Abstract
The selectins and beta2 integrins participate in the recruitment of neutrophils in acute pulmonary inflammation. However, the cell adhesion receptors that mediate lymphocyte trafficking into the lung have not been defined. This study examined the relationship between cell adhesion molecules on the pulmonary vasculature and on lymphocytes recovered from the lung during a pulmonary immune response to intratracheal (I.T.) sheep red blood cells (SRBCs) in sensitized C57BL/6J mice. Silver-enhanced immunogold staining and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of lung tissues revealed sustained induction of VCAM-1, E-selectin, and P-selectin on the pulmonary vasculature for up to 7 days after I.T.-SRBC challenge. Neither the MECA 79 nor MECA 367 antigens were induced on the pulmonary vasculature during this period. In the peripheral blood, both CD4 and CD8 T-cell subsets showed an initial increase in P-selectin ligand expression after I.T.-SRBC challenge. The number of P-selectin ligand-positive T cells in the peripheral blood fell as T cells with both P-selectin and, to a lesser extent, E-selectin ligands accumulated in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. We conclude that I.T.-SRBC challenge in sensitized mice elicits prolonged synthesis of P-selectin, E-selectin, and VCAM-1 by the lung vasculature as well as selectin ligand synthesis by responding T cells. Furthermore, the entry of selectin-ligand-positive T cells into the circulation and their accumulation in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid indicates that these receptors may contribute to T cell recruitment. Finally, VCAM-1 on the vasculature may also participate; however, the vascular addressins, required for homing to peripheral and mucosal lymphoid organs, are not essential for T-cell entry into the lung following I.T.-SRBC challenge.
Full text
PDF




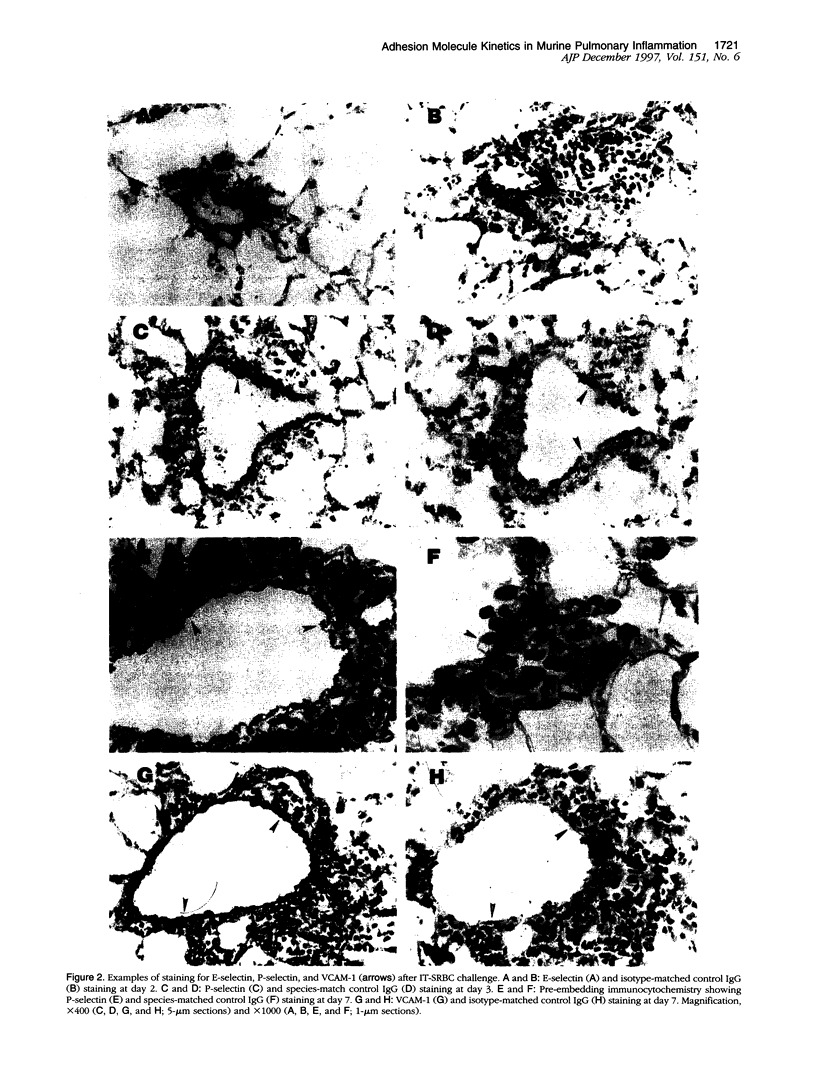
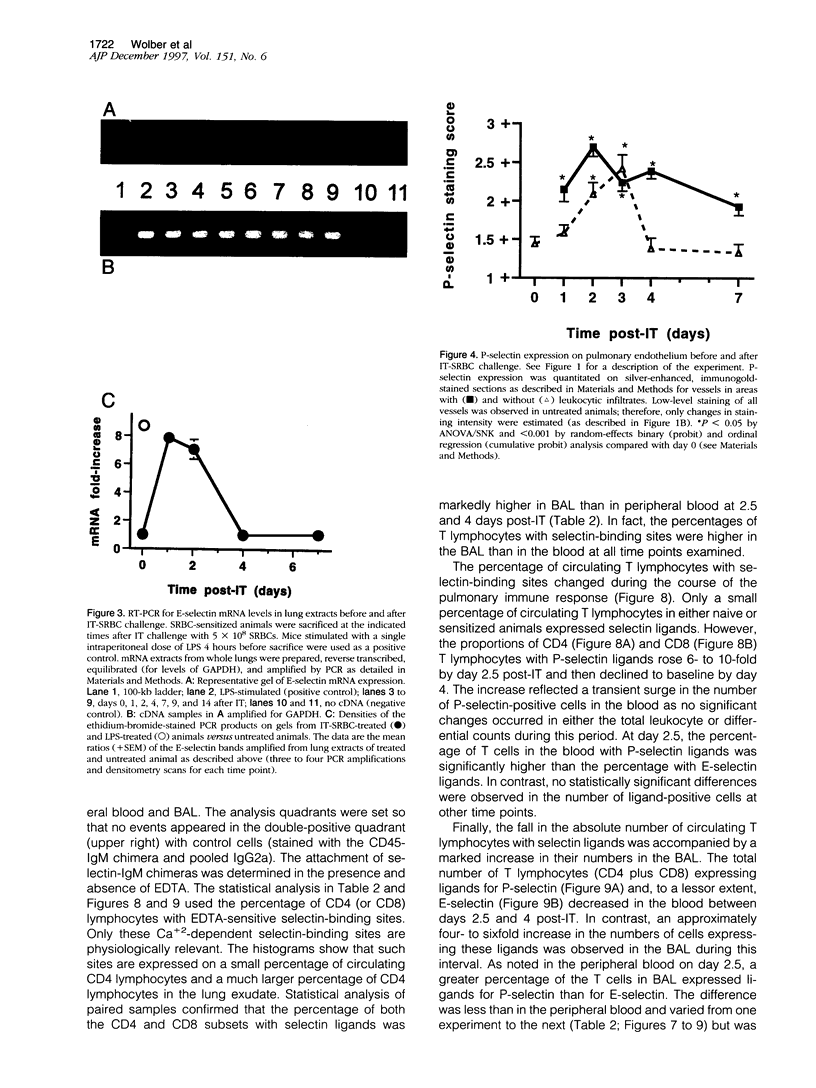
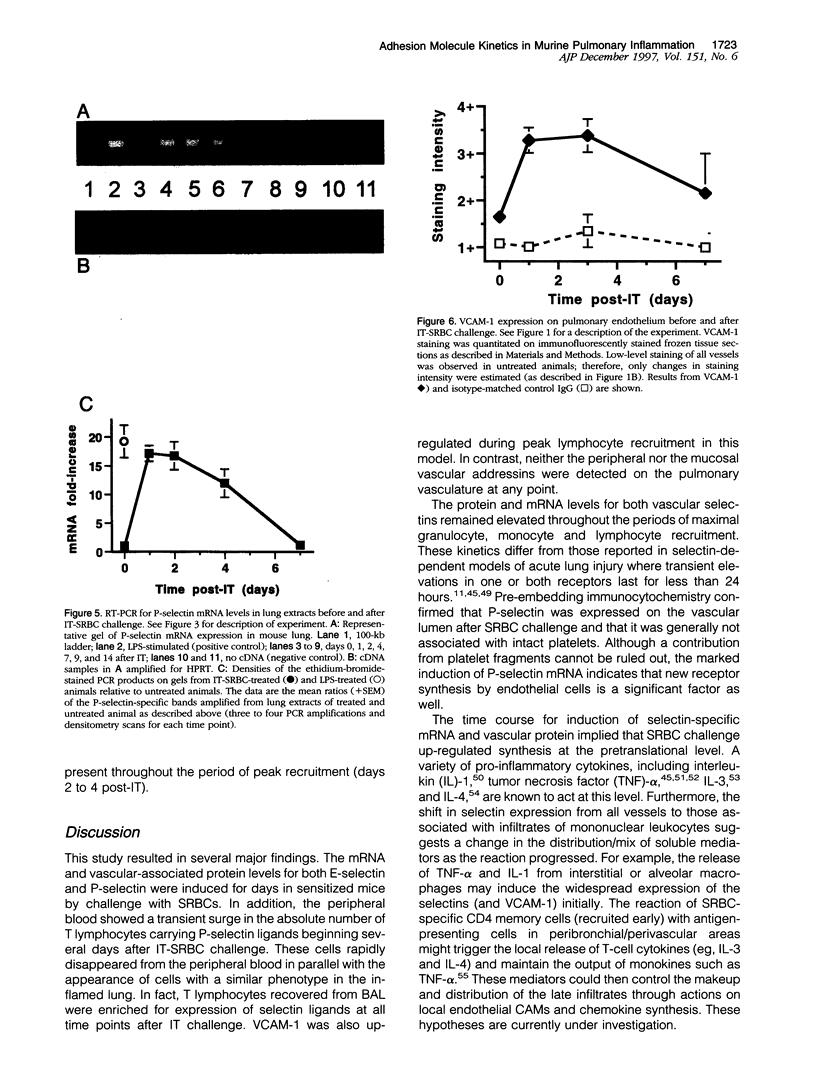
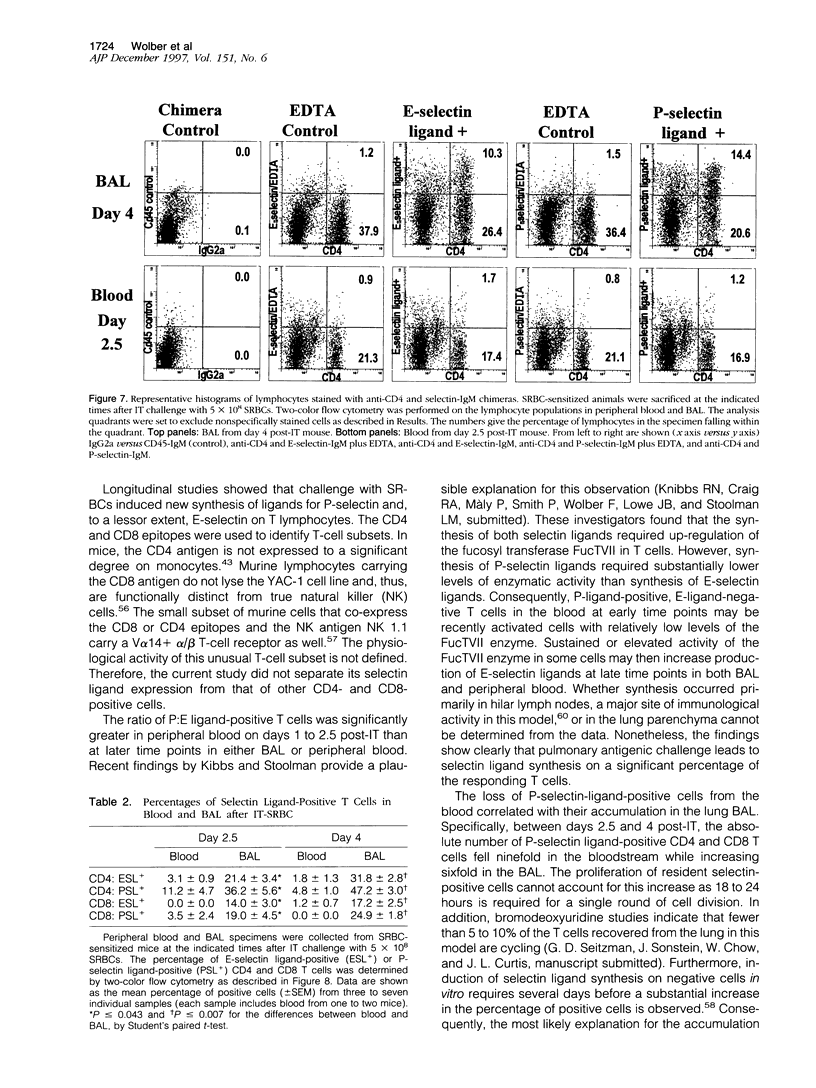


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alon R., Kassner P. D., Carr M. W., Finger E. B., Hemler M. E., Springer T. A. The integrin VLA-4 supports tethering and rolling in flow on VCAM-1. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(6):1243–1253. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.6.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austrup F., Vestweber D., Borges E., Löhning M., Bräuer R., Herz U., Renz H., Hallmann R., Scheffold A., Radbruch A. P- and E-selectin mediate recruitment of T-helper-1 but not T-helper-2 cells into inflammed tissues. Nature. 1997 Jan 2;385(6611):81–83. doi: 10.1038/385081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargatze R. F., Kurk S., Butcher E. C., Jutila M. A. Neutrophils roll on adherent neutrophils bound to cytokine-induced endothelial cells via L-selectin on the rolling cells. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1785–1792. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron J. L., Madri J. A., Ruddle N. H., Hashim G., Janeway C. A., Jr Surface expression of alpha 4 integrin by CD4 T cells is required for their entry into brain parenchyma. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):57–68. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron J. L., Reich E. P., Visintin I., Janeway C. A., Jr The pathogenesis of adoptive murine autoimmune diabetes requires an interaction between alpha 4-integrins and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1700–1708. doi: 10.1172/JCI117153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin C., Bargatze R. F., Campbell J. J., von Andrian U. H., Szabo M. C., Hasslen S. R., Nelson R. D., Berg E. L., Erlandsen S. L., Butcher E. C. alpha 4 integrins mediate lymphocyte attachment and rolling under physiologic flow. Cell. 1995 Feb 10;80(3):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90491-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Stengelin S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Seed B. Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1: an inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1160–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2466335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. K., Jutila M. A., Sedmak D. D., Beattie M. S., Orosz C. G. Lymphocyte entry into inflammatory tissues in vivo. Qualitative differences of high endothelial venule-like vessels in sponge matrix allografts vs isografts. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4219–4224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullard D. C., Kunkel E. J., Kubo H., Hicks M. J., Lorenzo I., Doyle N. A., Doerschuk C. M., Ley K., Beaudet A. L. Infectious susceptibility and severe deficiency of leukocyte rolling and recruitment in E-selectin and P-selectin double mutant mice. J Exp Med. 1996 May 1;183(5):2329–2336. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.5.2329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C., Picker L. J. Lymphocyte homing and homeostasis. Science. 1996 Apr 5;272(5258):60–66. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5258.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick B. S., Brady G., Miller R. G. Characterization of murine lymphokine-activated killer cell cultures separated according to cell size. Cell Immunol. 1993 Jan;146(1):1–10. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J. P., Andersson E. C., Scheynius A., Marker O., Thomsen A. R. Alpha 4 integrin directs virus-activated CD8+ T cells to sites of infection. J Immunol. 1995 May 15;154(10):5293–5301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker P. R., Jefferies W. A., Clark S. J., Chung L. P., Gordon S. Species heterogeneity in macrophage expression of the CD4 antigen. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):613–618. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis J. L., Byrd P. K., Warnock M. L., Kaltreider H. B. Requirement of CD4-positive T cells for cellular recruitment to the lungs of mice in response to a particulate intratracheal antigen. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1244–1254. doi: 10.1172/JCI115428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis J. L., Kaltreider H. B. Characterization of bronchoalveolar lymphocytes during a specific antibody-forming cell response in the lungs of mice. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Feb;139(2):393–400. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.2.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
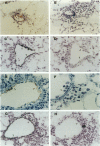
- Curtis J. L., Warnock M. L., Arraj S. M., Kaltreider H. B. Histologic analysis of an immune response in the lung parenchyma of mice. Angiopathy accompanies inflammatory cell influx. Am J Pathol. 1990 Sep;137(3):689–699. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davodeau F., Peyrat M. A., Necker A., Dominici R., Blanchard F., Leget C., Gaschet J., Costa P., Jacques Y., Godard A. Close phenotypic and functional similarities between human and murine alphabeta T cells expressing invariant TCR alpha-chains. J Immunol. 1997 Jun 15;158(12):5603–5611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerszten R. E., Luscinskas F. W., Ding H. T., Dichek D. A., Stoolman L. M., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Rosenzweig A. Adhesion of memory lymphocytes to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1-transduced human vascular endothelial cells under simulated physiological flow conditions in vitro. Circ Res. 1996 Dec;79(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1161/01.res.79.6.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B. Ras C-terminal processing enzymes--new drug targets? Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90352-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahne M., Jäger U., Isenmann S., Hallmann R., Vestweber D. Five tumor necrosis factor-inducible cell adhesion mechanisms on the surface of mouse endothelioma cells mediate the binding of leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(3):655–664. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.3.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahne M., Lenter M., Jäger U., Vestweber D. A novel soluble form of mouse VCAM-1 is generated from a glycolipid-anchored splicing variant. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Feb;24(2):421–428. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedeker D., Gibbons R. D. A random-effects ordinal regression model for multilevel analysis. Biometrics. 1994 Dec;50(4):933–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedeker D., Gibbons R. D. MIXREG: a computer program for mixed-effects regression analysis with autocorrelated errors. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 1996 May;49(3):229–252. doi: 10.1016/0169-2607(96)01723-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriques G. M., Miotla J. M., Cordeiro S. B., Wolitzky B. A., Woolley S. T., Hellewell P. G. Selectins mediate eosinophil recruitment in vivo: a comparison with their role in neutrophil influx. Blood. 1996 Jun 15;87(12):5297–5304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Issekutz T. B. Monocyte migration to arthritis in the rat utilizes both CD11/CD18 and very late activation antigen 4 integrin mechanisms. J Exp Med. 1995 Mar 1;181(3):1197–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.3.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz T. B. Dual inhibition of VLA-4 and LFA-1 maximally inhibits cutaneous delayed-type hypersensitivity-induced inflammation. Am J Pathol. 1993 Nov;143(5):1286–1293. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltreider H. B., Curtis J. L., Arraj S. M. The mechanism of appearance of specific antibody-forming cells in lungs of inbred mice after immunization with sheep erythrocytes intratracheally. II. Dose-dependence and kinetics of appearance of antibody-forming cells in hilar lymph nodes and lungs of unprimed and primed mice. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):87–92. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khew-Goodall Y., Butcher C. M., Litwin M. S., Newlands S., Korpelainen E. I., Noack L. M., Berndt M. C., Lopez A. F., Gamble J. R., Vadas M. A. Chronic expression of P-selectin on endothelial cells stimulated by the T-cell cytokine, interleukin-3. Blood. 1996 Feb 15;87(4):1432–1438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
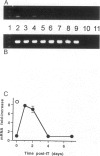
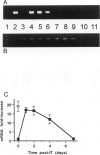
- Kikuta A., Rosen S. D. Localization of ligands for L-selectin in mouse peripheral lymph node high endothelial cells by colloidal gold conjugates. Blood. 1994 Dec 1;84(11):3766–3775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knibbs R. N., Craig R. A., Natsuka S., Chang A., Cameron M., Lowe J. B., Stoolman L. M. The fucosyltransferase FucT-VII regulates E-selectin ligand synthesis in human T cells. J Cell Biol. 1996 May;133(4):911–920. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.4.911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb M. F., Bice D. E., Lyons C. R., Schuyler M. R., Wilkes D. The regulation of pulmonary immunity. Adv Immunol. 1995;59:369–455. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60634-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. K., Bevilacqua B., Malik A. B. E-selectin ligands mediate tumor necrosis factor-induced neutrophil sequestration and pulmonary edema in guinea pig lungs. Circ Res. 1994 Dec;75(6):955–960. doi: 10.1161/01.res.75.6.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luscinskas F. W., Ding H., Lichtman A. H. P-selectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 mediate rolling and arrest, respectively, of CD4+ T lymphocytes on tumor necrosis factor alpha-activated vascular endothelium under flow. J Exp Med. 1995 Mar 1;181(3):1179–1186. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.3.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malý P., Thall A., Petryniak B., Rogers C. E., Smith P. L., Marks R. M., Kelly R. J., Gersten K. M., Cheng G., Saunders T. L. The alpha(1,3)fucosyltransferase Fuc-TVII controls leukocyte trafficking through an essential role in L-, E-, and P-selectin ligand biosynthesis. Cell. 1996 Aug 23;86(4):643–653. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie S. A., Streeter P. R., Bolt P. A., Butcher E. C., Picker L. J. The human peripheral lymph node vascular addressin. An inducible endothelial antigen involved in lymphocyte homing. Am J Pathol. 1993 Dec;143(6):1688–1698. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina A., Sánchez-Madrid F., Bricio T., Martín A., Barat A., Alvarez V., Mampaso F. Prevention of mercuric chloride-induced nephritis in the brown Norway rat by treatment with antibodies against the alpha 4 integrin. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 1;153(5):2313–2320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. S., Polley M. J., Bayer R. J., Nunn M. F., Paulson J. C., Ward P. A. Neutrophil-dependent acute lung injury. Requirement for P-selectin (GMP-140). J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1600–1607. doi: 10.1172/JCI116029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. S., Varani J., Dame M. K., Lane C. L., Smith C. W., Anderson D. C., Ward P. A. Role of endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 (ELAM-1) in neutrophil-mediated lung injury in rats. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1396–1406. doi: 10.1172/JCI115446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Sano H., Nishimura T., Yoshida S., Iwamoto I. Role of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1/very late activation antigen 4 and intercellular adhesion molecule 1/lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 interactions in antigen-induced eosinophil and T cell recruitment into the tissue. J Exp Med. 1994 Apr 1;179(4):1145–1154. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann B., Machleidt T., Lifka A., Pfeffer K., Vestweber D., Mak T. W., Holzmann B., Krönke M. Crucial role of 55-kilodalton TNF receptor in TNF-induced adhesion molecule expression and leukocyte organ infiltration. J Immunol. 1996 Feb 15;156(4):1587–1593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onrust S. V., Hartl P. M., Rosen S. D., Hanahan D. Modulation of L-selectin ligand expression during an immune response accompanying tumorigenesis in transgenic mice. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jan 1;97(1):54–64. doi: 10.1172/JCI118406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Kishimoto T. K., Smith C. W., Warnock R. A., Butcher E. C. ELAM-1 is an adhesion molecule for skin-homing T cells. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):796–799. doi: 10.1038/349796a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Martin R. J., Trumble A., Newman L. S., Collins P. A., Bergstresser P. R., Leung D. Y. Differential expression of lymphocyte homing receptors by human memory/effector T cells in pulmonary versus cutaneous immune effector sites. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Jun;24(6):1269–1277. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinsky D. J., Naka Y., Liao H., Oz M. C., Wagner D. D., Mayadas T. N., Johnson R. C., Hynes R. O., Heath M., Lawson C. A. Hypoxia-induced exocytosis of endothelial cell Weibel-Palade bodies. A mechanism for rapid neutrophil recruitment after cardiac preservation. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jan 15;97(2):493–500. doi: 10.1172/JCI118440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretolani M., Ruffié C., Lapa e Silva J. R., Joseph D., Lobb R. R., Vargaftig B. B. Antibody to very late activation antigen 4 prevents antigen-induced bronchial hyperreactivity and cellular infiltration in the guinea pig airways. J Exp Med. 1994 Sep 1;180(3):795–805. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabb H. A., Olivenstein R., Issekutz T. B., Renzi P. M., Martin J. G. The role of the leukocyte adhesion molecules VLA-4, LFA-1, and Mac-1 in allergic airway responses in the rat. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 May;149(5):1186–1191. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.5.8173758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridings P. C., Windsor A. C., Jutila M. A., Blocher C. R., Fisher B. J., Sholley M. M., Sugerman H. J., Fowler A. A., 3rd A dual-binding antibody to E- and L-selectin attenuates sepsis-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995 Jul;152(1):247–253. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.152.1.7541277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders W. E., Wilson R. W., Ballantyne C. M., Beaudet A. L. Molecular cloning and analysis of in vivo expression of murine P-selectin. Blood. 1992 Aug 1;80(3):795–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Traffic signals on endothelium for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:827–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.57.030195.004143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staite N. D., Justen J. M., Sly L. M., Beaudet A. L., Bullard D. C. Inhibition of delayed-type contact hypersensitivity in mice deficient in both E-selectin and P-selectin. Blood. 1996 Oct 15;88(8):2973–2979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoolman L. M. Adhesion molecules involved in leukocyte recruitment and lymphocyte recirculation. Chest. 1993 Feb;103(2 Suppl):79S–86S. doi: 10.1378/chest.103.2_supplement.79s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter P. R., Berg E. L., Rouse B. T., Bargatze R. F., Butcher E. C. A tissue-specific endothelial cell molecule involved in lymphocyte homing. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):41–46. doi: 10.1038/331041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam M., Saffaripour S., Watson S. R., Mayadas T. N., Hynes R. O., Wagner D. D. Reduced recruitment of inflammatory cells in a contact hypersensitivity response in P-selectin-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 1995 Jun 1;181(6):2277–2282. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.6.2277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang T., Frenette P. S., Hynes R. O., Wagner D. D., Mayadas T. N. Cytokine-induced meningitis is dramatically attenuated in mice deficient in endothelial selectins. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jun 1;97(11):2485–2490. doi: 10.1172/JCI118695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipping P. G., Huang X. R., Berndt M. C., Holdsworth S. R. P-selectin directs T lymphocyte-mediated injury in delayed-type hypersensitivity responses: studies in glomerulonephritis and cutaneous delayed-type hypersensitivity. Eur J Immunol. 1996 Feb;26(2):454–460. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller A., Isenmann S., Vestweber D. Cloning of the mouse endothelial selectins. Expression of both E- and P-selectin is inducible by tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15176–15183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N., Zou J. P., Li X. F., Takenaka H., Noda S., Fujii T., Ono S., Kobayashi Y., Mukaida N., Matsushima K. Regulatory mechanisms for production of IFN-gamma and TNF by antitumor T cells or macrophages in the tumor-bearing state. J Immunol. 1995 Mar 1;154(5):2281–2290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao L., Pan J., Setiadi H., Patel K. D., McEver R. P. Interleukin 4 or oncostatin M induces a prolonged increase in P-selectin mRNA and protein in human endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1996 Jul 1;184(1):81–92. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yednock T. A., Cannon C., Fritz L. C., Sanchez-Madrid F., Steinman L., Karin N. Prevention of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by antibodies against alpha 4 beta 1 integrin. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):63–66. doi: 10.1038/356063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Andrian U. H., Berger E. M., Ramezani L., Chambers J. D., Ochs H. D., Harlan J. M., Paulson J. C., Etzioni A., Arfors K. E. In vivo behavior of neutrophils from two patients with distinct inherited leukocyte adhesion deficiency syndromes. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2893–2897. doi: 10.1172/JCI116535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]