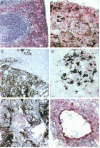
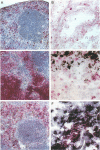
Abstract
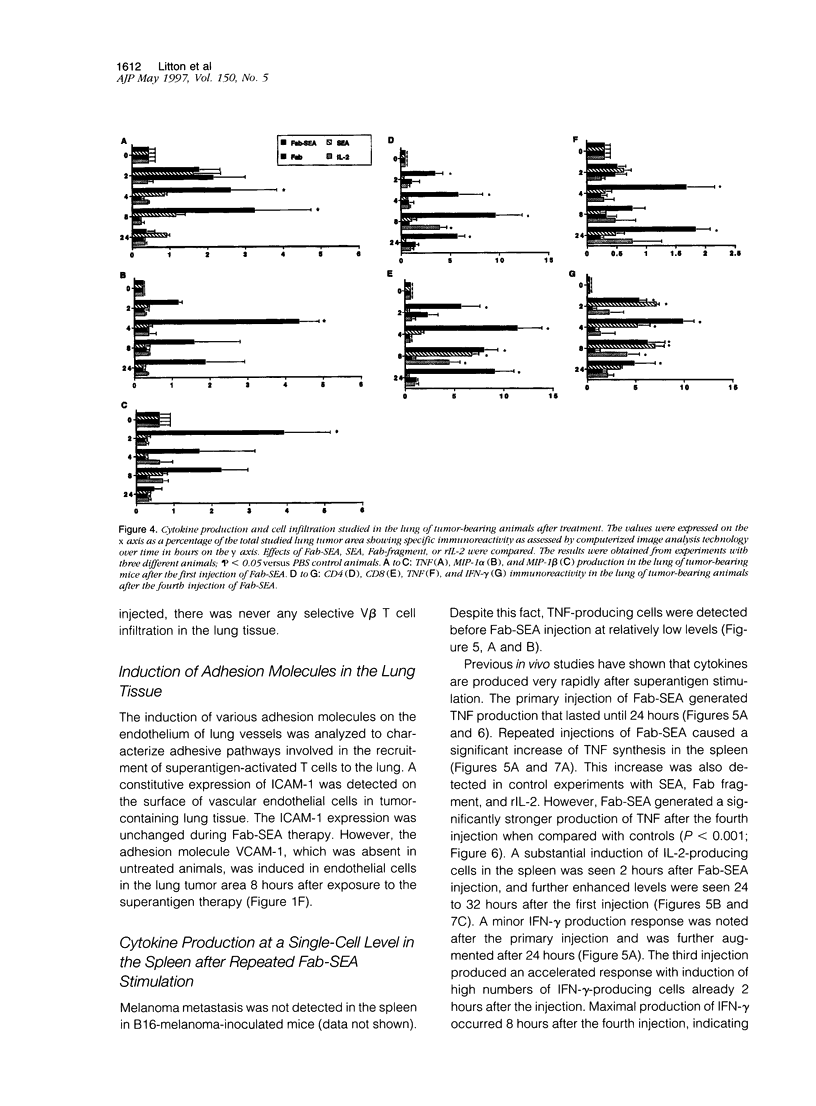
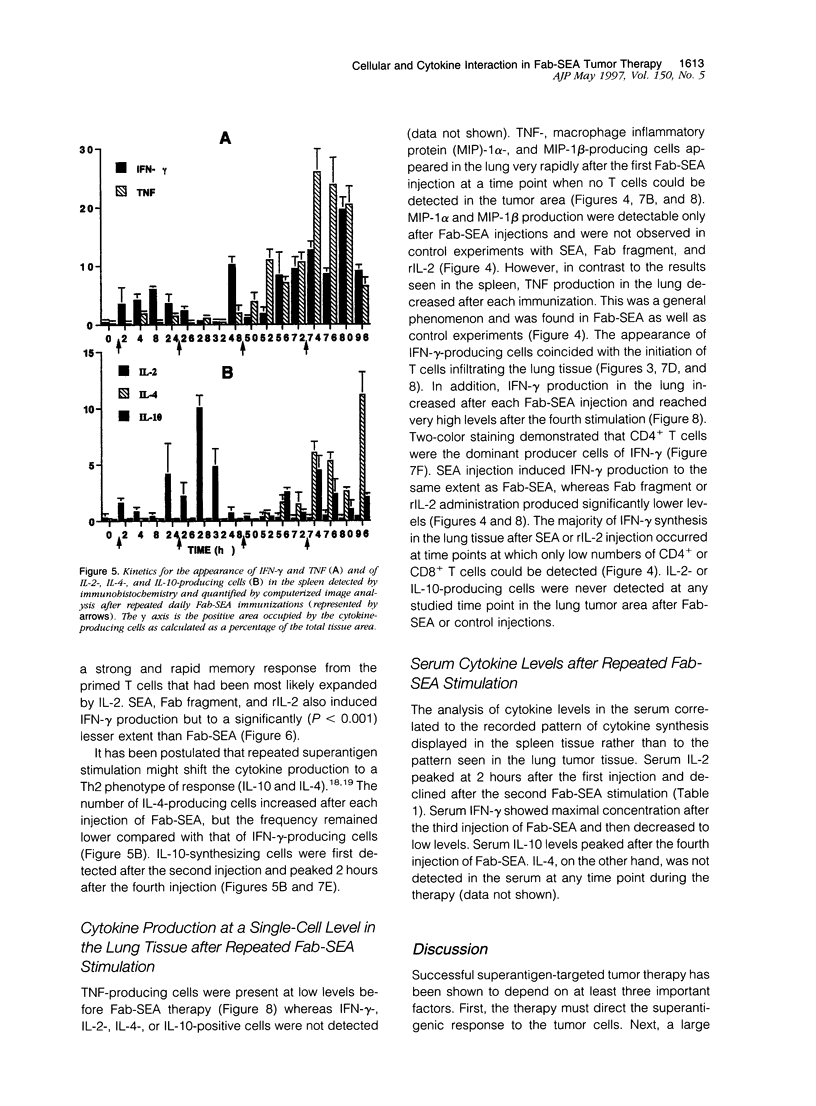
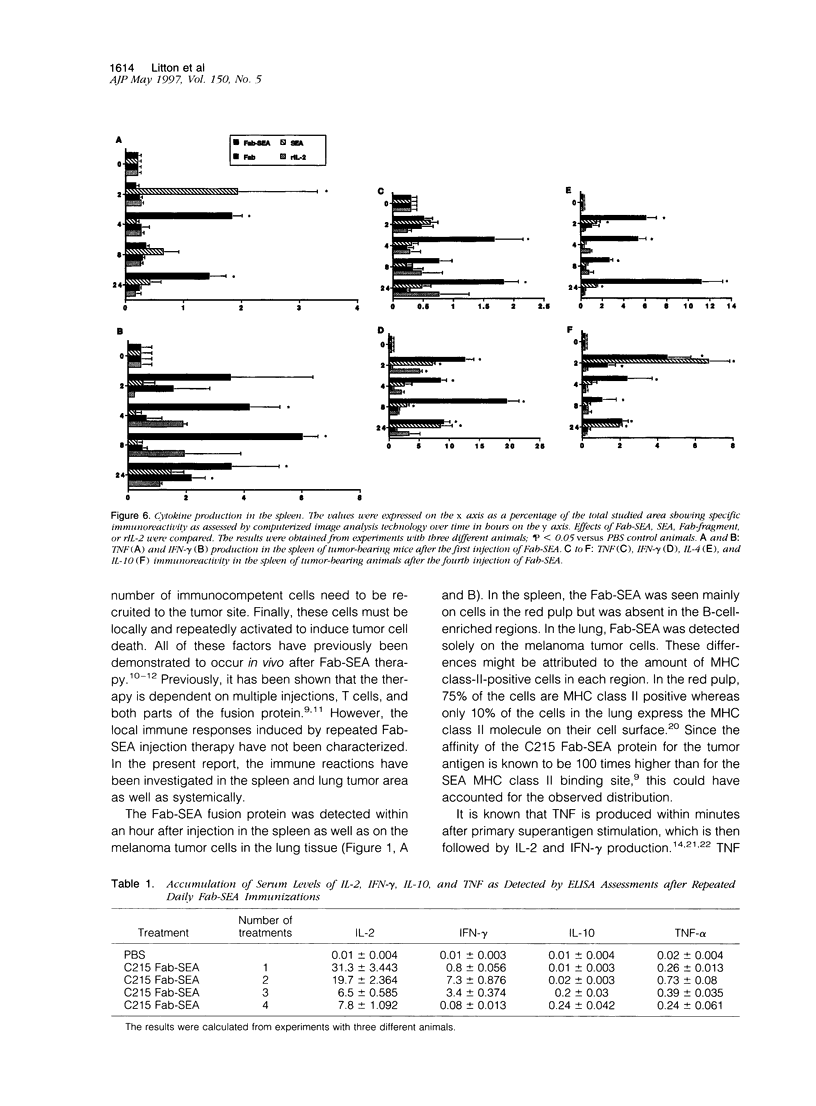
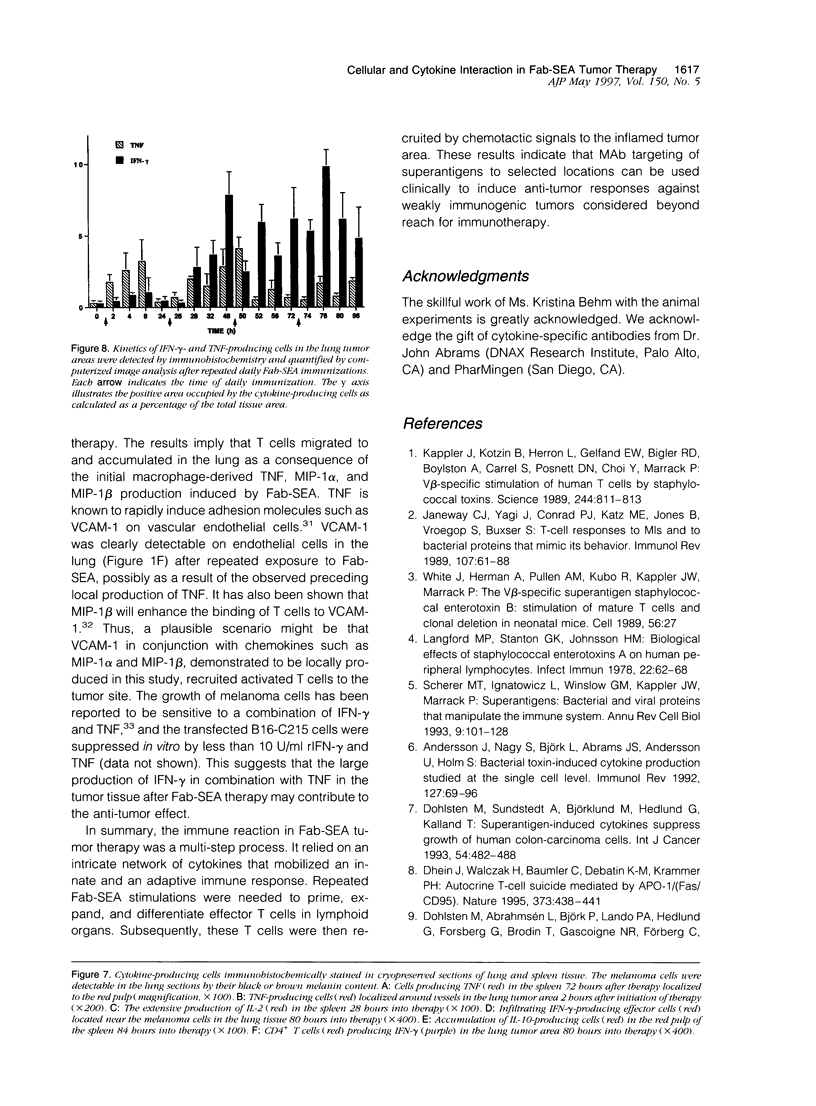
Repeated injections of a fusion protein containing the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) combined with a Fab fragment of a tumor-specific antibody is a highly efficient immunotherapy for mice expressing lung melanoma micrometastasis. In the present study, the systemic and local immune responses generated by this therapy were analyzed at a cellular level. Two distinct but coupled immune reactions occurred after repeated therapy. Tumor necrosis factor and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha and -1 beta were immediately synthesized, in the absence of T lymphocytes, at the local tumor site in the lung. This was followed by the induction of VCAM-1 adhesion molecule expression on pulmonary vascular endothelial cells. Concurrently, the early response in the spleen was characterized by the induction of selective T cells producing interleukin (IL)-2. The primed and expanded SEA-reactive V beta 3- and V beta 11-expressing T lymphocytes accumulated to the tumor area only after Fab-SEA therapy and were not present in the lung when SEA, Fab fragment, or recombinant IL-2 was injected. The tumor-infiltrating T cells produced large amounts of interferon-gamma, but no IL-2 or Th2 type of lymphokines were detected at the tumor site in the Fab-SEA-targeted antitumor immune response. These results emphasize the necessity to investigate several sites of antigen presentation to elucidate the effects of immunotherapy.
Full text
PDF


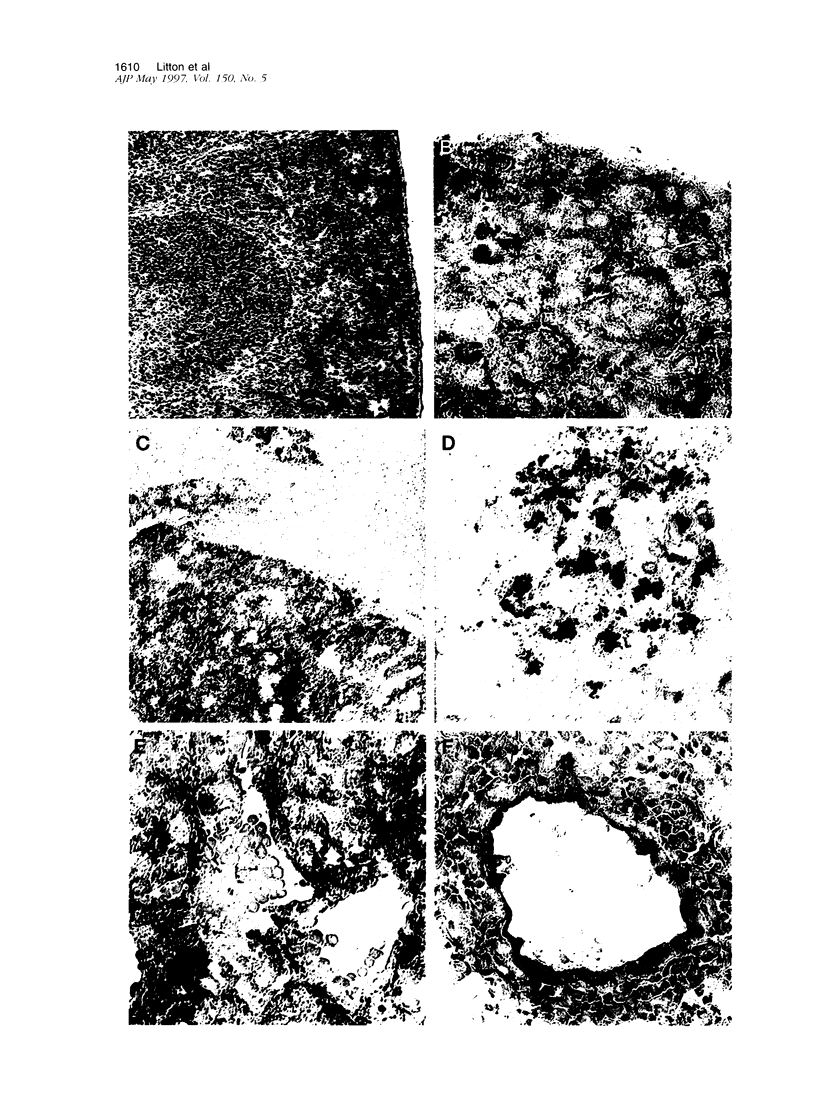
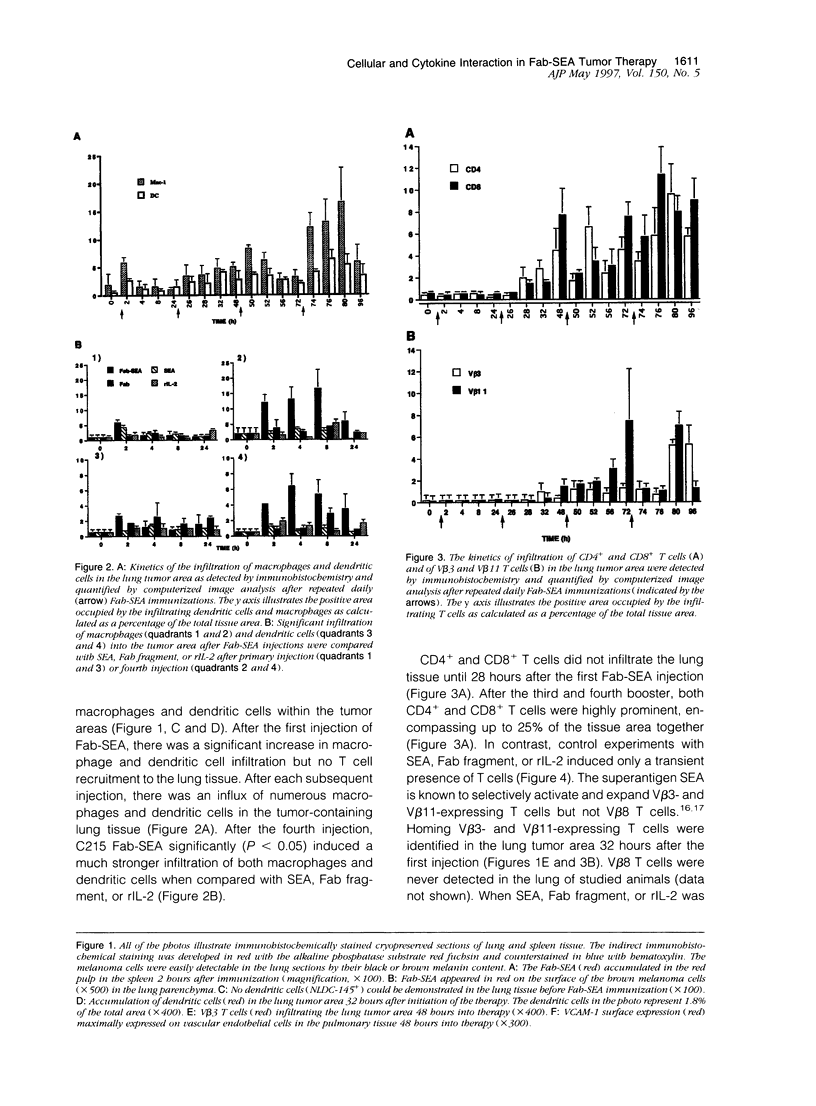


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Nagy S., Björk L., Abrams J., Holm S., Andersson U. Bacterial toxin-induced cytokine production studied at the single-cell level. Immunol Rev. 1992 Jun;127:69–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb01409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bette M., Schäfer M. K., van Rooijen N., Weihe E., Fleischer B. Distribution and kinetics of superantigen-induced cytokine gene expression in mouse spleen. J Exp Med. 1993 Nov 1;178(5):1531–1539. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhein J., Walczak H., Bäumler C., Debatin K. M., Krammer P. H. Autocrine T-cell suicide mediated by APO-1/(Fas/CD95) Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):438–441. doi: 10.1038/373438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Abrahmsén L., Björk P., Lando P. A., Hedlund G., Forsberg G., Brodin T., Gascoigne N. R., Förberg C., Lind P. Monoclonal antibody-superantigen fusion proteins: tumor-specific agents for T-cell-based tumor therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8945–8949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Björklund M., Sundstedt A., Hedlund G., Samson D., Kalland T. Immunopharmacology of the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin A in T-cell receptor V beta 3 transgenic mice. Immunology. 1993 Aug;79(4):520–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Hansson J., Ohlsson L., Litton M., Kalland T. Antibody-targeted superantigens are potent inducers of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Oct 10;92(21):9791–9795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.21.9791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Lando P. A., Björk P., Abrahmsén L., Ohlsson L., Lind P., Kalland T. Immunotherapy of human colon cancer by antibody-targeted superantigens. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1995 Sep;41(3):162–168. doi: 10.1007/BF01521342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Sundstedt A., Björklund M., Hedlund G., Kalland T. Superantigen-induced cytokines suppress growth of human colon-carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1993 May 28;54(3):482–488. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910540321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florquin S., Amraoui Z., Goldman M. T cells made deficient in interleukin-2 production by exposure to staphylococcal enterotoxin B in vivo are primed for interferon-gamma and interleukin-10 secretion. Eur J Immunol. 1995 May;25(5):1148–1153. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskins K. The T-cell receptor for antigen. Year Immunol. 1985:74–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann T., Baschieri S., Lees R. K., MacDonald H. R. In vivo responses of CD4+ and CD8+ cells to bacterial superantigens. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jul;22(7):1935–1938. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson K. R., Robinson H., Fraser J. D. Two adjacent residues in staphylococcal enterotoxins A and E determine T cell receptor V beta specificity. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):175–184. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Yagi J., Conrad P. J., Katz M. E., Jones B., Vroegop S., Buxser S. T-cell responses to Mls and to bacterial proteins that mimic its behavior. Immunol Rev. 1989 Feb;107:61–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J., Kotzin B., Herron L., Gelfand E. W., Bigler R. D., Boylston A., Carrel S., Posnett D. N., Choi Y., Marrack P. V beta-specific stimulation of human T cells by staphylococcal toxins. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):811–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2524876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe Y., Ochi A. Selective anergy of V beta 8+,CD4+ T cells in Staphylococcus enterotoxin B-primed mice. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1065–1070. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford M. P., Stanton G. J., Johnson H. M. Biological effects of staphylococcal enterotoxin A on human peripheral lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):62–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.62-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litton M. J., Dohlsten M., Lando P. A., Kalland T., Ohlsson L., Andersson J., Andersson U. Antibody-targeted superantigen therapy induces tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, excessive cytokine production, and apoptosis in human colon carcinoma. Eur J Immunol. 1996 Jan;26(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litton M. J., Sander B., Murphy E., O'Garra A., Abrams J. S. Early expression of cytokines in lymph nodes after treatment in vivo with Staphylococcus enterotoxin B. J Immunol Methods. 1994 Sep 30;175(1):47–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(94)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Baschieri S., Lees R. K. Clonal expansion precedes anergy and death of V beta 8+ peripheral T cells responding to staphylococcal enterotoxin B in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Aug;21(8):1963–1966. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehindate K., Thibodeau J., Dohlsten M., Kalland T., Sékaly R. P., Mourad W. Cross-linking of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules by staphylococcal enterotoxin A superantigen is a requirement for inflammatory cytokine gene expression. J Exp Med. 1995 Nov 1;182(5):1573–1577. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.5.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. E., Bevilacqua M. P. An inducible endothelial cell surface glycoprotein mediates melanoma adhesion. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.2588007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röcken M., Urban J., Shevach E. M. Antigen-specific activation, tolerization, and reactivation of the interleukin 4 pathway in vivo. J Exp Med. 1994 Jun 1;179(6):1885–1893. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.6.1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai M., Iigo M., Tamura T., Otsu A., Sasaki Y., Nakano H., Nakagawa K., Minato K., Ohe Y., Saijo N. Comparative study of the antitumor effect of two types of murine recombinant interferons, (beta) and (gamma), against B16-F10 melanoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1988;26(2):109–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00205602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer M. T., Ignatowicz L., Winslow G. M., Kappler J. W., Marrack P. Superantigens: bacterial and viral proteins that manipulate the immune system. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:101–128. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstedt A., Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Höidén I., Björklund M., Kalland T. Superantigens anergize cytokine production but not cytotoxicity in vivo. Immunology. 1994 May;82(1):117–125. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstedt A., Höidén I., Hansson J., Hedlund G., Kalland T., Dohlsten M. Superantigen-induced anergy in cytotoxic CD8+ T cells. J Immunol. 1995 Jun 15;154(12):6306–6313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto H., Yoshikai Y., Kishihara K., Matsuzaki G., Kuga H., Otani T., Nomoto K. Stimulation of all T cells bearing V beta 1, V beta 3, V beta 11 and V beta 12 by staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Mar;20(3):617–621. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Adams D. H., Hubscher S., Hirano H., Siebenlist U., Shaw S. T-cell adhesion induced by proteoglycan-immobilized cytokine MIP-1 beta. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):79–82. doi: 10.1038/361079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trede N. S., Geha R. S., Chatila T. Transcriptional activation of IL-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha genes by MHC class II ligands. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2310–2315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Herman A., Pullen A. M., Kubo R., Kappler J. W., Marrack P. The V beta-specific superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B: stimulation of mature T cells and clonal deletion in neonatal mice. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90980-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]