Abstract
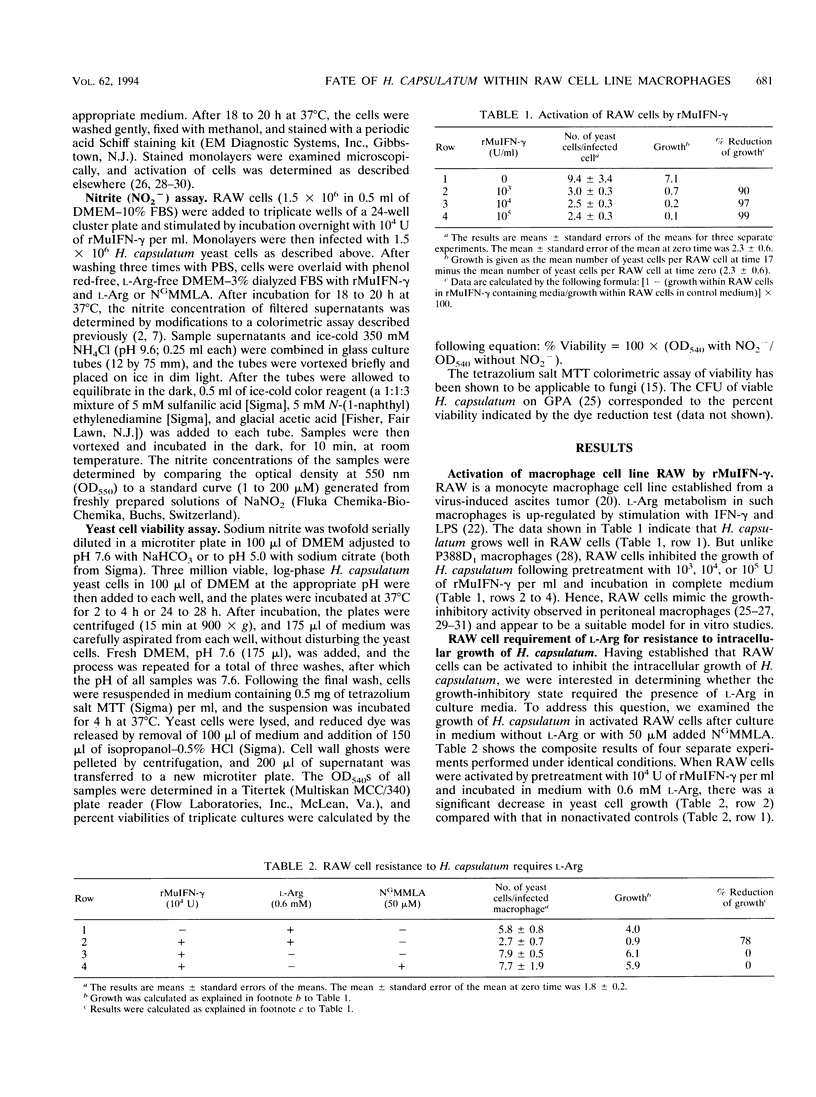
Macrophages of the RAW 264.7 cell line, activated by pretreatment with recombinant murine gamma interferon, inhibit the intracellular growth of Histoplasma capsulatum. Growth inhibition occurred by a mechanism that was operative only when L-Arg metabolism was allowed to occur. When activated macrophages were cultured in the absence of L-Arg or in the presence of NG-monomethyl-L-Arg, a competitive inhibitor of L-Arg metabolism, activation to the antihistoplasma growth-inhibitory state did not occur. An increase in levels of NO2-, an end product of L-Arg metabolism, was detected only after activation of RAW 264.7 cells to the growth-inhibitory state. In contrast, only baseline levels of NO2- were detected when L-Arg was excluded or when NG-monomethyl-L-Arg was added to the culture medium. Nitric oxide (NO.), a reactive intermediate product of L-Arg metabolism, was implicated as the relevant antihistoplasma effector molecule. When H. capsulatum yeast cells were cultured for 24 to 28 h in a system designed to generate soluble NO., a dose-dependent cytotoxic effect was observed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alspaugh J. A., Granger D. L. Inhibition of Cryptococcus neoformans replication by nitrogen oxides supports the role of these molecules as effectors of macrophage-mediated cytostasis. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2291–2296. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2291-2296.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew B. A rapid method for the assay of nitrate in urine using the nitrate reductase enzyme of Escherichia coli. Food Chem Toxicol. 1984 Jul;22(7):541–543. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(84)90224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Hibbs J. B., Jr Differentiation of murine macrophages to express nonspecific cytotoxicity for tumor cells results in L-arginine-dependent inhibition of mitochondrial iron-sulfur enzymes in the macrophage effector cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2829–2838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg L. G., Goldman W. E. Histoplasma capsulatum fails to trigger release of superoxide from macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.29-34.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg L. G., Goldman W. E., Schlesinger P. H. Histoplasma capsulatum modulates the acidification of phagolysosomes. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1605–1611. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg L. G., Schlesinger P. H., Goldman W. E. Phagosome-lysosome fusion in P388D1 macrophages infected with Histoplasma capsulatum. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Jun;43(6):483–491. doi: 10.1002/jlb.43.6.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr Synthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine: a recently discovered pathway induced by cytokines with antitumour and antimicrobial activity. Res Immunol. 1991 Sep;142(7):565–598. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(91)90103-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z., Rachlin E. M. Nitric oxide: a cytotoxic activated macrophage effector molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard D. H., Otto V., Gupta R. K. Lymphocyte-mediated cellular immunity in histoplasmosis. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):605–610. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.605-610.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourn R. G., Belloni P. Endothelial cell production of nitrogen oxides in response to interferon gamma in combination with tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, or endotoxin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 May 2;82(9):772–776. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.9.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane T. E., Wu-Hsieh B. A., Howard D. H. Gamma interferon cooperates with lipopolysaccharide to activate mouse splenic macrophages to an antihistoplasma state. Infect Immun. 1993 Apr;61(4):1468–1473. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.4.1468-1473.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane T. E., Wu-Hsieh B. A., Howard D. H. Iron limitation and the gamma interferon-mediated antihistoplasma state of murine macrophages. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2274–2278. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2274-2278.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., Diamond R. D. A rapid colorimetric assay of fungal viability with the tetrazolium salt MTT. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):938–945. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Cox F. E. Nonspecific defence mechanism: the role of nitric oxide. Immunol Today. 1991 Mar;12(3):A17–A21. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Millott S., Parkinson C., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Macrophage killing of Leishmania parasite in vivo is mediated by nitric oxide from L-arginine. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4794–4797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein C. J., Glatt C. S., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Cloned and expressed macrophage nitric oxide synthase contrasts with the brain enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6711–6715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Yoon P. S., Iyengar R., Leaf C. D., Wishnok J. S. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8706–8711. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauël J., Ransijn A., Buchmüller-Rouiller Y. Killing of Leishmania parasites in activated murine macrophages is based on an L-arginine-dependent process that produces nitrogen derivatives. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Jan;49(1):73–82. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raschke W. C., Baird S., Ralph P., Nakoinz I. Functional macrophage cell lines transformed by Abelson leukemia virus. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Induction of nitrite/nitrate synthesis in murine macrophages by BCG infection, lymphokines, or interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):518–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Synthesis of nitrite and nitrate in murine macrophage cell lines. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 1;47(21):5590–5594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Nathan C. F. Nitric oxide. A macrophage product responsible for cytostasis and respiratory inhibition in tumor target cells. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1543–1555. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton M., Granger D. L., Durack D. T. Mitochondrial iron loss from leukemia cells injured by macrophages. A possible mechanism for electron transport chain defects. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1311–1317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Hsieh B. A., Howard D. H. Inhibition of the intracellular growth of Histoplasma capsulatum by recombinant murine gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):1014–1016. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.1014-1016.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Hsieh B., Howard D. H. Inhibition of growth of Histoplasma capsulatum by lymphokine-stimulated macrophages. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2593–2597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Hsieh B., Howard D. H. Macrophage cell lines P388D1 and IC-21 stimulated with gamma interferon fail to inhibit the intracellular growth of Histoplasma capsulatum. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2903–2905. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2903-2905.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Hsieh B. Relative susceptibilities of inbred mouse strains C57BL/6 and A/J to infection with Histoplasma capsulatum. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3788–3792. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3788-3792.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Hsieh B., Zlotnik A., Howard D. H. T-cell hybridoma-produced lymphokine that activates macrophages to suppress intracellular growth of Histoplasma capsulatum. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):380–385. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.380-385.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


