Abstract
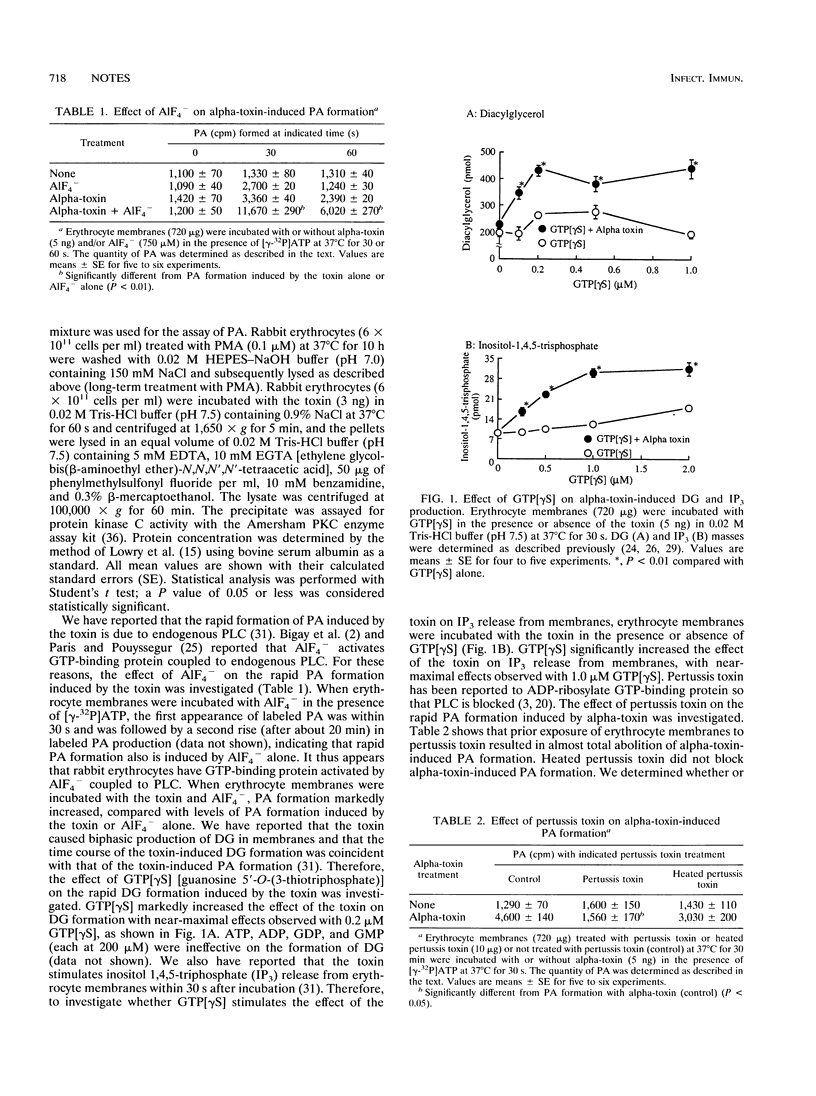
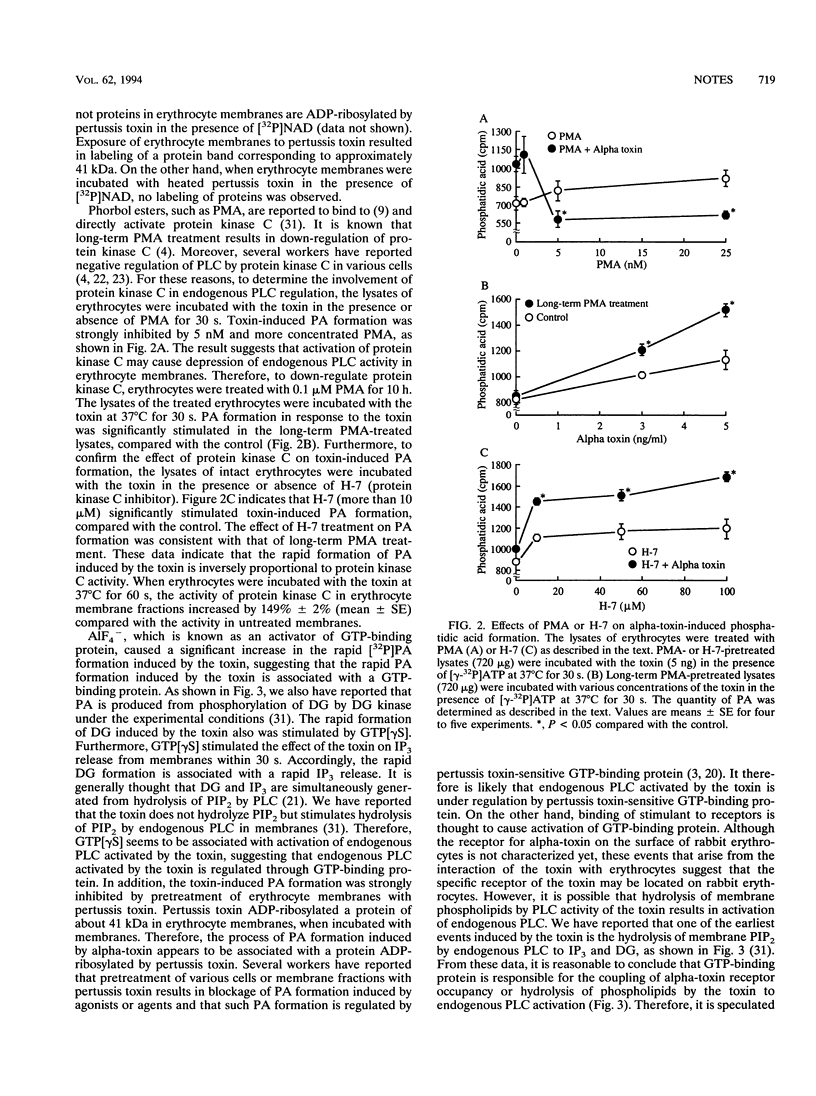
The rapid phosphatidic acid (PA) formation induced by Clostridium perfringens alpha-toxin was stimulated by AlF4- in rabbit erythrocyte membranes. GTP[gamma S] [guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate)] stimulated the rapid 1,2-diacylglycerol formation and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate release induced by the toxin. On the other hand, treatment of erythrocyte lysates with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) resulted in inhibition of toxin-induced PA production, and long-term PMA or 1-(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine (H-7) treatment of the lysates led to stimulation of PA formation. Furthermore, treatment of erythrocytes with the toxin caused an increase of protein kinase C activity in membrane fractions. The results suggest that toxin-induced PA formation is mediated by endogenous phospholipase C regulated through GTP-binding protein and protein kinase C in rabbit erythrocytes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agwu D. E., McPhail L. C., Chabot M. C., Daniel L. W., Wykle R. L., McCall C. E. Choline-linked phosphoglycerides. A source of phosphatidic acid and diglycerides in stimulated neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1405–1413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigay J., Deterre P., Pfister C., Chabre M. Fluoride complexes of aluminium or beryllium act on G-proteins as reversibly bound analogues of the gamma phosphate of GTP. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2907–2913. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Laposata M., Banga H. S., Rittenhouse S. E. Regulation of the phosphoinositide hydrolysis pathway in thrombin-stimulated platelets by a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding protein. Evaluation of its contribution to platelet activation and comparisons with the adenylate cyclase inhibitory protein, Gi. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16838–16847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Blakeley D. M., Hamon M. H., Laurie M. S., Corps A. N. Protein kinase C-mediated negative-feedback inhibition of unstimulated and bombesin-stimulated polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in Swiss-mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):631–639. doi: 10.1042/bj2450631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii Y., Nomura S., Oshita Y., Sakurai J. Excitatory effect of Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin on the rat isolated aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jul;88(3):531–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii Y., Sakurai J. Contraction of the rat isolated aorta caused by Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin (phospholipase C): evidence for the involvement of arachidonic acid metabolism. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):119–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11931.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Sastre F., Folch-Pi J. Thin-layer chromatography of the phosphoinositides. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jul;9(4):532–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetler K. Y., Gardner M. F., Aldern K. A. Assay of phospholipases C and D in presence of other lipid hydrolases. Methods Enzymol. 1991;197:125–134. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)97139-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Tanaka Y., Miyake R., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C as a possible receptor protein of tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11442–11445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopf G. S., Woolkalis M. J. ADP-ribosylation of G proteins with pertussis toxin. Methods Enzymol. 1991;195:257–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)95171-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug E. L., Kent C. Phospholipase C from Clostridium perfringens: preparation and characterization of homogeneous enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jun;231(2):400–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90403-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence W. D., Schoenl M., Davis P. J. Stimulation in vitro of rabbit erythrocyte cytosol phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity. A novel action of thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4766–4768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Cotecchia S., Lomasney J. W., DeBernardis J. F., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Phorbol esters promote alpha 1-adrenergic receptor phosphorylation and receptor uncoupling from inositol phospholipid metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5651–5655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACFARLANE M. G. The biochemistry of bacterial toxins; variation in haemolytic activity of immunologically distinct lecithinases towards erythrocytes from different species. Biochem J. 1950 Sep;47(3):270–279. doi: 10.1042/bj0470270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre D. E., McNicol A., Drummond A. H. Tumour-promoting phorbol esters inhibit agonist-induced phosphatidate formation and Ca2+ flux in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 28;180(2):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy A. C., Rozengurt E. Pasteurella multocida toxin selectively facilitates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis by bombesin, vasopressin, and endothelin. Requirement for a functional G protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25296–25303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ui M. Simultaneous inhibitions of inositol phospholipid breakdown, arachidonic acid release, and histamine secretion in mast cells by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible involvement of the toxin-specific substrate in the Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated biosignaling system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3584–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1365–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.6147898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orellana S. A., Solski P. A., Brown J. H. Phorbol ester inhibits phosphoinositide hydrolysis and calcium mobilization in cultured astrocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5236–5239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osugi T., Imaizumi T., Mizushima A., Uchida S., Yoshida H. Phorbol ester inhibits bradykinin-stimulated inositol trisphosphate formation and calcium mobilization in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid NG108-15 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Feb;240(2):617–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer S., Hughes K. T., Lee D. Y., Wakelam M. J. Development of a novel, Ins(1,4,5)P3-specific binding assay. Its use to determine the intracellular concentration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 in unstimulated and vasopressin-stimulated rat hepatocytes. Cell Signal. 1989;1(2):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S., Pouysségur J. Further evidence for a phospholipase C-coupled G protein in hamster fibroblasts. Induction of inositol phosphate formation by fluoroaluminate and vanadate and inhibition by pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):1970–1976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Loomis C. R., Bishop W. R., Stein R., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols present in platelets, hepatocytes, and ras- and sis-transformed normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8597–8600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Kim U. H., Wahl M. I., Brown A. B., Carpenter G., Huang K. P., Rhee S. G. Feedback regulation of phospholipase C-beta by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17941–17945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabban E., Laster Y., Loyter A. Resolution of the hemolytic and the hydrolytic activities of phospholipase-C preparation from Clostridium perfringens. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 24;28(3):373–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai J., Fujii Y., Shirotani M. Contraction induced by Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin in the isolated rat ileum. Toxicon. 1990;28(4):411–418. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(90)90079-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai J., Fujii Y., Torii K., Kobayashi K. Dissociation of various biological activities of Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin by chemical modification. Toxicon. 1989;27(3):317–323. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(89)90179-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai J., Ochi S., Tanaka H. Evidence for coupling of Clostridium perfringens alpha-toxin-induced hemolysis to stimulated phosphatidic acid formation in rabbit erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3711–3718. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3711-3718.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Chiba J., Sato Y. Monoclonal antibodies against alpha toxin of Clostridium perfringens. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 May;50(1-2):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90480-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talwar H. S., Fisher G. J., Voorhees J. J. Bradykinin induces phosphoinositide turnover, 1,2-diglyceride formation, and growth in cultured adult human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Dec;95(6):705–710. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12514507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heyningen W. E. The biochemistry of the gas gangrene toxins: Partial purification of the toxins of Cl. welchii, type A. Separation of alpha and theta toxins. Biochem J. 1941 Nov;35(10-11):1257–1269. doi: 10.1042/bj0351257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpi M., Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Shefcyk J., Huang C. K., Marsh M. L., Munoz J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis toxin inhibits fMet-Leu-Phe- but not phorbol ester-stimulated changes in rabbit neutrophils: role of G proteins in excitation response coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2708–2712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada S., Yasutomo Y., Kosano H., Kugai N., Nagata N. The effect of PGF2 alpha on parathyroid hormone-stimulated cyclic AMP production in mouse osteoblastic cell, MC3T3E1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 24;1074(1):182–188. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90059-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


