Abstract
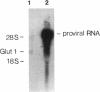
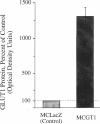
An environment of high glucose concentration stimulates the synthesis of extracellular matrix (ECM) in mesangial cell (MC) cultures. This may result from a similar increase in intracellular glucose concentration. We theorized that increased uptake, rather than glucose concentration per se is the major determinant of exaggerated ECM formation. To test this, we compared the effects of 35 mM glucose on ECM synthesis in normal MCs with those of 8 mM glucose in the same cells overexpressing the glucose transporter GLUT1 (MCGT1). Increasing medium glucose from 8 to 35 mM caused normal MCs to increase total collagen synthesis and catabolism, with a net 81-90% increase in accumulation. MCs transduced with the human GLUT1 gene (MCGT1) grown in 8 mM glucose had a 10-fold greater GLUT1 protein expression and a 1.9, 2.1, and 2.5-fold increase in cell myo-inositol, lactate production, and cell sorbitol content, respectively, as compared to control MCs transduced with bacterial beta-galactosidase (MCLacZ). MCGT1 also demonstrated increased glucose uptake (5-fold) and increased net utilization (43-fold), and greater synthesis of individual ECM components than MCLacZ. In addition, total collagen synthesis and catabolism were also enhanced with a net collagen accumulation 111-118% greater than controls. Thus, glucose transport activity is an important modulator of ECM formation by MCs; the presence of high extracellular glucose concentrations is not necessarily required for the stimulation of matrix synthesis.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abboud H. E. Platelet-derived growth factor and mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1992 Mar;41(3):581–583. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abboud H. E., Poptic E., DiCorleto P. Production of platelet-derived growth factorlike protein by rat mesangial cells in culture. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):675–683. doi: 10.1172/JCI113121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayo S. H., Radnik R. A., Garoni J. A., Glass W. F., 2nd, Kreisberg J. I. High glucose causes an increase in extracellular matrix proteins in cultured mesangial cells. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1339–1348. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayo S. H., Radnik R. A., Glass W. F., 2nd, Garoni J. A., Rampt E. R., Appling D. R., Kreisberg J. I. Increased extracellular matrix synthesis and mRNA in mesangial cells grown in high-glucose medium. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 2):F185–F191. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.2.F185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayo S. H., Radnik R., Garoni J. A., Troyer D. A., Kreisberg J. I. High glucose increases diacylglycerol mass and activates protein kinase C in mesangial cell cultures. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 2):F571–F577. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.4.F571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin S. A. Mammalian passive glucose transporters: members of an ubiquitous family of active and passive transport proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 8;1154(1):17–49. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(93)90015-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa J., Steffes M. W., Sutherland D. E., Connett J. E., Rao K. V., Mauer S. M. Effect of glycemic control on early diabetic renal lesions. A 5-year randomized controlled clinical trial of insulin-dependent diabetic kidney transplant recipients. JAMA. 1994 Aug 24;272(8):600–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilous R. W., Mauer S. M., Sutherland D. E., Najarian J. S., Goetz F. C., Steffes M. W. The effects of pancreas transplantation on the glomerular structure of renal allografts in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 13;321(2):80–85. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907133210204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilous R. W., Mauer S. M., Sutherland D. E., Steffes M. W. Mean glomerular volume and rate of development of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 1989 Sep;38(9):1142–1147. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.9.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch R. J., Woolf A. S., Fine L. G. Gene transfer into the mammalian kidney: direct retrovirus-transduction of regenerating tubular epithelial cells. Exp Nephrol. 1993 Jan-Feb;1(1):49–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatzilias A. A., Whiteside C. I. Cellular mechanisms of glucose-induced myo-inositol transport upregulation in rat mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 Sep;267(3 Pt 2):F459–F466. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.267.3.F459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi M. E., Kim E. G., Huang Q., Ballermann B. J. Rat mesangial cell hypertrophy in response to transforming growth factor-beta 1. Kidney Int. 1993 Nov;44(5):948–958. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Dumler F., Sastry K. S., Verghese C. P., Levin N. W. Effects of early diabetes on uridine diphosphosugar synthesis in the rat renal cortex. Kidney Int. 1982 May;21(5):676–682. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., DeRubertis F. R. Protein kinase C is activated in glomeruli from streptozotocin diabetic rats. Possible mediation by glucose. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1667–1675. doi: 10.1172/JCI114066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danne T., Spiro M. J., Spiro R. G. Effect of high glucose on type IV collagen production by cultured glomerular epithelial, endothelial, and mesangial cells. Diabetes. 1993 Jan;42(1):170–177. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.1.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi E., Shibata D., Matoba T. Modified colorimetric ninhydrin methods for peptidase assay. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):173–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumler F., Cortes P. Uracil ribonucleotide metabolism in rat and human glomerular epithelial and mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):C712–C718. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.6.C712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floege J., Eng E., Young B. A., Alpers C. E., Barrett T. B., Bowen-Pope D. F., Johnson R. J. Infusion of platelet-derived growth factor or basic fibroblast growth factor induces selective glomerular mesangial cell proliferation and matrix accumulation in rats. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2952–2962. doi: 10.1172/JCI116918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O., Geddes T. J. Reciprocal regulation of adipogenesis by Myc and C/EBP alpha. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):379–382. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O., Paielli D. L., Gilbert J. D. Ectopic expression of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha promotes the adipogenic program in a variety of mouse fibroblastic cells. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 15;8(14):1654–1663. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.14.1654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fumo P., Kuncio G. S., Ziyadeh F. N. PKC and high glucose stimulate collagen alpha 1 (IV) transcriptional activity in a reporter mesangial cell line. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 2):F632–F638. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.267.4.F632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert R. E., Tsalamandris C., Bach L. A., Panagiotopoulos S., O'Brien R. C., Allen T. J., Goodall I., Young V., Seeman E., Murray R. M. Long-term glycemic control and the rate of progression of early diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 1993 Oct;44(4):855–859. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Holman G. D. The glucose transporter family: structure, function and tissue-specific expression. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 15;295(Pt 2):329–341. doi: 10.1042/bj2950329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzman N. J., Crews F. T. Regulation of inositol transport by glucose and protein kinase C in mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1992 Jul;42(1):33–40. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haneda M., Kikkawa R., Horide N., Togawa M., Koya D., Kajiwara N., Ooshima A., Shigeta Y. Glucose enhances type IV collagen production in cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells. Diabetologia. 1991 Mar;34(3):198–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00418276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. A., Buxton J. M., Clancy B. M., Czech M. P. Insulin regulation of hexose transport in mouse 3T3-L1 cells expressing the human HepG2 glucose transporter. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20106–20116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. A., Buxton J. M., Czech M. P. Suppressed intrinsic catalytic activity of GLUT1 glucose transporters in insulin-sensitive 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7839–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. A., Buxton J. M., Czech M. P. Suppressed intrinsic catalytic activity of GLUT1 glucose transporters in insulin-sensitive 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7839–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverty T. P., Kelly C. J., Hoyer J. R., Alvarez R., Neilson E. G. Tubular antigen-binding proteins repress transcription of type IV collagen in the autoimmune target epithelium of experimental interstitial nephritis. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):517–523. doi: 10.1172/JCI115615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraki Y., Rosen O. M., Birnbaum M. J. Growth factors rapidly induce expression of the glucose transporter gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13655–13662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hundal H. S., Ramlal T., Reyes R., Leiter L. A., Klip A. Cellular mechanism of metformin action involves glucose transporter translocation from an intracellular pool to the plasma membrane in L6 muscle cells. Endocrinology. 1992 Sep;131(3):1165–1173. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.3.1505458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman W. H., Colowick S. P. Stimulation of glucose uptake by transforming growth factor beta: evidence for the requirement of epidermal growth factor-receptor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1346–1349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaka Y., Fujiwara Y., Ueda N., Kaneda Y., Kamada T., Imai E. Glomerulosclerosis induced by in vivo transfection of transforming growth factor-beta or platelet-derived growth factor gene into the rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2597–2601. doi: 10.1172/JCI116874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B. Facilitative glucose transporters: regulatory mechanisms and dysregulation in diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1367–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI115724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser N., Sasson S., Feener E. P., Boukobza-Vardi N., Higashi S., Moller D. E., Davidheiser S., Przybylski R. J., King G. L. Differential regulation of glucose transport and transporters by glucose in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Diabetes. 1993 Jan;42(1):80–89. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaname S., Uchida S., Ogata E., Kurokawa K. Autocrine secretion of transforming growth factor-beta in cultured rat mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1992 Dec;42(6):1319–1327. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa T., Tanaka M., Akamatsu Y. Regulation of glucose transport activity and expression of glucose transporter mRNA by serum, growth factors and phorbol ester in quiescent mouse fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 27;980(1):100–108. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Tsakiridis T., Marette A., Ortiz P. A. Regulation of expression of glucose transporters by glucose: a review of studies in vivo and in cell cultures. FASEB J. 1994 Jan;8(1):43–53. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.1.8299889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I., Ayo S. H. The glomerular mesangium in diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 1993 Jan;43(1):109–113. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I. Hyperglycemia and microangiopathy. Direct regulation by glucose of microvascular cells. Lab Invest. 1992 Oct;67(4):416–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I., Radnik R. A., Ayo S. H., Garoni J., Saikumar P. High glucose elevates c-fos and c-jun transcripts and proteins in mesangial cell cultures. Kidney Int. 1994 Jul;46(1):105–112. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loike J. D., Cao L., Brett J., Ogawa S., Silverstein S. C., Stern D. Hypoxia induces glucose transporter expression in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 1):C326–C333. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.2.C326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marette A., Richardson J. M., Ramlal T., Balon T. W., Vranic M., Pessin J. E., Klip A. Abundance, localization, and insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters in red and white muscle. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 1):C443–C452. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.2.C443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauer S. M., Steffes M. W., Ellis E. N., Sutherland D. E., Brown D. M., Goetz F. C. Structural-functional relationships in diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1143–1155. doi: 10.1172/JCI111523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., Maegawa H., Lee J., Dull T. J., Ulrich A., Olefsky J. M. A mutant insulin receptor with defective tyrosine kinase displays no biologic activity and does not undergo endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14663–14671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrall N. W., Wakelam M. J., Plevin R., Gould G. W. Insulin and platelet-derived growth factor acutely stimulate glucose transport in 3T3-L1 fibroblasts independently of protein kinase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 6;1177(2):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90040-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahman N. S., Jr, Leonhart K. L., Cosio F. G., Hebert C. L. Effects of high glucose on cellular proliferation and fibronectin production by cultured human mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1992 Feb;41(2):396–402. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda S., Languino L. R., Ruoslahti E., Border W. A. Elevated expression of transforming growth factor-beta and proteoglycan production in experimental glomerulonephritis. Possible role in expansion of the mesangial extracellular matrix. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):453–462. doi: 10.1172/JCI114731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen D. R., Peltonen J., Jaakkola S., Chu M. L., Uitto J. Collagen gene expression by cultured human skin fibroblasts. Abundant steady-state levels of type VI procollagen messenger RNAs. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):791–795. doi: 10.1172/JCI113959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen J., Ross J., Rabkin R. Effect of insulin therapy on established diabetic nephropathy in rats. Diabetes. 1988 Oct;37(10):1346–1350. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.10.1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan S. H., Varani J., Smith D. Rat lung fibroblast collagen metabolism in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):241–247. doi: 10.1172/JCI111953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasch R. Prevention of diabetic glomerulopathy in streptozotocin diabetic rats by insulin treatment. The mesangial regions. Diabetologia. 1979 Oct;17(4):243–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01235861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riser B. L., Cortes P., Zhao X., Bernstein J., Dumler F., Narins R. G. Intraglomerular pressure and mesangial stretching stimulate extracellular matrix formation in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1932–1943. doi: 10.1172/JCI116071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins B. J., Morrison E. D., Usher P., Flier J. S. Platelet-derived growth factor regulates glucose transporter expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16523–16526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarabia V., Lam L., Burdett E., Leiter L. A., Klip A. Glucose transport in human skeletal muscle cells in culture. Stimulation by insulin and metformin. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1386–1395. doi: 10.1172/JCI116005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinman J. I., Brown D. M., Michael A. F. Collagen synthesis by human glomerular cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 3;542(1):128–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90239-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyer-Hansen K., Hansen J., Gundersen H. J. Renal hypertrophy in experimental diabetes. A morphometric study. Diabetologia. 1980 Jun;18(6):501–505. doi: 10.1007/BF00261707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Berk A. J., Berget S. M. Transcription maps of adenovirus. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):750–768. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shetty M., Ismail-Beigi N., Loeb J. N., Ismail-Beigi F. Induction of GLUT1 mRNA in response to inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation. Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 1):C1224–C1229. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.5.C1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivitz W. I., DeSautel S. L., Kayano T., Bell G. I., Pessin J. E. Regulation of glucose transporter messenger RNA in insulin-deficient states. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):72–74. doi: 10.1038/340072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffes M. W., Bilous R. W., Sutherland D. E., Mauer S. M. Cell and matrix components of the glomerular mesangium in type I diabetes. Diabetes. 1992 Jun;41(6):679–684. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.6.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffes M. W., Brown D. M., Basgen J. M., Mauer S. M. Amelioration of mesangial volume and surface alterations following islet transplantation in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1980 Jul;29(7):509–515. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.7.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studer R. K., Craven P. A., DeRubertis F. R. Role for protein kinase C in the mediation of increased fibronectin accumulation by mesangial cells grown in high-glucose medium. Diabetes. 1993 Jan;42(1):118–126. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSANEV R., MARKOV G. G. Substances interfering with spectrophotometric estimation of nucleic acids and their elimination by the two-wavelength method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Aug 26;42:442–452. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90822-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Charron M. J., Lodish H. F. Molecular physiology of glucose transporters. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):209–218. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tordjman K. M., Leingang K. A., James D. E., Mueckler M. M. Differential regulation of two distinct glucose transporter species expressed in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: effect of chronic insulin and tolbutamide treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7761–7765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani J., Taylor C. G., Riser B., Shumaker D. K., Yeh K. Y., Dame M., Gibbs D. F., Todd R. F., 3rd, Dumler F., Bromberg J. Mesangial cell killing by leukocytes: role of leukocyte oxidants and proteolytic enzymes. Kidney Int. 1992 Nov;42(5):1169–1177. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. H., Moller D., Flier J. S., Nayak R. C., Smith R. J. Coordinate regulation of glucose transporter function, number, and gene expression by insulin and sulfonylureas in L6 rat skeletal muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):62–67. doi: 10.1172/JCI114170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf G., Sharma K., Chen Y., Ericksen M., Ziyadeh F. N. High glucose-induced proliferation in mesangial cells is reversed by autocrine TGF-beta. Kidney Int. 1992 Sep;42(3):647–656. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita E., Oguri K., Okayama E., Kawasaki K., Kobayashi S., Kihara I., Okayama M. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans synthesized by cultured mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):522–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziyadeh F. N., Sharma K., Ericksen M., Wolf G. Stimulation of collagen gene expression and protein synthesis in murine mesangial cells by high glucose is mediated by autocrine activation of transforming growth factor-beta. J Clin Invest. 1994 Feb;93(2):536–542. doi: 10.1172/JCI117004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]