro J. S., Bauduy M., Cordes P., Harada T., Israel D. I., Hewick R. M., Kerns K. M., LaPan P. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein induces bone formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2220–2224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winnier G., Blessing M., Labosky P. A., Hogan B. L. Bone morphogenetic protein-4 is required for mesoderm formation and patterning in the mouse. Genes Dev. 1995 Sep 1;9(17):2105–2116. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.17.2105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J. M. Bone morphogenetic proteins. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1989;1(4):267–280. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(89)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J. M., Rosen V., Celeste A. J., Mitsock L. M., Whitters M. J., Kriz R. W., Hewick R. M., Wang E. A. Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1528–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.3201241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Ono T., Nishioka H. Effect of NaN3 on oxygen-dependent lethality of UV-A in Escherichia coli mutants lacking active oxygen-defence and DNA-repair systems. J Radiat Res. 1996 Mar;37(1):29–37. doi: 10.1269/jrr.37.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita H., ten Dijke P., Huylebroeck D., Sampath T. K., Andries M., Smith J. C., Heldin C. H., Miyazono K. Osteogenic protein-1 binds to activin type II receptors and induces certain activin-like effects. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;130(1):217–226. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Dijke P., Miyazono K., Heldin C. H. Signaling via hetero-oligomeric complexes of type I and type II serine/threonine kinase receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996 Apr;8(2):139–145. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(96)80058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Dijke P., Yamashita H., Ichijo H., Franzén P., Laiho M., Miyazono K., Heldin C. H. Characterization of type I receptors for transforming growth factor-beta and activin. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):101–104. doi: 10.1126/science.8140412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Dijke P., Yamashita H., Sampath T. K., Reddi A. H., Estevez M., Riddle D. L., Ichijo H., Heldin C. H., Miyazono K. Identification of type I receptors for osteogenic protein-1 and bone morphogenetic protein-4. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 24;269(25):16985–16988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]