Abstract
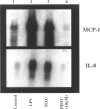
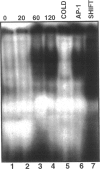
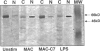
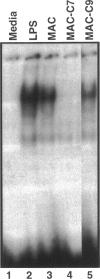
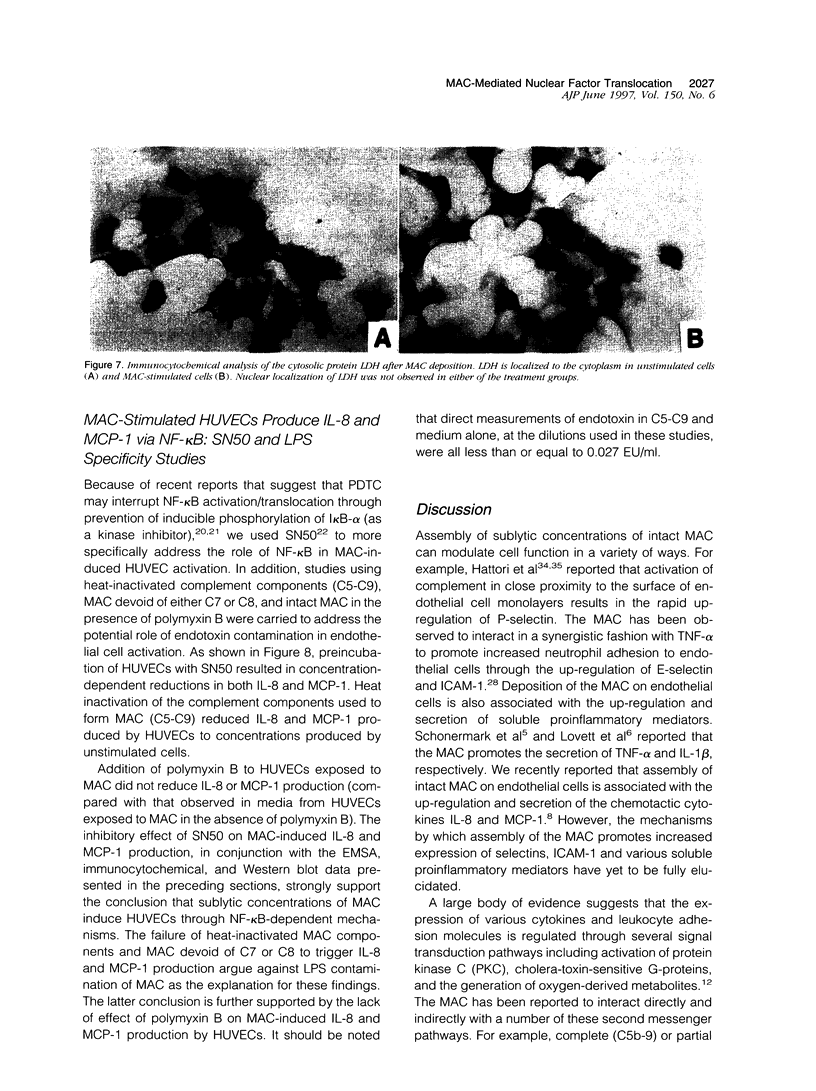
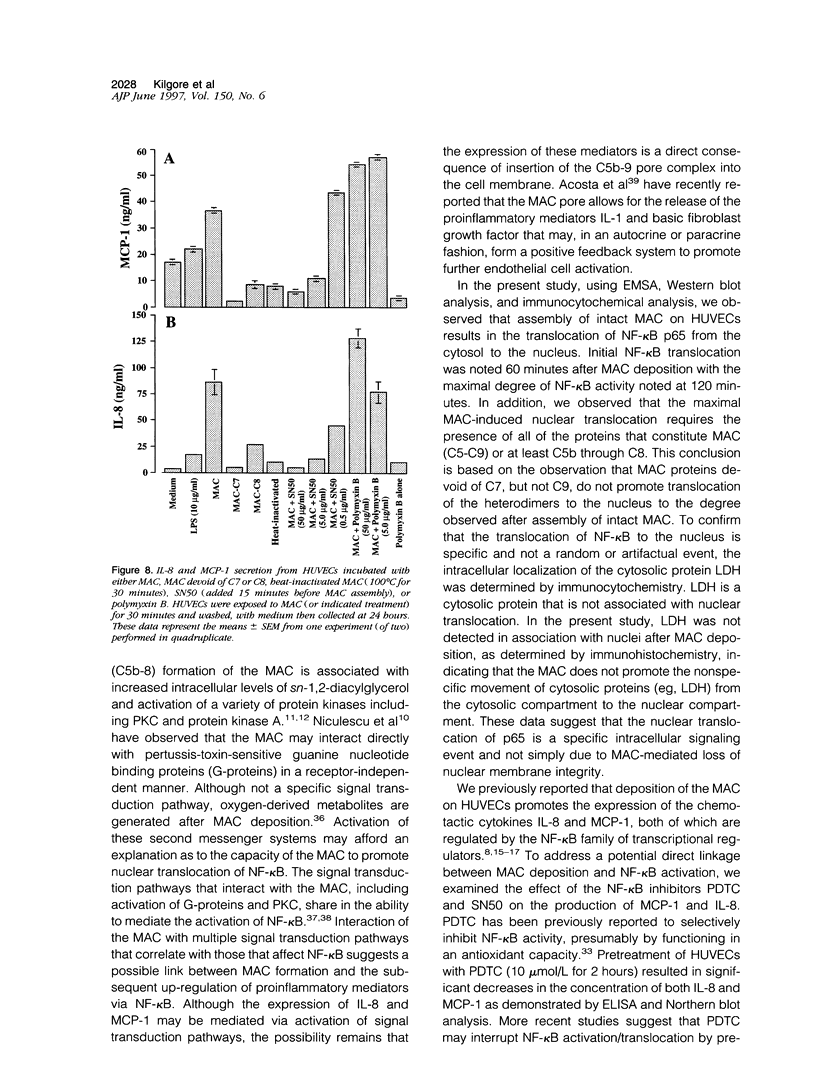
Activation of the complement cascade and subsequent assembly of the membrane attack complex (MAC) occur in a number of pathophysiological settings. When formed on the surface of endothelial cells in sublytic concentrations, the MAC can induce a number of proinflammatory activities, including the secretion of soluble mediators (eg, interleukin (IL)-8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1) and the up-regulation of cell surface adhesion molecules. Available data indicate that MAC-induced cell activation may occur through several complex signal transduction pathways, but little is known about the intranuclear mechanisms by which complement-derived products promote the up-regulation of inflammatory mediators. Using purified distal complement proteins (C5-9) to assemble functional MAC on early-passage human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), we examined mechanisms of MCP-1 and IL-8 induction. Formation of sublytic concentrations of MAC promoted an increase in nuclear factor (NF)-kappa B DNA binding activity within 60 minutes as determined by serial electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Cytosolic to nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B was confirmed by Western immunoblot and immunocytochemical analyses. Formation of the C5b-8 complex also promoted NF-kappa B translocation but to a lesser degree than observed in HUVECs containing complete MAC. No cytosolic to nuclear translocation of the p65 NF-kappa B subunit was observed in unstimulated HUVECs or in cells incubated with the MAC components devoid of C7. Preincubation of HUVECs with pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate prevented MAC-induced increases in IL-8 and MCP-1 mRNA concentrations and protein secretion. A direct cause and effect linkage between MAC assembly and NF-kappa B activation was established through examination of the pharmacological effect of the peptide SN50 on IL-8 and MCP-1 expression. SN50 is a recently engineered 26-amino-acid peptide that contains a lipophilic cell-membrane-permeable motif and a nuclear localization sequence that specifically competes with the nuclear localization sequence of the NF-kappa B p50 subunit. This study provides direct in vitro evidence that the distal complement system (MAC) can promote proinflammatory endothelial cell activation, specifically, increases in IL-8 and MCP-1 mRNA concentrations and protein secretion, and that cytosolic to nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B is necessary for this response.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acosta J. A., Benzaquen L. R., Goldstein D. J., Tosteson M. T., Halperin J. A. The transient pore formed by homologous terminal complement complexes functions as a bidirectional route for the transport of autocrine and paracrine signals across human cell membranes. Mol Med. 1996 Nov;2(6):755–765. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler S., Baker P. J., Johnson R. J., Ochi R. F., Pritzl P., Couser W. G. Complement membrane attack complex stimulates production of reactive oxygen metabolites by cultured rat mesangial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):762–767. doi: 10.1172/JCI112372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asghar S. S. Membrane regulators of complement activation and their aberrant expression in disease. Lab Invest. 1995 Mar;72(3):254–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzaquen L. R., Nicholson-Weller A., Halperin J. A. Terminal complement proteins C5b-9 release basic fibroblast growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor from endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1994 Mar 1;179(3):985–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.3.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlos T. M., Harlan J. M. Leukocyte-endothelial adhesion molecules. Blood. 1994 Oct 1;84(7):2068–2101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. F., Lang T. J., Shin M. L. Multiple signal messengers generated by terminal complement complexes and their role in terminal complement complex elimination. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):623–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T. Endothelial nuclear factor-kappa B and the initiation of the atherosclerotic lesion. Lab Invest. 1993 May;68(5):499–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Read M. A., Neish A. S., Whitley M. Z., Thanos D., Maniatis T. Transcriptional regulation of endothelial cell adhesion molecules: NF-kappa B and cytokine-inducible enhancers. FASEB J. 1995 Jul;9(10):899–909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeForge L. E., Preston A. M., Takeuchi E., Kenney J., Boxer L. A., Remick D. G. Regulation of interleukin 8 gene expression by oxidant stress. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25568–25576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finco T. S., Beg A. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr Inducible phosphorylation of I kappa B alpha is not sufficient for its dissociation from NF-kappa B and is inhibited by protease inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):11884–11888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.11884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghezzi P., Dinarello C. A., Bianchi M., Rosandich M. E., Repine J. E., White C. W. Hypoxia increases production of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor by human mononuclear cells. Cytokine. 1991 May;3(3):189–194. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori R., Hamilton K. K., Fugate R. D., McEver R. P., Sims P. J. Stimulated secretion of endothelial von Willebrand factor is accompanied by rapid redistribution to the cell surface of the intracellular granule membrane protein GMP-140. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7768–7771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori R., Hamilton K. K., McEver R. P., Sims P. J. Complement proteins C5b-9 induce secretion of high molecular weight multimers of endothelial von Willebrand factor and translocation of granule membrane protein GMP-140 to the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9053–9060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano M., Hirai S., Mizuno K., Osada S., Hosaka M., Ohno S. A protein kinase C isozyme, nPKC epsilon, is involved in the activation of NF-kappa B by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) in rat 3Y1 fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Jan 5;206(1):429–436. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J., Baichwal V., Cao Z. Regulatory elements and transcription factors controlling basal and cytokine-induced expression of the gene encoding intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 22;91(24):11641–11645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.24.11641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël N., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A., Aillet F., Virelizier J. L. Redox status of cells influences constitutive or induced NF-kappa B translocation and HIV long terminal repeat activity in human T and monocytic cell lines. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 15;149(10):3386–3393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnke A., Johnson J. P. Synergistic activation of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) by TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma is mediated by p65/p50 and p65/c-Rel and interferon-responsive factor Stat1 alpha (p91) that can be activated by both IFN-gamma and IFN-alpha. FEBS Lett. 1994 Nov 7;354(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilgore K. S., Flory C. M., Miller B. F., Evans V. M., Warren J. S. The membrane attack complex of complement induces interleukin-8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 secretion from human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1996 Sep;149(3):953–961. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilgore K. S., Shen J. P., Miller B. F., Ward P. A., Warren J. S. Enhancement by the complement membrane attack complex of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced endothelial cell expression of E-selectin and ICAM-1. J Immunol. 1995 Aug 1;155(3):1434–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kravchenko V. V., Pan Z., Han J., Herbert J. M., Ulevitch R. J., Ye R. D. Platelet-activating factor induces NF-kappa B activation through a G protein-coupled pathway. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 23;270(25):14928–14934. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.25.14928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. Z., Yao S. Y., Veach R. A., Torgerson T. R., Hawiger J. Inhibition of nuclear translocation of transcription factor NF-kappa B by a synthetic peptide containing a cell membrane-permeable motif and nuclear localization sequence. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 16;270(24):14255–14258. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.24.14255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett D. H., Haensch G. M., Goppelt M., Resch K., Gemsa D. Activation of glomerular mesangial cells by the terminal membrane attack complex of complement. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2473–2480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meichle A., Schütze S., Hensel G., Brunsing D., Krönke M. Protein kinase C-independent activation of nuclear factor kappa B by tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8339–8343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon S. D., Qin S., Guy G. R., Tan Y. H. Differential induction of nuclear NF-kappa B by protein phosphatase inhibitors in primary and transformed human cells. Requirement for both oxidation and phosphorylation in nuclear translocation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26805–26812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metinko A. P., Kunkel S. L., Standiford T. J., Strieter R. M. Anoxia-hyperoxia induces monocyte-derived interleukin-8. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):791–798. doi: 10.1172/JCI115953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto S., Maki M., Schmitt M. J., Hatanaka M., Verma I. M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced phosphorylation of I kappa B alpha is a signal for its degradation but not dissociation from NF-kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12740–12744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitor J. A., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. NF-kappa B: a family of inducible and differentially expressed enhancer-binding proteins in human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10028–10032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson-Weller A., Halperin J. A. Membrane signaling by complement C5b-9, the membrane attack complex. Immunol Res. 1993;12(3):244–257. doi: 10.1007/BF02918256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niculescu F., Rus H., Shin M. L. Receptor-independent activation of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins by terminal complement complexes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 11;269(6):4417–4423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry G. C., Mackman N. A set of inducible genes expressed by activated human monocytic and endothelial cells contain kappa B-like sites that specifically bind c-Rel-p65 heterodimers. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 19;269(33):20823–20825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Cotran R. S. Cytokines and endothelial cell biology. Physiol Rev. 1990 Apr;70(2):427–451. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.2.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read M. A., Whitley M. Z., Williams A. J., Collins T. NF-kappa B and I kappa B alpha: an inducible regulatory system in endothelial activation. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):503–512. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satriano J. A., Shuldiner M., Hora K., Xing Y., Shan Z., Schlondorff D. Oxygen radicals as second messengers for expression of the monocyte chemoattractant protein, JE/MCP-1, and the monocyte colony-stimulating factor, CSF-1, in response to tumor necrosis factor-alpha and immunoglobulin G. Evidence for involvement of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-dependent oxidase. J Clin Invest. 1993 Sep;92(3):1564–1571. doi: 10.1172/JCI116737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Meier B., Männel D. N., Dröge W., Baeuerle P. A. Dithiocarbamates as potent inhibitors of nuclear factor kappa B activation in intact cells. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1181–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Rieber P., Baeuerle P. A. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2247–2258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönermark M., Deppisch R., Riedasch G., Rother K., Hänsch G. M. Induction of mediator release from human glomerular mesangial cells by the terminal complement components C5b-9. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1991;96(4):331–337. doi: 10.1159/000235517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal F. J., Roederer M., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Intracellular thiols regulate activation of nuclear factor kappa B and transcription of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9943–9947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torzewski J., Oldroyd R., Lachmann P., Fitzsimmons C., Proudfoot D., Bowyer D. Complement-induced release of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 from human smooth muscle cells. A possible initiating event in atherosclerotic lesion formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1996 May;16(5):673–677. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.16.5.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt W., Hesse D. Activation of the fifth component of human complement by oxygen-derived free radicals, and by methionine oxidizing agents: a comparison. Immunobiology. 1992 Apr;184(4-5):384–391. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80595-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt W., Zimmermann B., Hesse D., Nolte R. Activation of the fifth component of human complement, C5, without cleavage, by methionine oxidizing agents. Mol Immunol. 1992 Feb;29(2):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(92)90106-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmer T., Ando B., Sims P. J. Complement C5b-9-stimulated platelet secretion is associated with a Ca2+-initiated activation of cellular protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13674–13681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel U., Baeuerle P. A. Purified human I kappa B can rapidly dissociate the complex of the NF-kappa B transcription factor with its cognate DNA. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90806-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]