Abstract
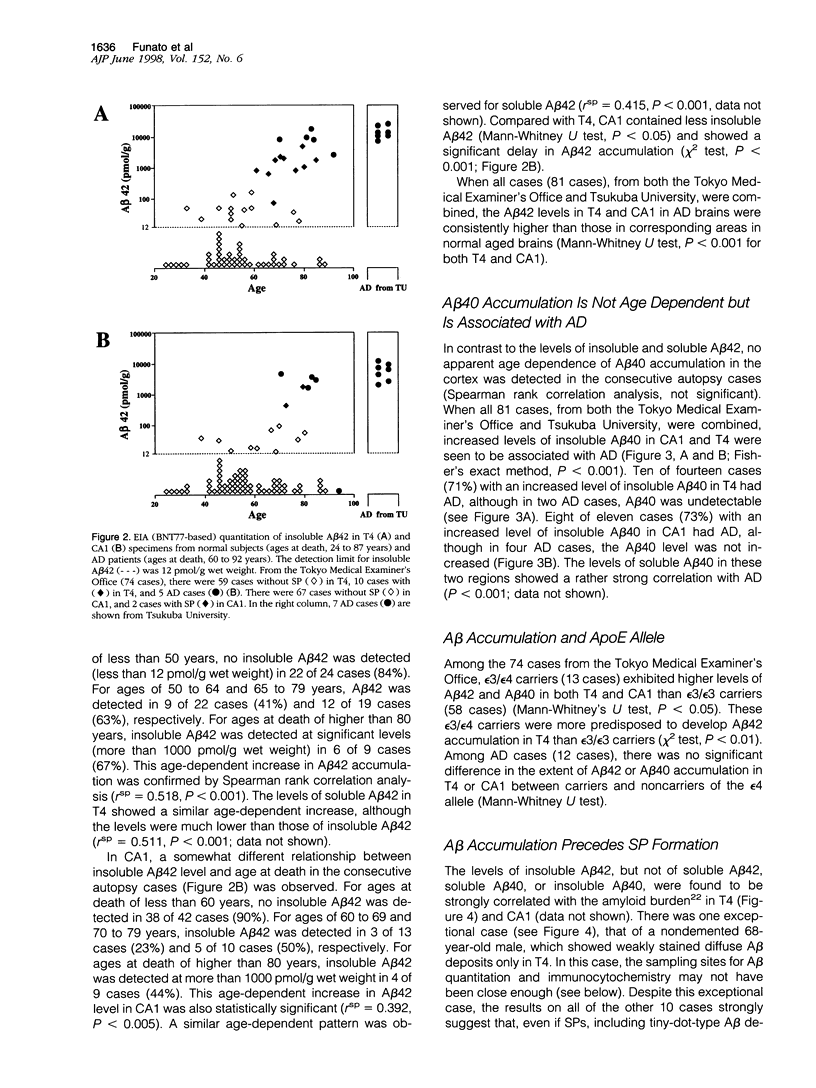
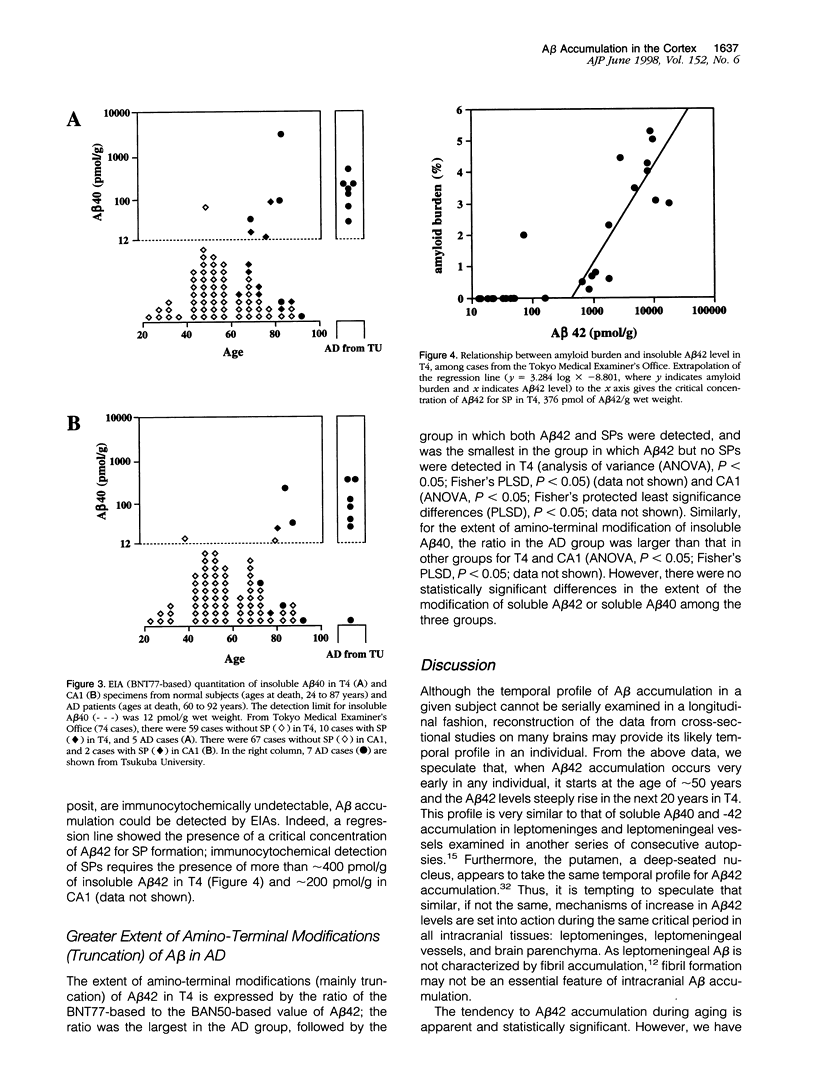
In this study we sought to learn about when and how amyloid beta-protein (A beta) accumulates in the cortex of normal individuals and about the difference in the A beta accumulation between normal aged and Alzheimer's disease (AD) brains. From consecutive autopsy cases and AD cases, hippocampus CA1 and occipitotemporal cortex T4 were sampled for A beta quantitation by the well characterized two-site enzyme immunoassays (EIAs). There was a strong tendency toward A beta 42 accumulation between the ages of 50 and 70 years in T4 and a little later in CA1. The A beta 42 levels were consistently higher in T4 than those in CA1 in any given case. The levels of A beta 42 in AD brains were significantly higher than those in control brains, and the extent of A beta 42 amino-terminal modification was also much greater in AD brains than that in control brains. Even in cases in which no senile plaques were immunocytochemically detected, EIAs clearly showed that significant amounts of A beta 42 already had accumulated. In contrast to A beta 42, A beta 40 showed no apparent age-dependent accumulation, and its high levels were found to be associated with AD.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asami-Odaka A., Ishibashi Y., Kikuchi T., Kitada C., Suzuki N. Long amyloid beta-protein secreted from wild-type human neuroblastoma IMR-32 cells. Biochemistry. 1995 Aug 15;34(32):10272–10278. doi: 10.1021/bi00032a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braak H., Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82(4):239–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00308809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies L., Wolska B., Hilbich C., Multhaup G., Martins R., Simms G., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L. A4 amyloid protein deposition and the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: prevalence in aged brains determined by immunocytochemistry compared with conventional neuropathologic techniques. Neurology. 1988 Nov;38(11):1688–1693. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.11.1688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff K., Eckman C., Zehr C., Yu X., Prada C. M., Perez-tur J., Hutton M., Buee L., Harigaya Y., Yager D. Increased amyloid-beta42(43) in brains of mice expressing mutant presenilin 1. Nature. 1996 Oct 24;383(6602):710–713. doi: 10.1038/383710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Asami-Odaka A., Suzuki N., Shimada H., Ihara Y., Iwatsubo T. Amyloid beta protein deposition in normal aging has the same characteristics as that in Alzheimer's disease. Predominance of A beta 42(43) and association of A beta 40 with cored plaques. Am J Pathol. 1996 Jan;148(1):259–265. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing M., Mori H., Mirra S. S. Abeta-peptide length and apolipoprotein E genotype in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1996 Mar;39(3):395–399. doi: 10.1002/ana.410390320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowing E., Roher A. E., Woods A. S., Cotter R. J., Chaney M., Little S. P., Ball M. J. Chemical characterization of A beta 17-42 peptide, a component of diffuse amyloid deposits of Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):10987–10990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravina S. A., Ho L., Eckman C. B., Long K. E., Otvos L., Jr, Younkin L. H., Suzuki N., Younkin S. G. Amyloid beta protein (A beta) in Alzheimer's disease brain. Biochemical and immunocytochemical analysis with antibodies specific for forms ending at A beta 40 or A beta 42(43). J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 31;270(13):7013–7016. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.13.7013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamano T., Yoshimura M., Yamazaki T., Shinkai Y., Yanagisawa K., Kuriyama M., Ihara Y. Amyloid beta-protein (A beta) accumulation in the leptomeninges during aging and in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1997 Aug;56(8):922–932. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199708000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Vernier D. T. Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res. 1990 Mar;31(3):545–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Marzloff K., Arriagada P. V. The lack of accumulation of senile plaques or amyloid burden in Alzheimer's disease suggests a dynamic balance between amyloid deposition and resolution. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1993 Nov;52(6):594–600. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199311000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Tamaoka A., Mizusawa H., Shoji S., Ohtake T., Fraser P. E., Takahashi H., Tsuji S., Gearing M., Mizutani T. Abeta1-40 but not Abeta1-42 levels in cortex correlate with apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele dosage in sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 1997 Feb 14;748(1-2):250–252. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(96)01363-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsubo T., Mann D. M., Odaka A., Suzuki N., Ihara Y. Amyloid beta protein (A beta) deposition: A beta 42(43) precedes A beta 40 in Down syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1995 Mar;37(3):294–299. doi: 10.1002/ana.410370305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsubo T., Odaka A., Suzuki N., Mizusawa H., Nukina N., Ihara Y. Visualization of A beta 42(43) and A beta 40 in senile plaques with end-specific A beta monoclonals: evidence that an initially deposited species is A beta 42(43). Neuron. 1994 Jul;13(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90458-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson-Wood K., Lee M., Motter R., Hu K., Gordon G., Barbour R., Khan K., Gordon M., Tan H., Games D. Amyloid precursor protein processing and A beta42 deposition in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Feb 18;94(4):1550–1555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.4.1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo Y. M., Emmerling M. R., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Kasunic T. C., Kirkpatrick J. B., Murdoch G. H., Ball M. J., Roher A. E. Water-soluble Abeta (N-40, N-42) oligomers in normal and Alzheimer disease brains. J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 23;271(8):4077–4081. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.8.4077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue L. F., Brachova L., Civin W. H., Rogers J. Inflammation, A beta deposition, and neurofibrillary tangle formation as correlates of Alzheimer's disease neurodegeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1996 Oct;55(10):1083–1088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Takio K., Ogawara M., Selkoe D. J. Mass spectrometry of purified amyloid beta protein in Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17082–17086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi J., Yoshimura M., Morishima-Kawashima M., Funato H., Miyakawa T., Yamazaki T., Ihara Y. Amyloid beta-protein (A beta) accumulation in the putamen and mammillary body during aging and in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1998 Apr;57(4):343–352. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199804000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanaga M., Yasuda T., Tenjo E., Nadano D., Fujiki N., Kishi K. Transferrin polymorphisms in Japanese populations: north-south cline in the distribution of the TF*C2 allele. Hum Biol. 1991 Apr;63(2):186–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namekata K., Imagawa M., Terashi A., Ohta S., Oyama F., Ihara Y. Association of transferrin C2 allele with late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Hum Genet. 1997 Dec;101(2):126–129. doi: 10.1007/s004390050600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namekata K., Oyama F., Imagawa M., Ihara Y. Human transferrin (Tf): a single mutation at codon 570 determines Tf C1 or Tf C2 variant. Hum Genet. 1997 Sep;100(3-4):457–458. doi: 10.1007/s004390050533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polvikoski T., Sulkava R., Haltia M., Kainulainen K., Vuorio A., Verkkoniemi A., Niinistö L., Halonen P., Kontula K. Apolipoprotein E, dementia, and cortical deposition of beta-amyloid protein. N Engl J Med. 1995 Nov 9;333(19):1242–1247. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199511093331902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebeck G. W., Reiter J. S., Strickland D. K., Hyman B. T. Apolipoprotein E in sporadic Alzheimer's disease: allelic variation and receptor interactions. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):575–580. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roher A. E., Chaney M. O., Kuo Y. M., Webster S. D., Stine W. B., Haverkamp L. J., Woods A. S., Cotter R. J., Tuohy J. M., Krafft G. A. Morphology and toxicity of Abeta-(1-42) dimer derived from neuritic and vascular amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Chem. 1996 Aug 23;271(34):20631–20635. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.34.20631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roher A. E., Lowenson J. D., Clarke S., Wolkow C., Wang R., Cotter R. J., Reardon I. M., Zürcher-Neely H. A., Heinrikson R. L., Ball M. J. Structural alterations in the peptide backbone of beta-amyloid core protein may account for its deposition and stability in Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3072–3083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saido T. C., Yamao-Harigaya W., Iwatsubo T., Kawashima S. Amino- and carboxyl-terminal heterogeneity of beta-amyloid peptides deposited in human brain. Neurosci Lett. 1996 Sep 13;215(3):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(96)12970-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D. E., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Crain B. J., Hulette C. M., Joo S. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Goldgaber D., Roses A. D. Increased amyloid beta-peptide deposition in cerebral cortex as a consequence of apolipoprotein E genotype in late-onset Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9649–9653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J. Alzheimer's disease: a central role for amyloid. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1994 Sep;53(5):438–447. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199409000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai Y., Yoshimura M., Ito Y., Odaka A., Suzuki N., Yanagisawa K., Ihara Y. Amyloid beta-proteins 1-40 and 1-42(43) in the soluble fraction of extra- and intracranial blood vessels. Ann Neurol. 1995 Sep;38(3):421–428. doi: 10.1002/ana.410380312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai Y., Yoshimura M., Morishima-Kawashima M., Ito Y., Shimada H., Yanagisawa K., Ihara Y. Amyloid beta-protein deposition in the leptomeninges and cerebral cortex. Ann Neurol. 1997 Dec;42(6):899–908. doi: 10.1002/ana.410420612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Cheung T. T., Cai X. D., Odaka A., Otvos L., Jr, Eckman C., Golde T. E., Younkin S. G. An increased percentage of long amyloid beta protein secreted by familial amyloid beta protein precursor (beta APP717) mutants. Science. 1994 May 27;264(5163):1336–1340. doi: 10.1126/science.8191290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoka A., Odaka A., Ishibashi Y., Usami M., Sahara N., Suzuki N., Nukina N., Mizusawa H., Shoji S., Kanazawa I. APP717 missense mutation affects the ratio of amyloid beta protein species (A beta 1-42/43 and a beta 1-40) in familial Alzheimer's disease brain. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 30;269(52):32721–32724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tierney M. C., Fisher R. H., Lewis A. J., Zorzitto M. L., Snow W. G., Reid D. W., Nieuwstraten P. The NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group criteria for the clinical diagnosis of probable Alzheimer's disease: a clinicopathologic study of 57 cases. Neurology. 1988 Mar;38(3):359–364. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T., Maruyama K., Saido T. C., Kume H., Shinozaki K., Tokuhiro S., Capell A., Walter J., Grünberg J., Haass C. The presenilin 2 mutation (N141I) linked to familial Alzheimer disease (Volga German families) increases the secretion of amyloid beta protein ending at the 42nd (or 43rd) residue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Mar 4;94(5):2025–2030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.5.2025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Vorbrodt A. W., Wegiel J. Amyloid angiopathy and blood-brain barrier changes in Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997 Sep 26;826:161–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1997.tb48468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa K., Odaka A., Suzuki N., Ihara Y. GM1 ganglioside-bound amyloid beta-protein (A beta): a possible form of preamyloid in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Med. 1995 Oct;1(10):1062–1066. doi: 10.1038/nm1095-1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa T., Yamakawa-Kobayashi K., Komatsuzaki Y., Arinami T., Oguni E., Mizusawa H., Shoji S., Hamaguchi H. Dose-dependent association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset, sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1994 Oct;36(4):656–659. doi: 10.1002/ana.410360416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


