Abstract
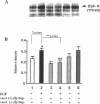
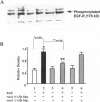
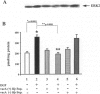
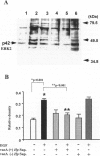
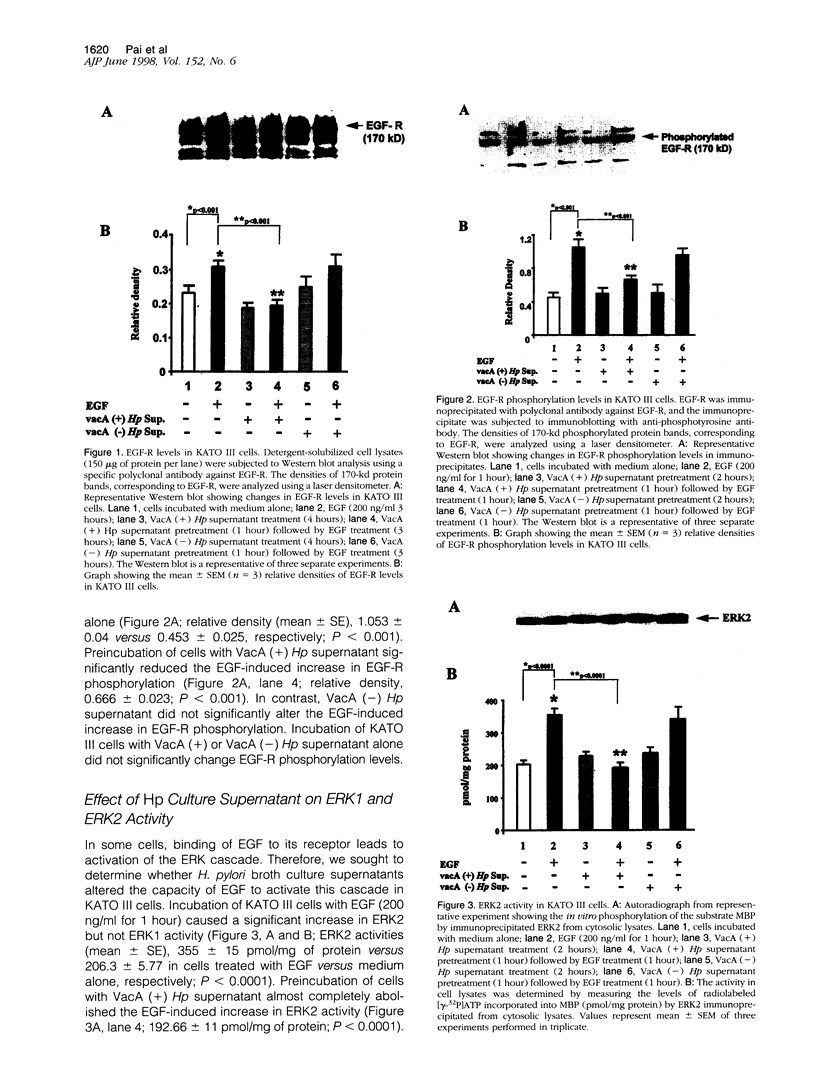
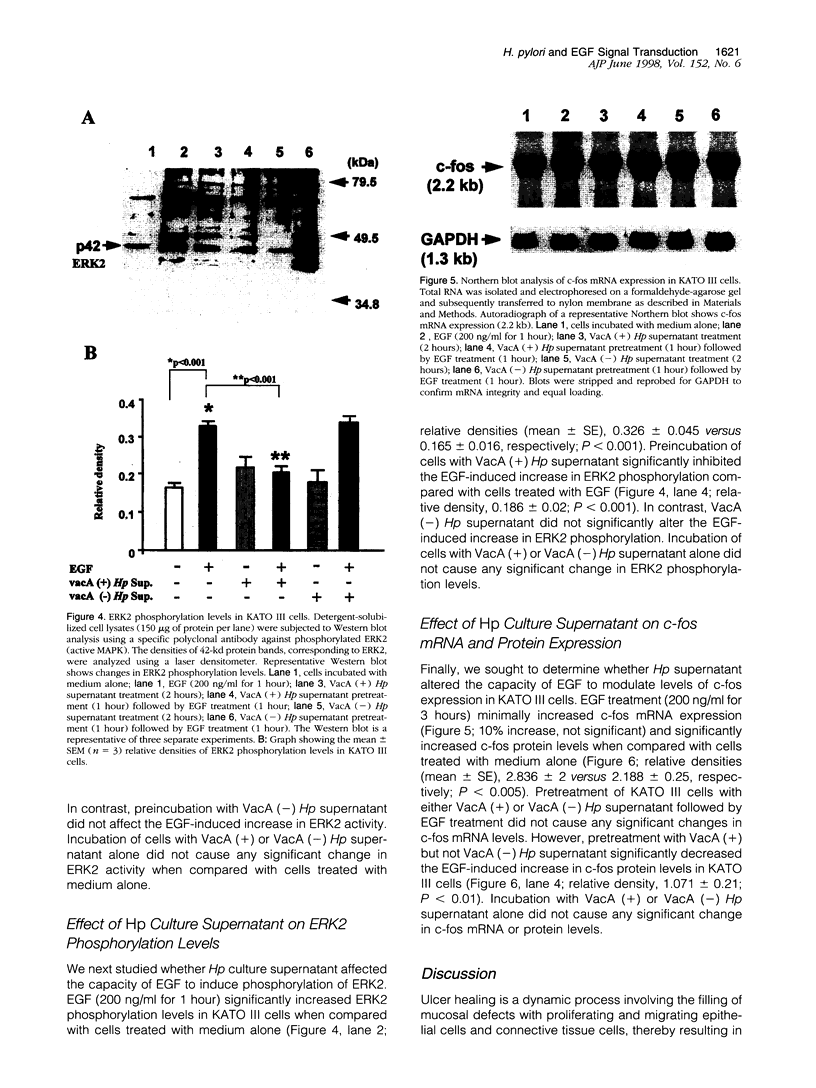
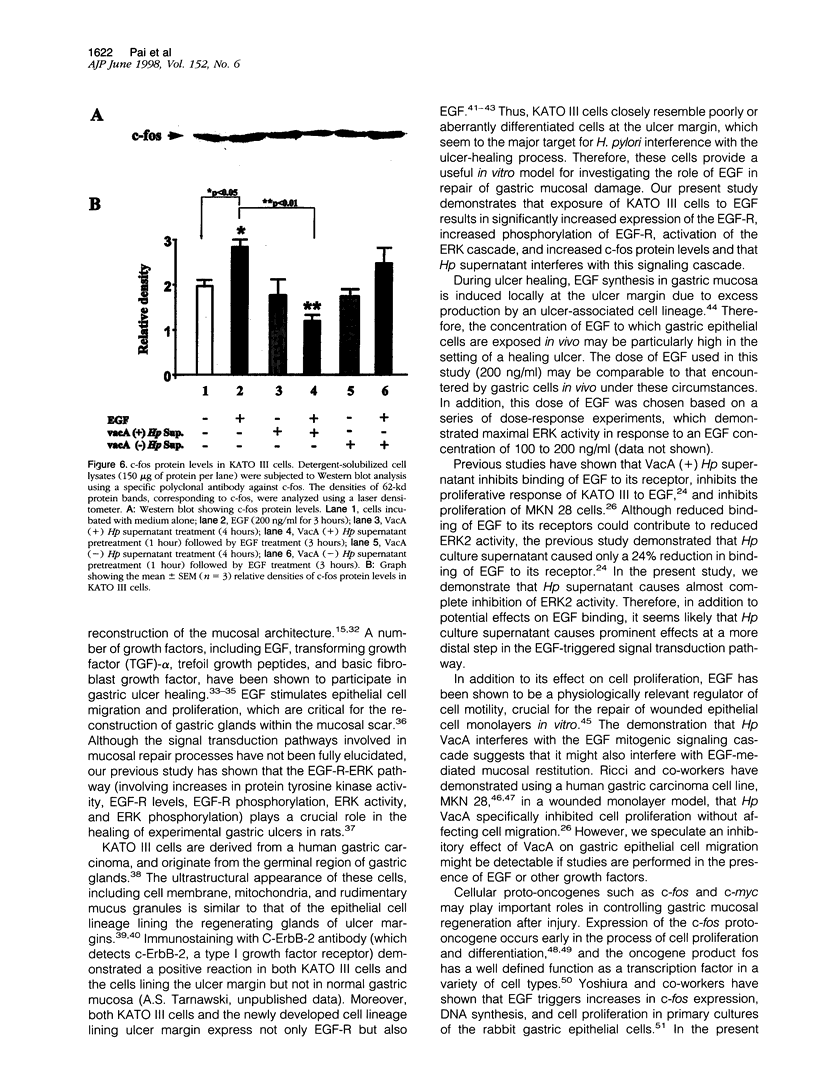
The mechanisms by which Helicobacter pylori infection leads to gastroduodenal ulceration remain poorly understood. Previous studies have shown that H. pylori vacuolating cytotoxin (VacA) inhibits proliferation of gastric epithelial cells, which suggests that H pylori may interfere with gastric mucosal repair mechanisms. In this study, we investigated the effects of H. pylori broth culture supernatants on epidermal growth factor (EGF)-mediated signal transduction pathways in a gastric carcinoma cell line (KATO III). Exposure of these cells to EGF resulted in increased expression and phosphorylation of the EGF receptor (EGF-R), increased ERK2 activity and phosphorylation, and increased c-fos protein levels. Preincubation of cells with broth culture supernatant from VacA (+) H. pylori strain 60190 inhibited the capacity of EGF to induce each of these effects. In contrast, preincubation of cells with broth culture supernatant from an isogenic VacA-mutant strain (H. pylori 60190-v1) failed to inhibit the effects of EGF. These results suggest that the H. pylori vacuolating cytotoxin interferes with EGF-activated signal transduction pathways, which are known to be essential for cell proliferation and ulcer healing.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basson M. D., Modlin I. M., Madri J. A. Human enterocyte (Caco-2) migration is modulated in vitro by extracellular matrix composition and epidermal growth factor. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):15–23. doi: 10.1172/JCI115828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonstra J., Rijken P., Humbel B., Cremers F., Verkleij A., van Bergen en Henegouwen P. The epidermal growth factor. Cell Biol Int. 1995 May;19(5):413–430. doi: 10.1006/cbir.1995.1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg K. B., Sambhi M. P. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor-mediated DNA synthesis by a specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor in vascular smooth muscle cells of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Hypertens Suppl. 1989 Dec;7(6):S144–S145. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198900076-00068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Blaser M. J. Helicobacter pylori infection, a paradigm for chronic mucosal inflammation: pathogenesis and implications for eradication and prevention. Adv Intern Med. 1996;41:85–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Blaser M. J. Purification and characterization of the vacuolating toxin from Helicobacter pylori. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10570–10575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Hanson P. I., Heuser J. E. Acid-induced dissociation of VacA, the Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin, reveals its pattern of assembly. J Cell Biol. 1997 Aug 25;138(4):759–769. doi: 10.1083/jcb.138.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Puryear W., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Effect of urease on HeLa cell vacuolation induced by Helicobacter pylori cytotoxin. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1264–1270. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1264-1270.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Tummuru M. K., Cao P., Thompson S. A., Blaser M. J. Divergence of genetic sequences for the vacuolating cytotoxin among Helicobacter pylori strains. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10566–10573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara Y., Wyle F., Arakawa T., Domek M. J., Fukuda T., Kobayashi K., Tarnawski A. Helicobacter pylori culture supernatant inhibits binding and proliferative response of human gastric cells to epidermal growth factor: implications for H.pylori interference with ulcer healing? Digestion. 1997;58(3):299–303. doi: 10.1159/000201458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser F., Poulsom R., Chinery R., Rogers L. A., Hanby A. M., Wright N. A., Hoffmann W. hP1.B, a human P-domain peptide homologous with rat intestinal trefoil factor, is expressed also in the ulcer-associated cell lineage and the uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6961–6965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch-Ernst K. I., Paul D., Kahl G. F., Höhne M. W. Expression of c-fos and c-myc protooncogenes in an immortalized hepatocyte line harbouring SV40 T antigen and hGH as transgenes. Transgenic Res. 1993 Mar;2(2):101–108. doi: 10.1007/BF01969383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Protein kinases and phosphatases: the yin and yang of protein phosphorylation and signaling. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90405-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji H., Baldwin G. S., Burgess A. W., Moritz R. L., Ward L. D., Simpson R. J. Epidermal growth factor induces serine phosphorylation of stathmin in a human colon carcinoma cell line (LIM 1215). J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13396–13405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Dembinski A., Warzecha Z., Brzozowski T., Gregory H. Role of epidermal growth factor in healing of chronic gastroduodenal ulcers in rats. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jun;94(6):1300–1307. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90667-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Carter C. A., Pleiman C. M., Gardner A. M., Blumer K. J., Johnson G. L. A divergence in the MAP kinase regulatory network defined by MEK kinase and Raf. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):315–319. doi: 10.1126/science.8385802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leunk R. D., Johnson P. T., David B. C., Kraft W. G., Morgan D. R. Cytotoxic activity in broth-culture filtrates of Campylobacter pylori. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(2):93–99. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-2-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupetti P., Heuser J. E., Manetti R., Massari P., Lanzavecchia S., Bellon P. L., Dallai R., Rappuoli R., Telford J. L. Oligomeric and subunit structure of the Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin. J Cell Biol. 1996 May;133(4):801–807. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A. P., Fligiel S. E., Jaszewski R., Tureaud J., Dutta S., Chelluderai B. Inhibition of gastric mucosal regeneration by tyrphostin: evaluation of the role of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. J Lab Clin Med. 1996 Aug;128(2):173–180. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2143(96)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Warren J. R. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984 Jun 16;1(8390):1311–1315. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91816-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naef M., Yokoyama M., Friess H., Büchler M. W., Korc M. Co-expression of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor and related peptides in human gastric carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1996 May 3;66(3):315–321. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19960503)66:3<315::AID-IJC8>3.0.CO;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Murray J. M. Antisense RNA of proto-oncogene c-fos blocks renewed growth of quiescent 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):639–649. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai R., Ohta M., Itani R. M., Sarfeh I. J., Tarnawski A. S. Induction of mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway during gastric ulcer healing in rats. Gastroenterology. 1998 Apr;114(4):706–713. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70584-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papini E., Satin B., Bucci C., de Bernard M., Telford J. L., Manetti R., Rappuoli R., Zerial M., Montecucco C. The small GTP binding protein rab7 is essential for cellular vacuolation induced by Helicobacter pylori cytotoxin. EMBO J. 1997 Jan 2;16(1):15–24. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papini E., de Bernard M., Milia E., Bugnoli M., Zerial M., Rappuoli R., Montecucco C. Cellular vacuoles induced by Helicobacter pylori originate from late endosomal compartments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):9720–9724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prins B. A., Weber M. J., Hu R. M., Pedram A., Daniels M., Levin E. R. Atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinase through the clearance receptor. Potential role in the inhibition of astrocyte proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jun 14;271(24):14156–14162. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.24.14156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ran W., Dean M., Levine R. A., Henkle C., Campisi J. Induction of c-fos and c-myc mRNA by epidermal growth factor or calcium ionophore is cAMP dependent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8216–8220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranger S., Martin P., Roussanne M. C., Denis F. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus antibodies in the general population and in selected groups of patients in Limoges, France. Gut. 1993;34(2 Suppl):S50–S51. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.2_suppl.s50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relan N. K., Fligiel S. E., Dutta S., Tureaud J., Chauhan D. P., Majumdar A. P. Induction of EGF-receptor tyrosine kinase during early reparative phase of gastric mucosa and effects of aging. Lab Invest. 1995 Nov;73(5):717–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricci V., Ciacci C., Zarrilli R., Sommi P., Tummuru M. K., Del Vecchio Blanco C., Bruni C. B., Cover T. L., Blaser M. J., Romano M. Effect of Helicobacter pylori on gastric epithelial cell migration and proliferation in vitro: role of VacA and CagA. Infect Immun. 1996 Jul;64(7):2829–2833. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.7.2829-2833.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano M., Razandi M., Sekhon S., Krause W. J., Ivey K. J. Human cell line for study of damage to gastric epithelial cells in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 1988 Apr;111(4):430–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman J. V. MAP kinase and the activation of quiescent cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling K., Luk D., Morgan J. I., Curran T. Regulation of a fos-lacZ fusion gene: a paradigm for quantitative analysis of stimulus-transcription coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J. SH2/SH3 signaling proteins. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi M., Sakakibara K., Fujii G. Establishment of cultured cell lines derived from a human gastric carcinoma. Jpn J Exp Med. 1978 Feb;48(1):61–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick J. V., Tompkins L. S. Helicobacter pylori and gastroduodenal disease: pathogenesis and host-parasite interaction. Infect Agents Dis. 1992 Dec;1(6):294–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo S., Folkman J., Vattay P., Morales R. E., Pinkus G. S., Kato K. Accelerated healing of duodenal ulcers by oral administration of a mutein of basic fibroblast growth factor in rats. Gastroenterology. 1994 Apr;106(4):1106–1111. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90773-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarnawski A., Stachura J., Durbin T., Sarfeh I. J., Gergely H. Increased expression of epidermal growth factor receptor during gastric ulcer healing in rats. Gastroenterology. 1992 Feb;102(2):695–698. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90123-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarnawski A., Stachura J., Krause W. J., Douglass T. G., Gergely H. Quality of gastric ulcer healing: a new, emerging concept. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1991;13 (Suppl 1):S42–S47. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199112001-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarnawski A., Tanoue K., Santos A. M., Sarfeh I. J. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of gastric ulcer healing. Is the quality of mucosal scar affected by treatment? Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1995;210:9–14. doi: 10.3109/00365529509090261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tureaud J., Sarkar F. H., Fligiel S. E., Kulkarni S., Jaszewski R., Reddy K., Yu Y., Majumdar A. P. Increased expression of EGFR in gastric mucosa of aged rats. Am J Physiol. 1997 Aug;273(2 Pt 1):G389–G398. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1997.273.2.G389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet. 1983 Jun 4;1(8336):1273–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright N. A., Pike C., Elia G. Induction of a novel epidermal growth factor-secreting cell lineage by mucosal ulceration in human gastrointestinal stem cells. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):82–85. doi: 10.1038/343082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Dent P., Jelinek T., Wolfman A., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Inhibition of the EGF-activated MAP kinase signaling pathway by adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Science. 1993 Nov 12;262(5136):1065–1069. doi: 10.1126/science.7694366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyle F. A., Tarnawski A., Dabros W., Gergely H. Campylobacter pylori interactions with gastric cell tissue culture. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1990;12 (Suppl 1):S99–103. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199001001-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshiura K., Ota S., Terano A., Takahashi M., Hata Y., Kawabe T., Mutoh H., Hiraishi H., Nakata R., Okano K. Growth regulation of rabbit gastric epithelial cells and protooncogene expression. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Jul;39(7):1454–1463. doi: 10.1007/BF02088048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]