Abstract
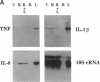
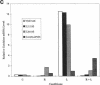
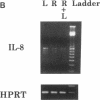
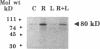
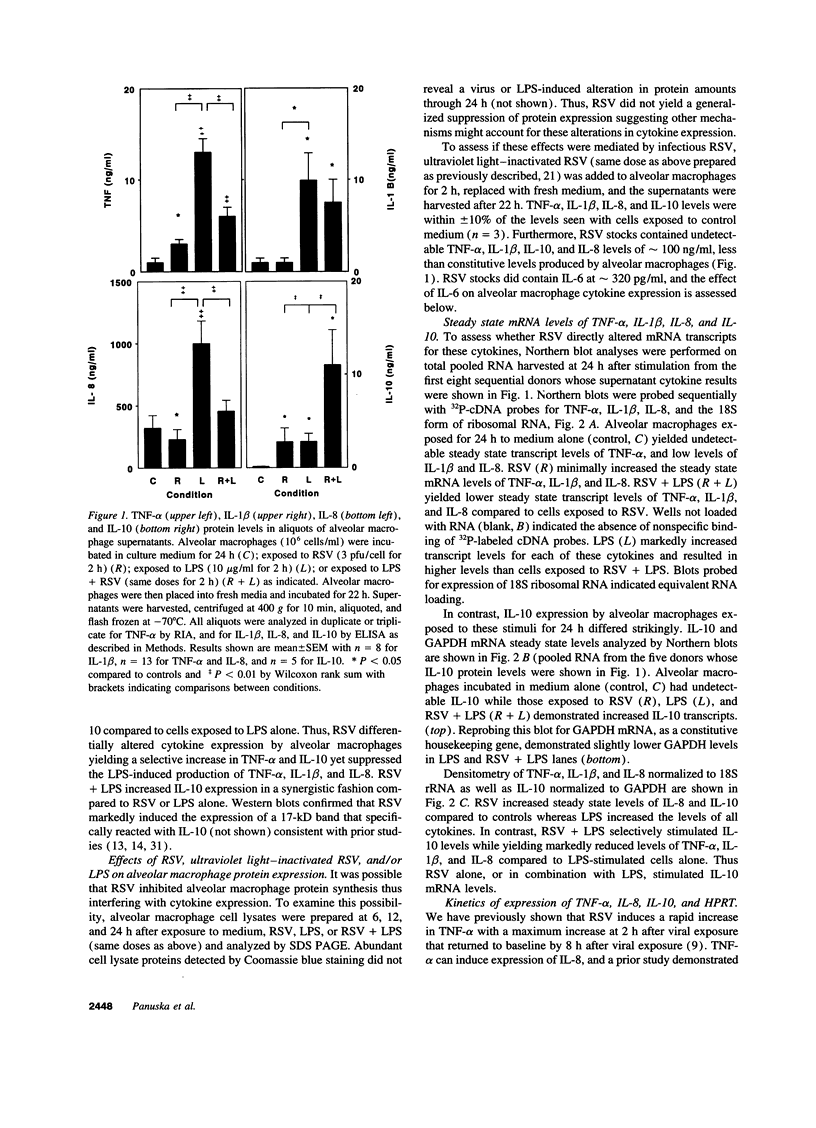
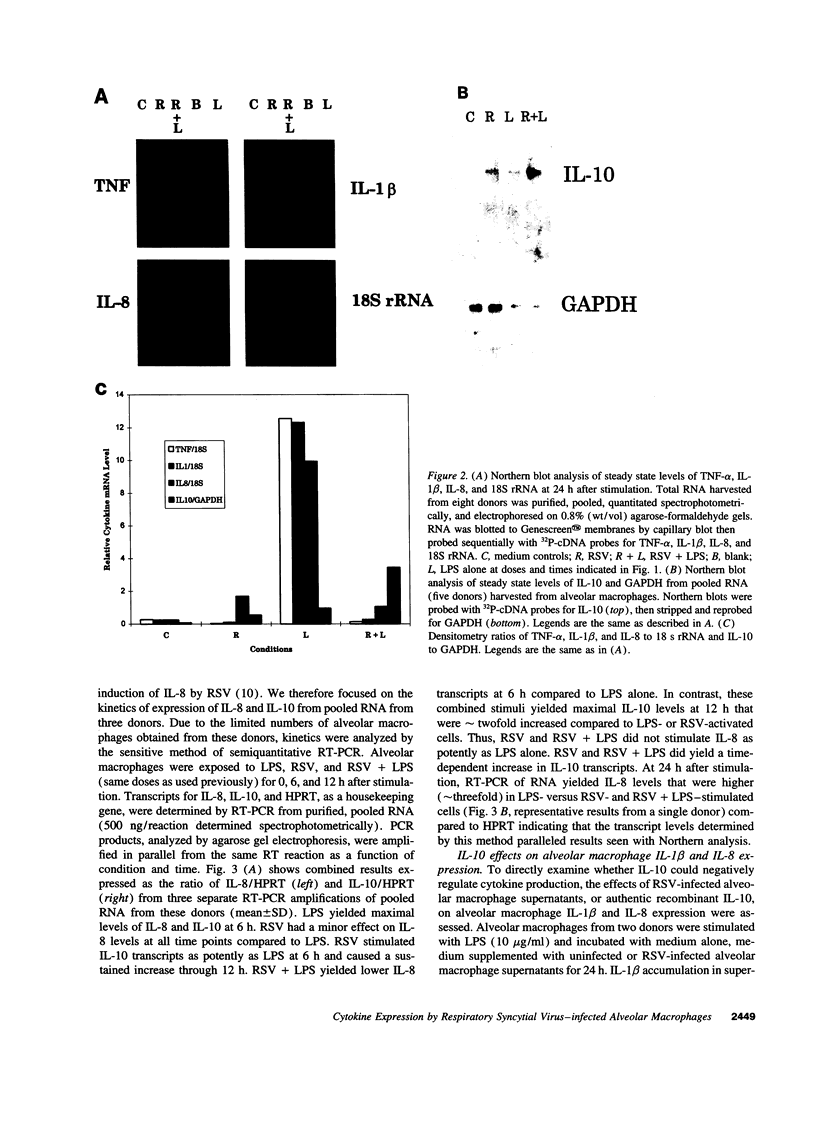
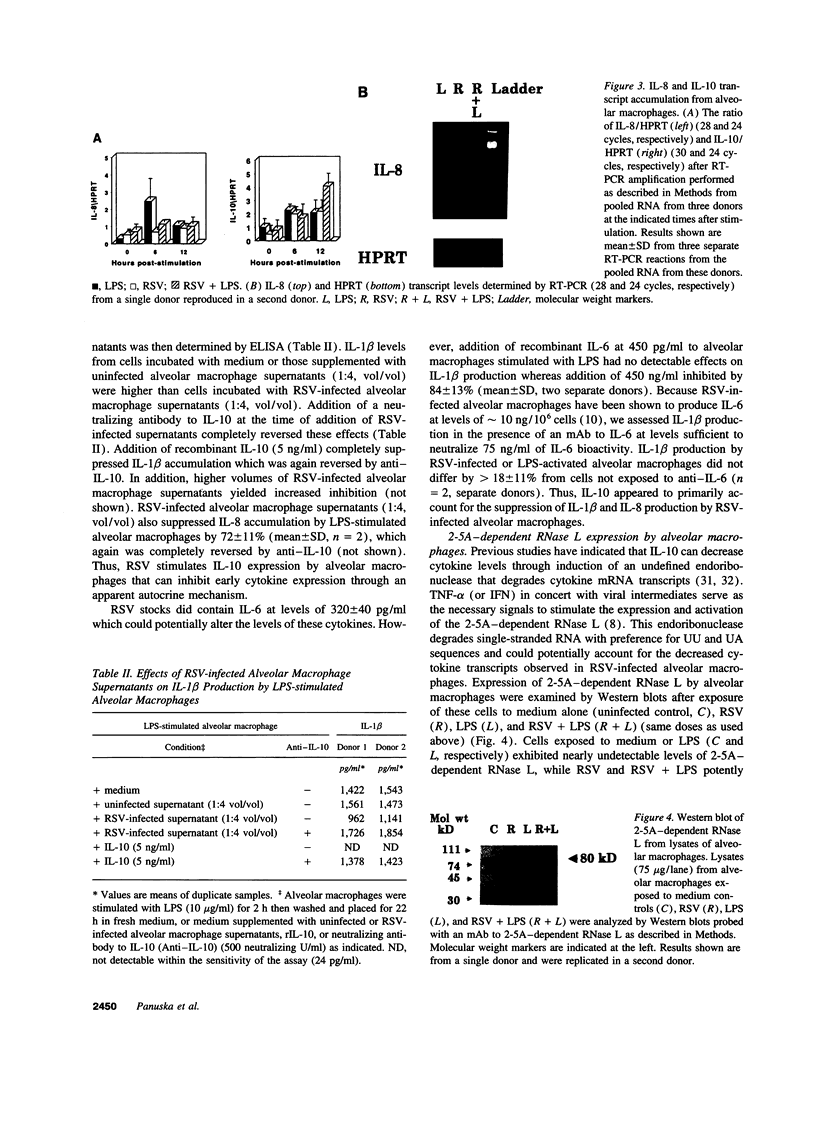
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes repeated infections thought to be due to an ineffective immune response. We examined the hypothesis that incomplete immunity may result, in part, from RSV-infected alveolar macrophage production of IL-10 which can interfere with the production of immunoregulatory cytokines. We also assessed whether RSV induced the expression of the 2',5' oligoadenylate (2-5A)-dependent RNase L, an endoribonuclease involved in the antiviral activities of interferons. Human alveolar macrophages were exposed to medium (uninfected control), RSV, LPS, and RSV + LPS then were assessed for expression of the cytokines TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-8, IL-10, as well as 2-5A-dependent RNase L. LPS up-regulated the expression of protein and mRNA for all cytokines. RSV stimulated the protein levels of TNF-alpha, did not alter IL-1 beta, and decreased IL-8. RSV markedly stimulated protein expression of IL-10 and 2-5A-dependent RNase L. RSV had minor effects on the steady state mRNA levels of TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta, and IL-8, yet potently induced IL-10. Cells costimulated with RSV + LPS demonstrated reduced protein and mRNA levels of TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-8 but synergistically increased IL-10 levels compared to RSV- or LPS-activated cells. Kinetic analysis indicated that RSV induced a delayed and sustained increase in IL-10 transcripts. Furthermore, RSV-infected alveolar macrophage supernatants suppressed IL-1 beta and IL-8 production by LPS-stimulated alveolar macrophages as did recombinant IL-10. Anti-IL-10 neutralized these effects. These studies indicate that RSV is capable of suppressing production of early immunoregulatory cytokines through induction of IL-10 perhaps mediated by 2-5A-dependent RNase L (or other endoribonucleases) accounting for the ineffective immune response to this virus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baggiolini M., Walz A., Kunkel S. L. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI114265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker S., Quay J., Soukup J. Cytokine (tumor necrosis factor, IL-6, and IL-8) production by respiratory syncytial virus-infected human alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4307–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan C., Paik J., Vodovotz Y., Nathan C. Contrasting mechanisms for suppression of macrophage cytokine release by transforming growth factor-beta and interleukin-10. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23301–23308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan C., Vodovotz Y., Nathan C. Macrophage deactivation by interleukin 10. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1549–1555. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirino N. M., Panuska J. R., Villani A., Taraf H., Rebert N. A., Merolla R., Tsivitse P., Gilbert I. A. Restricted replication of respiratory syncytial virus in human alveolar macrophages. J Gen Virol. 1993 Aug;74(Pt 8):1527–1537. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-8-1527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connors M., Giese N. A., Kulkarni A. B., Firestone C. Y., Morse H. C., 3rd, Murphy B. R. Enhanced pulmonary histopathology induced by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) challenge of formalin-inactivated RSV-immunized BALB/c mice is abrogated by depletion of interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-10. J Virol. 1994 Aug;68(8):5321–5325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.8.5321-5325.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe J. E., Jr, Murphy B. R., Chanock R. M., Williamson R. A., Barbas C. F., 3rd, Burton D. R. Recombinant human respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) monoclonal antibody Fab is effective therapeutically when introduced directly into the lungs of RSV-infected mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1386–1390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong B., Silverman R. H. 2-5A-dependent RNase molecules dimerize during activation by 2-5A. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 24;270(8):4133–4137. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.8.4133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias J. A., Zheng T., Einarsson O., Landry M., Trow T., Rebert N., Panuska J. Epithelial interleukin-11. Regulation by cytokines, respiratory syncytial virus, and retinoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 2;269(35):22261–22268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fels A. O., Cohn Z. A. The alveolar macrophage. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Feb;60(2):353–369. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentino D. F., Zlotnik A., Mosmann T. R., Howard M., O'Garra A. IL-10 inhibits cytokine production by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3815–3822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. B., Douglas R. G., Jr, Simons R. L., Geiman J. M. Interferon production in children with respiratory syncytial, influenza, and parainfluenza virus infections. J Pediatr. 1978 Jul;93(1):28–32. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassel B. A., Zhou A., Sotomayor C., Maran A., Silverman R. H. A dominant negative mutant of 2-5A-dependent RNase suppresses antiproliferative and antiviral effects of interferon. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3297–3304. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05999.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman C. A. From the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and the World Health Organization. Respiratory syncytial and parainfluenza viruses. J Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;161(3):402–406. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.3.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley J. Cytokines of the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Mar;141(3):765–788. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.3.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurilla M. G., Swaminathan S., Welsh R. M., Kieff E., Brutkiewicz R. R. Effects of virally expressed interleukin-10 on vaccinia virus infection in mice. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7623–7628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7623-7628.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestan J., Brockhaus M., Kirchner H., Jacobsen H. Antiviral activity of tumour necrosis factor. Synergism with interferons and induction of oligo-2',5'-adenylate synthetase. J Gen Virol. 1988 Dec;69(Pt 12):3113–3120. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-12-3113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metinko A. P., Kunkel S. L., Standiford T. J., Strieter R. M. Anoxia-hyperoxia induces monocyte-derived interleukin-8. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):791–798. doi: 10.1172/JCI115953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midulla F., Villani A., Panuska J. R., Dab I., Kolls J. K., Merolla R., Ronchetti R. Respiratory syncytial virus lung infection in infants: immunoregulatory role of infected alveolar macrophages. J Infect Dis. 1993 Dec;168(6):1515–1519. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.6.1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabioullin R., Sone S., Mizuno K., Yano S., Nishioka Y., Haku T., Ogura T. Interleukin-10 is a potent inhibitor of tumor cytotoxicity by human monocytes and alveolar macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1994 Apr;55(4):437–442. doi: 10.1002/jlb.55.4.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panuska J. R., Cirino N. M., Midulla F., Despot J. E., McFadden E. R., Jr, Huang Y. T. Productive infection of isolated human alveolar macrophages by respiratory syncytial virus. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):113–119. doi: 10.1172/JCI114672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panuska J. R., Hertz M. I., Taraf H., Villani A., Cirino N. M. Respiratory syncytial virus infection of alveolar macrophages in adult transplant patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Apr;145(4 Pt 1):934–939. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.4_Pt_1.934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panuska J. R., Midulla F., Cirino N. M., Villani A., Gilbert I. A., McFadden E. R., Jr, Huang Y. T. Virus-induced alterations in macrophage production of tumor necrosis factor and prostaglandin E2. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 1):L396–L402. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.259.6.L396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin J. A., Sylvester I., Smith S., Yoshimura T., Leonard E. J. Macrophages cultured in vitro release leukotriene B4 and neutrophil attractant/activation protein (interleukin 8) sequentially in response to stimulation with lipopolysaccharide and zymosan. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1556–1564. doi: 10.1172/JCI114875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts N. J., Jr, Hiscott J., Signs D. J. The limited role of the human interferon system response to respiratory syncytial virus challenge: analysis and comparison to influenza virus challenge. Microb Pathog. 1992 Jun;12(6):409–414. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salkind A. R., McCarthy D. O., Nichols J. E., Domurat F. M., Walsh E. E., Roberts N. J., Jr Interleukin-1-inhibitor activity induced by respiratory syncytial virus: abrogation of virus-specific and alternate human lymphocyte proliferative responses. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):71–77. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salkind A. R., Nichols J. E., Roberts N. J., Jr Suppressed expression of ICAM-1 and LFA-1 and abrogation of leukocyte collaboration after exposure of human mononuclear leukocytes to respiratory syncytial virus in vitro. Comparison with exposure to influenza virus. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):505–511. doi: 10.1172/JCI115332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarawar S. R., Doherty P. C. Concurrent production of interleukin-2, interleukin-10, and gamma interferon in the regional lymph nodes of mice with influenza pneumonia. J Virol. 1994 May;68(5):3112–3119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.5.3112-3119.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford T. J., Kunkel S. L., Kasahara K., Milia M. J., Rolfe M. W., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 gene expression from human alveolar macrophages: the role of adherence. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Dec;5(6):579–585. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.6.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. P., Rooney C. M. The interleukin-10 homolog encoded by Epstein-Barr virus enhances the reactivation of virus-specific cytotoxic T cell and HLA-unrestricted killer cell responses. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):773–782. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90253-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Chensue S. W., Basha M. A., Standiford T. J., Lynch J. P., Baggiolini M., Kunkel S. L. Human alveolar macrophage gene expression of interleukin-8 by tumor necrosis factor-alpha, lipopolysaccharide, and interleukin-1 beta. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):321–326. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/2.4.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvester I., Rankin J. A., Yoshimura T., Tanaka S., Leonard E. J. Secretion of neutrophil attractant/activation protein by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated lung macrophages determined by both enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and N-terminal sequence analysis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Mar;141(3):683–688. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.3.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tristram D. A., Welliver R. C., Mohar C. K., Hogerman D. A., Hildreth S. W., Paradiso P. Immunogenicity and safety of respiratory syncytial virus subunit vaccine in seropositive children 18-36 months old. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jan;167(1):191–195. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.1.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Cerottini J. C. Antigen presentation. FASEB J. 1989 Nov;3(13):2496–2502. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.13.2572499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira P., de Waal-Malefyt R., Dang M. N., Johnson K. E., Kastelein R., Fiorentino D. F., deVries J. E., Roncarolo M. G., Mosmann T. R., Moore K. W. Isolation and expression of human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor cDNA clones: homology to Epstein-Barr virus open reading frame BCRFI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1172–1176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P., Wu P., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. IL-10 inhibits transcription of cytokine genes in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 15;153(2):811–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welliver R. C., Wong D. T., Sun M., Middleton E., Jr, Vaughan R. S., Ogra P. L. The development of respiratory syncytial virus-specific IgE and the release of histamine in nasopharyngeal secretions after infection. N Engl J Med. 1981 Oct 8;305(15):841–846. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198110083051501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. Tumour necrosis factors alpha and beta inhibit virus replication and synergize with interferons. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):819–822. doi: 10.1038/323819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou A., Hassel B. A., Silverman R. H. Expression cloning of 2-5A-dependent RNAase: a uniquely regulated mediator of interferon action. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):753–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90403-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waal Malefyt R., Abrams J., Bennett B., Figdor C. G., de Vries J. E. Interleukin 10(IL-10) inhibits cytokine synthesis by human monocytes: an autoregulatory role of IL-10 produced by monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1209–1220. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]