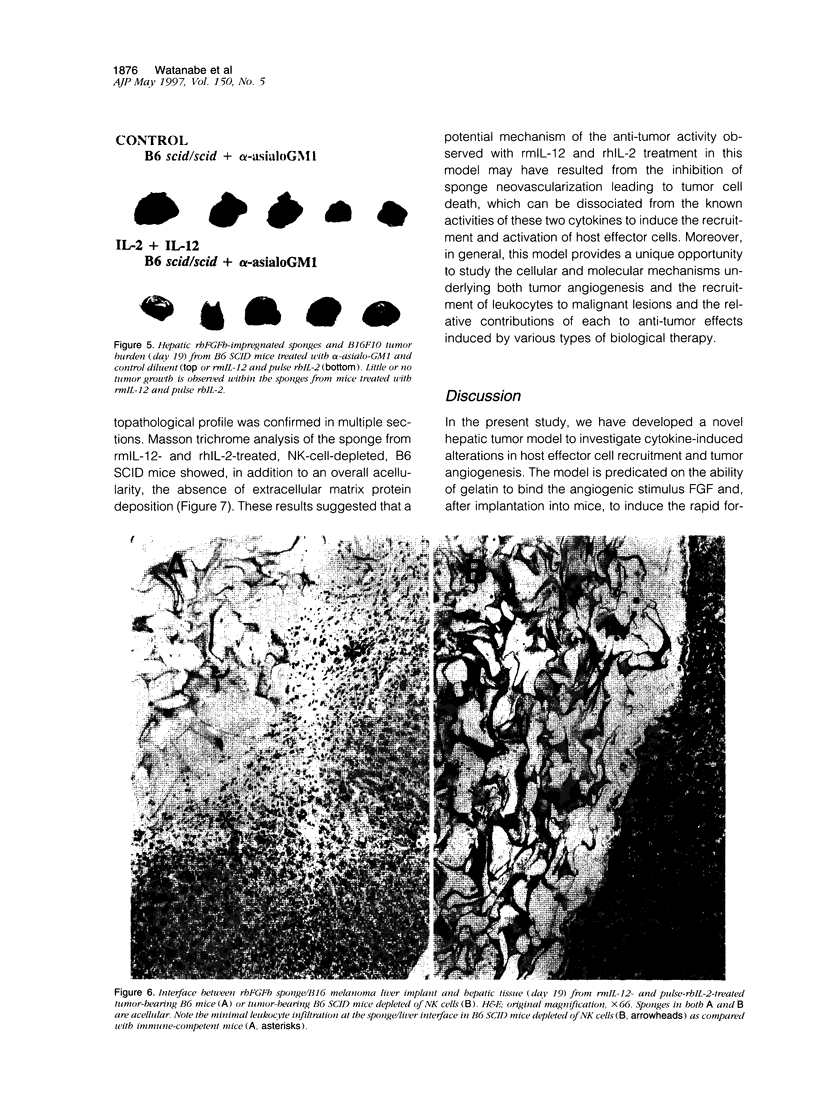
Abstract
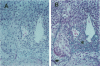
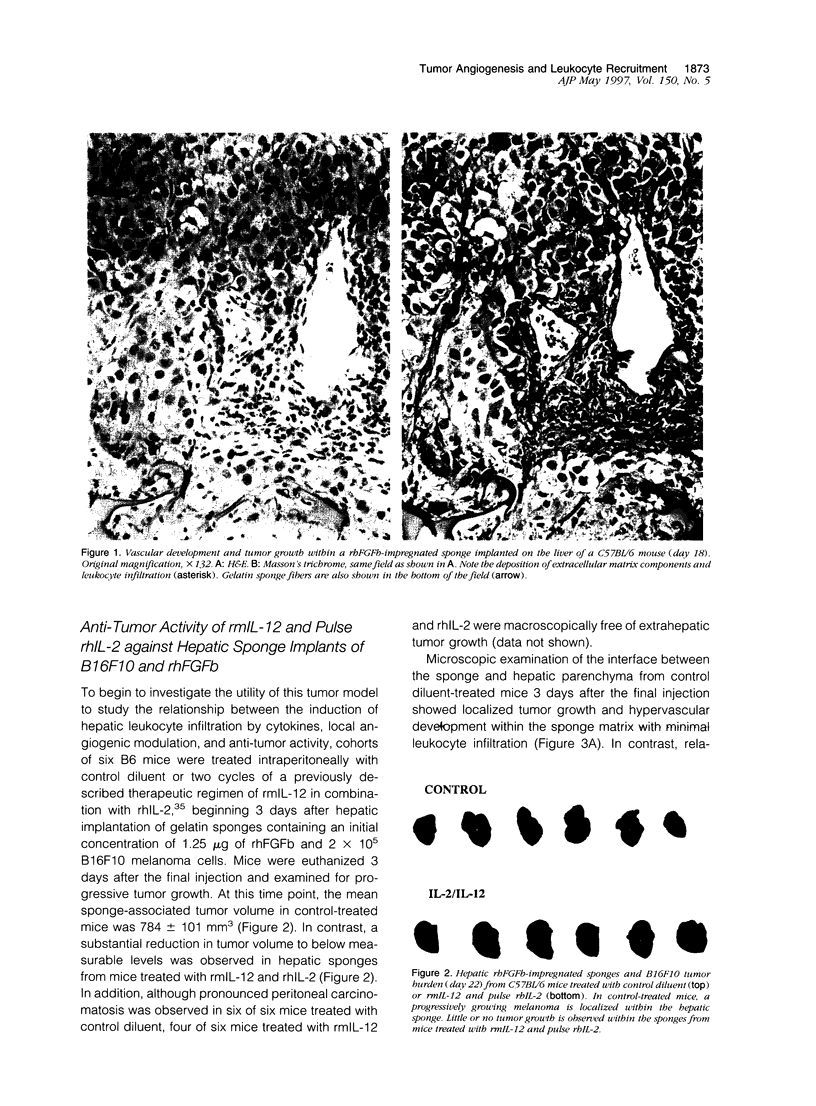
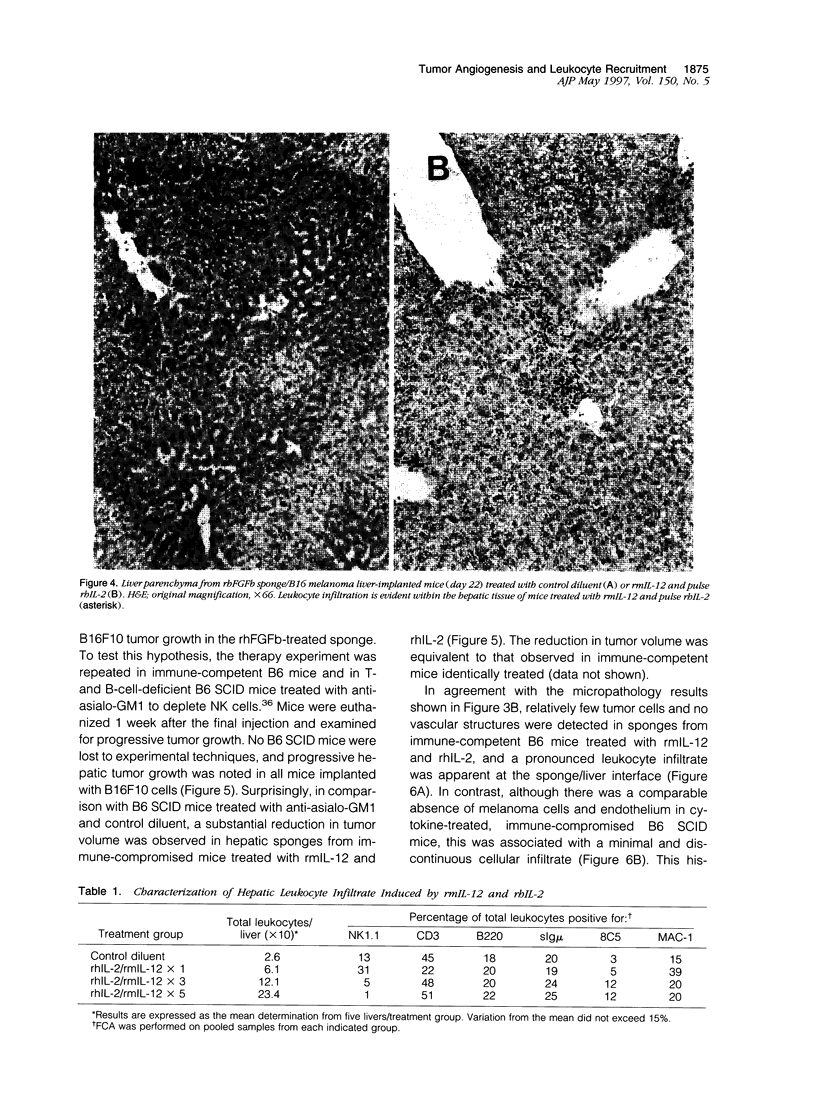
The regulation of tumor growth by cytokine-induced alterations in host effector cell recruitment and activation is intimately associated with leukocyte adhesion and angiogenic modulation. In the present study, we have developed a novel tumor model to investigate this complex series of events in response to cytokine administration. Gelatin sponges containing recombinant human basic fibroblast growth factor (rhFGFb) and B16F10 melanoma cells were implanted onto the serosal surface of the left lateral hepatic lobe in syngeneic C57BL/6 mice. The tumor model was characterized by progressive tumor growth initially localized within the sponge and the subsequent development of peritoneal carcinomatosis. Microscopic examination of the sponge matrix revealed well developed tumor-associated vascular structures and areas of endothelial cell activation as evidenced by leukocyte margination. Treatment of mice 3 days after sponge implantation with a therapeutic regimen consisting of pulse recombinant human interleukin-2 (rhIL-2) combined with recombinant murine interleukin-12 (rmIL-12) resulted in a marked hepatic mononuclear infiltrate and inhibition of tumor growth. In contrast to the control group, sponges from mice treated with rhIL-2/rmIL-12 demonstrated an overall lack of cellularity and vascular structure. The regimen of rhIL-2 in combination with rmIL-12 was equally effective against gelatin sponge implants of rhFGFb/B16F10 melanoma in SCID mice treated with anti-asialo-GM1 in the absence of a mononuclear infiltration, suggesting that T, B, and/or NK cells were not the principal mediators of the anti-tumor response in this tumor model. The absence of vascularity within the sponge after treatment suggests that a potential mechanism of rhIL-2/rmIL-12 anti-tumor activity is the inhibition of neovascular growth associated with the establishment of tumor lesions. This potential mechanism could be dissociated from the known activities of these two cytokines to induce the recruitment and activation of host effector cells. Moreover, this model provides a unique opportunity to study the cellular and molecular mechanism(s) underlying both tumor angiogenesis and leukocyte recruitment to metastatic lesions.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angiolillo A. L., Sgadari C., Taub D. D., Liao F., Farber J. M., Maheshwari S., Kleinman H. K., Reaman G. H., Tosato G. Human interferon-inducible protein 10 is a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis in vivo. J Exp Med. 1995 Jul 1;182(1):155–162. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basse P., Herberman R. B., Nannmark U., Johansson B. R., Hokland M., Wasserman K., Goldfarb R. H. Accumulation of adoptively transferred adherent, lymphokine-activated killer cells in murine metastases. J Exp Med. 1991 Aug 1;174(2):479–488. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Baruch A., Michiel D. F., Oppenheim J. J. Signals and receptors involved in recruitment of inflammatory cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 19;270(20):11703–11706. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.20.11703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergese S. D., Pelletier R. P., Ohye R. G., Vallera D. A., Orosz C. G. Treatment of mice with anti-CD3 mAb induces endothelial vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression. Transplantation. 1994 Mar 15;57(5):711–717. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199403150-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P. Endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecules. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:767–804. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.004003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Y., Chen C., Weatherbee J. A., Tsang M., Folkman J. gro-beta, a -C-X-C- chemokine, is an angiogenesis inhibitor that suppresses the growth of Lewis lung carcinoma in mice. J Exp Med. 1995 Dec 1;182(6):2069–2077. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.6.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlos T. M., Harlan J. M. Leukocyte-endothelial adhesion molecules. Blood. 1994 Oct 1;84(7):2068–2101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Parangi S., Tolentino M. J., Folkman J. A strategy to discover circulating angiogenesis inhibitors generated by human tumors. Cancer Res. 1995 Oct 1;55(19):4230–4233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claffey K. P., Brown L. F., del Aguila L. F., Tognazzi K., Yeo K. T., Manseau E. J., Dvorak H. F. Expression of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor by melanoma cells increases tumor growth, angiogenesis, and experimental metastasis. Cancer Res. 1996 Jan 1;56(1):172–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmen U., Bergese S. D., Qian S., Pelletier R. P., Wu H., Sedmak D. D., Fung J. J., Orosz C. G. Patterns of inflammatory vascular endothelial changes in murine liver grafts. Transplantation. 1995 Sep 27;60(6):577–584. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199509270-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Brown L. F., Detmar M., Dvorak A. M. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor, microvascular hyperpermeability, and angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1995 May;146(5):1029–1039. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Ellis L. M. The implications of angiogenesis for the biology and therapy of cancer metastasis. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):185–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Modulation of the organ microenvironment for treatment of cancer metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995 Nov 1;87(21):1588–1592. doi: 10.1093/jnci/87.21.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogler W. E., Volker K., McCormick K. L., Watanabe M., Ortaldo J. R., Wiltrout R. H. NK cell infiltration into lung, liver, and subcutaneous B16 melanoma is mediated by VCAM-1/VLA-4 interaction. J Immunol. 1996 Jun 15;156(12):4707–4714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1995 Jan;1(1):27–31. doi: 10.1038/nm0195-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis inhibitors generated by tumors. Mol Med. 1995 Jan;1(2):120–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander M., Brooks P. C., Shaffer R. W., Kincaid C. M., Varner J. A., Cheresh D. A. Definition of two angiogenic pathways by distinct alpha v integrins. Science. 1995 Dec 1;270(5241):1500–1502. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5241.1500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesel R. E., Maciag T. Molecular mechanisms of angiogenesis: fibroblast growth factor signal transduction. FASEB J. 1995 Jul;9(10):919–925. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.9.10.7542215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffioen A. W., Damen C. A., Blijham G. H., Groenewegen G. Tumor angiogenesis is accompanied by a decreased inflammatory response of tumor-associated endothelium. Blood. 1996 Jul 15;88(2):667–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N., Berlin C. Structure and function of adhesion receptors in leukocyte trafficking. Immunol Today. 1995 Jul;16(7):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kibbey M. C., Corcoran M. L., Wahl L. M., Kleinman H. K. Laminin SIKVAV peptide-induced angiogenesis in vivo is potentiated by neutrophils. J Cell Physiol. 1994 Jul;160(1):185–193. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041600121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Soker S. VEGF/VPF: the angiogenesis factor found? Curr Biol. 1993 Oct 1;3(10):699–702. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90073-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Halloran M. M., Haskell C. J., Shah M. R., Polverini P. J. Angiogenesis mediated by soluble forms of E-selectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Nature. 1995 Aug 10;376(6540):517–519. doi: 10.1038/376517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Polverini P. J., Kunkel S. L., Harlow L. A., DiPietro L. A., Elner V. M., Elner S. G., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 as a macrophage-derived mediator of angiogenesis. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1798–1801. doi: 10.1126/science.1281554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee M. J., Wiltrout R. H., McCormick K. L., Sayers T. J., Pilaro A. M. A method for obtaining and culturing large numbers of purified organ-derived murine endothelial cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1994 Apr;55(4):467–475. doi: 10.1002/jlb.55.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magram J., Connaughton S. E., Warrier R. R., Carvajal D. M., Wu C. Y., Ferrante J., Stewart C., Sarmiento U., Faherty D. A., Gately M. K. IL-12-deficient mice are defective in IFN gamma production and type 1 cytokine responses. Immunity. 1996 May;4(5):471–481. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melani C., Pupa S. M., Stoppacciaro A., Ménard S., Colnaghi M. I., Parmiani G., Colombo M. P. An in vivo model to compare human leukocyte infiltration in carcinoma xenografts producing different chemokines. Int J Cancer. 1995 Sep 4;62(5):572–578. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910620514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melder R. J., Koenig G. C., Witwer B. P., Safabakhsh N., Munn L. L., Jain R. K. During angiogenesis, vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor regulate natural killer cell adhesion to tumor endothelium. Nat Med. 1996 Sep;2(9):992–997. doi: 10.1038/nm0996-992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melder R. J., Salehi H. A., Jain R. K. Interaction of activated natural killer cells with normal and tumor vessels in cranial windows in mice. Microvasc Res. 1995 Jul;50(1):35–44. doi: 10.1006/mvre.1995.1036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly M. S., Holmgren L., Shing Y., Chen C., Rosenthal R. A., Moses M., Lane W. S., Cao Y., Sage E. H., Folkman J. Angiostatin: a novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the suppression of metastases by a Lewis lung carcinoma. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. A., Brown R. A., Kurt R. A., Akporiaye E. T. Studies of in vivo recruitment and activation of cytotoxic lymphocytes using a gelatin-sponge model of concomitant tumor immunity. Int J Cancer. 1995 Aug 9;62(4):421–427. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910620411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier R. P., Morgan C. J., Sedmak D. D., Miyake K., Kincade P. W., Ferguson R. M., Orosz C. G. Analysis of inflammatory endothelial changes, including VCAM-1 expression, in murine cardiac grafts. Transplantation. 1993 Feb;55(2):315–320. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199302000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilaro A. M., Taub D. D., McCormick K. L., Williams H. M., Sayers T. J., Fogler W. E., Wiltrout R. H. TNF-alpha is a principal cytokine involved in the recruitment of NK cells to liver parenchyma. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 1;153(1):333–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pili R., Guo Y., Chang J., Nakanishi H., Martin G. R., Passaniti A. Altered angiogenesis underlying age-dependent changes in tumor growth. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Sep 7;86(17):1303–1314. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.17.1303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sgadari C., Angiolillo A. L., Tosato G. Inhibition of angiogenesis by interleukin-12 is mediated by the interferon-inducible protein 10. Blood. 1996 May 1;87(9):3877–3882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., Elner V. M., Martonyi C. L., Koch A. E., Polverini P. J., Elner S. G. Interleukin-8. A corneal factor that induces neovascularization. Am J Pathol. 1992 Dec;141(6):1279–1284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Polverini P. J., Arenberg D. A., Kunkel S. L. The role of CXC chemokines as regulators of angiogenesis. Shock. 1995 Sep;4(3):155–160. doi: 10.1097/00024382-199509000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. A., Anderson K. D., DiPietro J. M., Zwiebel J. A., Zametta M., Anderson W. F., Maciag T. Site-directed neovessel formation in vivo. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1349–1352. doi: 10.1126/science.2457952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12: a proinflammatory cytokine with immunoregulatory functions that bridge innate resistance and antigen-specific adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voest E. E., Kenyon B. M., O'Reilly M. S., Truitt G., D'Amato R. J., Folkman J. Inhibition of angiogenesis in vivo by interleukin 12. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995 Apr 19;87(8):581–586. doi: 10.1093/jnci/87.8.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpert O. V., Stellmach V., Bouck N. The modulation of thrombospondin and other naturally occurring inhibitors of angiogenesis during tumor progression. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1995;36(2):119–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00666034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Ohtsuka K., Kimura M., Ikarashi Y., Ohmori K., Kusumi A., Ohteki T., Seki S., Abo T. Details of an isolation method for hepatic lymphocytes in mice. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Feb 5;146(2):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90223-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigginton J. M., Komschlies K. L., Back T. C., Franco J. L., Brunda M. J., Wiltrout R. H. Administration of interleukin 12 with pulse interleukin 2 and the rapid and complete eradication of murine renal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996 Jan 3;88(1):38–43. doi: 10.1093/jnci/88.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu N. Z., Klitzman B., Dodge R., Dewhirst M. W. Diminished leukocyte-endothelium interaction in tumor microvessels. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 1;52(15):4265–4268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]