Abstract
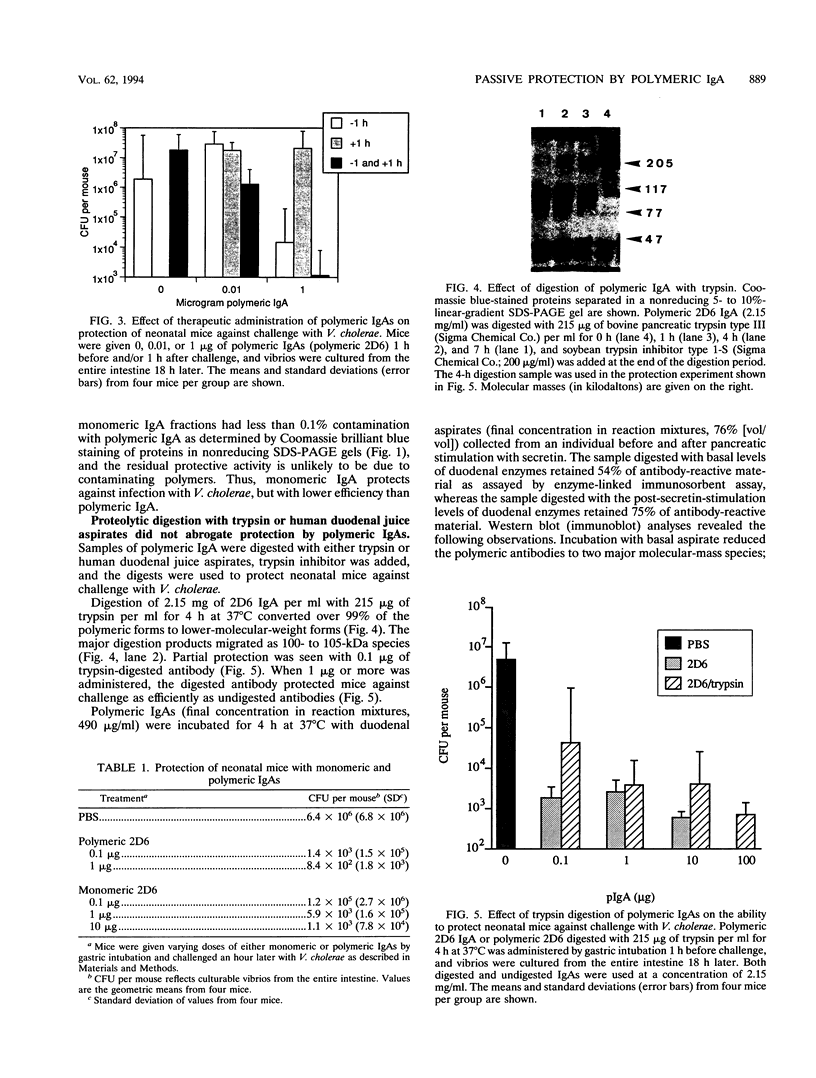
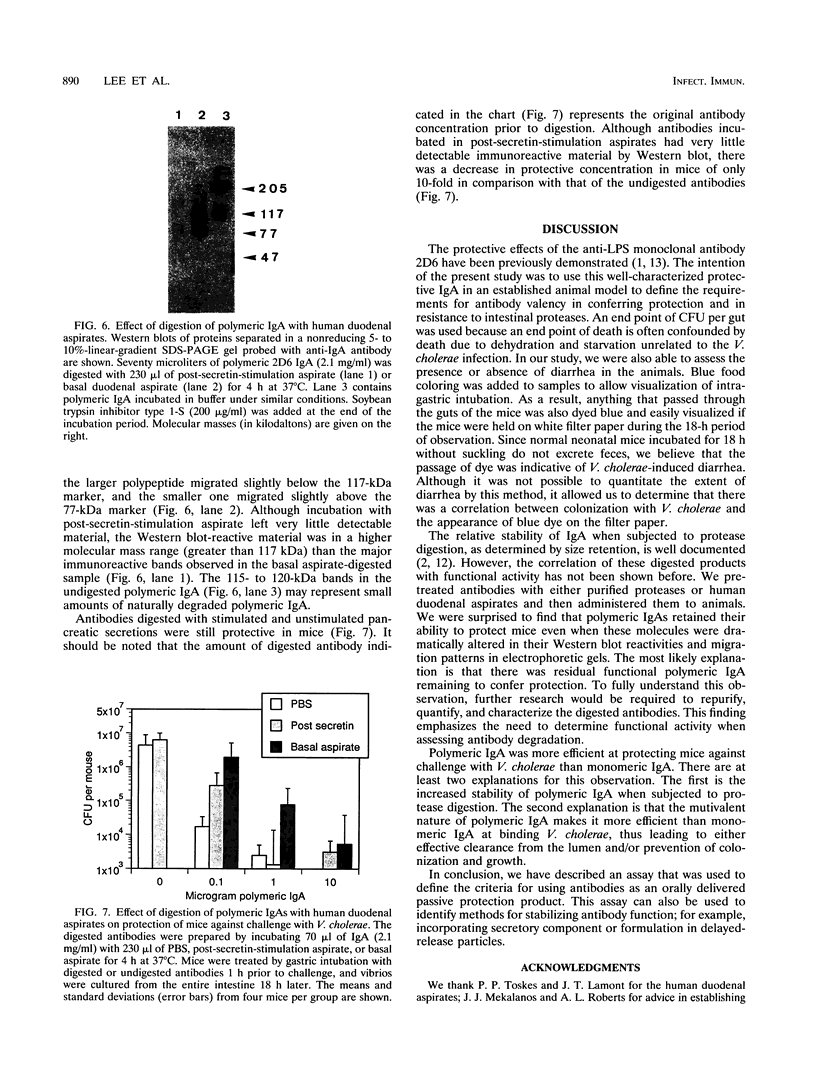
A simple animal model was used to demonstrate passive protection by immunoglobulin A (IgA) against a mucosal pathogen, Vibrio cholerae. Oral administration of a monoclonal IgA directed against a lipopolysaccharide component of the vibrio protected neonatal mice against oral challenge, as measured by reduced intestinal colonization. A single dose of 0.1 microgram of polymeric monoclonal IgA given 1 h prior to challenge reduced the number of recoverable vibrios by at least 100-fold. An additional dose 3 h before challenge or 1 h after challenge did not enhance protection. A 10-fold-higher concentration of monomeric IgA was required to achieve the same level of protection as that conferred by polymeric IgA. Polymeric IgA digested with trypsin or human duodenal aspirates to lower-molecular-weight fragments retained most of its ability to protect mice against challenge.
Full text
PDF
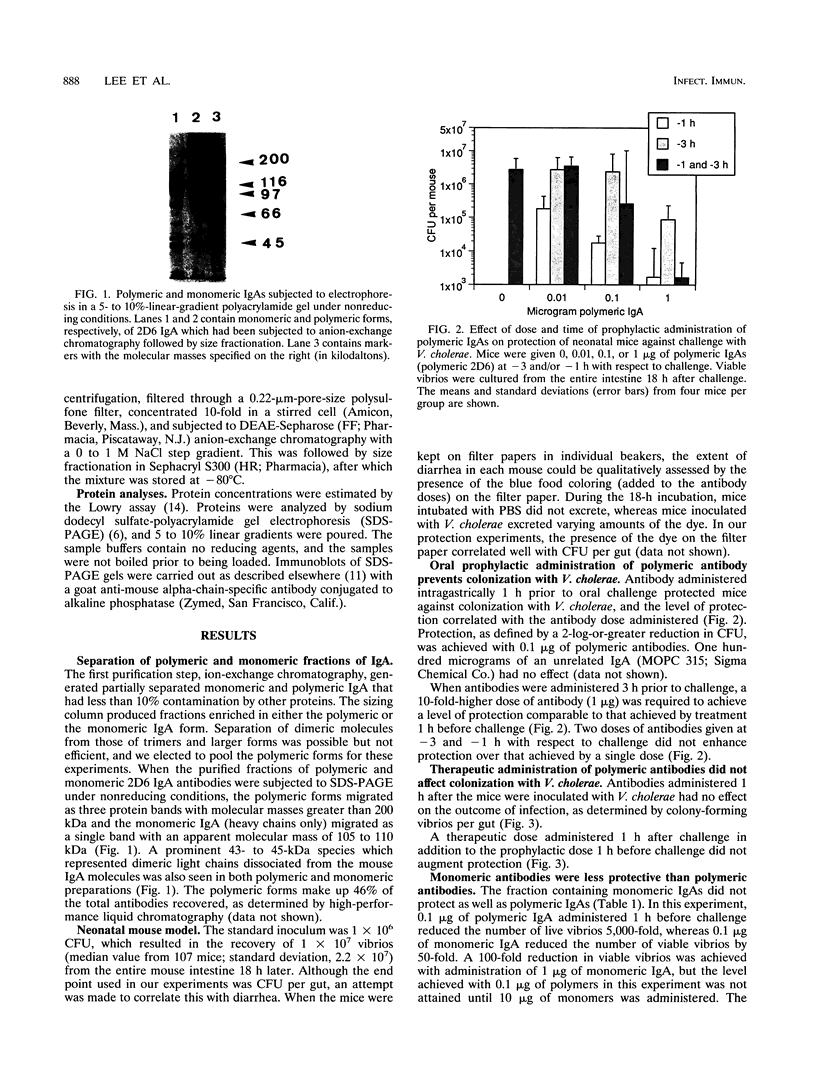

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown W. R., Newcomb R. W., Ishizaka K. Proteolytic degradation of exocrine and serum immunoglobulins. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jul;49(7):1374–1380. doi: 10.1172/JCI106354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chitnis D. S., Sharma K. D., Kamat R. S. Role of somatic antigen of Vibrio cholerae in adhesion to intestinal mucosa. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(1):53–61. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., O'Brien P. C., Macsai M. S. Role of chemotaxis in the association of motile bacteria with intestinal mucosa: in vivo studies. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):234–240. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.234-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M. Mechanisms of disease and immunity in cholera: a review. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S105–S112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L. New knowledge on pathogenesis of bacterial enteric infections as applied to vaccine development. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):510–550. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.510-550.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A. S., Dutta P., Dutta D., Ghose A. C. Antibacterial and antitoxin responses in the serum and milk of cholera patients. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.1-8.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A. S., Ghose A. C. Evaluation of the biological properties of different classes of human antibodies in relation to cholera. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):9–14. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.9-14.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Miller V. L., Furlong D. B., Mekalanos J. J. Use of phoA gene fusions to identify a pilus colonization factor coordinately regulated with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underdown B. J., Dorrington K. J. Studies on the structural and conformational basis for the relative resistance of serum and secretory immunoglobulin A to proteolysis. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):949–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winner L., 3rd, Mack J., Weltzin R., Mekalanos J. J., Kraehenbuhl J. P., Neutra M. R. New model for analysis of mucosal immunity: intestinal secretion of specific monoclonal immunoglobulin A from hybridoma tumors protects against Vibrio cholerae infection. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):977–982. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.977-982.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAK B., COHEN J. Automatic analysis of tissue culture proteins with stable Folin reagents. Clin Chim Acta. 1961 Sep;6:665–670. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(61)90112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]