Abstract
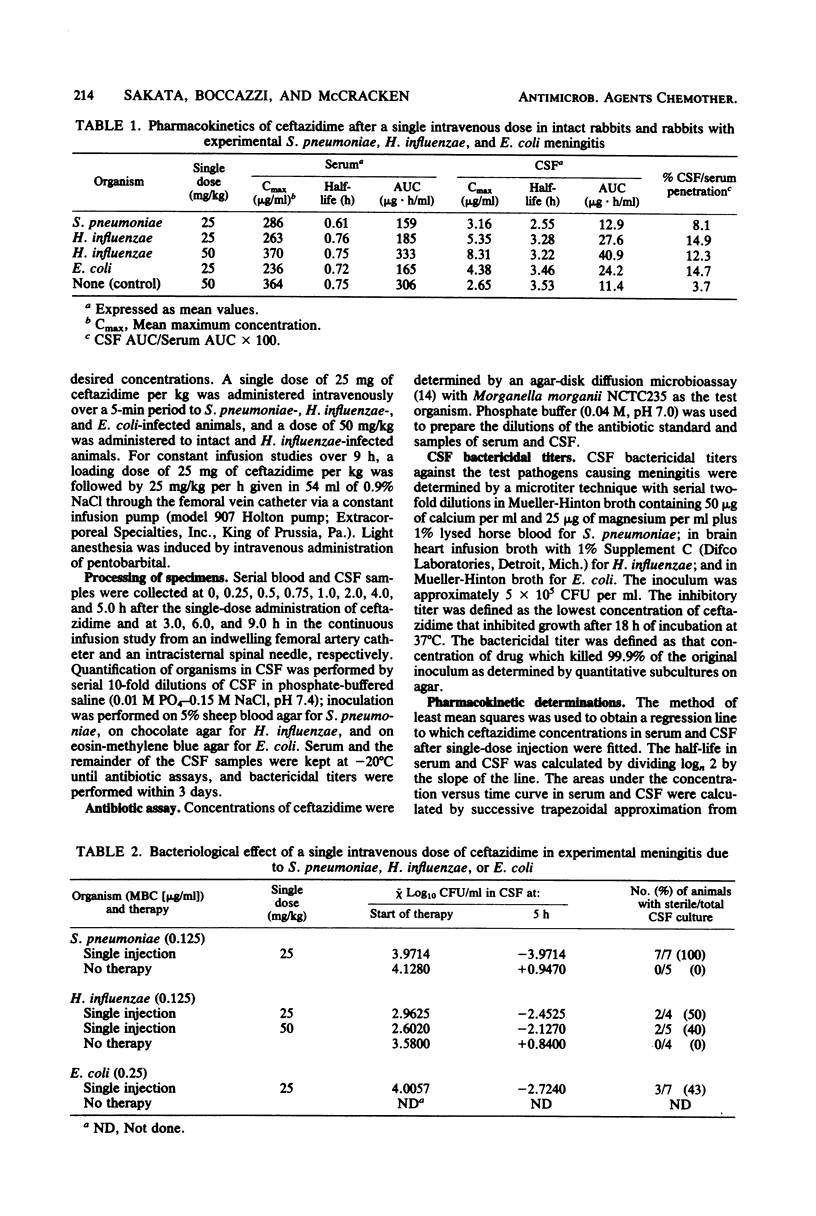
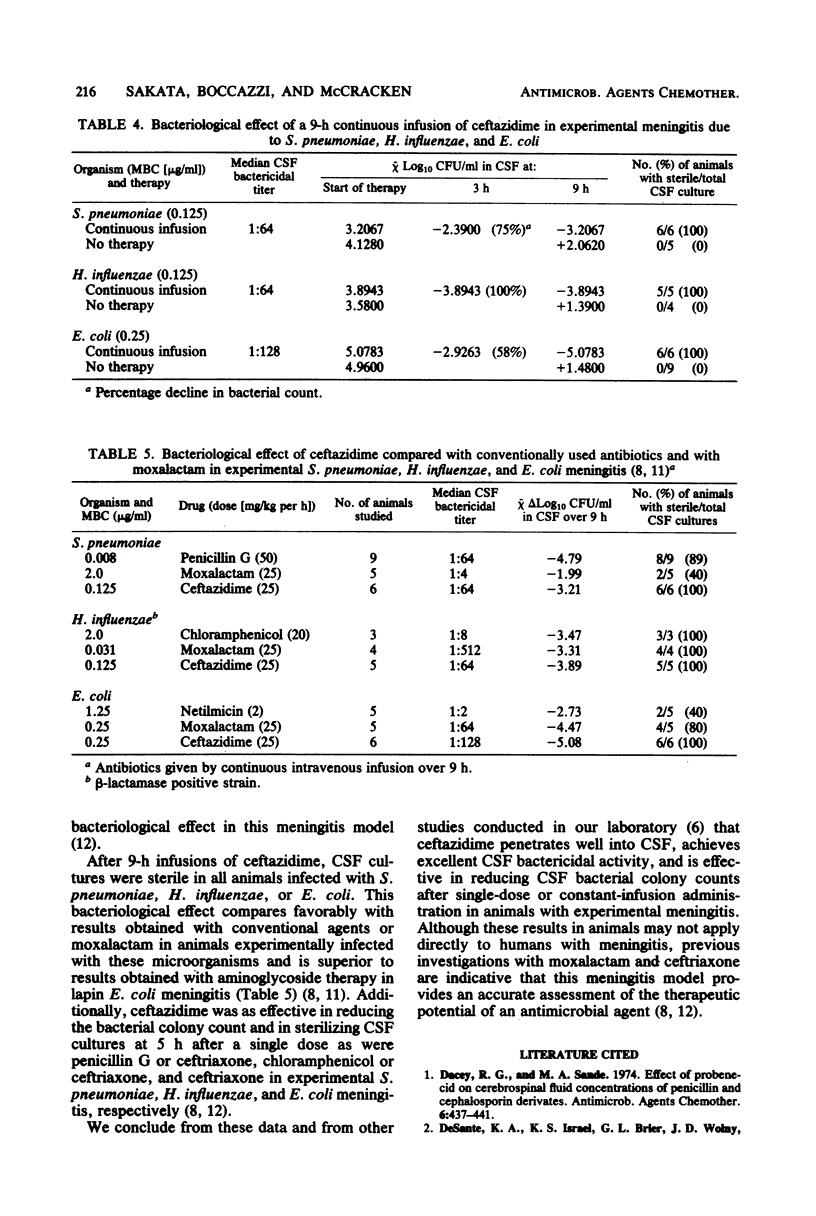
The pharmacokinetics and bacteriological effect of ceftazidime were evaluated in rabbits experimentally infected with Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae type b, and Escherichia coli K1. The mean penetration of ceftazidime into cerebrospinal fluid after single-dose or constant-infusion administration ranged from 7.8 to 14.9%. The median cerebrospinal fluid bactericidal titers were 1:64 against S. pneumoniae and H. influenzae and 1:128 against E. coli. The bacterial colony counts in cerebrospinal fluid were reduced by 58% to 100% (-2.3 to -3.9 log10 CFU/ml) in 3 h and by 100% (-3.2 to -5.1 log10 CFU/ml) in 9 h of constant infusion, whereas in untreated infected animals, bacterial counts increased from +1.4 to +2.1 log10 CFU/ml in 9 h. These data on ceftazidime compare favorably with those on penicillin, chloramphenicol, netilmicin, and moxalactam in this experimental meningitis model.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chopra I., Howe T. G., Linton A. H., Linton K. B., Richmond M. H., Speller D. C. The tetracyclines: prospects at the beginning of the 1980s. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jul;8(1):5–21. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Gorski S., Person A., Mangura C., Chmel H. Clindamycin elimination in patients with liver disease. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Oct;8(4):277–281. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.4.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimdahl A., von Konow L., Nord C. E. Beta-lactamase-producing Bacteroides species in the oral cavity in relation to penicillin therapy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Sep;8(3):225–229. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. L., Mason E. O., Jr, Garcia H., Kvernland S. J., Loiselle E. M., Anderson D. C., Mintz A. A., Feigin R. D. Pharmacokinetics and cerebrospinal fluid penetration of moxalactam in children with bacterial meningitis. J Pediatr. 1981 Jan;98(1):152–157. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80562-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Nelson J. D., Grimm L. Pharmacokinetics and bacteriological efficacy of cefoperazone, ceftriaxone, and moxalactam in experimental Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):262–267. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. Antibacterial activity and beta-lactamase stability of ceftazidime, an aminothiazolyl cephalosporin potentially active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):11–18. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord C. E., Olsson-Liljequist B. Resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Bacteroides species. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl 500):33–42. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_d.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Acred P., Harper P. B., Ryan D. M., Kirby S. M., Harding S. M. GR 20263, a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin with anti-pseudomonal activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 May;17(5):876–883. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.5.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaad U. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Loock C. A., Thomas M. L. Pharmacokinetics and bacteriological efficacy of moxalactam (LY127935), netilmicin, and ampicillin in experimental gram-negative enteric bacillary meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):406–411. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scribner R. K., Marks M. I., Weber A. H., Tarpay M. M., Welch D. F. Activities of various beta-lactams and aminoglycosides, alone and in combination, against isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from patients with cystic fibrosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):939–943. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Baker S., Livingston R. Comparison of cefotaxime and moxalactam pharmacokinetics and tissue levels. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):369–371. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


