Abstract
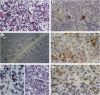
Hodgkin's disease (HD) shows rare neoplastic Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells embedded in an abundant reactive infiltrate containing, among other cell types, neutrophilic granulocytes. Interleukin (IL)-8 is chemotactic for neutrophils. The expression of IL-8 was tested by in situ hybridization with 35S-labeled IL-8-specific RNA probes on 38 cases of HD. Reactive lesions, non-Hodgkin's lymphomas of B and T phenotype, and Langerhans cell histiocytosis served as controls. IL-8 expression was observed in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells in 3 of 33 cases of classical HD and in reactive cells in 20 of 33 HD cases as evidenced by combined isotopic in situ hybridization and immunohistology for the demonstration of cell-type-characteristic antigens or enzyme histochemistry for chloroacetate esterase. IL-8-positive cells were more numerous in cases of nodular sclerosing HD as compared with the mixed cellularity histotype (P = 0.01). The number of IL-8-positive cells and the density of neutrophils were positively correlated (P < 0. 01). In 5 cases of lymphocyte-predominant HD, IL-8 expression was not displayed. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma cases contained IL-8 transcripts only in 1 of 23 cases in sparse reactive cells. In 4 of 7 cases of Langerhans cell histiocytosis, IL-8-specific signals were displayed in S100-negative cells. In conclusion, IL-8 expression in HD is largely confined to reactive cells and associated with infiltration by neutrophils. Elaboration of other cytokines by Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells and reactive cells may explain the frequent expression of this cytokine in HD, particularly in the nodular sclerosing type.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abruzzo L. V., Thornton A. J., Liebert M., Grossman H. B., Evanoff H., Westwick J., Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L. Cytokine-induced gene expression of interleukin-8 in human transitional cell carcinomas and renal cell carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1992 Feb;140(2):365–373. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antony V. B., Godbey S. W., Kunkel S. L., Hott J. W., Hartman D. L., Burdick M. D., Strieter R. M. Recruitment of inflammatory cells to the pleural space. Chemotactic cytokines, IL-8, and monocyte chemotactic peptide-1 in human pleural fluids. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):7216–7223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Dewald B., Moser B. Interleukin-8 and related chemotactic cytokines--CXC and CC chemokines. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:97–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Walz A., Kunkel S. L. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI114265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargou R. C., Mapara M. Y., Zugck C., Daniel P. T., Pawlita M., Döhner H., Dörken B. Characterization of a novel Hodgkin cell line, HD-MyZ, with myelomonocytic features mimicking Hodgkin's disease in severe combined immunodeficient mice. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1257–1268. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown Z., Strieter R. M., Chensue S. W., Ceska M., Lindley I., Neild G. H., Kunkel S. L., Westwick J. Cytokine-activated human mesangial cells generate the neutrophil chemoattractant, interleukin 8. Kidney Int. 1991 Jul;40(1):86–90. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree J. E., Wyatt J. I., Trejdosiewicz L. K., Peichl P., Nichols P. H., Ramsay N., Primrose J. N., Lindley I. J. Interleukin-8 expression in Helicobacter pylori infected, normal, and neoplastic gastroduodenal mucosa. J Clin Pathol. 1994 Jan;47(1):61–66. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drexler H. G. Recent results on the biology of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. II. Continuous cell lines. Leuk Lymphoma. 1993 Jan;9(1-2):1–25. doi: 10.3109/10428199309148499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foss H. D., Herbst H., Hummel M., Araujo I., Latza U., Rancsò C., Dallenbach F., Stein H. Patterns of cytokine gene expression in infectious mononucleosis. Blood. 1994 Feb 1;83(3):707–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foss H. D., Herbst H., Oelmann E., Samol J., Grebe M., Blankenstein T., Matthes J., Qin Z. H., Falini B., Pileri S. Lymphotoxin, tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-6 gene transcripts are present in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells of most Hodgkin's disease cases. Br J Haematol. 1993 Aug;84(4):627–635. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1993.tb03138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland J. S., Suputtamongkol Y., Remick D. G., Chaowagul W., Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., White N. J., Griffin G. E. Prolonged elevation of interleukin-8 and interleukin-6 concentrations in plasma and of leukocyte interleukin-8 mRNA levels during septicemic and localized Pseudomonas pseudomallei infection. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2402–2408. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2402-2408.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss H. J., Brach M. A., Drexler H. G., Bonifer R., Mertelsmann R. H., Herrmann F. Expression of cytokine genes, cytokine receptor genes, and transcription factors in cultured Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Jun 15;52(12):3353–3360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Kunkel S. L., Pearce W. H., Shah M. R., Parikh D., Evanoff H. L., Haines G. K., Burdick M. D., Strieter R. M. Enhanced production of the chemotactic cytokines interleukin-8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in human abdominal aortic aneurysms. Am J Pathol. 1993 May;142(5):1423–1431. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Polverini P. J., Kunkel S. L., Harlow L. A., DiPietro L. A., Elner V. M., Elner S. G., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 as a macrophage-derived mediator of angiogenesis. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1798–1801. doi: 10.1126/science.1281554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen C. G., Anderson A. O., Appella E., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K. The neutrophil-activating protein (NAP-1) is also chemotactic for T lymphocytes. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1464–1466. doi: 10.1126/science.2648569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahida Y. R., Ceska M., Effenberger F., Kurlak L., Lindley I., Hawkey C. J. Enhanced synthesis of neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin-8 in active ulcerative colitis. Clin Sci (Lond) 1992 Mar;82(3):273–275. doi: 10.1042/cs0820273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Morishita K., Yoshimura T., Lavu S., Kobayashi Y., Lew W., Appella E., Kung H. F., Leonard E. J., Oppenheim J. J. Molecular cloning of a human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor (MDNCF) and the induction of MDNCF mRNA by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1883–1893. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milani S., Herbst H., Schuppan D., Hahn E. G., Stein H. In situ hybridization for procollagen types I, III and IV mRNA in normal and fibrotic rat liver: evidence for predominant expression in nonparenchymal liver cells. Hepatology. 1989 Jul;10(1):84–92. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff B. J., Karabin G. D., Barker J. N., Griffiths C. E., Sarma V., Mitra R. S., Elder J. T., Kunkel S. L., Dixit V. M. Cellular localization of interleukin-8 and its inducer, tumor necrosis factor-alpha in psoriasis. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):129–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schadendorf D., Möller A., Algermissen B., Worm M., Sticherling M., Czarnetzki B. M. IL-8 produced by human malignant melanoma cells in vitro is an essential autocrine growth factor. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 1;151(5):2667–2675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmouder R. L., Strieter R. M., Wiggins R. C., Chensue S. W., Kunkel S. L. In vitro and in vivo interleukin-8 production in human renal cortical epithelia. Kidney Int. 1992 Jan;41(1):191–198. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz M., Dewald B., Gerber N., Baggiolini M. Enhanced production of neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin-8 in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):463–469. doi: 10.1172/JCI115018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenzato G. Tumour necrosis factor: a cytokine with multiple biological activities. Br J Cancer. 1990 Mar;61(3):354–361. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Polverini P. J., Kunkel S. L., Orringer M. B., Whyte R. I., Burdick M. D., Wilke C. A., Strieter R. M. Inhibition of interleukin 8 attenuates angiogenesis in bronchogenic carcinoma. J Exp Med. 1994 May 1;179(5):1409–1415. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.5.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sticherling M., Bornscheuer E., Schröder J. M., Christophers E. Immunohistochemical studies on NAP-1/IL-8 in contact eczema and atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol Res. 1992;284(2):82–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00373374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sticherling M., Schröder J. M., Christophers E. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against the novel neutrophil activating peptide NAP/IL-8. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 1;143(5):1628–1634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Kasahara K., Allen R. M., Standiford T. J., Rolfe M. W., Becker F. S., Chensue S. W., Kunkel S. L. Cytokine-induced neutrophil-derived interleukin-8. Am J Pathol. 1992 Aug;141(2):397–407. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., Elner V. M., Martonyi C. L., Koch A. E., Polverini P. J., Elner S. G. Interleukin-8. A corneal factor that induces neovascularization. Am J Pathol. 1992 Dec;141(6):1279–1284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Baker E., Callen D. F., Hyland V. J., Wong G., Clark S., Jones S. S., Eglinton L. K., Shannon M. F., Lopez A. F. Interleukin 4 is at 5q31 and interleukin 6 is at 7p15. Hum Genet. 1988 Aug;79(4):335–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00282171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unemori E. N., Amento E. P., Bauer E. A., Horuk R. Melanoma growth-stimulatory activity/GRO decreases collagen expression by human fibroblasts. Regulation by C-X-C but not C-C cytokines. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1338–1342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Meir E., Ceska M., Effenberger F., Walz A., Grouzmann E., Desbaillets I., Frei K., Fontana A., de Tribolet N. Interleukin-8 is produced in neoplastic and infectious diseases of the human central nervous system. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 15;52(16):4297–4305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. J. Specificity of riboprobes for intracellular RNA in hybridization histochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Jul;36(7):811–813. doi: 10.1177/36.7.2454986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xerri L., Birg F., Guigou V., Bouabdallah R., Poizot-Martin I., Hassoun J. In situ expression of the IL-1-alpha and TNF-alpha genes by Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. Int J Cancer. 1992 Mar 12;50(5):689–693. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910500504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]