Abstract
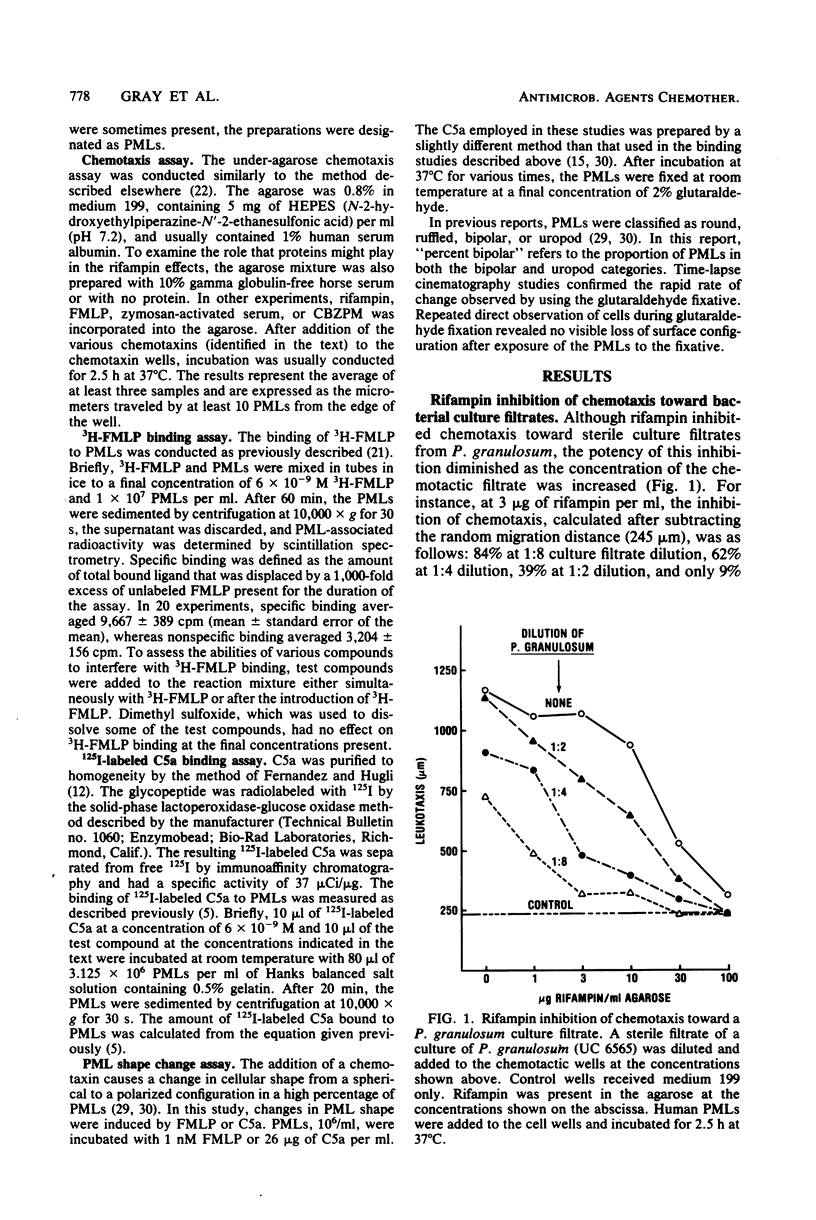
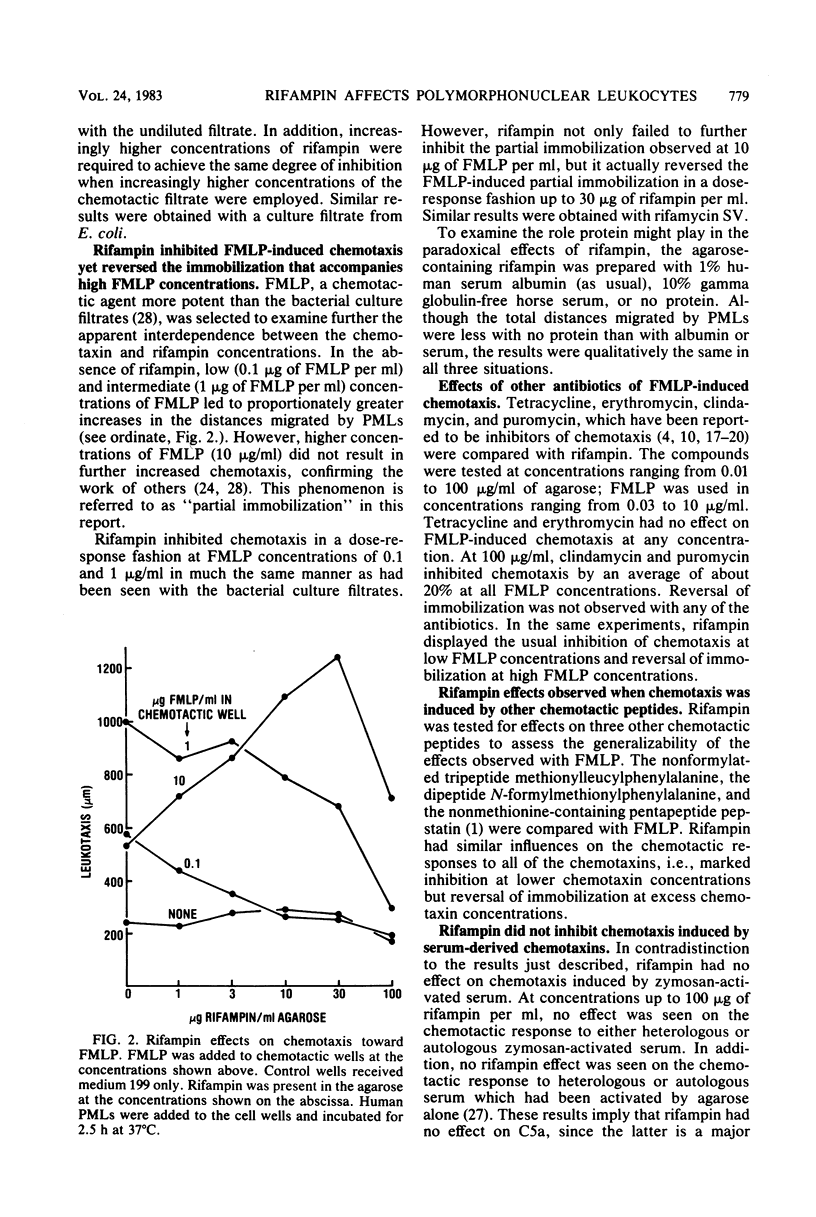
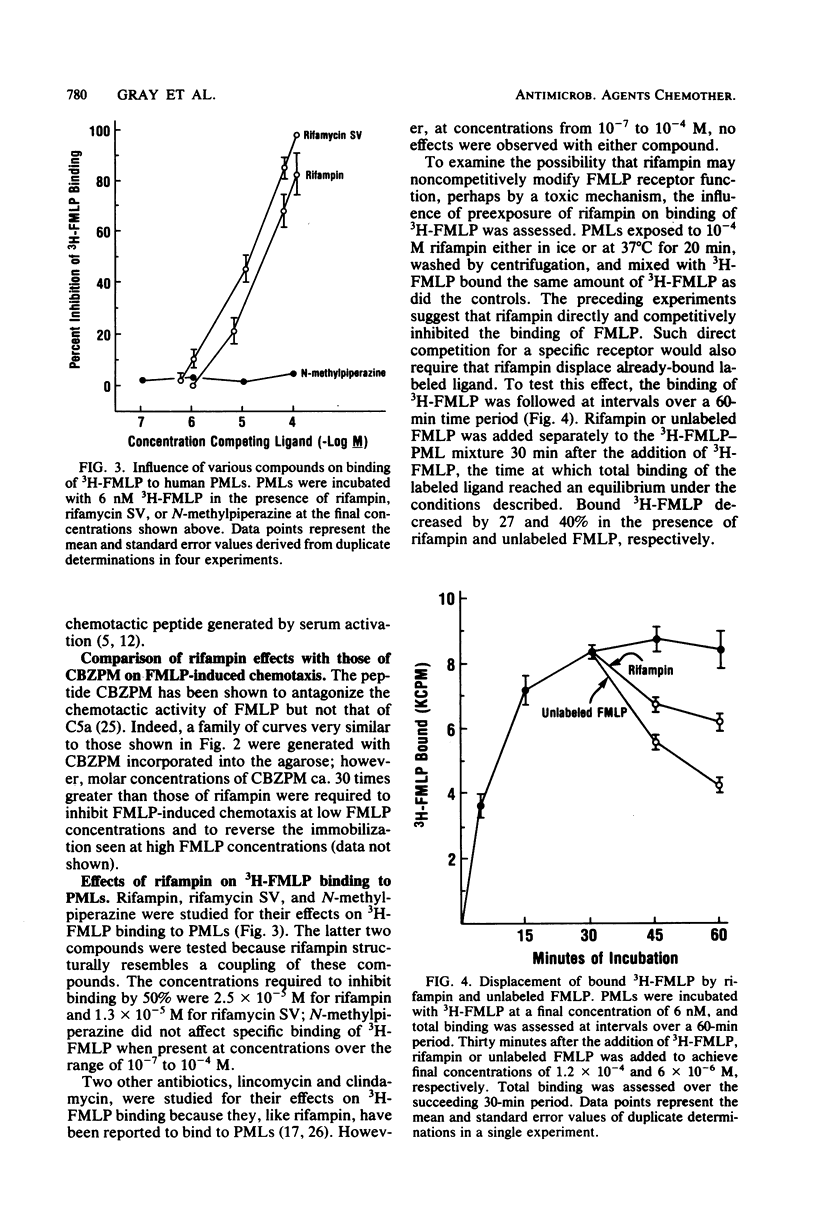
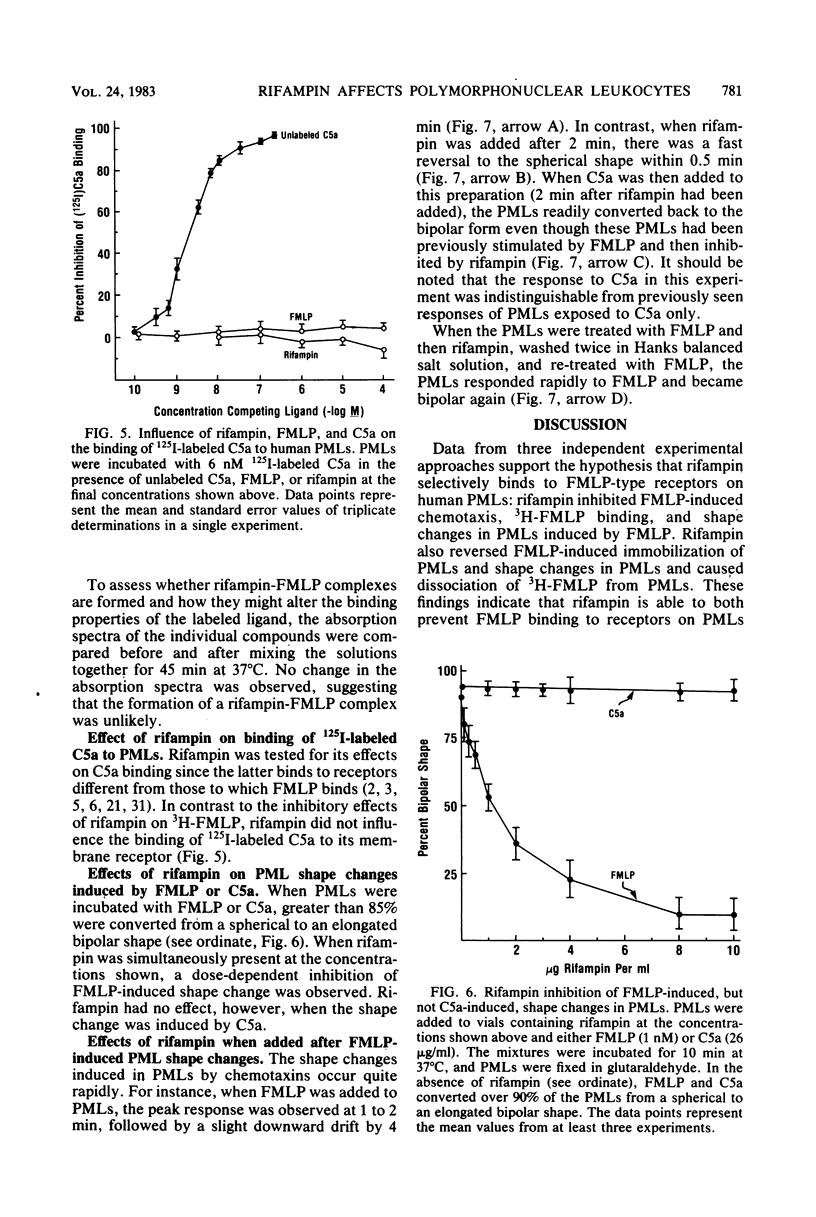
Three independent experimental approaches support the hypothesis that rifampin competes for receptors on polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMLs) with small peptide chemoattractants, e.g., N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine (FMLP), but not with serum-derived chemoattractants (C5a). First, rifampin inhibited chemotaxis induced with FMLP but reversed the immobilization of PMLs that occurred at high FMLP concentrations. Second, rifampin competed with radiolabeled FMLP for binding sites on PMLs and displaced already-bound radiolabeled FMLP. Third, rifampin blocked and reversed the bipolar shape changes induced in PMLs by FMLP. These effects occurred at concentrations attained during rifampin therapy and were not due to rifampin toxicity. In contrast, no effect of rifampin was observed on serum-derived chemoattractants (C5a) in any of the three systems. The evidence suggests, therefore, that rifampin is a ligand for FMLP-type receptors on PMLs.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. K., Douglas S. D. Pepstatin A--a human leukocyte chemoattractant. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Oct;14(2):244–250. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Schiffmann E., Day A. R., Freer R. J., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Demonstration of a receptor on rabbit neutrophils for chemotactic peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):810–817. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswanikumar S., Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. Role of a peptidase in phagocyte chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2439–2442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers B. M. Leukocyte motility. II. Effect of absence of glucose in medium; effect of presence of deoxyglucose, dinitrophenol, puromycin, actinomycin D, and trypsin on the response to chemotactic substance; effect of segregation of cells from chemotactic substance. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1967 Mar;45(2):269–280. doi: 10.1139/y67-029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Hugli T. E. Demonstration of specific C5a receptor on intact human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3943–3947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Lane T. A., Rowe J. G., Hugli T. E. Quantitative comparisons of neutrophil chemotaxis in four animal species. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Mar;15(3):525–535. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine L. F., Johnson D. P., Rhode S. L., 3rd, Hagerman C. R., Pierce W. E., Peckinpaugh R. O. Rifampin: effect of two-day treatment on the meningococcal carrier state and the relationship to the levels of drug in sera and saliva. Am J Med Sci. 1971 Feb;261(2):79–83. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197102000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson J. M., Mitchison D. A., Lee S. K., Ong Y. Y., O'Mahoney M. G., Girling D. J., Nunn A. J. Serum rifampicin concentration related to dose size and to the incidence of the 'flu' syndrome during intermittent rifampicin administration. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Sep;3(5):445–452. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.5.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English D., Andersen B. R. Single-step separation of red blood cells. Granulocytes and mononuclear leukocytes on discontinuous density gradients of Ficoll-Hypaque. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterly N. B., Furey N. L., Flanagan L. E. The effect of antimicrobial agents on leukocyte chemotaxis. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Jan;70(1):51–55. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12543487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon R. J., Lees A. W., Allan G. W., Smith J., Tyrrell W. F. Probenecid and rifampicin serum levels. Lancet. 1975 Oct 25;2(7939):792–794. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Hugli T. E. Partial characterization of human C5a anaphylatoxin. I. Chemical description of the carbohydrate and polypeptide prtions of human C5a. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1688–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Schmeling D. Effect of antibiotics of chemotaxis of human leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):580–584. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Rosenthal A. S. The regulatory role of divalent cations in human granulocyte chemotaxis. Evidence for an association between calcium exchanges and microtubule assembly. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):594–609. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnham J. C., Taylor T., Turner P., Chasseaud L. F. Serum concentrations and bioavailability of rifampicin and isoniazid in combination. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;3(5):897–902. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1976.tb00644.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Styrt B. Clindamycin uptake by human neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1981 Nov;144(5):472–479. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.5.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majeski J. A., Alexander J. W. Evaluation of tetracycline in the neutrophil chemotactic response. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Aug;90(2):259–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majeski J. A., McClellan M. A., Alexander J. W. Effect of antibiotics on the in vitro neutrophil chemotactic response. Am Surg. 1976 Oct;42(10):785–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. R., Warr G. A., Couch R. B., Yeager H., Knight V. Effects of tetracycline on leukotaxis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):110–116. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Ackerman S. K., Fiegel V. D., Bauman M. P., Douglas S. D. Cytotaxin receptors of neutrophils: evidence that F-methionyl peptides and pepstatin share a common receptor. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):996–999. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.996-999.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Quie P. G., Simmons R. L. Chemotaxis under agarose: a new and simple method for measuring chemotaxis and spontaneous migration of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1650–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitti V., Delli Veneri F., Ninni A., Meola G. Rifampicin blood serum levels and half-life during prolonged administration in tuberculous patients. Chemotherapy. 1972;17(2):121–129. doi: 10.1159/000220845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Showell H. J., Vitkauskas G., Becker E. L., Ward P. A. Selective neutrophil desensitization to chemotactic factors. J Cell Biol. 1979 Mar;80(3):564–572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.3.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Showell H. J., Kreutzer D. L., Ward P. A., Becker E. L. Inhibition of in vivo and in vitro neutrophil responses to chemotactic factors by a competitive antagonist. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1326–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokesch R. C., Hand W. L. Antibiotic entry into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):373–380. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repo H. Leukocyte migration agarose test for the assessment of human neutrophil chemotaxis. I. Effects of environmental factors on neutrophil migration under agarose. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(3):203–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Hollers J. C. Motility and adhesiveness in human neutrophils. Redistribution of chemotactic factor-induced adhesion sites. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):804–812. doi: 10.1172/JCI109731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Hollers J. C., Patrick R. A., Hassett C. Motility and adhesiveness in human neutrophils. Effects of chemotactic factors. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):221–229. doi: 10.1172/JCI109293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Lefkowitz R. J. Specific receptor sites for chemotactic peptides on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


