Abstract
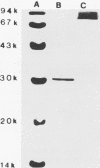
Studies were carried out on some biological activities of Helicobacter pylori porins in vitro. We extracted and purified a porin with an apparent molecular mass of 30 kDa. Human polymorphonuclear leukocytes preincubated with H. pylori porins showed a decrease of chemotaxis, of adherence to nylon wool, and of chemiluminescence. Used as chemotaxins in place of zymosan-activated serum or as chemotaxinogens in place of zymosan, the porins induced polymorphonuclear leukocyte migration. Human monocytes and lymphocytes cultivated in the presence of H. pylori porins released cytokines. Release of the various cytokines studied was obtained with differentiated kinetics and at various porin concentrations. Starting only 3 h after culture, tumor necrosis factor alpha is released quickly, reaching a peak at 18 h, at a porin concentration of 1 microgram/ml/10(6) cells. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) appears later, with a peak at 10 micrograms/ml/10(6) cells, while IL-8 is released after 6 h of culture, with a peak at 24 h, at a porin concentration of 10 micrograms/ml/10(6) cells, while IL-8 is released after 6 h of culture, with a peak at 24 h, at a porin concentration of 10 micrograms/ml/10(6) cells. Lymphocytes stimulated by H. pylori porins release gamma interferon after 18 h of culture at higher concentrations of porins (20 micrograms/ml/10(6) cells). Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor is released from 6 to 48 h at a concentration of 1 microgram/ml/10(6) cells, while both IL-3 and IL-4 are released after 18 h of culture at different porin concentrations (0.1 and 1 microgram/ml/10(6) cells, respectively). Our results lead us to think that during H. pylori infection, surface components, porins in particular, are able to induce a series of chain reactions ranging from the inflammatory to the immunological responses.
Full text
PDF


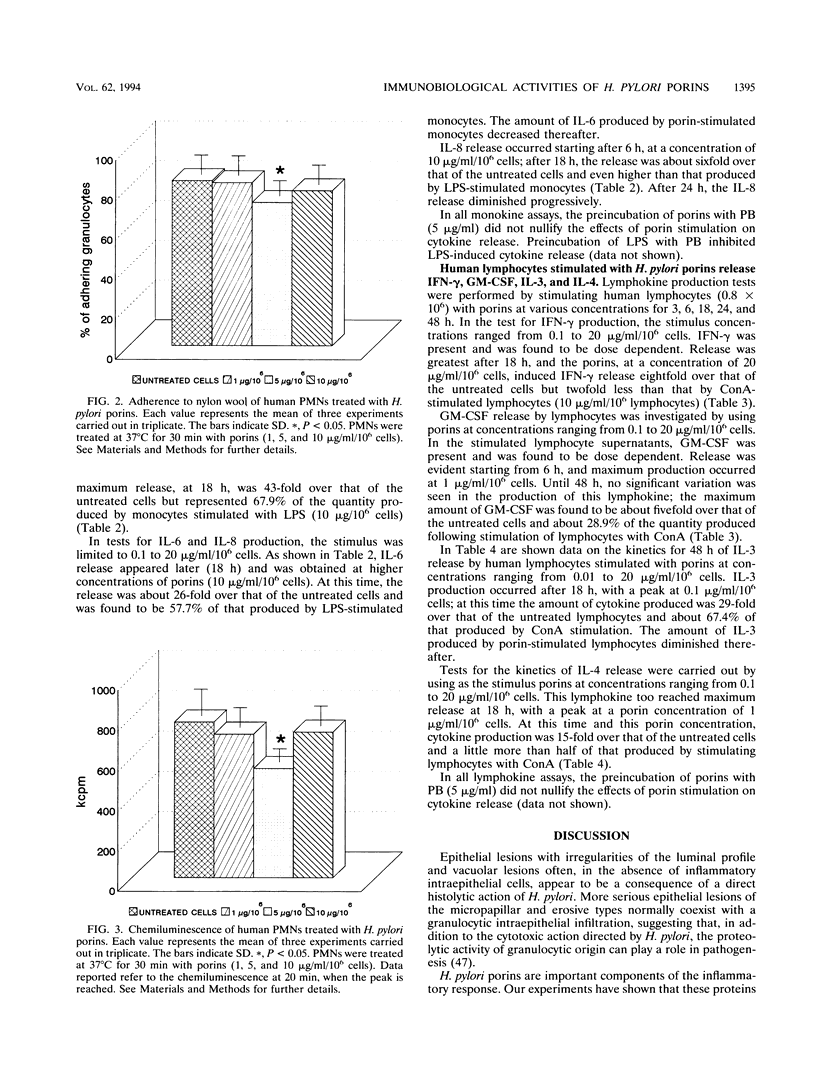
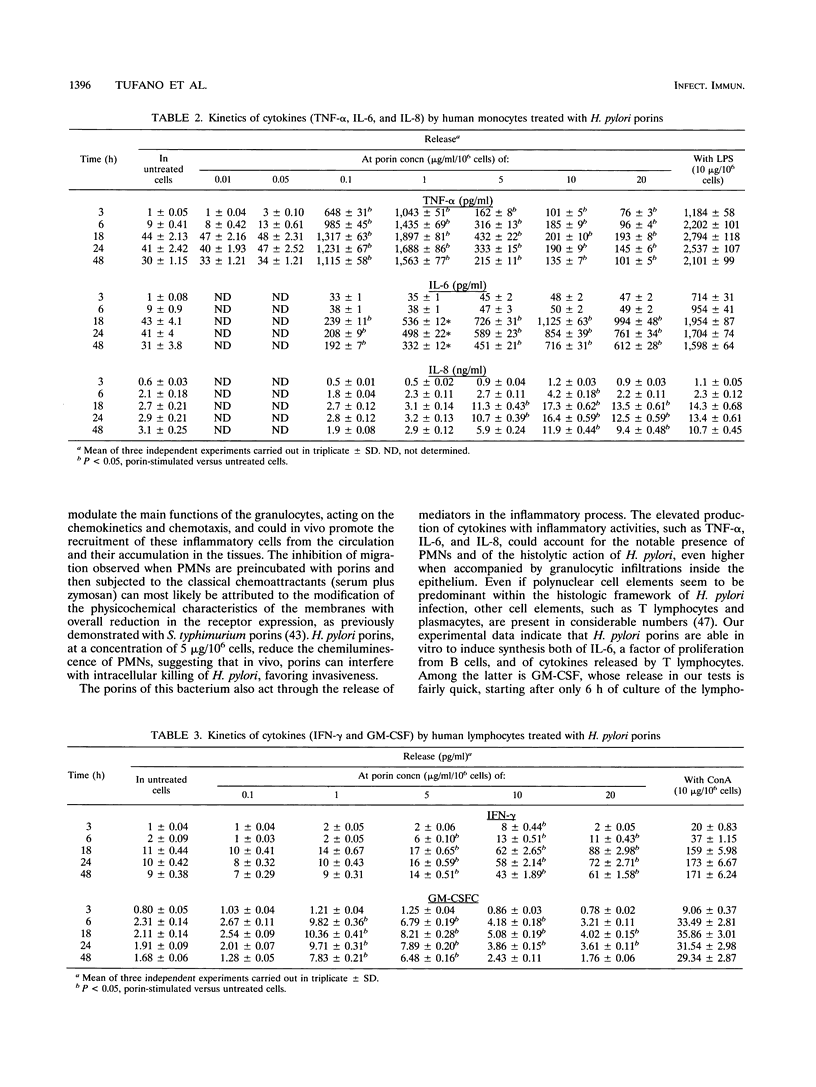
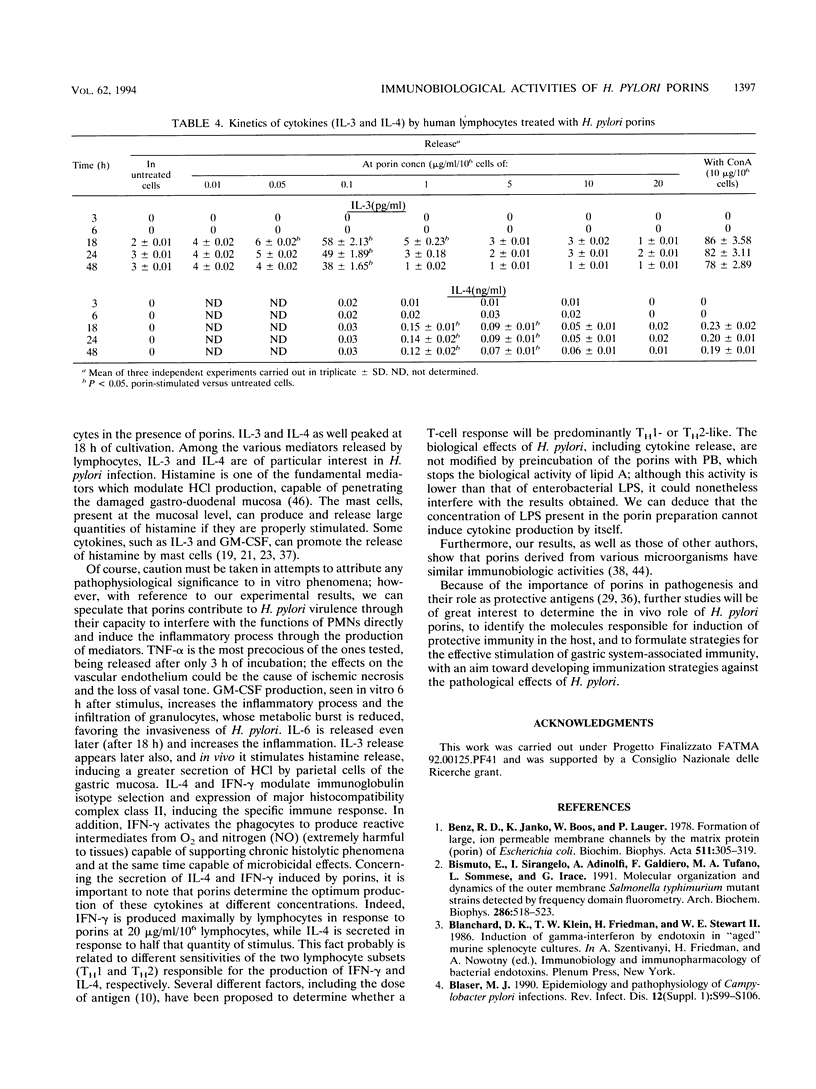


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benz R., Janko K., Boos W., Läuger P. Formation of large, ion-permeable membrane channels by the matrix protein (porin) of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 17;511(3):305–319. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bismuto E., Sirangelo I., Adinolfi A., Galdiero F., Tufano M. A., Sommese L., Irace G. Molecular organization and dynamics of the outer membrane of Salmonella thyphimurium mutant strains detected by frequency domain fluorometry. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 May 1;286(2):518–523. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90074-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J. Epidemiology and pathophysiology of Campylobacter pylori infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jan-Feb;12 (Suppl 1):S99–106. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_1.s99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Biancone L., Iorio E. L., Silvestro L., Da Col R., Capasso C., Rossano F., Servillo L., Balestrieri C., Tufano M. A. Porins and lipopolysaccharide stimulate platelet activating factor synthesis by human mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1992 Dec;42(6):1309–1318. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Salvidio G., Biesecker G., Brentjens J., Andres G. Heymann antibodies induce complement-dependent injury of rat glomerular visceral epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):2906–2914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Donato A., Draetta G. F., Illiano G., Tufano M. A., Sommese L., Galdiero F. Do porins inhibit the macrophage phagocyting activity by stimulating the adenylate cyclase? J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1986;11(2):87–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberg M. A., Keppler D., Galanos C. Requirement for lipopolysaccharide-responsive macrophages in galactosamine-induced sensitization to endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):891–895. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.891-895.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajewski T. F., Schell S. R., Nau G., Fitch F. W. Regulation of T-cell activation: differences among T-cell subsets. Immunol Rev. 1989 Oct;111:79–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdiero F., Gorga F., Bentivoglio C., Mancuso R., Galdiero E., Tufano M. A. The action of LPS porins and peptidoglycan fragments on human spermatozoa. Infection. 1988;16(6):349–353. doi: 10.1007/BF01644545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdiero F., Tufano M. A., Galdiero M., Masiello S., Di Rosa M. Inflammatory effects of Salmonella typhimurium porins. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3183–3186. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3183-3186.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdiero F., de L'ero G. C., Benedetto N., Galdiero M., Tufano M. A. Release of cytokines induced by Salmonella typhimurium porins. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):155–161. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.155-161.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Henning U. Cell envelope and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Isolation and preliminary characterization of the major ghost-membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 1;47(2):343–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Harnish D., Lansdorp P., Baumann H. Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Siehnel R., Martin N. Outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1069–1075. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindennach I., Henning U. The major proteins of the Excherichia coli outer cell envelope membrane. Preparative isolation of all major membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):207–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., De Weck A. L., Stadler B. M. Characterization of a human basophil-like cell promoting activity. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):221–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber A. R., Kunkel S. L., Todd R. F., 3rd, Weiss S. J. Regulation of transendothelial neutrophil migration by endogenous interleukin-8. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):99–102. doi: 10.1126/science.1718038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Keller J., Oroszlan S., Henderson L. E., Copeland T. D., Fitch F., Prystowsky M. B., Goldwasser E., Schrader J. W., Palaszynski E. Biologic properties of homogeneous interleukin 3. I. Demonstration of WEHI-3 growth factor activity, mast cell growth factor activity, p cell-stimulating factor activity, colony-stimulating factor activity, and histamine-producing cell-stimulating factor activity. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause P. J., Maderazo E. G., Scroggs M. Abnormalities of neutrophil adherence in newborns. Pediatrics. 1982 Feb;69(2):184–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Yokota T., Otsuka T., Meyerson P., Villaret D., Coffman R., Mosmann T., Rennick D., Roehm N., Smith C. Isolation and characterization of a mouse interleukin cDNA clone that expresses B-cell stimulatory factor 1 activities and T-cell- and mast-cell-stimulating activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2061–2065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Warren J. R. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984 Jun 16;1(8390):1311–1315. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91816-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muotiala A., Helander I. M., Pyhälä L., Kosunen T. U., Moran A. P. Low biological activity of Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1714–1716. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1714-1716.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Quie P. G., Simmons R. L. Chemotaxis under agarose: a new and simple method for measuring chemotaxis and spontaneous migration of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1650–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijsten M. W., de Groot E. R., ten Duis H. J., Klasen H. J., Hack C. E., Aarden L. A. Serum levels of interleukin-6 and acute phase responses. Lancet. 1987 Oct 17;2(8564):921–921. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91413-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny P., Chubb A. P., Cownley K., Montaraz J. A., Beesley J. E. Bordetella adenylate cyclase: a genus specific protective antigen and virulence factor. Dev Biol Stand. 1985;61:27–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson W. L. Helicobacter pylori and peptic ulcer disease. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 11;324(15):1043–1048. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104113241507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauws E. A., Tytgat G. N. Cure of duodenal ulcer associated with eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Lancet. 1990 May 26;335(8700):1233–1235. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91301-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkind D., Palmer J. D. Neutralization of endotoxin toxicity in chick embryos by antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):815–819. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.815-819.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P., Wakefield D., Breit S. N., Easter J. F., Penny R. Chemiluminescent response to pathogenic organisms: normal human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):744–752. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.744-752.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Rosenbusch J. P. Matrix protein in planar membranes: clusters of channels in a native environment and their functional reassembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2302–2306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta D. K., Sengupta T. K., Ghose A. C. Major outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae and their role in induction of protective immunity through inhibition of intestinal colonization. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4848–4855. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4848-4855.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Rennick D. M. Characterization of a murine lymphokine distinct from interleukin 2 and interleukin 3 (IL-3) possessing a T-cell growth factor activity and a mast-cell growth factor activity that synergizes with IL-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1857–1861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada H., Ogawa T., Yoshimura F., Otsuka K., Kokeguchi S., Kato K., Umemoto T., Kotani S. Immunobiological activities of a porin fraction isolated from Fusobacterium nucleatum ATCC 10953. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):855–863. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.855-863.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufano M. A., Berlingieri M. T., Sommese L., Galdiero F. Immune response in mice and effects on cells by outer membrane porins from Salmonella typhimurium. Microbiologica. 1984 Oct;7(4):353–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufano M. A., Biancone L., Rossano F., Capasso C., Baroni A., De Martino A., Iorio E. L., Silvestro L., Camussi G. Outer-membrane porins from gram-negative bacteria stimulate platelet-activating-factor biosynthesis by cultured human endothelial cells. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jun 15;214(3):685–693. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufano M. A., Ianniello R., Galdiero M., De Martino L., Galdiero F. Effect of Salmonella typhimurium porins on biological activities of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Microb Pathog. 1989 Nov;7(5):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufano M. A., Sommese L., Capasso C., Folgore A., Scafa F., Galdiero E. Comparative study of some biological activities of porins extracted from various microorganisms. Microbiologica. 1986 Oct;9(4):431–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufano M. A., Tetta C., Biancone L., Iorio E. L., Baroni A., Giovane A., Camussi G. Salmonella typhimurium porins stimulate platelet-activating factor synthesis by human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 1;149(3):1023–1030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe M. M., Soll A. H. The physiology of gastric acid secretion. N Engl J Med. 1988 Dec 29;319(26):1707–1715. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812293192605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. I., Rathbone B. J., Heatley R. V. Local immune response to gastric Campylobacter in non-ulcer dyspepsia. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Aug;39(8):863–870. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.8.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]