Abstract
The aims of this study were (1) to carry out a nutritional assessment of selected Irish athletes and (2) to provide individual results and specific advice to each athlete on how to achieve an optimum diet.
Dietary intakes were measured by a three-day weighed dietary record technique designed to evaluate each athlete's usual eating habits. The results were evaluated against a set of dietary standards in order to determine adequacy.
Nutritional status was also assessed in a limited form by selected anthropometric and biochemical measurements.
A total of 148 subjects took part in the assessment which began in May, 1979 and continued until April, 1980. The sports involved included: canoeing, cycling, rowing, swimming, hockey, squash and track and field events.
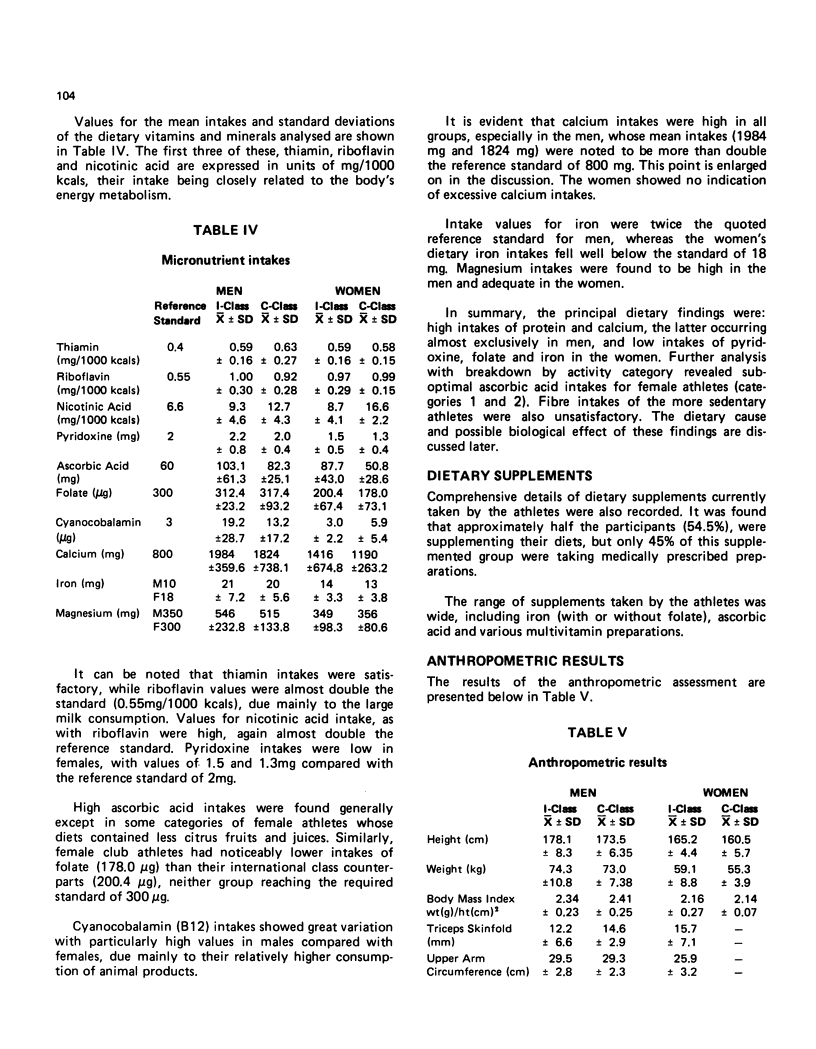
The results indicated a range of sub-optimal dietary patterns relating in particular to abnormal intakes of folate, iron, pyridoxine and calcium. The significance and applications of these findings are discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Consolazio C. F., Johnson H. L., Nelson R. A., Dramise J. G., Skala J. H. Protein metabolism during intensive physical training in the young adult. Am J Clin Nutr. 1975 Jan;28(1):29–35. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/28.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. D., Finch C. A. Assessing iron status of a population. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Oct;32(10):2115–2119. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.10.2115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbourt U., Medalie J. H. Weight-height indices. Choice of the most suitable index and its association with selected variables among 10,000 adult males of heterogeneous origin. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1974 May;28(2):116–126. doi: 10.1136/jech.28.2.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luhby A. L., Brin M., Gordon M., Davis P., Murphy M., Spiegel H. Vitamin B 6 metabolism in users of oral contraceptive agents. I. Abnormal urinary xanthurenic acid excretion and its correction by pyridoxine. Am J Clin Nutr. 1971 Jun;24(6):684–693. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/24.6.684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr J. W. Individual dietary surveys: purposes and methods. World Rev Nutr Diet. 1971;13:105–164. doi: 10.1159/000391884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R., Woodcock N. A., Blakely J. D., MacKellar I. Metabolic responses of adolescent boys to two levels of dietary magnesium and protein. II. Effect of magnesium and and protein level on calcium balance. Am J Clin Nutr. 1973 May;26(5):519–523. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/26.5.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmore J. H., Behnke A. R. An anthropometric estimation of body density and lean body weight in young men. J Appl Physiol. 1969 Jul;27(1):25–31. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1969.27.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmore J. H., Behnke A. R. An anthropometric estimation of body density and lean body weight in young women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Mar;23(3):267–274. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]