Abstract
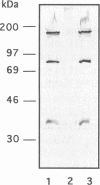
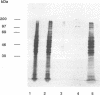
The spatial arrangement of three P1 operon-encoded proteins--attachment protein P1 (ORF5 gene product) and the ORF6-derived proteins of 40 and 90 kDa--in the membrane of Mycoplasma pneumoniae M129 was investigated by nearest-neighbor analysis. For these studies, the homobivalent, thiol-cleavable, and nonmembrane-permeating cross-linking reagent 3,3'-dithiobis(sulfosuccinimidylpropionate) (DTSSP) was used. The cross-linked proteins were isolated by immunoprecipitation with antibodies directed against fusion proteins of selected regions of the 40-kDa, the 90-kDa, or the P1 protein. The individual components of the immunoprecipitated protein complexes were identified by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, autoradiography, and immunoblot analysis. This study showed that the P1 protein, the ORF6 gene product, and an unidentified 30-kDa protein were linked to each other in the intact bacterial membrane by the reagent DTSSP, indicating that these proteins are located at a maximal distance of 12 A (1 A = 0.1 nm) on the tip structure of M. pneumoniae.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Blobel G. Immunoprecipitation of proteins from cell-free translations. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:111–120. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barile M. F., Chandler D. K., Yoshida H., Grabowski M. W., Harasawa R., Razin S. Parameters of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in Syrian hamsters. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2443–2449. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2443-2449.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Cole R. M., Krause D. C., Leith D. K. Molecular basis for cytadsorption of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1514–1522. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1514-1522.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Morrison-Plummer J., Drouillard D., Puleo-Scheppke B., Tryon V. V., Holt S. C. Identification of a 32-kilodalton protein of Mycoplasma pneumoniae associated with hemadsorption. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 May;23(5):474–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallo S. F., Chavoya A., Baseman J. B. Characterization of the gene for a 30-kilodalton adhesion-related protein of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4163–4165. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4163-4165.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldner J., Göbel U., Bredt W. Mycoplasma pneumoniae adhesin localized to tip structure by monoclonal antibody. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):765–767. doi: 10.1038/298765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzoso G., Hu P. C., Meloni G. A., Barile M. F. The immunodominant 90-kilodalton protein is localized on the terminal tip structure of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1993 Apr;61(4):1523–1530. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.4.1523-1530.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Wilson R. M., Baseman J. B. Two-dimensional gel electrophoretic comparison of proteins from virulent and avirulent strains of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):468–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.468-475.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Cole R. M., Huang Y. S., Graham J. A., Gardner D. E., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: role of a surface protein in the attachment organelle. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.6801766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Surface parasitism by Mycoplasma pneumoniae of respiratory epithelium. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1328–1343. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Serological comparison of virulent and avirulent Mycoplasma pneumoniae by monoclonal antibodies. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Sep;20(9):870–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inamine J. M., Denny T. P., Loechel S., Schaper U., Huang C. H., Bott K. F., Hu P. C. Nucleotide sequence of the P1 attachment-protein gene of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Gene. 1988 Apr 29;64(2):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inamine J. M., Loechel S., Hu P. C. Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of the P1 operon of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Lee K. K. Juxtaposition of the genes encoding Mycoplasma pneumoniae cytadherence-accessory proteins HMW1 and HMW3. Gene. 1991 Oct 30;107(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90300-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Leith D. K., Baseman J. B. Reacquisition of specific proteins confers virulence in Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):830–836. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.830-836.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Leith D. K., Wilson R. M., Baseman J. B. Identification of Mycoplasma pneumoniae proteins associated with hemadsorption and virulence. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):809–817. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.809-817.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küpper H., Keller W., Kurz C., Forss S., Schaller H., Franze R., Strohmaier K., Marquardt O., Zaslavsky V. G., Hofschneider P. H. Cloning of cDNA of major antigen of foot and mouth disease virus and expression in E. coli. Nature. 1981 Feb 12;289(5798):555–559. doi: 10.1038/289555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layh-Schmitt G., Herrmann R. Localization and biochemical characterization of the ORF6 gene product of the Mycoplasma pneumoniae P1 operon. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2906–2913. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2906-2913.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layh-Schmitt G. The ORF6 gene product of the P1 operon of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1993 Apr;278(2-3):287–295. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80845-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Sawyer W. D., Haak R. A. Cross-linking analysis of the outer membrane proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):785–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.785-791.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle K. F., Lee K. K., Krause D. C. Nucleotide sequence analysis reveals novel features of the phase-variable cytadherence accessory protein HMW3 of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1633–1641. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1633-1641.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Mycoplasmas: the smallest pathogenic procaryotes. Isr J Med Sci. 1981 Jul;17(7):510–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperker B., Hu P., Herrmann R. Identification of gene products of the P1 operon of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):299–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staros J. V. N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide active esters: bis(N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide) esters of two dicarboxylic acids are hydrophilic, membrane-impermeant, protein cross-linkers. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):3950–3955. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens M. K., Krause D. C. Localization of the Mycoplasma pneumoniae cytadherence-accessory proteins HMW1 and HMW4 in the cytoskeletonlike Triton shell. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1041–1050. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1041-1050.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strebel K., Beck E., Strohmaier K., Schaller H. Characterization of foot-and-mouth disease virus gene products with antisera against bacterially synthesized fusion proteins. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):983–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.983-991.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su C. J., Tryon V. V., Baseman J. B. Cloning and sequence analysis of cytadhesin P1 gene from Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3023–3029. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3023-3029.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]