Abstract
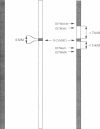
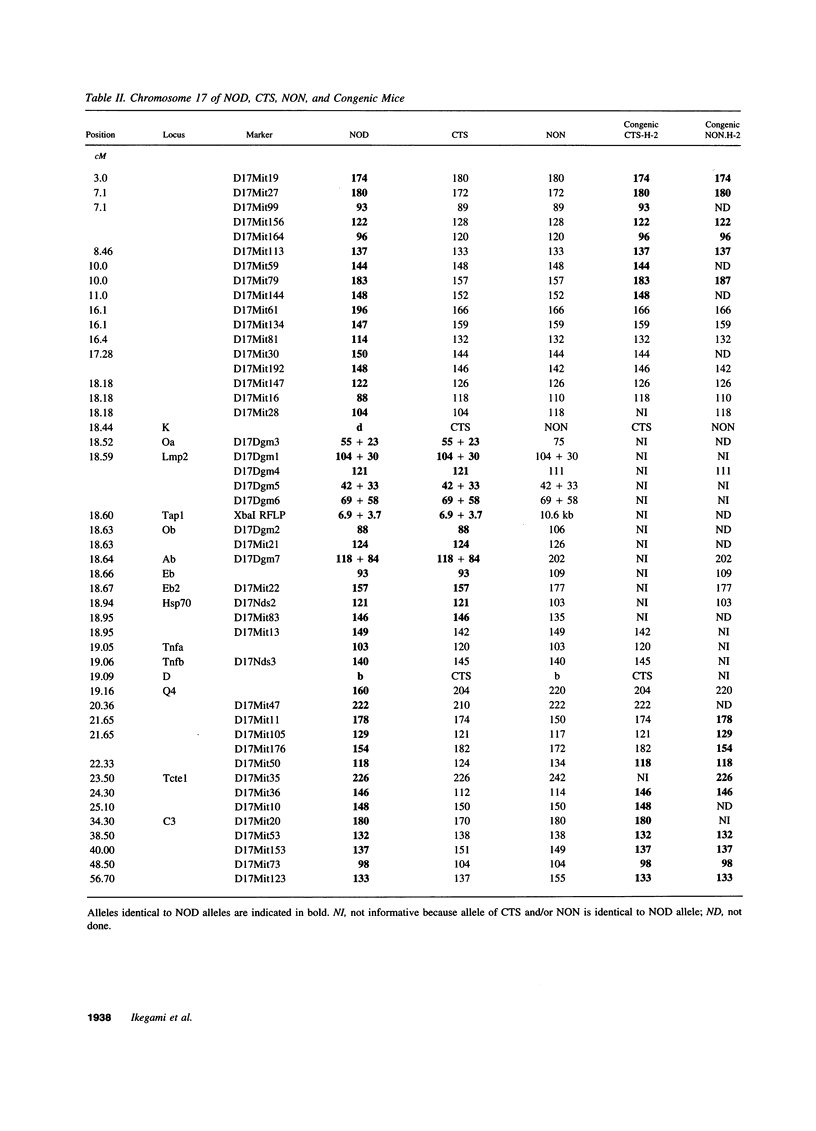
The number and exact locations of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-linked diabetogenic genes (Idd-1) are unknown because of strong linkage disequilibrium within the MHC. By using a congenic NOD mouse strain that possesses a recombinant MHC from a diabetes-resistant sister strain, we have now shown that Idd-1 consists of at least two components, one in and one outside the class II A and E regions. A new susceptibility gene (Idd-16) was mapped to the < 11-centiMorgan segment of chromosome 17 adjacent to, but distinct from, previously known Idd-1 candidates, class II A, E, and Tap genes. The coding sequences and splicing donor and acceptor sequences of the Tnfa gene, a candidate gene for Idd-16, were identical in the NOD, CTS, and BALB/c alleles, ruling out amino acid changes in the TNF molecule as a determinant of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus susceptibility. Our results not only map a new MHC-linked diabetogenic gene(s) but also suggest a new way to fine map disease susceptibility genes within a region where strong linkage disequilibrium exists.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acha-Orbea H., McDevitt H. O. The first external domain of the nonobese diabetic mouse class II I-A beta chain is unique. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2435–2439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño L., Eisenbarth G. S. Type-I diabetes: a chronic autoimmune disease of human, mouse, and rat. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:647–679. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. L., Kawaguchi Y., Bennett S. T., Copeman J. B., Cordell H. J., Pritchard L. E., Reed P. W., Gough S. C., Jenkins S. C., Palmer S. M. A genome-wide search for human type 1 diabetes susceptibility genes. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):130–136. doi: 10.1038/371130a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faustman D., Li X. P., Lin H. Y., Fu Y. E., Eisenbarth G., Avruch J., Guo J. Linkage of faulty major histocompatibility complex class I to autoimmune diabetes. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1756–1761. doi: 10.1126/science.1763324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forejt J., Artzt K., Barlow D. P., Hamvas R. M., Lindahl K. F., Lyon M. F., Klein J., Silver L. M. Mouse chromosome 17. Mamm Genome. 1994;5(Spec No):S238–S258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Palmer S. M., Rodrigues N. R., Cordell H. J., Hearne C. M., Cornall R. J., Prins J. B., McShane P., Lathrop G. M., Peterson L. B. Polygenic control of autoimmune diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):404–409. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Huez G., Beutler B. Interactive effects of the tumor necrosis factor promoter and 3'-untranslated regions. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):1843–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Buse J. B., Jackson R. A., Glimcher L., Dorf M. E., Minami M., Makino S., Moriwaki K., Kuzuya H., Imura H. The NOD mouse: recessive diabetogenic gene in the major histocompatibility complex. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):733–735. doi: 10.1126/science.3003909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami H., Eisenbarth G. S., Hattori M. Major histocompatibility complex-linked diabetogenic gene of the nonobese diabetic mouse. Analysis of genomic DNA amplified by the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):18–24. doi: 10.1172/JCI114410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami H., Makino S., Harada M., Eisenbarth G. S., Hattori M. The cataract Shionogi mouse, a sister strain of the non-obese diabetic mouse: similar class II but different class I gene products. Diabetologia. 1988 Apr;31(4):254–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00290594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., Aiso S., Michie S. A., McDevitt H. O., Acha-Orbea H. Prevention of diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice by tumor necrosis factor (TNF): similarities between TNF-alpha and interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongeneel C. V., Acha-Orbea H., Blankenstein T. A polymorphic microsatellite in the tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter identifies an allele unique to the NZW mouse strain. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):2141–2146. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson L., Peterson P. A. The alpha chain gene of H-2O has an unexpected location in the major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):477–483. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide Y., Yoshida T. O. The unique nucleotide sequence of the A beta gene in the NOD mouse is shared with its nondiabetic sister strains, the ILI and the CTS mouse. Int Immunol. 1990;2(2):189–192. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Hammerling U., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Sequence of gene and cDNA encoding murine major histocompatibility complex class II gene A beta 2. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14111–14119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li F., Guo J., Fu Y., Yan G., Faustman D. Abnormal class I assembly and peptide presentation in the nonobese diabetic mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11128–11132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love J. M., Knight A. M., McAleer M. A., Todd J. A. Towards construction of a high resolution map of the mouse genome using PCR-analysed microsatellites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4123–4130. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund T., O'Reilly L., Hutchings P., Kanagawa O., Simpson E., Gravely R., Chandler P., Dyson J., Picard J. K., Edwards A. Prevention of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in non-obese diabetic mice by transgenes encoding modified I-A beta-chain or normal I-E alpha-chain. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):727–729. doi: 10.1038/345727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Kunimoto K., Muraoka Y., Mizushima Y., Katagiri K., Tochino Y. Breeding of a non-obese, diabetic strain of mice. Jikken Dobutsu. 1980 Jan;29(1):1–13. doi: 10.1538/expanim1978.29.1_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrup-Poulsen T., Helqvist S., Wogensen L. D., Mølvig J., Pociot F., Johannesen J., Nerup J. Cytokine and free radicals as effector molecules in the destruction of pancreatic beta cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;164:169–193. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75741-9_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medema J. P., Streilein J. W., Graser R., Vincek V. Nucleotide sequence of the tumor necrosis factor: a gene in seven different inbred mouse strains. Immunogenetics. 1994;40(3):243–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00167088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki T., Matsuda Y., Toyonaga T., Miyazaki J., Yazaki Y., Yamamura K. Prevention of autoimmune insulitis in nonobese diabetic mice by expression of major histocompatibility complex class I Ld molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9519–9523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki T., Uno M., Uehira M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kimoto M., Nishimoto H., Miyazaki J., Yamamura K. Direct evidence for the contribution of the unique I-ANOD to the development of insulitis in non-obese diabetic mice. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):722–724. doi: 10.1038/345722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi K., Kobayashi T., Murase T., Nakatsuji T., Inoko H., Tsuji K., Kosaka K. Association of HLA-A24 with complete beta-cell destruction in IDDM. Diabetes. 1993 Jul;42(7):1086–1093. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.7.1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolin P. L., Pressey A., DeLarato N. H., Fischer P. A., Peterson L. B., Wicker L. S. I-E+ nonobese diabetic mice develop insulitis and diabetes. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):793–803. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prins J. B., Todd J. A., Rodrigues N. R., Ghosh S., Hogarth P. M., Wicker L. S., Gaffney E., Podolin P. L., Fischer P. A., Sirotina A. Linkage on chromosome 3 of autoimmune diabetes and defective Fc receptor for IgG in NOD mice. Science. 1993 Apr 30;260(5108):695–698. doi: 10.1126/science.8480181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochazka M., Leiter E. H., Serreze D. V., Coleman D. L. Three recessive loci required for insulin-dependent diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):286–289. doi: 10.1126/science.2885918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochazka M., Serreze D. V., Worthen S. M., Leiter E. H. Genetic control of diabetogenesis in NOD/Lt mice. Development and analysis of congenic stocks. Diabetes. 1989 Nov;38(11):1446–1455. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.11.1446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha B. K., Shields J. J., Miller R. D., Hansen T. H., Shreffler D. C. A highly polymorphic microsatellite in the class II Eb gene allows tracing of major histocompatibility complex evolution in mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5312–5316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh J., Seino H., Abo T., Tanaka S., Shintani S., Ohta S., Tamura K., Sawai T., Nobunaga T., Oteki T. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor alpha suppresses autoimmune diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1345–1348. doi: 10.1172/JCI114304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serreze D. V., Prochazka M., Reifsnyder P. C., Bridgett M. M., Leiter E. H. Use of recombinant congenic and congenic strains of NOD mice to identify a new insulin-dependent diabetes resistance gene. J Exp Med. 1994 Oct 1;180(4):1553–1558. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.4.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Shimizu N., Shiojiri S., Horiguchi S., Ito H. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene for mouse tumor necrosis factor. DNA. 1988 Apr;7(3):193–201. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroishi T., Hanzawa N., Sagai T., Ishiura M., Gojobori T., Steinmetz M., Moriwaki K. Recombinational hotspot specific to female meiosis in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Immunogenetics. 1990;31(2):79–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00661217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slattery R. M., Kjer-Nielsen L., Allison J., Charlton B., Mandel T. E., Miller J. F. Prevention of diabetes in non-obese diabetic I-Ak transgenic mice. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):724–726. doi: 10.1038/345724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson G., Robinson W. P., Kuhner M. K., Joe S., MacDonald M. J., Gottschall J. L., Barbosa J., Rich S. S., Bertrams J., Baur M. P. Genetic heterogeneity, modes of inheritance, and risk estimates for a joint study of Caucasians with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Dec;43(6):799–816. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Aitman T. J., Cornall R. J., Ghosh S., Hall J. R., Hearne C. M., Knight A. M., Love J. M., McAleer M. A., Prins J. B. Genetic analysis of autoimmune type 1 diabetes mellitus in mice. Nature. 1991 Jun 13;351(6327):542–547. doi: 10.1038/351542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Bell J. I., McDevitt H. O. HLA-DQ beta gene contributes to susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):599–604. doi: 10.1038/329599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicker L. S., Appel M. C., Dotta F., Pressey A., Miller B. J., DeLarato N. H., Fischer P. A., Boltz R. C., Jr, Peterson L. B. Autoimmune syndromes in major histocompatibility complex (MHC) congenic strains of nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. The NOD MHC is dominant for insulitis and cyclophosphamide-induced diabetes. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):67–77. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicker L. S., Miller B. J., Coker L. Z., McNally S. E., Scott S., Mullen Y., Appel M. C. Genetic control of diabetes and insulitis in the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1639–1654. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicker L. S., Todd J. A., Prins J. B., Podolin P. L., Renjilian R. J., Peterson L. B. Resistance alleles at two non-major histocompatibility complex-linked insulin-dependent diabetes loci on chromosome 3, Idd3 and Idd10, protect nonobese diabetic mice from diabetes. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1705–1713. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. D., Tisch R., Singer S. M., Cao Z. A., Liblau R. S., Schreiber R. D., McDevitt H. O. Effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha on insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in NOD mice. I. The early development of autoimmunity and the diabetogenic process. J Exp Med. 1994 Sep 1;180(3):995–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.3.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou P., Cao H., Smart M., David C. Molecular basis of genetic polymorphism in major histocompatibility complex-linked proteasome gene (Lmp-2). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2681–2684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou P., Zanelli E., Smart M., David C. Genomic organization and tissue expression of mouse proteasome gene Lmp-2. Genomics. 1993 Jun;16(3):664–668. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]