Abstract
Galectin-3 is a member of a newly named family of beta-galactoside-binding animal lectins, which has been described with a number of possible important biological functions, including the regulation of cell growth and association with tumor transformation. This protein has a wide tissue distribution but is notably not expressed by normal lymphocytes. We have previously shown that galectin-3 is markedly up-regulated in HTLV-I-infected T cells, most likely mediated by the viral transactivating protein Tax. In this study, we surveyed various lymphomas by immunohistochemistry and found the expression of galectin-3 in all of the 8 cases of Ki-1+ anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL). Immunoreactivity for galectin-3 was found in a majority of the neoplastic cells in the ALCLs studied. In contrast, only 2 of the 35 cases of other types of lymphoma, including various Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, were positive. Unlike the cases of ALCL, immunoreactivity for galectin-3 in these 3 cases was found only sporadically in a small number of neoplastic cells. Thus, galectin-3 may prove to be a useful marker for ALCL and its expression in neoplastic cells in ALCL may contribute to the biological behavior of this specific type of lymphoma.
Full text
PDF

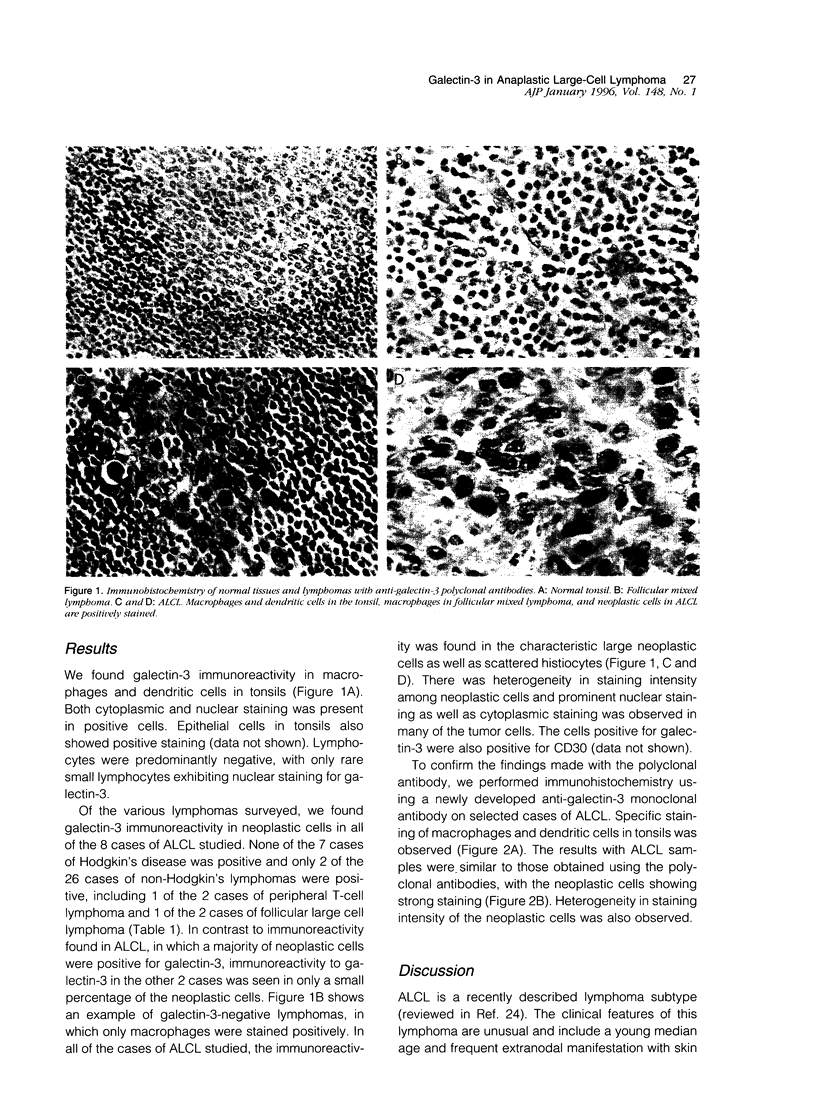



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrandt K., Orida N. K., Liu F. T. An IgE-binding protein with a distinctive repetitive sequence and homology with an IgG receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6859–6863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostopoulos I., Hummel M., Kaudewitz P., Herbst H., Braun-Falco O., Stein H. Detection of HTLV-I proviral sequences in CD30-positive large cell cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Am J Pathol. 1990 Dec;137(6):1317–1322. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barondes S. H., Castronovo V., Cooper D. N., Cummings R. D., Drickamer K., Feizi T., Gitt M. A., Hirabayashi J., Hughes C., Kasai K. Galectins: a family of animal beta-galactoside-binding lectins. Cell. 1994 Feb 25;76(4):597–598. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90498-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barondes S. H., Cooper D. N., Gitt M. A., Leffler H. Galectins. Structure and function of a large family of animal lectins. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 19;269(33):20807–20810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman I. M. Transformation in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Sep;101(3):249–250. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12365124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone A., Gloghini A., De Re V., Tamaro P., Boiocchi M., Volpe R. Histopathologic, immunophenotypic, and genotypic analysis of Ki-1 anaplastic large cell lymphomas that express histiocyte-associated antigens. Cancer. 1990 Dec 15;66(12):2547–2556. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19901215)66:12<2547::aid-cncr2820661217>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherayil B. J., Chaitovitz S., Wong C., Pillai S. Molecular cloning of a human macrophage lectin specific for galactose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7324–7328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherayil B. J., Weiner S. J., Pillai S. The Mac-2 antigen is a galactose-specific lectin that binds IgE. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):1959–1972. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K. Two distinct classes of carbohydrate-recognition domains in animal lectins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9557–9560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falini B., Pileri S., Pizzolo G., Dürkop H., Flenghi L., Stirpe F., Martelli M. F., Stein H. CD30 (Ki-1) molecule: a new cytokine receptor of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily as a tool for diagnosis and immunotherapy. Blood. 1995 Jan 1;85(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigeri L. G., Liu F. T. Surface expression of functional IgE binding protein, an endogenous lectin, on mast cells and macrophages. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):861–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigeri L. G., Zuberi R. I., Liu F. T. Epsilon BP, a beta-galactoside-binding animal lectin, recognizes IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI) and activates mast cells. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 3;32(30):7644–7649. doi: 10.1021/bi00081a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W. Human T cell lymphotropic virus type I and cutaneous T cell leukemia/lymphoma. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1581–1585. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu D. K., Zuberi R. I., Liu F. T. Biochemical and biophysical characterization of human recombinant IgE-binding protein, an S-type animal lectin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14167–14174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia S., Wang J. L. Carbohydrate binding protein 35. Complementary DNA sequence reveals homology with proteins of the heterogeneous nuclear RNP. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6009–6011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinov K. N., Shames B., Izuno G., Liu F. T. Expression of epsilon BP, a beta-galactoside-binding soluble lectin, in normal and neoplastic epidermis. Exp Dermatol. 1994 Feb;3(1):9–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1994.tb00260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffler H., Masiarz F. R., Barondes S. H. Soluble lactose-binding vertebrate lectins: a growing family. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):9222–9229. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Albrandt K., Mendel E., Kulczycki A., Jr, Orida N. K. Identification of an IgE-binding protein by molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4100–4104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T. Molecular biology of IgE-binding protein, IgE-binding factors, and IgE receptors. Crit Rev Immunol. 1990;10(3):289–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T. S-type mammalian lectins in allergic inflammation. Immunol Today. 1993 Oct;14(10):486–490. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90263-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manca N., Piacentini E., Gelmi M., Calzavara P., Manganoni M. A., Glukhov A., Gargiulo F., De Francesco M., Pirali F., De Panfilis G. Persistence of human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) sequences in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with mycosis fungoides. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1973–1978. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehul B., Bawumia S., Martin S. R., Hughes R. C. Structure of baby hamster kidney carbohydrate-binding protein CBP30, an S-type animal lectin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 8;269(27):18250–18258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz A., Meromsky L., Zvibel I., Lotan R. Transformation-related changes in the expression of endogenous cell lectins. Int J Cancer. 1987 Mar 15;39(3):353–360. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910390314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz A., Pazerini G., Carmi P. Identification of the metastasis-associated, galactoside-binding lectin as a chimeric gene product with homology to an IgE-binding protein. Cancer Res. 1989 Jul 1;49(13):3489–3493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz A., Zhu D. G., Hogan V., Shah N., Raz T., Karkash R., Pazerini G., Carmi P. Evidence for the role of 34-kDa galactoside-binding lectin in transformation and metastasis. Int J Cancer. 1990 Nov 15;46(5):871–877. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910460520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. W., Albrandt K., Keller D., Liu F. T. Human IgE-binding protein: a soluble lectin exhibiting a highly conserved interspecies sequence and differential recognition of IgE glycoforms. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 4;29(35):8093–8100. doi: 10.1021/bi00487a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roff C. F., Wang J. L. Endogenous lectins from cultured cells. Isolation and characterization of carbohydrate-binding proteins from 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10657–10663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Lis H. Lectins as cell recognition molecules. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):227–234. doi: 10.1126/science.2552581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Mason D. Y., Gerdes J., O'Connor N., Wainscoat J., Pallesen G., Gatter K., Falini B., Delsol G., Lemke H. The expression of the Hodgkin's disease associated antigen Ki-1 in reactive and neoplastic lymphoid tissue: evidence that Reed-Sternberg cells and histiocytic malignancies are derived from activated lymphoid cells. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):848–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto Y., Tanaka H., Tanabe O., Kuramoto A., Sasaki N., Nanba K. A patient with anaplastic large cell lymphoma (Ki-1 lymphoma) showing clonal integration of HTLV-1 proviral DNA. Leukemia. 1994 Mar;8(3):507–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willemze R., Beljaards R. C. Spectrum of primary cutaneous CD30 (Ki-1)-positive lymphoproliferative disorders. A proposal for classification and guidelines for management and treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993 Jun;28(6):973–980. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(93)70140-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo H. J., Shaw L. M., Messier J. M., Mercurio A. M. The major non-integrin laminin binding protein of macrophages is identical to carbohydrate binding protein 35 (Mac-2). J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7097–7099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. S., Bahler D. W., Hoppe R. T., Warnke R. A., Sklar J. L., Levy R. Transformation of mycosis fungoides: T-cell receptor beta gene analysis demonstrates a common clonal origin for plaque-type mycosis fungoides and CD30+ large-cell lymphoma. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Sep;101(3):296–300. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12365416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]