Abstract
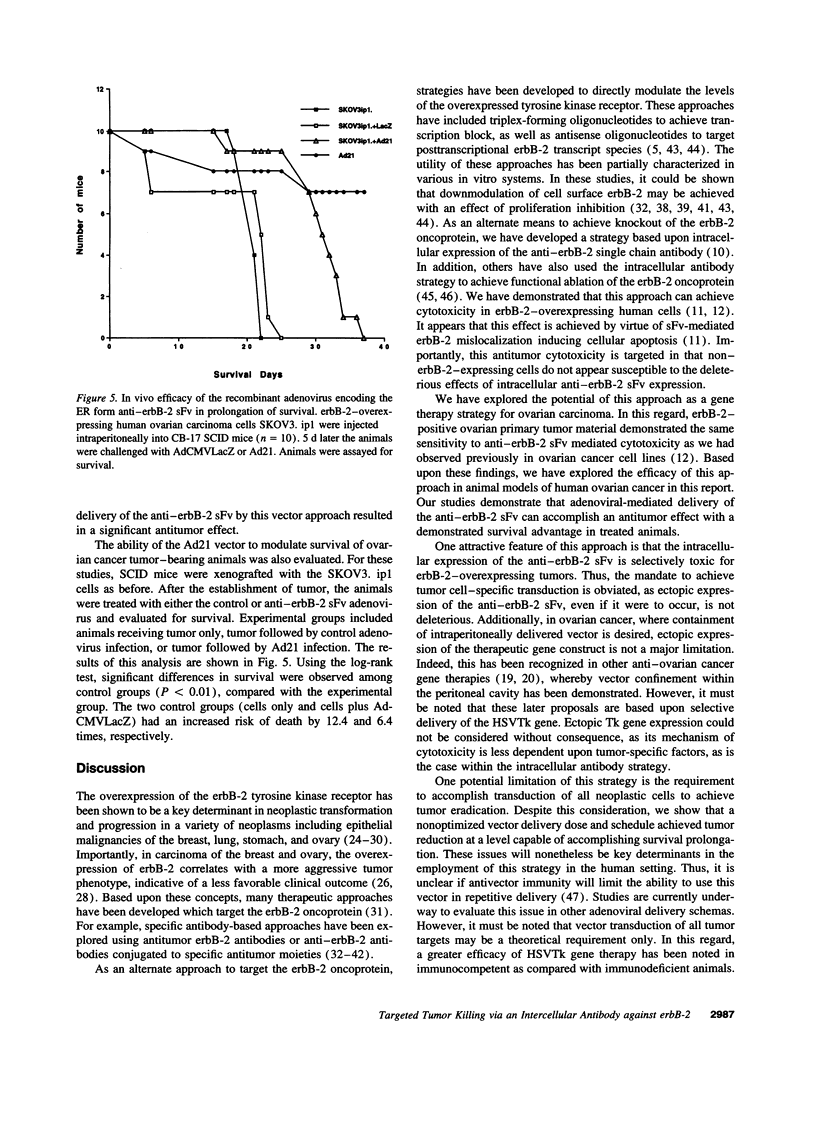
Specific killing of erbB-2-overexpressing tumor cells can be achieved using expression of an intracellular antibody directed against the erbB-2 oncoprotein. We have developed a strategy using a recombinant adenovirus encoding an anti-erbB-2 single chain antibody to achieve targeted tumor cell killing in vivo and can show significantly prolonged survival of animals carrying a human ovarian carcinoma tumor burden within their peritoneal cavities. This strategy of gene therapy for ovarian carcinoma offers the potential to achieve highly specific, targeted killing of human tumor cells and thus establishes the rationale to undertake human clinical trials on this basis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Markowitz S., Fearon E. R., Willson J. K., Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):912–915. doi: 10.1126/science.2144057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga R. Oncogenes and the strategy of growth factors. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):927–930. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker T. C., Noel R. J., Coats W. S., Gómez-Foix A. M., Alam T., Gerard R. D., Newgard C. B. Use of recombinant adenovirus for metabolic engineering of mammalian cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;43(Pt A):161–189. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60603-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beerli R. R., Wels W., Hynes N. E. Intracellular expression of single chain antibodies reverts ErbB-2 transformation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):23931–23936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertram J., Killian M., Brysch W., Schlingensiepen K. H., Kneba M. Reduction of erbB2 gene product in mamma carcinoma cell lines by erbB2 mRNA-specific and tyrosine kinase consensus phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Apr 15;200(1):661–667. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein R., Shew J. Y., Chen P. L., Scully P., Lee W. H. Suppression of tumorigenicity of human prostate carcinoma cells by replacing a mutated RB gene. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):712–715. doi: 10.1126/science.2300823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody S. L., Jaffe H. A., Han S. K., Wersto R. P., Crystal R. G. Direct in vivo gene transfer and expression in malignant cells using adenovirus vectors. Hum Gene Ther. 1994 Apr;5(4):437–447. doi: 10.1089/hum.1994.5.4-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brysch W., Magal E., Louis J. C., Kunst M., Klinger I., Schlingensiepen R., Schlingensiepen K. H. Inhibition of p185c-erbB-2 proto-oncogene expression by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides down-regulates p185-associated tyrosine-kinase activity and strongly inhibits mammary tumor-cell proliferation. Cancer Gene Ther. 1994 Jun;1(2):99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P., Presta L., Gorman C. M., Ridgway J. B., Henner D., Wong W. L., Rowland A. M., Kotts C., Carver M. E., Shepard H. M. Humanization of an anti-p185HER2 antibody for human cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4285–4289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. R., Maxwell I. H., Glode L. M., Maxwell F., Stevens J. O., Purner M. B., Wagner E., Curiel D. T., Curiel T. J. Gene therapy for B-cell lymphoma in a SCID mouse model using an immunoglobulin-regulated diphtheria toxin gene delivered by a novel adenovirus-polylysine conjugate. Cancer Biother. 1994 Summer;9(2):131–141. doi: 10.1089/cbr.1994.9.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney M., Czernuszewicz G., Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Hogan M. E. Site-specific oligonucleotide binding represses transcription of the human c-myc gene in vitro. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):456–459. doi: 10.1126/science.3293213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curiel D. T. High-efficiency gene transfer employing adenovirus-polylysine-DNA complexes. Nat Immun. 1994 Mar-Jun;13(2-3):141–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curiel D. T., Wagner E., Cotten M., Birnstiel M. L., Agarwal S., Li C. M., Loechel S., Hu P. C. High-efficiency gene transfer mediated by adenovirus coupled to DNA-polylysine complexes. Hum Gene Ther. 1992 Apr;3(2):147–154. doi: 10.1089/hum.1992.3.2-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Santes K., Slamon D., Anderson S. K., Shepard M., Fendly B., Maneval D., Press O. Radiolabeled antibody targeting of the HER-2/neu oncoprotein. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 1;52(7):1916–1923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshane J., Cabrera G., Grim J. E., Siegal G. P., Pike J., Alvarez R. D., Curiel D. T. Targeted eradication of ovarian cancer mediated by intracellular expression of anti-erbB-2 single-chain antibody. Gynecol Oncol. 1995 Oct;59(1):8–14. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1995.1260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshane J., Loechel F., Conry R. M., Siegal G. P., King C. R., Curiel D. T. Intracellular single-chain antibody directed against erbB2 down-regulates cell surface erbB2 and exhibits a selective anti-proliferative effect in erbB2 overexpressing cancer cell lines. Gene Ther. 1994 Sep;1(5):332–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drebin J. A., Link V. C., Stern D. F., Weinberg R. A., Greene M. I. Down-modulation of an oncogene protein product and reversion of the transformed phenotype by monoclonal antibodies. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):697–706. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebbinghaus S. W., Gee J. E., Rodu B., Mayfield C. A., Sanders G., Miller D. M. Triplex formation inhibits HER-2/neu transcription in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2433–2439. doi: 10.1172/JCI116850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fendly B. M., Kotts C., Vetterlein D., Lewis G. D., Winget M., Carver M. E., Watson S. R., Sarup J., Saks S., Ullrich A. The extracellular domain of HER2/neu is a potential immunogen for active specific immunotherapy of breast cancer. J Biol Response Mod. 1990 Oct;9(5):449–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fendly B. M., Winget M., Hudziak R. M., Lipari M. T., Napier M. A., Ullrich A. Characterization of murine monoclonal antibodies reactive to either the human epidermal growth factor receptor or HER2/neu gene product. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 1;50(5):1550–1558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng M., Cabrera G., Deshane J., Scanlon K. J., Curiel D. T. Neoplastic reversion accomplished by high efficiency adenoviral-mediated delivery of an anti-ras ribozyme. Cancer Res. 1995 May 15;55(10):2024–2028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanella B. C., Vardeman D. M., Williams L. J., Taylor D. J., de Ipolyi P. D., Greeff P. J., Stehlin J. S., Ullrich A., Cailleau R., Slamon D. J. Heterotransplantation of human breast carcinomas in nude mice. Correlation between successful heterotransplants, poor prognosis and amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Int J Cancer. 1991 Jan 2;47(1):66–71. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graus-Porta D., Beerli R. R., Hynes N. E. Single-chain antibody-mediated intracellular retention of ErbB-2 impairs Neu differentiation factor and epidermal growth factor signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1182–1191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock M. C., Langton B. C., Chan T., Toy P., Monahan J. J., Mischak R. P., Shawver L. K. A monoclonal antibody against the c-erbB-2 protein enhances the cytotoxicity of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum against human breast and ovarian tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991 Sep 1;51(17):4575–4580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwerth I. M., Wels W., Marte B. M., Hynes N. E. Monoclonal antibodies against the extracellular domain of the erbB-2 receptor function as partial ligand agonists. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15160–15167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. J., Yee J. K., Shew J. Y., Chen P. L., Bookstein R., Friedmann T., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. Suppression of the neoplastic phenotype by replacement of the RB gene in human cancer cells. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1563–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.3201247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudziak R. M., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Increased expression of the putative growth factor receptor p185HER2 causes transformation and tumorigenesis of NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz E., Stancovski I., Sela M., Yarden Y. Suppression and promotion of tumor growth by monoclonal antibodies to ErbB-2 differentially correlate with cellular uptake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3353–3357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N. E. Amplification and overexpression of the erbB-2 gene in human tumors: its involvement in tumor development, significance as a prognostic factor, and potential as a target for cancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 1993 Feb;4(1):19–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida T., Tsujisaki M., Hanzawa Y., Hirakawa T., Hinoda Y., Imai K., Yachi A. Significance of erbB-2 gene product as a target molecule for cancer therapy. Scand J Immunol. 1994 May;39(5):459–466. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1994.tb03401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida T., Tsujisaki M., Hinoda Y., Imai K., Yachi A. Establishment and characterization of mouse-human chimeric monoclonal antibody to erbB-2 product. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1994 Feb;85(2):172–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1994.tb02079.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern J. A., Torney L., Weiner D., Gazdar A., Shepard H. M., Fendly B. Inhibition of human lung cancer cell line growth by an anti-p185HER2 antibody. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Oct;9(4):448–454. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/9.4.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay T., Tainsky M., Cavender A. C., Roth J. A. Specific inhibition of K-ras expression and tumorigenicity of lung cancer cells by antisense RNA. Cancer Res. 1991 Mar 15;51(6):1744–1748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi M., Murakami M., Bennett W., Lupu R., Hui F., Jr, Harris C. C., Gerwin B. I. Biological consequences of overexpression of a transfected c-erbB-2 gene in immortalized human bronchial epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1993 May 1;53(9):2035–2043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta Y., Tone T., Shitara T., Funato T., Jiao L., Kashfian B. I., Yoshida E., Horng M., Tsai P., Lauterbach K. H-ras ribozyme-mediated alteration of the human melanoma phenotype. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994 May 31;716:242–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb21716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press M. F., Pike M. C., Hung G., Zhou J. Y., Ma Y., George J., Dietz-Band J., James W., Slamon D. J., Batsakis J. G. Amplification and overexpression of HER-2/neu in carcinomas of the salivary gland: correlation with poor prognosis. Cancer Res. 1994 Nov 1;54(21):5675–5682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi J. J. Therapeutic antisense and ribozymes. Br Med Bull. 1995 Jan;51(1):217–225. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Godolphin W., Jones L. A., Holt J. A., Wong S. G., Keith D. E., Levin W. J., Stuart S. G., Udove J., Ullrich A. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):707–712. doi: 10.1126/science.2470152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe W. R., Kaiser L. R., Hwang H. C., Amin K. M., Pilewski J. M., Eck S. J., Wilson J. M., Albelda S. M. Successful adenovirus-mediated gene transfer in an in vivo model of human malignant mesothelioma. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994 Jun;57(6):1395–1401. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(94)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Carbone D., Takahashi T., Nau M. M., Hida T., Linnoila I., Ueda R., Minna J. D. Wild-type but not mutant p53 suppresses the growth of human lung cancer cells bearing multiple genetic lesions. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 15;52(8):2340–2343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vile R. G., Nelson J. A., Castleden S., Chong H., Hart I. R. Systemic gene therapy of murine melanoma using tissue specific expression of the HSVtk gene involves an immune component. Cancer Res. 1994 Dec 1;54(23):6228–6234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wels W., Harwerth I. M., Mueller M., Groner B., Hynes N. E. Selective inhibition of tumor cell growth by a recombinant single-chain antibody-toxin specific for the erbB-2 receptor. Cancer Res. 1992 Nov 15;52(22):6310–6317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yei S., Mittereder N., Tang K., O'Sullivan C., Trapnell B. C. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer for cystic fibrosis: quantitative evaluation of repeated in vivo vector administration to the lung. Gene Ther. 1994 May;1(3):192–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D., Wang S. S., Dulski K. M., Tsai C. M., Nicolson G. L., Hung M. C. c-erbB-2/neu overexpression enhances metastatic potential of human lung cancer cells by induction of metastasis-associated properties. Cancer Res. 1994 Jun 15;54(12):3260–3266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D., Wolf J. K., Scanlon M., Price J. E., Hung M. C. Enhanced c-erbB-2/neu expression in human ovarian cancer cells correlates with more severe malignancy that can be suppressed by E1A. Cancer Res. 1993 Feb 15;53(4):891–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]