Abstract
Protein kinase C (PKC) modulates growth, differentiation and apoptosis in a cell-specific fashion. Overexpression of PKC-alpha in MCF-7 breast cancer cells (MCF-7-PKC-alpha cell) leads to expression of a more transformed phenotype. The response of MCF-7 and MCF-7-PKC-alpha cells to phorbol esters (TPA) was examined. TPA-treated MCF-7 cells demonstrated a modest cytostatic response associated with a G1 arrest that was accompanied by Cip1 expression and retinoblastoma hypophosphorylation. While p53 was detected in MCF-7 cells, evidence for TPA-induced stimulation of p53 transcriptional activity was not evident. In contrast, TPA treatment induced death of MCF-7-PKC-alpha cells. Bryostatin 1, another PKC activator, exerted modest cytostatic effects on MCF-7 cells while producing a cytotoxic response at low doses in MCF-7-PKC-alpha cells that waned at higher concentrations. TPA-treated MCF-7-PKC-alpha cells accumulated in G2/M, did not express p53, displayed decreased Cip1 expression, and demonstrated a reduction in retinoblastoma hypophosphorylation. TPA-treated MCF-7-PKC-alpha cells expressed gadd-45 which occurred before the onset of apoptosis. Thus, alterations in the PKC pathway can modulate the decision of a breast cancer cell to undergo death or differentiation. In addition, these data show that PKC activation can induce expression of gadd45 in a p53-independent fashion.
Full text
PDF


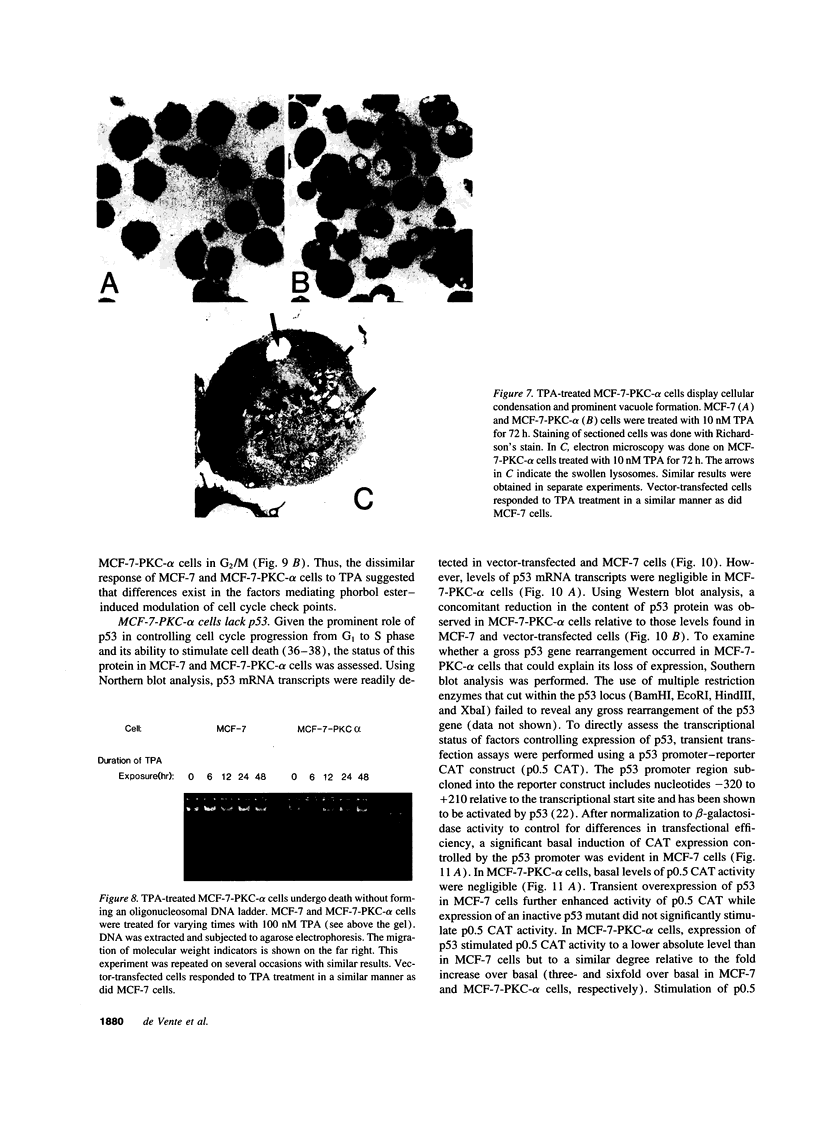
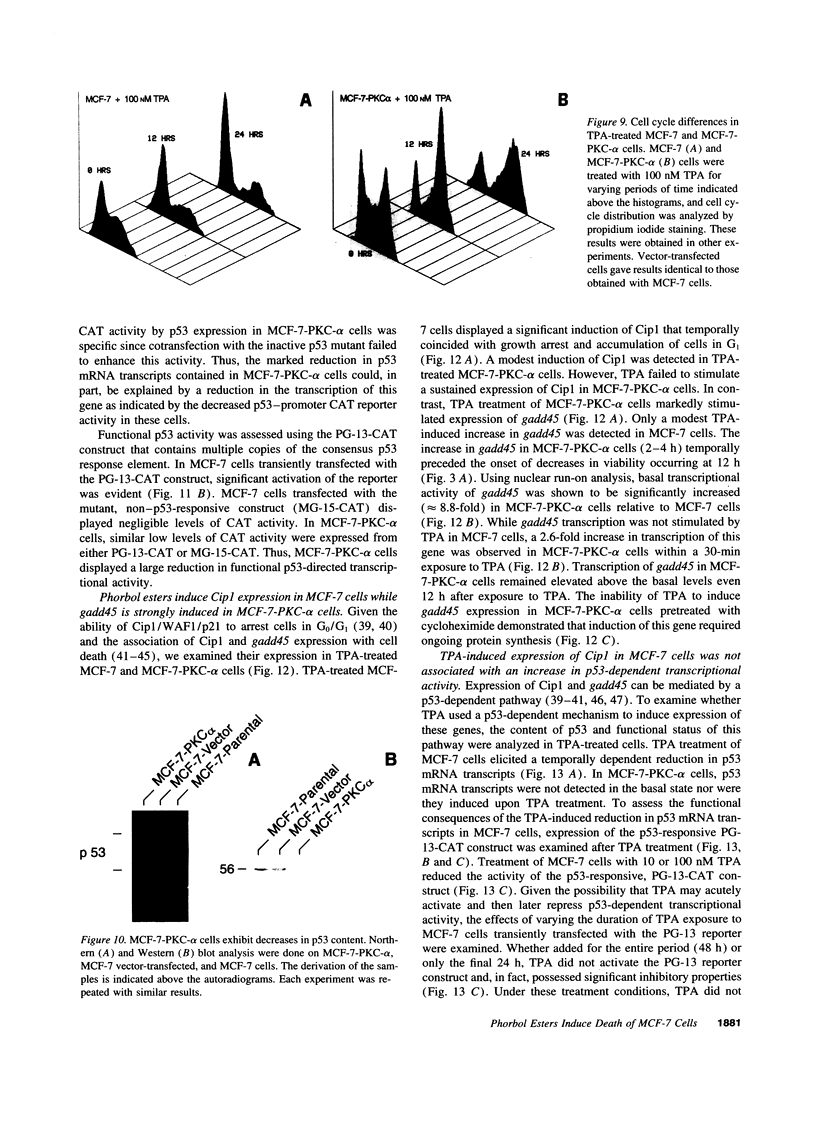
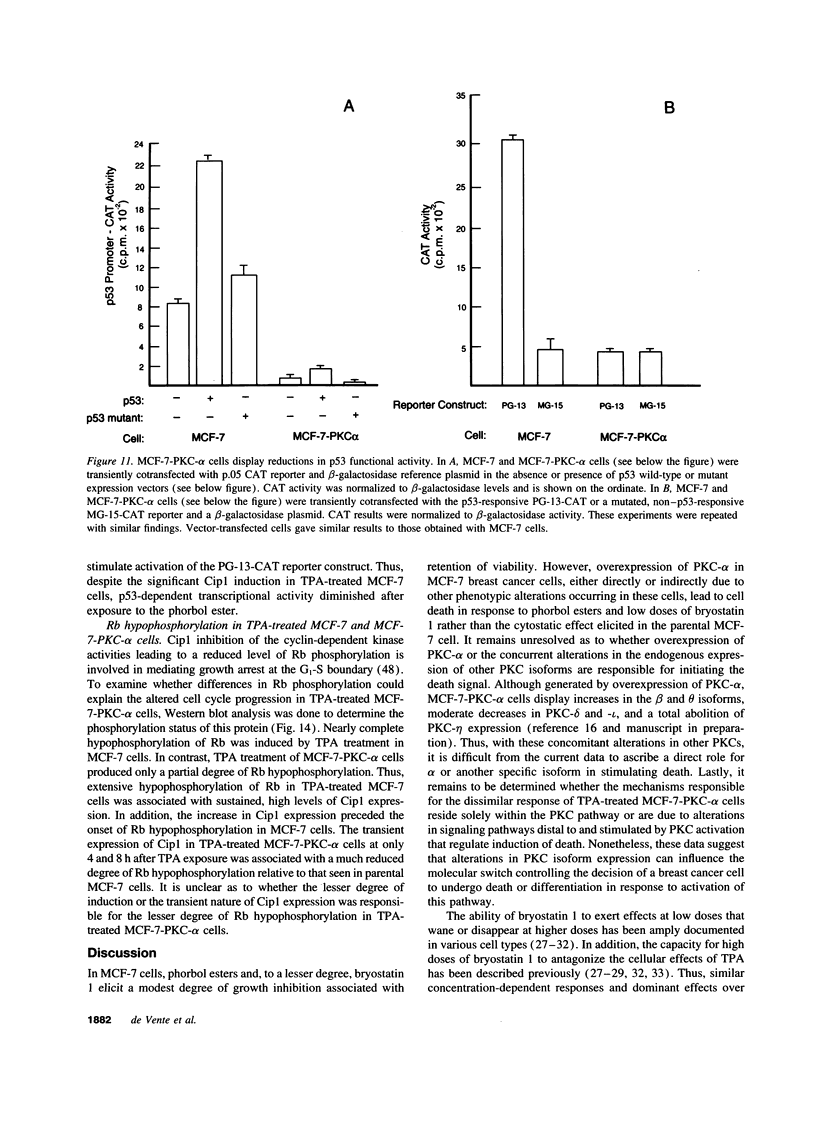

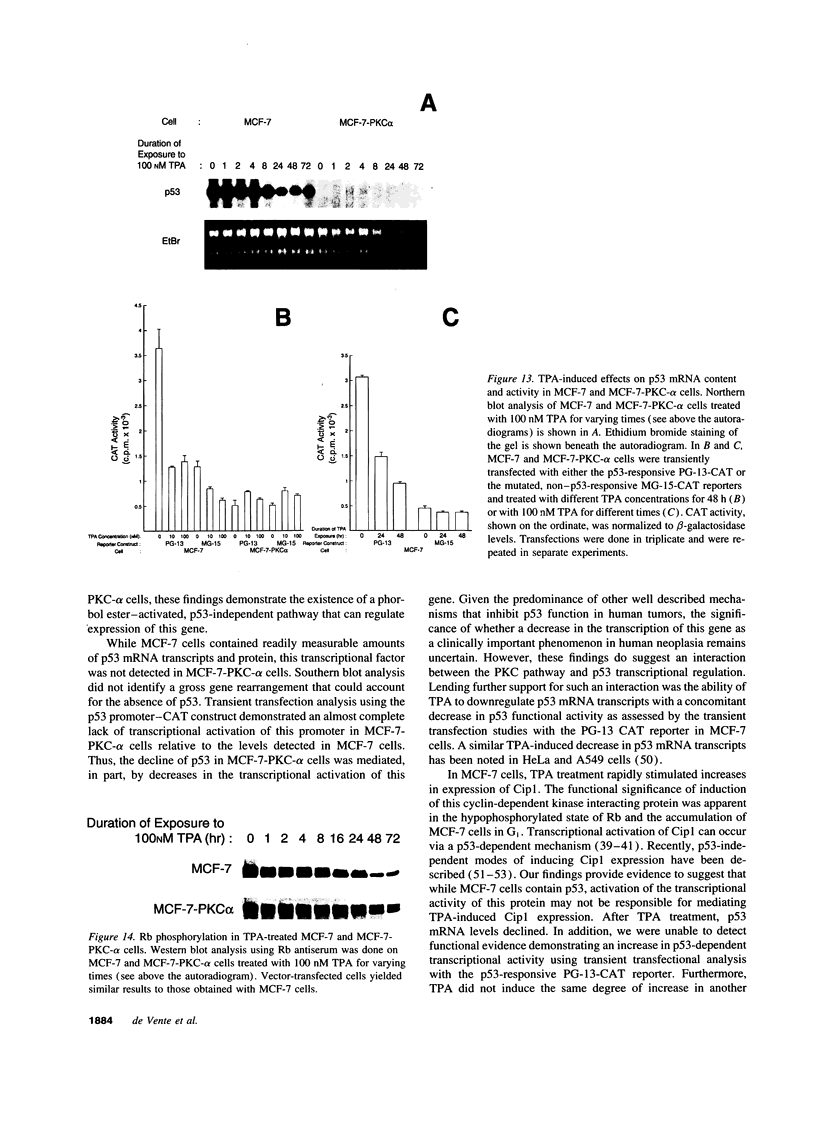


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki S., Simada Y., Kaji K., Hayashi H. Role of protein kinase C in the inhibition by fibroblast growth factor of apoptosis in serum-depleted endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1081–1085. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91557-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borner C., Wyss R., Regazzi R., Eppenberger U., Fabbro D. Immunological quantitation of phospholipid/Ca2+-dependent protein kinase of human mammary carcinoma cells: inverse relationship to estrogen receptors. Int J Cancer. 1987 Sep 15;40(3):344–348. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Purdie C. A., Harrison D. J., Morris R. G., Bird C. C., Hooper M. L., Wyllie A. H. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):849–852. doi: 10.1038/362849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale I. L., Gescher A. Effects of activators of protein kinase C, including bryostatins 1 and 2, on the growth of A549 human lung carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1989 Jan 15;43(1):158–163. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz Z., Bruno S., Del Bino G., Gorczyca W., Hotz M. A., Lassota P., Traganos F. Features of apoptotic cells measured by flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1992;13(8):795–808. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990130802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker L. V., Parker P. J. Protein kinase C--a question of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabbro D., Regazzi R., Costa S. D., Borner C., Eppenberger U. Protein kinase C desensitization by phorbol esters and its impact on growth of human breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 26;135(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90943-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes I. J., Zalewski P. D., Giannakis C., Cowled P. A. Induction of apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and its prevention by phorbol ester. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Feb;198(2):367–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90393-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Jackman J., Hollander M. C., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Genotoxic-stress-response genes and growth-arrest genes. gadd, MyD, and other genes induced by treatments eliciting growth arrest. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Nov 21;663:139–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb38657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr Mammalian genes induced by radiation; activation of genes associated with growth control. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:507–526. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Blumberg P. M., Pettit G. R., Herald C. L., Shores R., Yuspa S. H. Bryostatin 1, an activator of protein kinase C, inhibits tumor promotion by phorbol esters in SENCAR mouse skin. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Sep;8(9):1343–1346. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.9.1343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B., Liebermann D. A. Molecular controls of apoptosis: differentiation/growth arrest primary response genes, proto-oncogenes, and tumor suppressor genes as positive & negative modulators. Oncogene. 1994 Jul;9(7):1807–1812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander M. C., Alamo I., Jackman J., Wang M. G., McBride O. W., Fornace A. J., Jr Analysis of the mammalian gadd45 gene and its response to DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24385–24393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug H., Sarre T. F. Protein kinase C isoenzymes: divergence in signal transduction? Biochem J. 1993 Apr 15;291(Pt 2):329–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2910329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isakov N., Galron D., Mustelin T., Pettit G. R., Altman A. Inhibition of phorbol ester-induced T cell proliferation by bryostatin is associated with rapid degradation of protein kinase C. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1195–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii H. H., Gobé G. C. Epstein-Barr virus infection is associated with increased apoptosis in untreated and phorbol ester-treated human Burkitt's lymphoma (AW-Ramos) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 May 14;192(3):1415–1423. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issandou M., Bayard F., Darbon J. M. Inhibition of MCF-7 cell growth by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate and 1,2-dioctanoyl-sn-glycerol: distinct effects on protein kinase C activity. Cancer Res. 1988 Dec 1;48(23):6943–6950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang H., Lin J., Su Z. Z., Collart F. R., Huberman E., Fisher P. B. Induction of differentiation in human promyelocytic HL-60 leukemia cells activates p21, WAF1/CIP1, expression in the absence of p53. Oncogene. 1994 Nov;9(11):3397–3406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. J., Prestigiacomo L. J., Tyler G., May W. S., Davidson N. E. Differential effects of bryostatin 1 and phorbol ester on human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1992 Mar 1;52(5):1278–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Reeves J. A., Ashendel C. L. Differing modulation of protein kinase C by bryostatin 1 and phorbol esters in JB6 mouse epidermal cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8437–8442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. A., Karaszkiewicz J. W., Anderson W. B. Elevated level of nuclear protein kinase C in multidrug-resistant MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 1;52(13):3750–3759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Schmitt E. M., Smith S. W., Osborne B. A., Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. doi: 10.1038/362847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Hartzell P., Jondal M., Orrenius S. Inhibition of DNA fragmentation in thymocytes and isolated thymocyte nuclei by agents that stimulate protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13399–13402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeall J., Sánchez A., Gray P. P., Chesterman C. N., Sleigh M. J. Hyperinducible gene expression from a metallothionein promoter containing additional metal-responsive elements. Gene. 1989 Mar 15;76(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michieli P., Chedid M., Lin D., Pierce J. H., Mercer W. E., Givol D. Induction of WAF1/CIP1 by a p53-independent pathway. Cancer Res. 1994 Jul 1;54(13):3391–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara K., Cao X. R., Yen A., Chandler S., Driscoll B., Murphree A. L., T'Ang A., Fung Y. K. Cell cycle-dependent regulation of phosphorylation of the human retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1300–1303. doi: 10.1126/science.2588006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti I., Migliorati G., Pagliacci M. C., Grignani F., Riccardi C. A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Jun 3;139(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90198-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brian C., Vogel V. G., Singletary S. E., Ward N. E. Elevated protein kinase C expression in human breast tumor biopsies relative to normal breast tissue. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 15;49(12):3215–3217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhammer F., Wilson J. W., Dive C., Morris I. D., Hickman J. A., Wakeling A. E., Walker P. R., Sikorska M. Apoptotic death in epithelial cells: cleavage of DNA to 300 and/or 50 kb fragments prior to or in the absence of internucleosomal fragmentation. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3679–3684. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papathanasiou M. A., Kerr N. C., Robbins J. H., McBride O. W., Alamo I., Jr, Barrett S. F., Hickson I. D., Fornace A. J., Jr Induction by ionizing radiation of the gadd45 gene in cultured human cells: lack of mediation by protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1009–1016. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip P. A., Rea D., Thavasu P., Carmichael J., Stuart N. S., Rockett H., Talbot D. C., Ganesan T., Pettit G. R., Balkwill F. Phase I study of bryostatin 1: assessment of interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha induction in vivo. The Cancer Research Campaign Phase I Committee. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Nov 17;85(22):1812–1818. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.22.1812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendiville J., Crowther D., Thatcher N., Woll P. J., Fox B. W., McGown A., Testa N., Stern P., McDermott R., Potter M. A phase I study of intravenous bryostatin 1 in patients with advanced cancer. Br J Cancer. 1993 Aug;68(2):418–424. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seynaeve C. M., Stetler-Stevenson M., Sebers S., Kaur G., Sausville E. A., Worland P. J. Cell cycle arrest and growth inhibition by the protein kinase antagonist UCN-01 in human breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1993 May 1;53(9):2081–2086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skouv J., Jensen P. O., Forchhammer J., Larsen J. K., Lund L. R. Tumor-promoting phorbol ester transiently down-modulates the p53 level and blocks the cell cycle. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Mar;5(3):329–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. A., Hoffman B., Iro A., Guillouf C., Liebermann D. A., el-Houseini M. E. Induction of p21 (WAF-1/CIP1) during differentiation. Oncogene. 1994 Nov;9(11):3389–3396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y., Pommier Y., Colburn N. H. Acquisition of a growth-inhibitory response to phorbol ester involves DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 1;52(7):1907–1915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szallasi Z., Denning M. F., Smith C. B., Dlugosz A. A., Yuspa S. H., Pettit G. R., Blumberg P. M. Bryostatin 1 protects protein kinase C-delta from down-regulation in mouse keratinocytes in parallel with its inhibition of phorbol ester-induced differentiation. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;46(5):840–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szallasi Z., Smith C. B., Pettit G. R., Blumberg P. M. Differential regulation of protein kinase C isozymes by bryostatin 1 and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):2118–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valette A., Gas N., Jozan S., Roubinet F., Dupont M. A., Bayard F. Influence of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate on proliferation and maturation of human breast carcinoma cells (MCF-7): relationship to cell cycle events. Cancer Res. 1987 Mar 15;47(6):1615–1620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ways D. K., Kukoly C. A., deVente J., Hooker J. L., Bryant W. O., Posekany K. J., Fletcher D. J., Cook P. P., Parker P. J. MCF-7 breast cancer cells transfected with protein kinase C-alpha exhibit altered expression of other protein kinase C isoforms and display a more aggressive neoplastic phenotype. J Clin Invest. 1995 Apr;95(4):1906–1915. doi: 10.1172/JCI117872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ways D. K., Qin W., Garris T. O., Chen J., Hao E., Cooper D. R., Usala S. J., Parker P. J., Cook P. P. Effects of chronic phorbol ester treatment on protein kinase C activity, content, and gene expression in the human monoblastoid U937 cell. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Feb;5(2):161–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan Q., Lord K. A., Alamo I., Jr, Hollander M. C., Carrier F., Ron D., Kohn K. W., Hoffman B., Liebermann D. A., Fornace A. J., Jr The gadd and MyD genes define a novel set of mammalian genes encoding acidic proteins that synergistically suppress cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2361–2371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vente J., Kiley S., Garris T., Bryant W., Hooker J., Posekany K., Parker P., Cook P., Fletcher D., Ways D. K. Phorbol ester treatment of U937 cells with altered protein kinase C content and distribution induces cell death rather than differentiation. Cell Growth Differ. 1995 Apr;6(4):371–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Harper J. W., O'Connor P. M., Velculescu V. E., Canman C. E., Jackman J., Pietenpol J. A., Burrell M., Hill D. E., Wang Y. WAF1/CIP1 is induced in p53-mediated G1 arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 1;54(5):1169–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]