Abstract
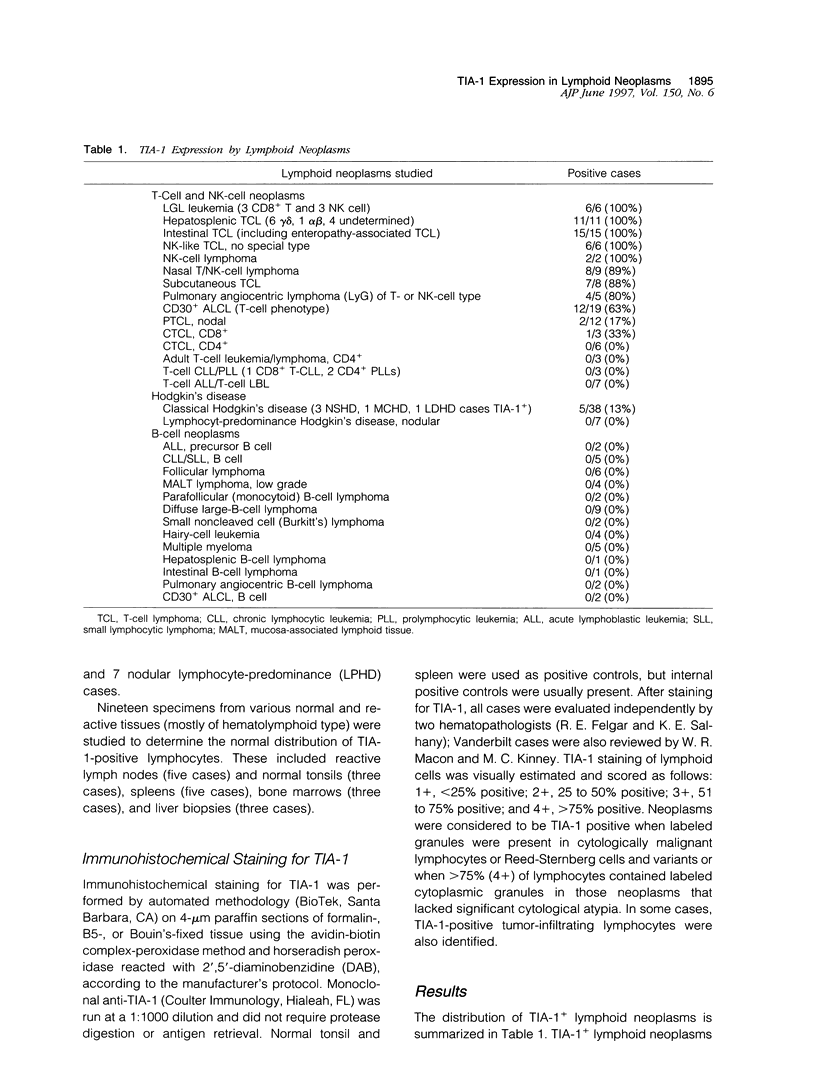
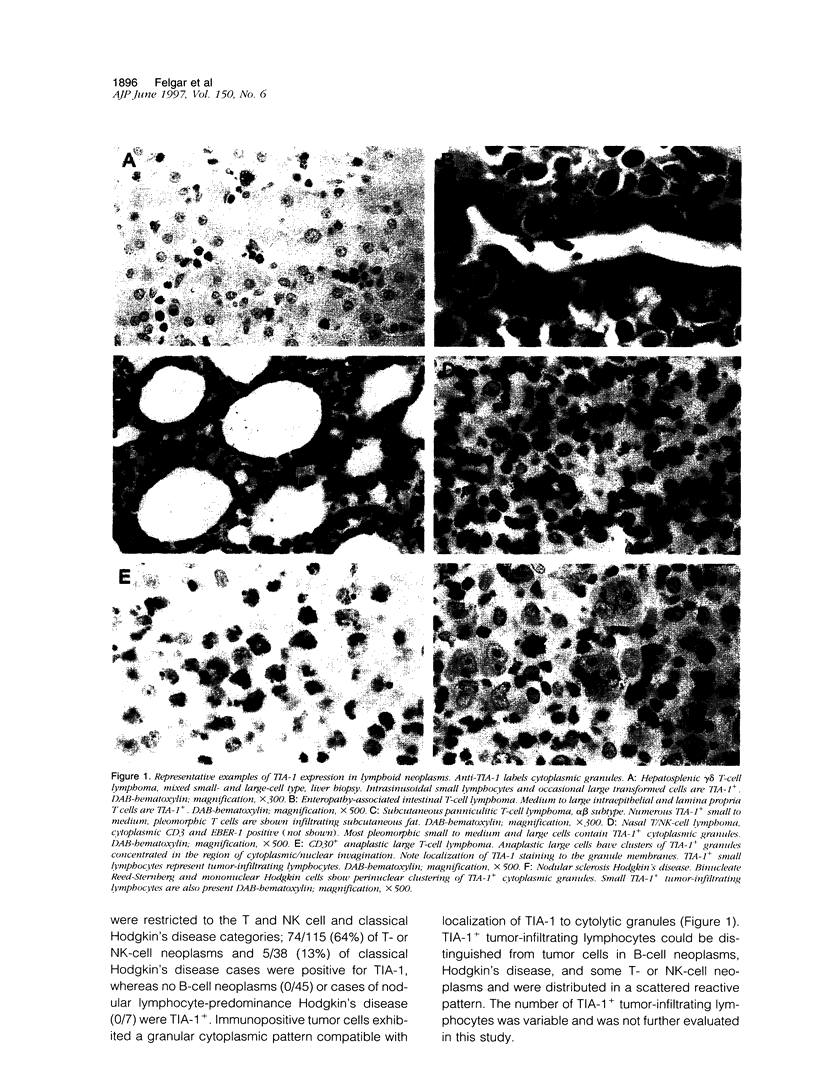
TIA-I is a 15-kd cytotoxic granule-associated protein expressed in natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. TIA-1 expression was evaluated by paraffin immunohistochemistry in 115 T- or NK-cell neoplasms, 45 B-cell neoplasms, and 45 Hodgkin's lymphomas. TIA-1-positive granules were identified within the cytoplasm of neoplastic cells in 6/6 large granular lymphocytic leukemias, 11/11 hepatosplenic T-cell lymphomas, 15/15 intestinal T-cell lymphomas, 6/6 NK-like T-cell lymphomas of no special type, 2/2 NK-cell lymphomas, 8/9 nasal T/NK-cell lymphomas, 7/8 subcutaneous T-cell lymphomas, 4/5 pulmonary T- or NK-cell angiocentric lymphomas (lymphomatoid granulomatosis), 12/19 T-cell anaplastic large-cell lymphomas, 2/12 nodal peripheral T-cell lymphomas, 1/3 CD8+ cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, and 5/38 classical Hodgkin's disease. All B-cell neoplasms, nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin's disease (7 cases), CD4+ cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (6 cases), adult T-cell leukemia/lymphomas (3 cases), T-cell chronic or prolymphocytic leukemias (3 cases), and T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphomas (7-cases) were TIA-1 negative. These findings indicate that most large granular lymphocytic leukemias, hepatosplenic T-cell lymphomas, intestinal T-cell lymphomas, NK-like T-cell lymphomas, NK-cell lymphomas, nasal T/NK-cell lymphomas, subcutaneous T-cell lymphomas, pulmonary angiocentric lymphomas of T or NK phenotype, and anaplastic large-cell lymphomas are cytotoxic T-or NK-cell neoplasms.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Nagler-Anderson C., O'Brien C., Levine H., Watkins S., Slayter H. S., Blue M. L., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with a 15-kDa cytoplasmic granule-associated protein defines a subpopulation of CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):574–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P. TIA-1: structural and functional studies on a new class of cytolytic effector molecule. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995;198:131–143. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-79414-8_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berke G. The CTL's kiss of death. Cell. 1995 Apr 7;81(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90365-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg G., Dummer R., Wilhelm M., Nestle F., Ott M. M., Feller A., Hefner H., Lanz U., Schwinn A., Wiede J. A subcutaneous delta-positive T-cell lymphoma that produces interferon gamma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 10;325(15):1078–1081. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110103251506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. K., Tsang W. Y., Wong K. F. Classification of natural killer cell neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994 Nov;18(11):1177–1179. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199411000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. C., Link S., Mawle A., Check I., Brynes R. K., Winton E. F. Heterogeneity of large granular lymphocyte proliferations: delineation of two major subtypes. Blood. 1986 Nov;68(5):1142–1153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke C. B., Krenacs L., Stetler-Stevenson M., Greiner T. C., Raffeld M., Kingma D. W., Abruzzo L., Frantz C., Kaviani M., Jaffe E. S. Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity of cytotoxic gamma delta T-cell origin. Blood. 1996 Dec 1;88(11):4265–4274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A., Chang C., Franz-Bacon K., McClanahan T., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Molecular cloning of NKB1. A natural killer cell receptor for HLA-B allotypes. J Immunol. 1995 Sep 1;155(5):2306–2310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emile J. F., Boulland M. L., Haioun C., Kanavaros P., Petrella T., Delfau-Larue M. H., Bensussan A., Farcet J. P., Gaulard P. CD5-CD56+ T-cell receptor silent peripheral T-cell lymphomas are natural killer cell lymphomas. Blood. 1996 Feb 15;87(4):1466–1473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcão R. P., Voltarelli J. C., Simões B. P., Pestana D. N., Zago M. A., Figueiredo M. S. Malignant T gamma/delta lymphoproliferative disease with natural killer lytic activity. Am J Hematol. 1992 Oct;41(2):128–131. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830410211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foss H. D., Anagnostopoulos I., Araujo I., Assaf C., Demel G., Kummer J. A., Hummel M., Stein H. Anaplastic large-cell lymphomas of T-cell and null-cell phenotype express cytotoxic molecules. Blood. 1996 Nov 15;88(10):4005–4011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumperz J. E., Parham P. The enigma of the natural killer cell. Nature. 1995 Nov 16;378(6554):245–248. doi: 10.1038/378245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris N. L., Jaffe E. S., Stein H., Banks P. M., Chan J. K., Cleary M. L., Delsol G., De Wolf-Peeters C., Falini B., Gatter K. C. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 1994 Sep 1;84(5):1361–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. Mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:31–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. S. Classification of natural killer (NK) cell and NK-like T-cell malignancies. Blood. 1996 Feb 15;87(4):1207–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenacs L., Wellmann A., Sorbara L., Himmelmann A. W., Bagdi E., Jaffe E. S., Raffeld M. Cytotoxic cell antigen expression in anaplastic large cell lymphomas of T- and null-cell type and Hodgkin's disease: evidence for distinct cellular origin. Blood. 1997 Feb 1;89(3):980–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kärre K. Express yourself or die: peptides, MHC molecules, and NK cells. Science. 1995 Feb 17;267(5200):978–979. doi: 10.1126/science.7863341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loughran T. P., Jr Clonal diseases of large granular lymphocytes. Blood. 1993 Jul 1;82(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowin B., Peitsch M. C., Tschopp J. Perforin and granzymes: crucial effector molecules in cytolytic T lymphocyte and natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995;198:1–24. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-79414-8_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macon W. R., Williams M. E., Greer J. P., Hammer R. D., Glick A. D., Collins R. D., Cousar J. B. Natural killer-like T-cell lymphomas: aggressive lymphomas of T-large granular lymphocytes. Blood. 1996 Feb 15;87(4):1474–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnati M. S., Peruzzi M., Parker K. C., Biddison W. E., Ciccone E., Moretta A., Long E. O. Peptide specificity in the recognition of MHC class I by natural killer cell clones. Science. 1995 Feb 17;267(5200):1016–1018. doi: 10.1126/science.7863326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A. R., Chan W. C., Perry D. A., Greiner T. C., Weisenburger D. D. Aggressive natural killer cell lymphoma of the small intestine. Mod Pathol. 1995 Jun;8(5):467–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori N., Yatabe Y., Oka K., Kinoshita T., Kobayashi T., Ono T., Asai J. Expression of perforin in nasal lymphoma. Additional evidence of its natural killer cell derivation. Am J Pathol. 1996 Aug;149(2):699–705. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng C. S., Chan J. K., Lo S. T. Expression of natural killer cell markers in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Hum Pathol. 1987 Dec;18(12):1257–1262. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(87)80410-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudejans J. J., Kummer J. A., Jiwa M., van der Valk P., Ossenkoppele G. J., Kluin P. M., Kluin-Nelemans J. C., Meijer C. J. Granzyme B expression in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1996 Jan;148(1):233–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H., Held W. Natural killer cell receptors: the offs and ons of NK cell recognition. Cell. 1995 Sep 8;82(5):697–700. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90466-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita M., Akamatsu M., Ohshima K., Kimura N., Suzumiya J., Kikuchi M., Okamura T., Nakayama J., Imayama S., Uike N. Angiocentric immunoproliferative lesions of the skin show lobular panniculitis and are mainly disorders of large granular lymphocytes. Hum Pathol. 1995 Dec;26(12):1321–1328. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian Q., Streuli M., Saito H., Schlossman S. F., Anderson P. A polyadenylate binding protein localized to the granules of cytolytic lymphocytes induces DNA fragmentation in target cells. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):629–639. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90536-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:187–376. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60664-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Nabholz M. Perforin-mediated target cell lysis by cytolytic T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:279–302. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. F., Chan J. K., Ng C. S. CD56 (NCAM)-positive malignant lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 1994 Jun;14(1-2):29–36. doi: 10.3109/10428199409049648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin P. C., Kummer J. A., van der Valk P., van Heerde P., Kluin P. M., Willemze R., Ossenkoppele G. J., Radaszkiewicz T., Meijer C. J. Granzyme B-expressing peripheral T-cell lymphomas: neoplastic equivalents of activated cytotoxic T cells with preference for mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue localization. Blood. 1994 Dec 1;84(11):3785–3791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]