Abstract
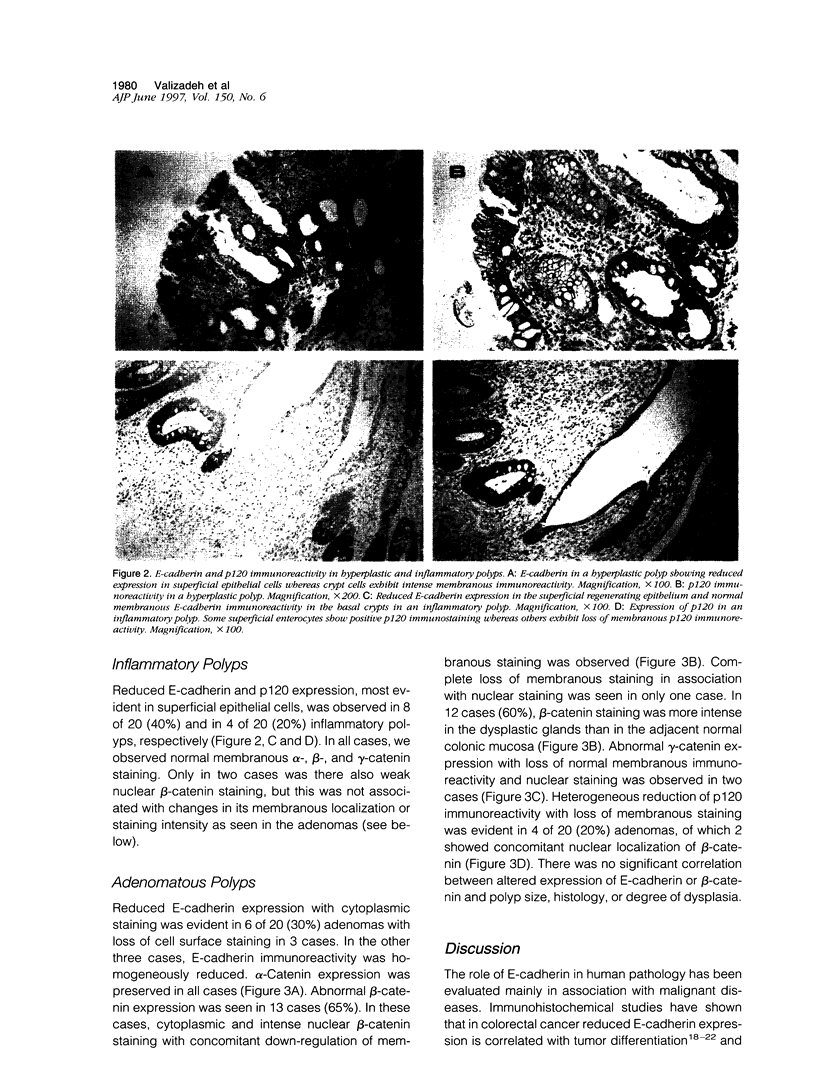
E-cadherin and its associated cytoplasmic proteins alpha-, beta-, and gamma-catenin and p120 protein play a crucial role in the maintenance of normal tissue architecture. Perturbation in any of these molecules results in loss of intercellular adhesion and cell transformation. In this study, we have used immunohistochemistry to localize E-cadherin, alpha-, beta-, and gamma-catenin, and p120 in paraffin-embedded tissues from 60 patients with colonic polyps. Specimens consisted of 20 samples each from hyperplastic, inflammatory, and sporadic adenomatous polyps. Ten histologically normal colonic samples were also studied. Normal colonic epithelial cells showed strong E-cadherin/ catenin/p120 immunostaining at the cell-cell junction. In 65% (13/20) of adenomatous polyps, beta-catenin showed abnormal nuclear localization with increased expression and loss of membranous staining compared with the adjacent normal mucosa. In two cases (10%), gamma-catenin was seen in the nuclei. Heterogeneous p120 immunoreactivity was observed in four cases (20%), of which two also showed beta-catenin nuclear localization. Preserved membranous alpha-catenin staining was seen in all cases. E-cadherin was down-regulated in 6 of 20 (30%) adenomas with loss of cell surface staining in 3 cases. All hyperplastic and 40% (8/20) of inflammatory polyps showed weak E-cadherin expression on the surface epithelium. Similar changes in p120 expression were seen in all hyperplastic and 20% (4/20) of inflammatory polyps. There were no concomitant changes in alpha-, beta-, or gamma-catenin expression. These results indicate that changes in catenin expression and cellular localization occur early in dysplastic colonic lesions.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behrens J., Mareel M. M., Van Roy F. M., Birchmeier W. Dissecting tumor cell invasion: epithelial cells acquire invasive properties after the loss of uvomorulin-mediated cell-cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2435–2447. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley R. S., Cowin P., Brown A. M. Expression of Wnt-1 in PC12 cells results in modulation of plakoglobin and E-cadherin and increased cellular adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 2):1857–1865. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breen E., Steele G., Jr, Mercurio A. M. Role of the E-cadherin/alpha-catenin complex in modulating cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesive properties of invasive colon carcinoma cells. Ann Surg Oncol. 1995 Sep;2(5):378–385. doi: 10.1007/BF02306369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. M., Reynolds A. B. The tyrosine kinase substrate p120cas binds directly to E-cadherin but not to the adenomatous polyposis coli protein or alpha-catenin. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;15(9):4819–4824. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.9.4819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorudi S., Sheffield J. P., Poulsom R., Northover J. M., Hart I. R. E-cadherin expression in colorectal cancer. An immunocytochemical and in situ hybridization study. Am J Pathol. 1993 Apr;142(4):981–986. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimori T., Takeichi M. Disruption of epithelial cell-cell adhesion by exogenous expression of a mutated nonfunctional N-cadherin. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):37–47. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardi G., Kandemir O., Liu D., Guida M., Benvestito S., Ruers T. G., Benjamin I. S., Northover J. M., Stamp G. W., Talbot I. C. Changes in E-cadherin immunoreactivity in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence of the large bowel. Virchows Arch. 1995;426(2):149–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00192636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B. M., McCrea P. D. Catenins as mediators of the cytoplasmic functions of cadherins. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993;17:155–158. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1993.supplement_17.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston M. L., Gordon J. I. In vivo analysis of cadherin function in the mouse intestinal epithelium: essential roles in adhesion, maintenance of differentiation, and regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;129(2):489–506. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.2.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston M. L., Gordon J. I. Inflammatory bowel disease and adenomas in mice expressing a dominant negative N-cadherin. Science. 1995 Nov 17;270(5239):1203–1207. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5239.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston M. L., Wong M. H., Gordon J. I. Forced expression of E-cadherin in the mouse intestinal epithelium slows cell migration and provides evidence for nonautonomous regulation of cell fate in a self-renewing system. Genes Dev. 1996 Apr 15;10(8):985–996. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.8.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinck L., Näthke I. S., Papkoff J., Nelson W. J. Dynamics of cadherin/catenin complex formation: novel protein interactions and pathways of complex assembly. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(6):1327–1340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.6.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S., Kimoto N., Shimoyama Y., Hirohashi S., Takeichi M. Identification of a neural alpha-catenin as a key regulator of cadherin function and multicellular organization. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90103-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inomata M., Ochiai A., Akimoto S., Kitano S., Hirohashi S. Alteration of beta-catenin expression in colonic epithelial cells of familial adenomatous polyposis patients. Cancer Res. 1996 May 1;56(9):2213–2217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jawhari A., Jordan S., Poole S., Browne P., Pignatelli M., Farthing M. J. Abnormal immunoreactivity of the E-cadherin-catenin complex in gastric carcinoma: relationship with patient survival. Gastroenterology. 1997 Jan;112(1):46–54. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(97)70218-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawanishi J., Kato J., Sasaki K., Fujii S., Watanabe N., Niitsu Y. Loss of E-cadherin-dependent cell-cell adhesion due to mutation of the beta-catenin gene in a human cancer cell line, HSC-39. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1175–1181. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella A. R., Green B., Lepts G. C., Hill C. L., Bowie G., Taylor B. A. The role of the cell-cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin in large bowel tumour cell invasion and metastasis. Br J Cancer. 1993 May;67(5):904–909. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrea P. D., Turck C. W., Gumbiner B. A homolog of the armadillo protein in Drosophila (plakoglobin) associated with E-cadherin. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1359–1361. doi: 10.1126/science.1962194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munemitsu S., Albert I., Souza B., Rubinfeld B., Polakis P. Regulation of intracellular beta-catenin levels by the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor-suppressor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):3046–3050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.3046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam A. K., Savage F. J., Boulos P. B., Stamp G. W., Liu D., Pignatelli M. Loss of cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion molecules in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 1993 Sep;68(3):507–514. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa M., Ringwald M., Kemler R. Uvomorulin-catenin complex formation is regulated by a specific domain in the cytoplasmic region of the cell adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4246–4250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peifer M., Sweeton D., Casey M., Wieschaus E. wingless signal and Zeste-white 3 kinase trigger opposing changes in the intracellular distribution of Armadillo. Development. 1994 Feb;120(2):369–380. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.2.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli M., Liu D., Nasim M. M., Stamp G. W., Hirano S., Takeichi M. Morphoregulatory activities of E-cadherin and beta-1 integrins in colorectal tumour cells. Br J Cancer. 1992 Oct;66(4):629–634. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polakis P. Mutations in the APC gene and their implications for protein structure and function. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Feb;5(1):66–71. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(95)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell S. M., Zilz N., Beazer-Barclay Y., Bryan T. M., Hamilton S. R., Thibodeau S. N., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. APC mutations occur early during colorectal tumorigenesis. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):235–237. doi: 10.1038/359235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Herbert L., Cleveland J. L., Berg S. T., Gaut J. R. p120, a novel substrate of protein tyrosine kinase receptors and of p60v-src, is related to cadherin-binding factors beta-catenin, plakoglobin and armadillo. Oncogene. 1992 Dec;7(12):2439–2445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinfeld B., Souza B., Albert I., Munemitsu S., Polakis P. The APC protein and E-cadherin form similar but independent complexes with alpha-catenin, beta-catenin, and plakoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 10;270(10):5549–5555. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.10.5549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinfeld B., Souza B., Albert I., Müller O., Chamberlain S. H., Masiarz F. R., Munemitsu S., Polakis P. Association of the APC gene product with beta-catenin. Science. 1993 Dec 10;262(5140):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.8259518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibamoto S., Hayakawa M., Takeuchi K., Hori T., Miyazawa K., Kitamura N., Johnson K. R., Wheelock M. J., Matsuyoshi N., Takeichi M. Association of p120, a tyrosine kinase substrate, with E-cadherin/catenin complexes. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(5):949–957. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.5.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibamoto S., Hayakawa M., Takeuchi K., Hori T., Oku N., Miyazawa K., Kitamura N., Takeichi M., Ito F. Tyrosine phosphorylation of beta-catenin and plakoglobin enhanced by hepatocyte growth factor and epidermal growth factor in human carcinoma cells. Cell Adhes Commun. 1994 Jan;1(4):295–305. doi: 10.3109/15419069409097261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozaki H., Iihara K., Oka H., Kadowaki T., Matsui S., Gofuku J., Inoue M., Nagafuchi A., Tsukita S., Mori T. Immunohistochemical detection of alpha-catenin expression in human cancers. Am J Pathol. 1994 Apr;144(4):667–674. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su L. K., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. Association of the APC tumor suppressor protein with catenins. Science. 1993 Dec 10;262(5140):1734–1737. doi: 10.1126/science.8259519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama T., Shiozaki H., Shibamoto S., Oka H., Kimura Y., Tamura S., Inoue M., Monden T., Ito F., Monden M. Beta-catenin expression in human cancers. Am J Pathol. 1996 Jan;148(1):39–46. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi M. Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.2006419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vleminckx K., Vakaet L., Jr, Mareel M., Fiers W., van Roy F. Genetic manipulation of E-cadherin expression by epithelial tumor cells reveals an invasion suppressor role. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):107–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90143-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilding J., Vousden K. H., Soutter W. P., McCrea P. D., Del Buono R., Pignatelli M. E-cadherin transfection down-regulates the epidermal growth factor receptor and reverses the invasive phenotype of human papilloma virus-transfected keratinocytes. Cancer Res. 1996 Nov 15;56(22):5285–5292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen F., Samos C. H., Nusse R. Biological activity of soluble wingless protein in cultured Drosophila imaginal disc cells. Nature. 1994 Mar 24;368(6469):342–344. doi: 10.1038/368342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Wurff A. A., ten Kate J., van der Linden E. P., Dinjens W. N., Arends J. W., Bosman F. T. L-CAM expression in normal, premalignant, and malignant colon mucosa. J Pathol. 1992 Nov;168(3):287–291. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





