Abstract
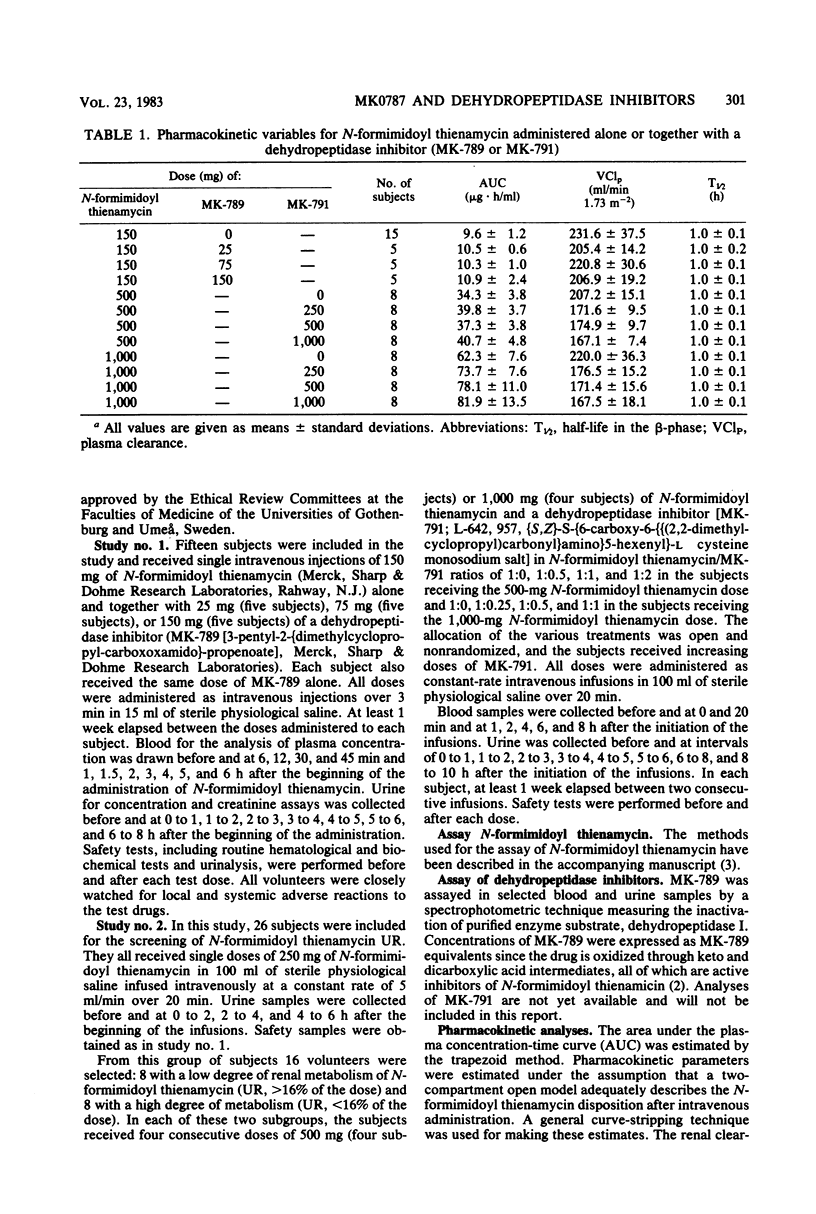
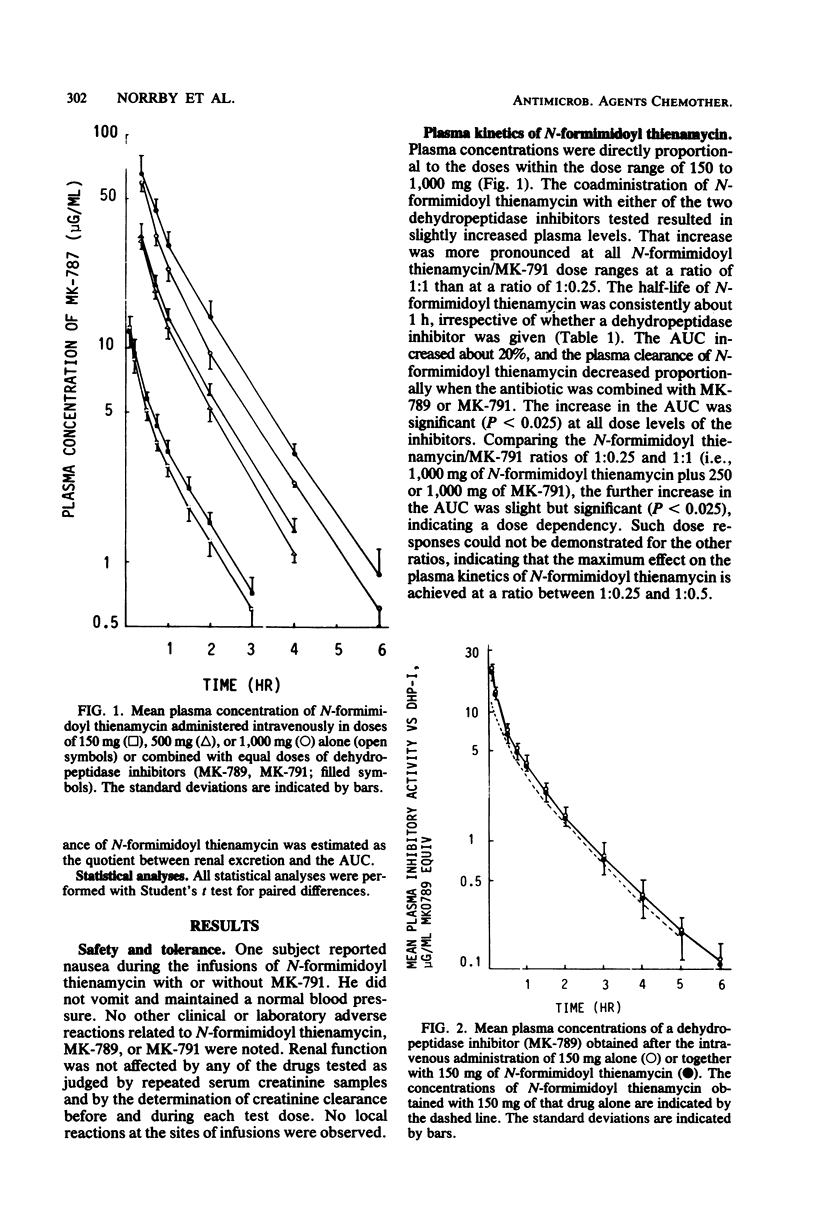
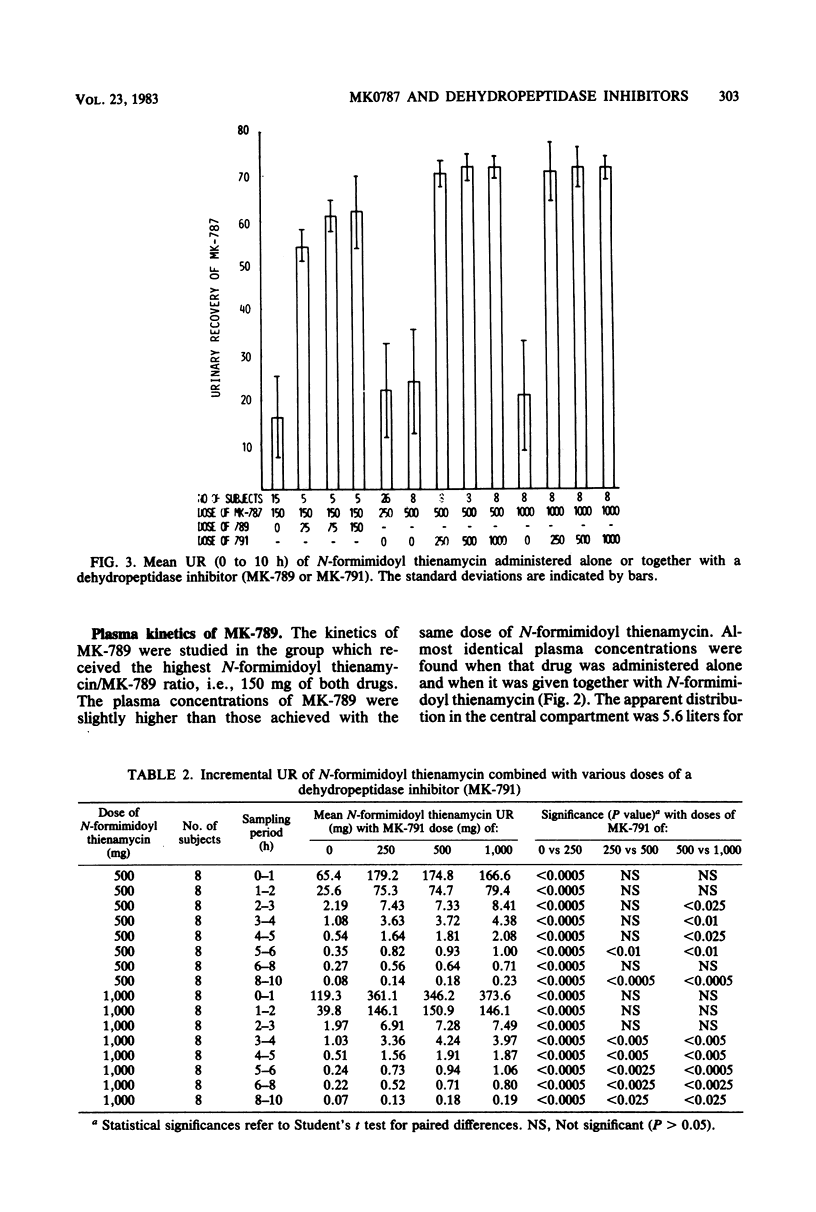
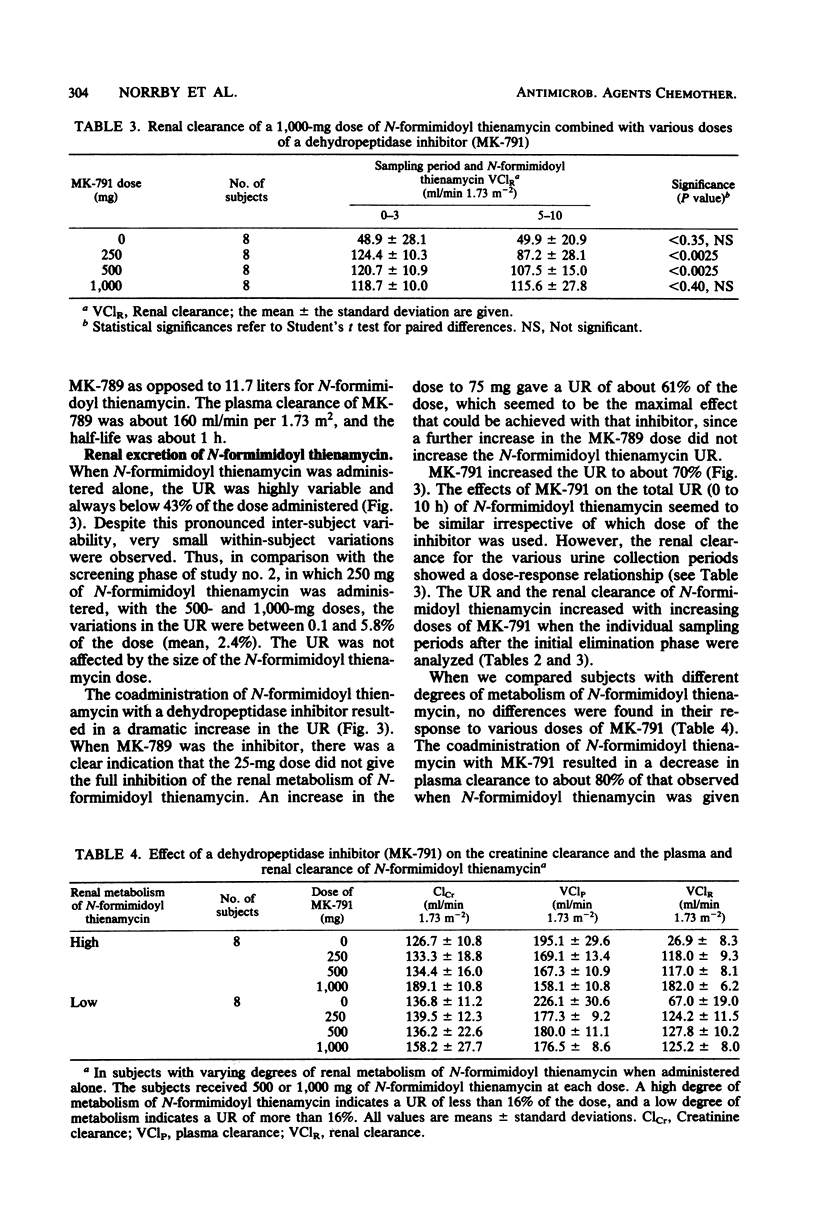
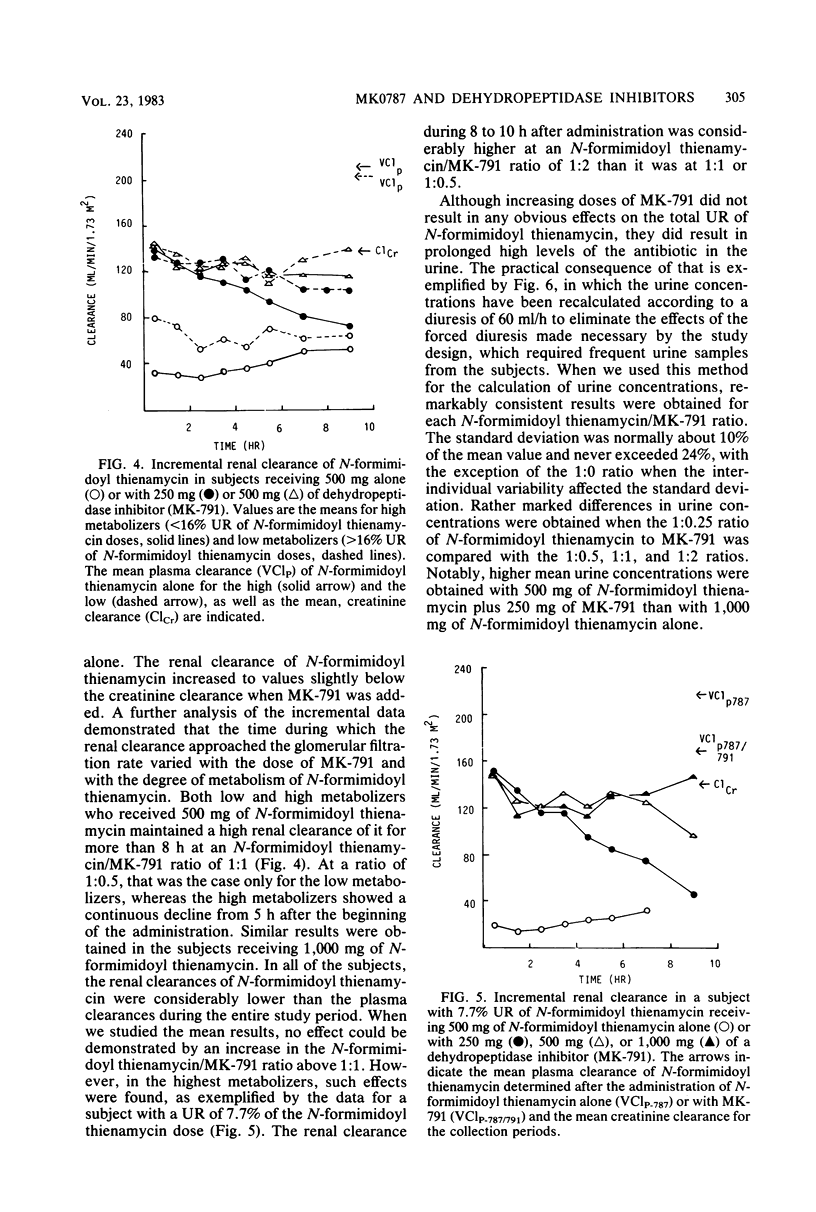
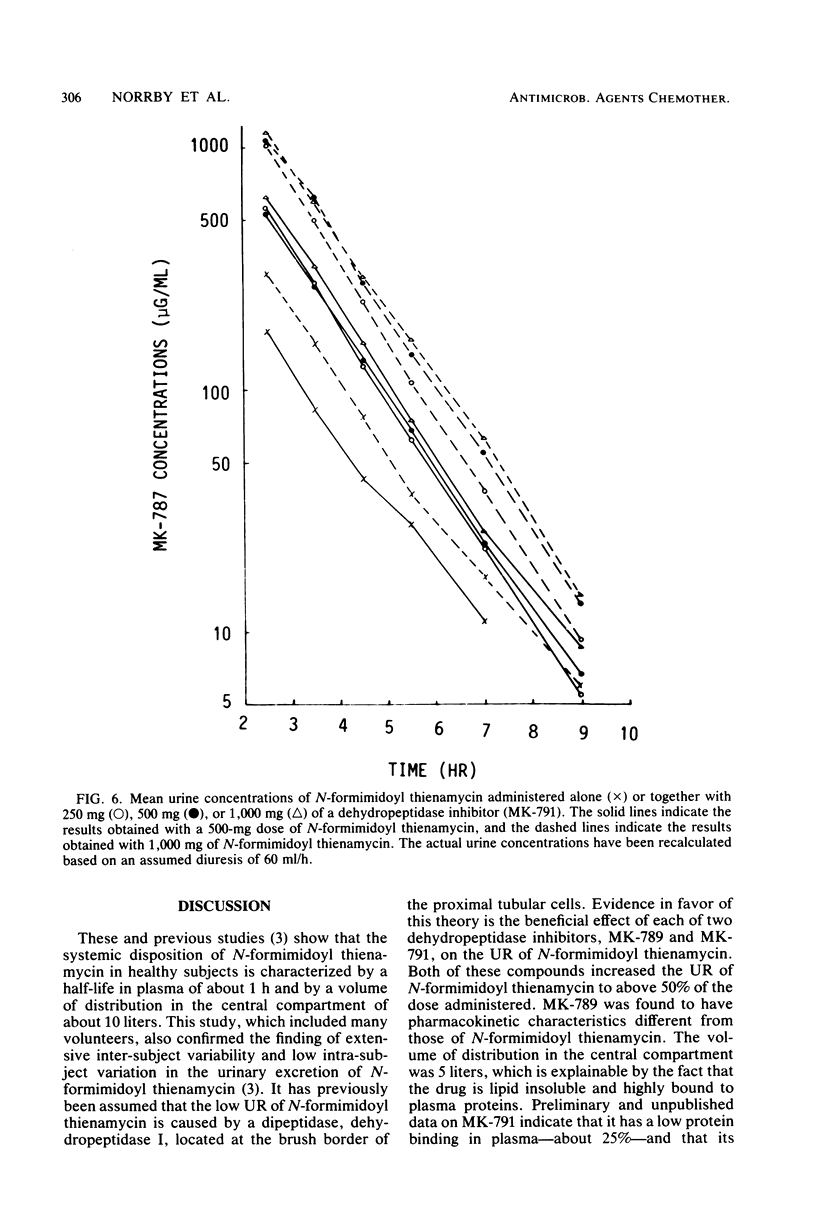
N-Formimidoyl thienamycin (MK0787) undergoes renal metabolism by a dipeptidase, dehydropeptidase I, located on the brush border of the proximal tubular cells. The effects of two inhibitors (MK-789 and MK-791) of dehydropeptidase I on the pharmacokinetics of N-formimidoyl thienamycin were studied in 41 healthy subjects receiving various combinations of N-formimidoyl thienamycin and MK-789 or MK-791. Both inhibitors affected the plasma kinetics of N-formimidoyl thienamycin only to a small extent. Plasma concentrations and the area under the plasma concentration curve increased about 20% with a proportional decrease in plasma clearance. Plasma half-life was not altered significantly. Coadministration of MK-789 or MK-791 resulted in uniform and marked increases in urinary recovery and renal clearance of N-formimidoyl thienamycin. Thus, at an N-formimidoyl thienamycin/MK-791 ratio of 1:0.25 or higher, the urinary recovery was about 72% in all subjects, whereas it varied between 7.7 and 43% when N-formimidoyl thienamycin was given alone. The ratio of the N-formimidoyl thienamycin and MK-791 doses affected response. At relatively higher doses of MK-791, significant increases of N-formimidoyl thienamycin urinary recovery, renal clearance, and urine concentrations occurred during the later part of the 10-h observation period after each administration. At a 1:1 ratio of the two drugs, the inhibition of renal metabolism of N-formimidoyl thienamycin was maintained for at least 8 h, whereas renal clearance declined as soon as 4 h after the administration of a 1:0.25 ratio. The results indicated that MK-789 and MK-791 alter the renal excretion of N-formimidoyl thienamycin from glomerular filtration plus tubular secretion to glomerular filtration only, possibly by competitively inhibiting the penetration of N-formimidoyl thienamycin into the proximal tubular cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kim K. E., Onesti G., Ramirez O., Brest A. N., Swartz C. Creatinine clearance in renal disease. A reappraisal. Br Med J. 1969 Oct 4;4(5674):11–14. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5674.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropp H., Sundelof J. G., Hajdu R., Kahan F. M. Metabolism of thienamycin and related carbapenem antibiotics by the renal dipeptidase, dehydropeptidase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):62–70. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby S. R., Alestig K., Ferber F., Huber J. L., Jones K. H., Kahan F. M., Meisinger M. A., Rogers J. D. Pharmacokinetics and tolerance of N-formimidoyl thienamycin (MK0787) in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Feb;23(2):293–299. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.2.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


